534 Clin Med IV (Delirium, Dementia)
1/35
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
36 Terms
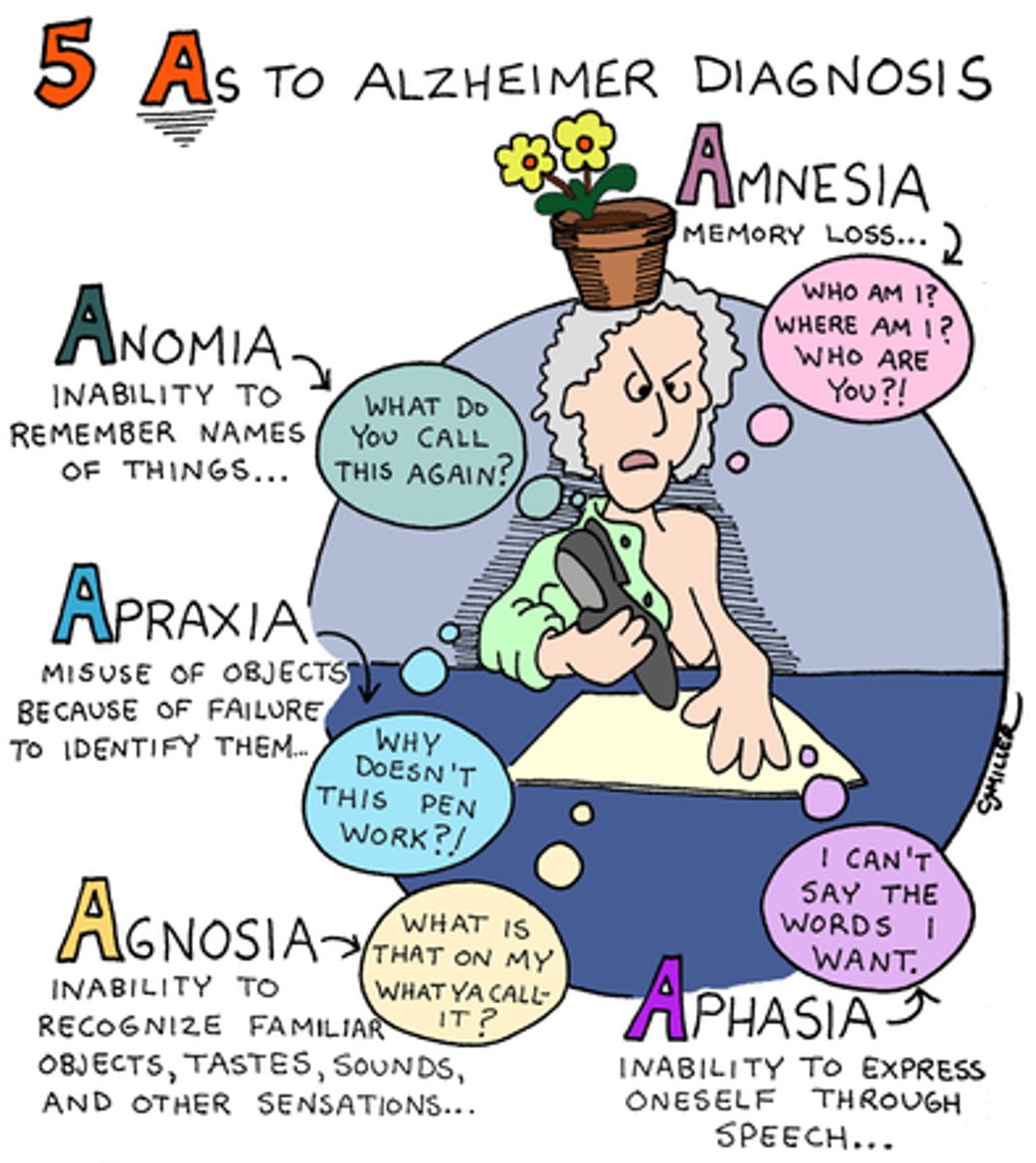
What is an acquired disorder characterized by a progressive decline in intellectual function?
What is most commonly affected?
What must be present for a diagnosis?
Dementia
Episodic memory
1+ cognitive deficit which interferes with ADLs (not due to delirium)
How does the DSM-V categorize dementia?
Major neurocognitive disorder
How often does the prevalence of dementia double?
What is the most common cause?
What is the most common type?
Every 5 years
Aging
Alzheimer's (2/3)
How will a patient with dementia present? (5)
What may occur in late stage disease?
Progressive recent memory loss (losing things, missed appts)
Personality changes (agitation, restless)
Impaired language, executive function
Depression
Impaired gait
Bed bound (pressure ulcers, malnutrition, dehydration)
T/F: There are medications which delay the progression of cognitive impairment in dementia
False
What are two characteristics of Alzheimers dementia?
How will a patient present?
Amyloid Plaques + Neurofibrillary Tangles
Recent memory loss
Apathy
Irritability
Aphasia
Delusions/Paranoia
Type of dementia caused by infarcts and atherosclerosis which can be sudden onset or a stepwise decline?
What is the best predictor of cognitive impairment?
What must there be evidence of?
Is this type more or less severe compared to others?
Clinical presentation?
Vascular
Lacunar infarts
Cerebrovascular disease (clinical or radiographic evidence)
Less
Impaired recall but better recognition
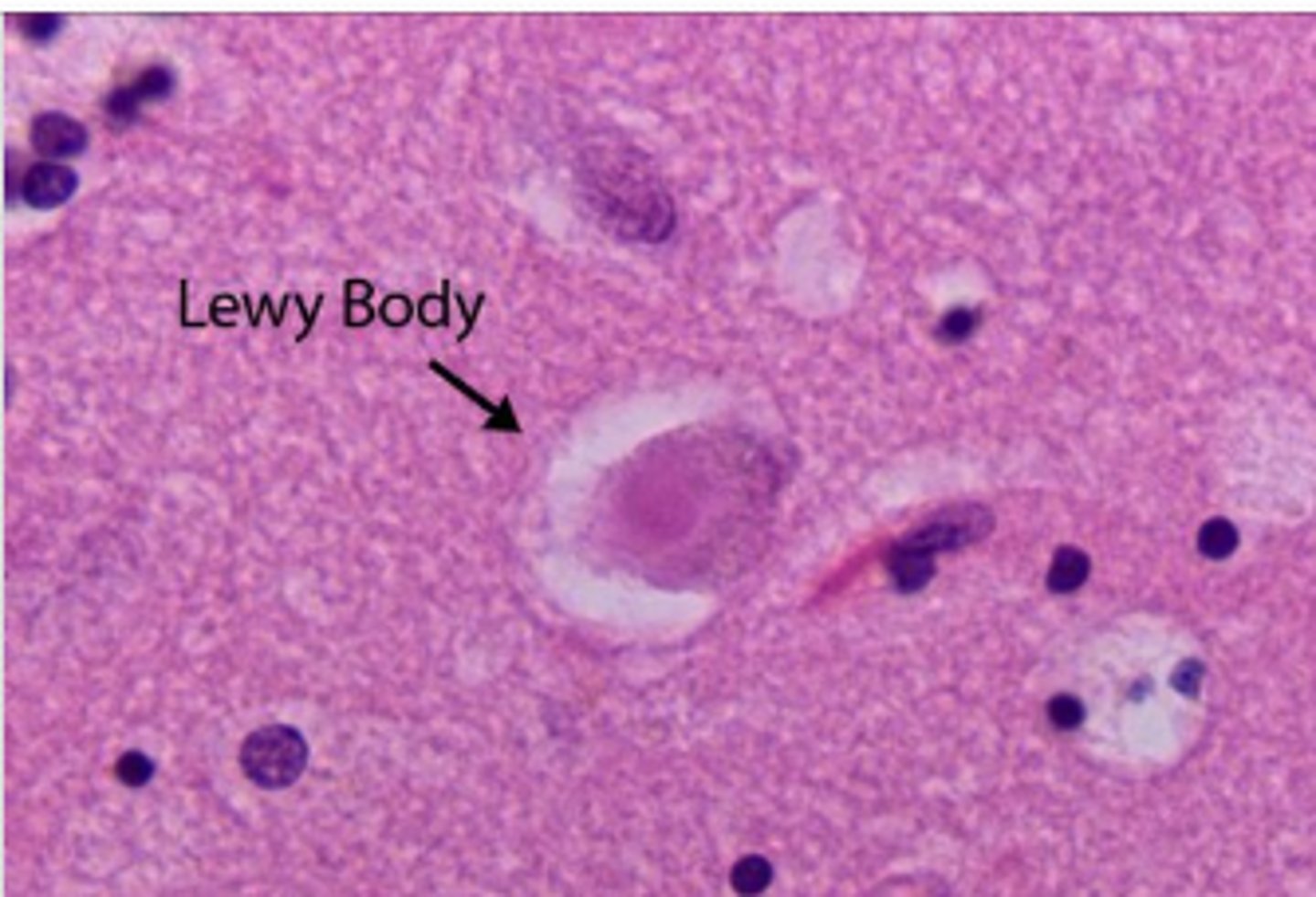
Type of dementia involving spherical eosiniphillic intraneuronal inclusions surrounded by a clear halo?
What accompanies the cognitive changes?
What other symptoms may be present?
Lewey Body
Movement disorder (Parkisonism)
REM disorder, visual hallucinations
What are the two variants of frontotemporal dementia?
When does this onset?
Behavioral -> changes in personality sparing memory
Language -> progressive non-fluent aphasia
Earlier (50s)
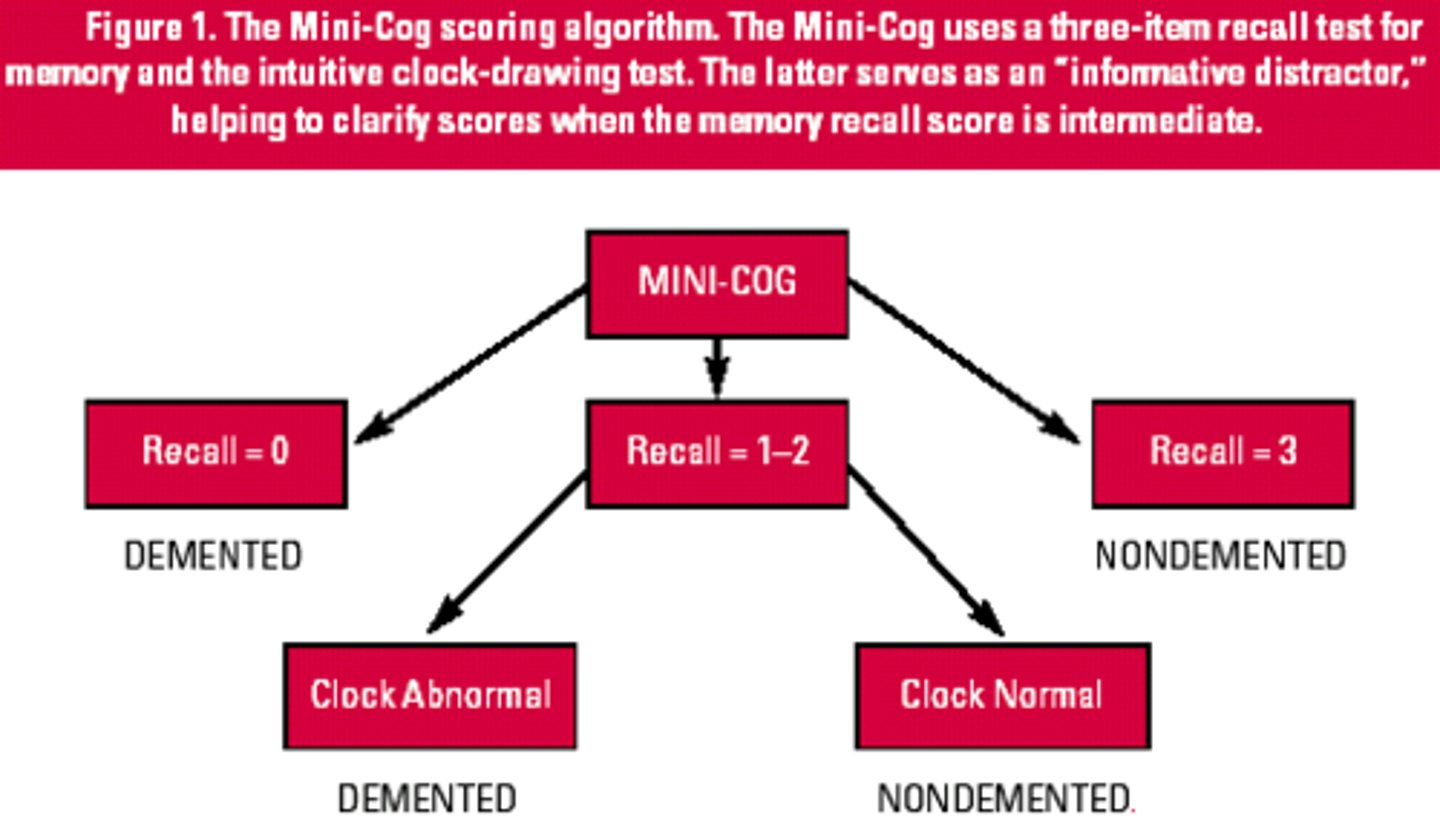
What is recommended in those with suspected cognitive impairment?
What two tools may be used?
Screening
MOCA, Mini-Cog
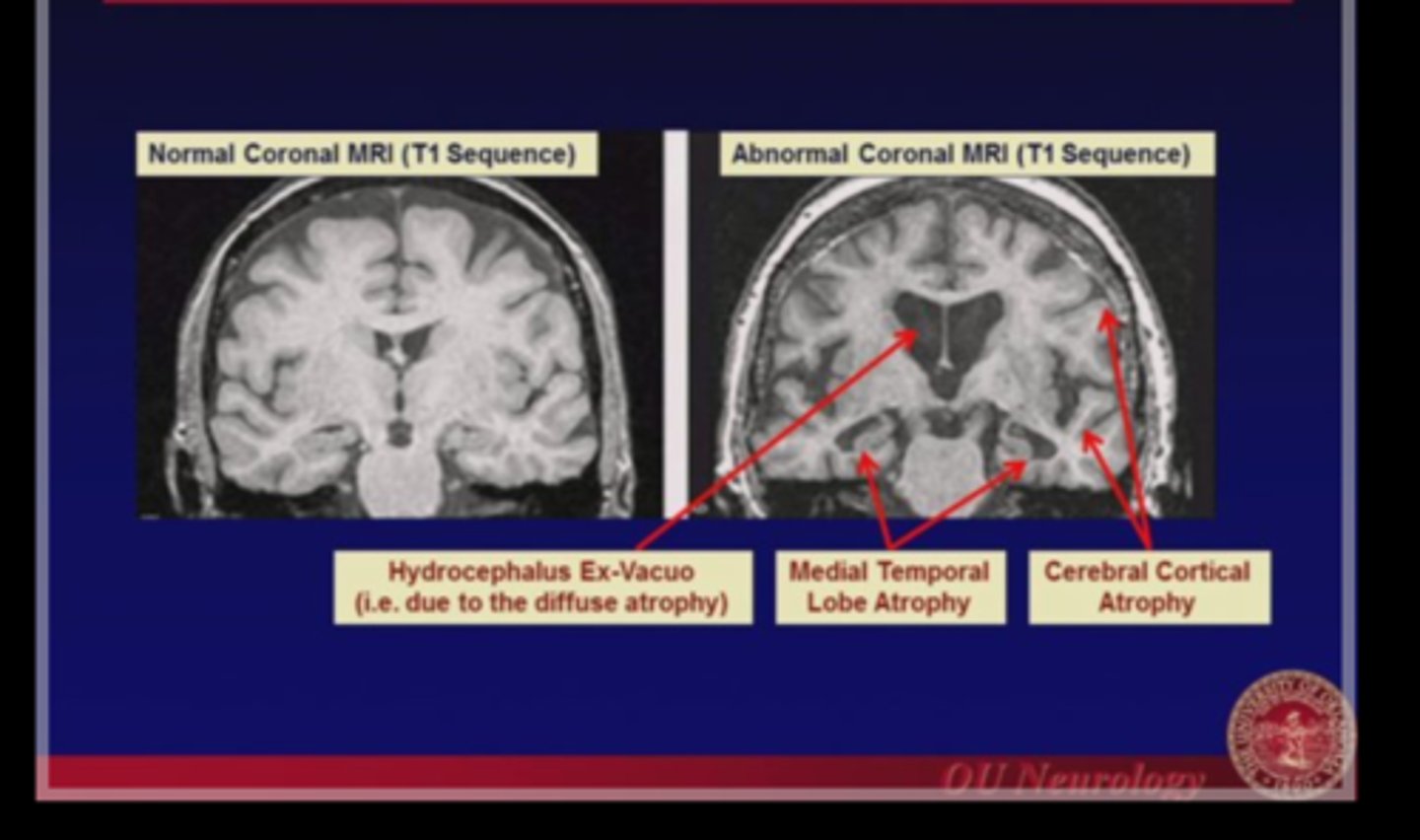
What imaging do we get for dementia?
What six labs should we assess for reversible causes?
CT (+/- MRI)
TFTs, B12, RPR, HIV, heavy metals, LFTs
What agents do we use to treat dementia?
What NMDA antagonist can we use alone or in combination?
What recombinant monoclonal antibody can we use?
What vitamin may be used?
Acetylcholinesterase inhibitors (donepezil, rivastigmine, galantamine)
Memantine
Aducanumab
Vitamin E
What else must we consider regarding dementia treatment?
Accommodate behaviors (routine, distract)
Caregiver support
What agents can we use for neuropsychiatric behaviors in dementia, but can increase mortality and QT prolongation?
What agent can be used to treat agitation in dementia?
SGAs (risperidone, olanzapine, quetiapine, aripripazole)
Citalopram
Patients with moderate to severe dementia should not do what?
What advanced planning is needed?
Drive
Financial
What is the life expectancy for dementia?
Which type has a more rapidly declining course?
What is considered a terminal illness?
3 to 15 years
Lewy Body
End-stage
What is the problem with depression in elderly patients?
Unlike dementia, depression is what?
What does the incidence of depression increase with?
May not admit to depressed mood
Treatable
Aging
What does depression in the elderly present with?
What type of symptoms are likely to be present?
Somatic symptoms (insomnia/hypersomnia, fatigue, concentration, decreased appetite)
Psychotic
What must be present for a diagnosis of depression?
What is the time criteria for diagnosis?
What accompanying symptoms are likely to be present?
Depressed Mood or Loss of Interest
2 weeks
Sleep, appetite, fatigue
What is highly sensitive for detecting depression in the elderly?
2 Question Screen:
Have you felt depressed or hopeless in the last 2 weeks?
Have you felt little interest or pleasure in doing things?
What is the first line for depression treatment?
What can be used to treat concomitant appetite issues?
What can be used to treat concomitant neurologic pain?
SSRIs (citalopram, sertraline)
Mirtazapine
Duloxetine
Start low and go slow
How long do we treat depression for before switching medications?
How long do we continue treatment following remission since recurrence is common?
6 weeks
6 months
What is the non-pharmacologic treatment for depression?
When do we refer or admit these patients?
CBT, lifestyle (socialize, exercise, reduce alcohol)
SI, catatonia, psychosis/mania, ECT treatment
Acute onset of confusion, attention and cognition?
Delirium
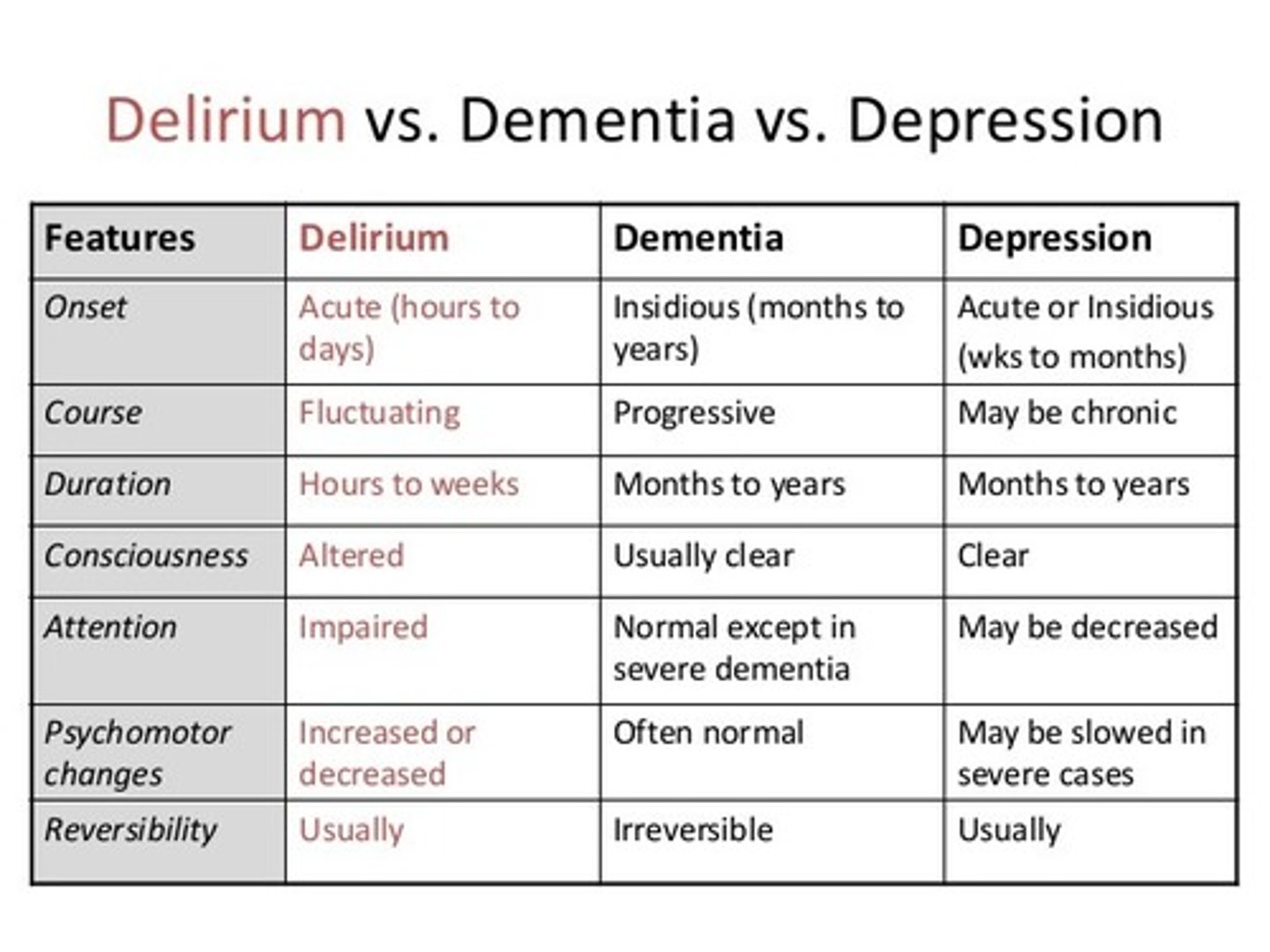
What is the difference between delirium and dementia?
Delirium: Acute onset, fluctuating course, deficits in attention, psychomotor behavioral disturbances, reversible, functional
Dementia: Gradual onset, progressive course, deficits in memory, irreversible, structural
Delirium is the most common complication of what?
What percent of hospice and ICU patients experience delirium?
What percent of cases go unrecognized?
What is the one year mortality?
Post-operative
80%
70%
35-40%
What is acute onset attention issues which can have a fluctuating course?
Leading risk factor?
Etiology?
Delirium
Dementia (delirium worsens dementia course)
Vulnerability (dementia, illness/infection, age, depression, sensory impairment)
+ Insult (ICU, major surgery/anesthesia, sleep deprivation, metabolic derangement)
What are predisposing factors for delirium?
What are precipitating factors for delirium?
Cognitive issues, severe illness, depression, sensory issues, age
ICU, surgery, restraints, polypharmacy, sleep deprivation, catheterization, metabolic derangement
Hallmark of delirium?
Acute onset ATTENTION DEFICIT
Delirium has disturbances in what two regions of the brain?
What does EEG show that indicates cerebral dysfunction?
What does SPECT show?
What neurotransmitter abnormalities may be present?
Cortical, Subcortical
Symmetric slowing
Reduced cerebral bloodflow
ACh decrease, Dopamine increase
Acute onset of agitation, irritability, restlessness and hallucinations. What type of delirium is this?
Acute onset of inattention, cognitive slowing and lethargy. What type of delirium is this?
What symptom is common among both?
What is true of the clinical course?
Hyperactive
Hypoactive
Inattention
Fluctuating
What should we be looking for of on PE with delirium?
What exam must we perform?
What labs should we get?
What screening tool can we use?
Infection, hypoxia, dehydration *MEDICATIONS*
Neurological
CBC, CMP, albumin, UA, ABG +/- imaging (CXR, MRI)
CAM

What is the first line treatment for delirium?
REVERSE UNDERLYING CAUSE
Hydration
Ambulation
Socialization/Re-Orientation
Activities
Sleep schedule
Vision/Hearing aids
NO MEDS!!!!
T/F: Medications have been shown to prevent delirium or improve outcomes
FALSE
There are no medications that prevent delirium or improve outcomes
What must we eliminate in delirium patients?
What may be used to treat agitation but has no improvement with outcomes?
What may be used for seizures or alcohol withdrawal?
Restraints, indwelling catheters, excess medications
Haloperidol
Benzodiazepines
Most episodes of delirium resolve with what?
What percent of patients will have persistent symptoms?
Treatment of underlying cause
25%
Delirium worsens clinical outcomes and delays recovery of physical function