SBI3U exam review
1/241
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
242 Terms
chromosomes
a package of DNA containing part or all of the genetic material of an organism
zygote
a fertilized egg cell
DNA
aka deoxyribonucleic acid
made up of nucleotides
DNA is classified as a protein
yes
centromere
it links a pair of sister chromatids together during cell division
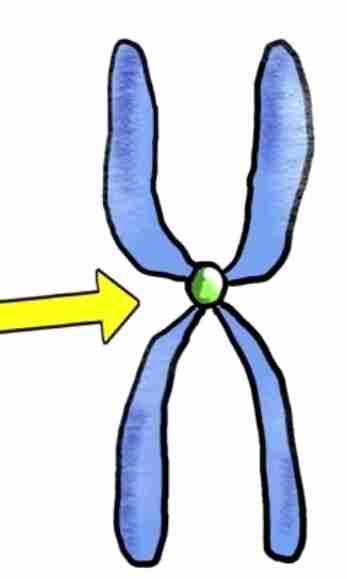
nucleotide
the building blocks that make up RNA and DNA
chromatin
made up of dna & histone proteins
found during interphase of the cell cycle
tetrad
a pair of chromosomes
What is the complementary base pairing rule
Adenine (A) bonds with Thymine (T)
Cytosine (C) bonds with Guanine (G)
what is hydrogen bonding
a type of chemical bond that weakly attaches a molecule to another molecule
how many H-bonds are between A & T
2 hydrogen bonds
how many h-bonds are between C & G
3 hydrogen bonds
what is a gene
a piece of heredity material that is passed on from parent to offspring
what is an allele
a version of a gene at a particular position on a chromosome
what is heredity
the process of passing traits from parents to offspring
what is homologous chromosomes
a pair of chromosomes w/ the same type of genes
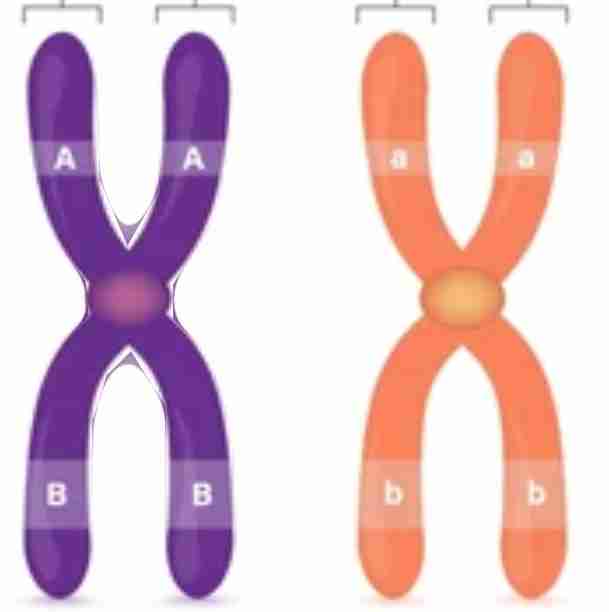
haploid cells (n)
a cell w/ a single set of chromosomes
humans sex cells have 23 chromosomes
diploid cells (2n)
a cell that has 2 complete sets of chromosomes
that # for humans is 46 chromosomes
autosomal chromosome
any chromosome that is not a sex chromosome
sex chromosome
Chromosomes that determine a individual's biological sex
somatic cells
any cell that is not a sex cell
are also diploid cells
gametes (sex cells)
the reproductive cells of any animal or plant
humans only have 23 chromosomes in their sex cells
are also haploid cells
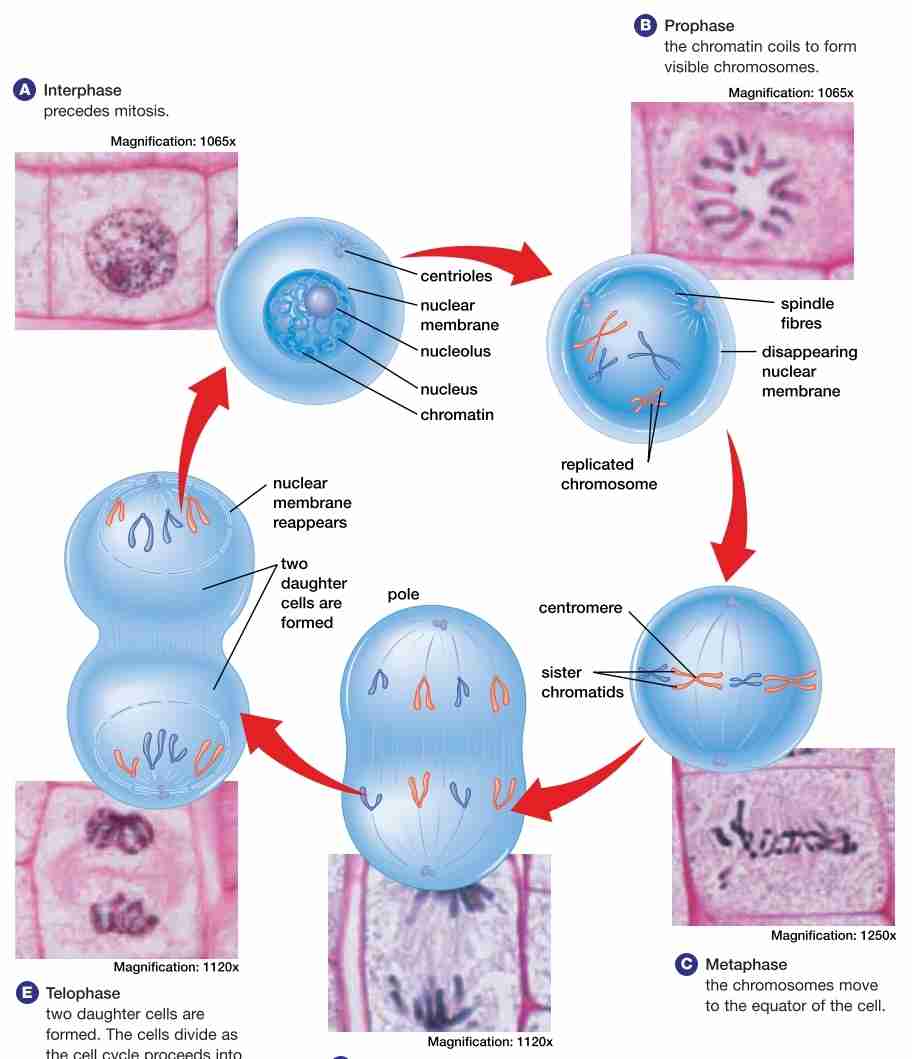
stages of mitosis
Interphase (G1,S, G2)
Prophase
Metaphase
Anaphase
Telophase
purpose of mitosis
is cell divison ; for a mother cell to produce 2 daughter cells in the end
total # of chromosome for a human cell at the prophase stage of mitosis
46 chromosomes
the "n" description of the cell at interphase
2n
total # of chromosomes for a human cell at the prophase stage of mitosis
46 chromosomes
the "n" description of the cell at prophase
2×2n
total # of chromosome for a human cell at the end of the telophase stage of mitosis
46 chromosomes
the "n" description of the cell at the end of telophase
2n
where does mitosis occur
in somatic cells
G1 phase of Interphase
cell does most of its growing; making it take in more nutrients
DNA is spread throughout the nucleus as chromatin
cell increases in size
cell has 2n diffuse chromosomes (diploid)
S Phase (synthesis phase) of Interphase
cell continues to grow
the diffuse chromosome duplicates, producing a 2x2n # of diffuse chromosomes
G2 phase of Interphase
cell has 2x2 n chromosomes within the nucleus
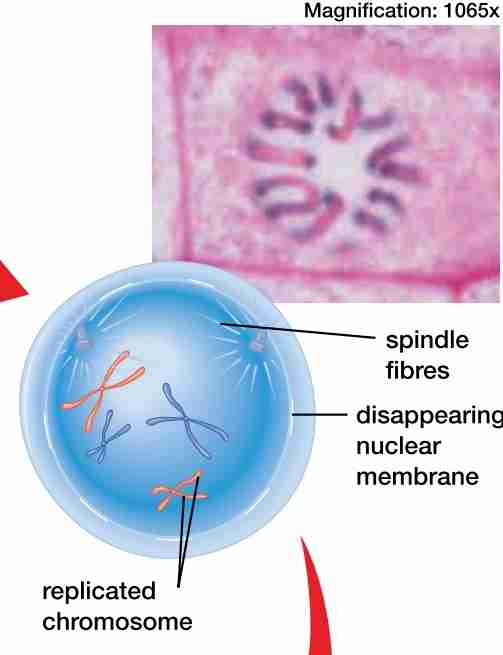
prophase
nuclear membrane dissolves
chromatin condenses into chromosome, each w/ 2 sister chromatinds attached by a centomere
spindle fibers & centrioles assemble
centrioles move to the poles of the cell
2x2n
what is meiosis
a special cell division that involves the production of reproductive cells
purpose of meiosis
to produce sex cells (sperms & eggs) that have half the genetic information of somatic cells
stages of meiosis
In meiosis I
Prophase I
Metaphase I
Anaphase I
Telophase I
In meiosis II
Prophase II
Metaphase II
Anaphase II
Telophase II
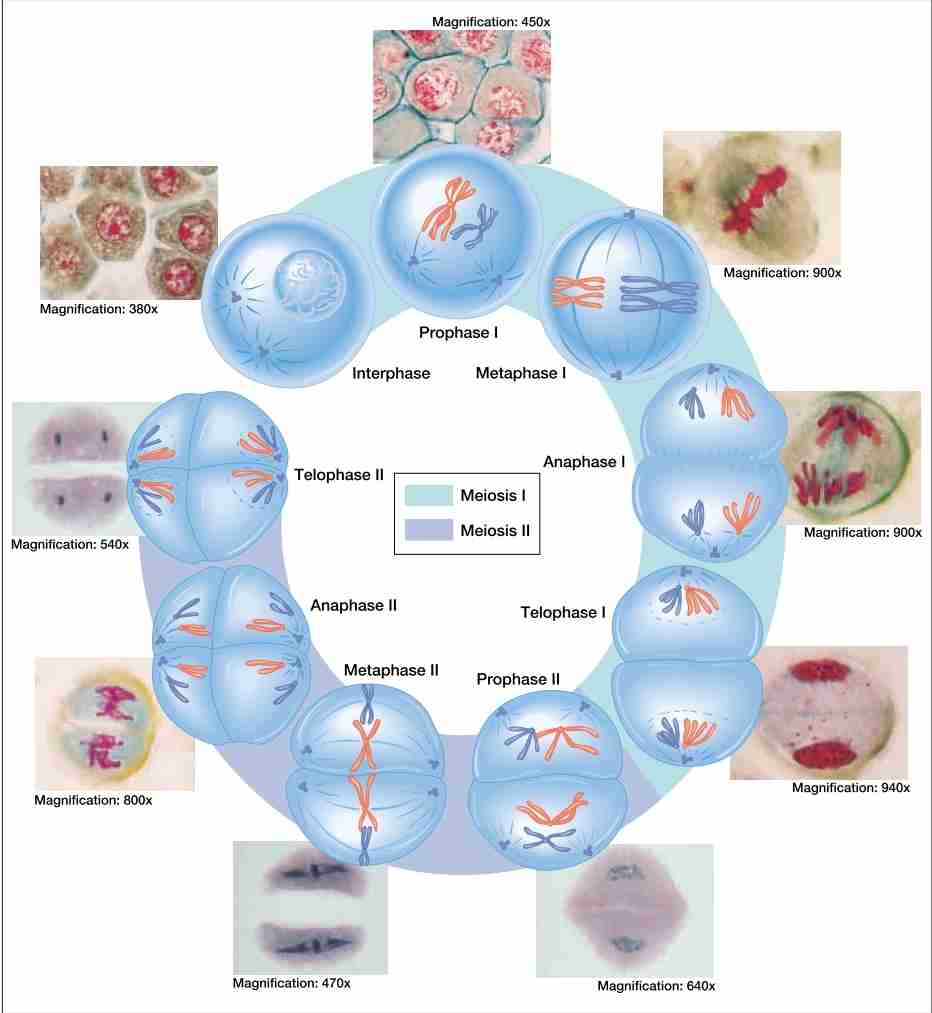
where does meiosis occur
in sex cells
synapsis
when 2 duplicated homologous chromosomes line up side by side
non-disjunction mistakes
when homologous chromosome fail to separate properly during cell division
mistakes during crossing over
duplication
deletion
inversion
translocation
duplication
when one chromosome ends up with two copies of a gene

deletion
the other chromosome would have no copies of that gene

inversion
the gene order on a chromosome switches
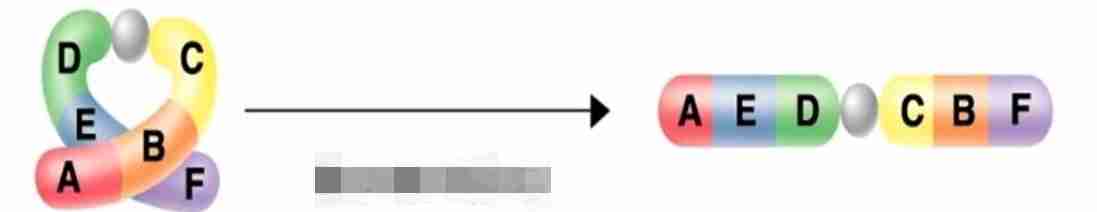
translocation
a gene from one chromosome ends up on a non-homologous chromosome

aneuploidy
the presence of an abnormal # of chromosomes in a cell
polyploidy
cells that have more than 2 sets of homologous chromosomes
gametogenesis
the process where diploid gametes undergo meiosis to produce haploid gametes
polar body
a useless cell formed during oogenesis; it has chromosomes, but not much else
do all ovulated oocytes finish meiosis
oocytes only finish meiosis if they become fertilized
name of each cell that enters the body during spermatogenesis
spermatocyte
name of the cells that enter the body during oogenesis
oocyte
who determines the gender of a zygote
the father
blood type A+ can receive blood from
A+, A-, O+, O-
blood type A - can receive blood from
A-, O-
the antibodies present in blood type A’s plasma
Anti-B
the antigens present on type A's red blood cells
A antigen
blood type B + can receive blood from
B+, B-, O+, O-
blood type B- can receive blood from
B-, O-
the antibodies present in type B's plasma
Anti-A
the antigens present on type B's RBCs
B antigen
AB+ can receive blood from
all blood types
AB- can receive blood from
AB-, A -, B-, O-
the antibodies present in type AB's plasma
none
the antigens found on type AB'S RBCs
A & B antigen
O+ can receive blood from
O+, O-
O- can receive blood from
O-
the antibodies found in type O's plasma
A & B antibodies
the antigens found on type O's RBCs
no antigens
the universal blood recipient
type AB+
the universal blood donor
type O-
8 different types of blood
A+
A-
B+
B-
AB+
AB-
O+
O-
Rhogram shot
A preventive treatment given to Rh-negative mothers during and after pregnancy to prevent Rh incompatibility with Rh-positive babies.
Rh Incompatibility
A medical condition that occurs when an Rh-negative mother is pregnant with an Rh-positive baby, leading to potential complications.
What is an antigen?
a foreign substance that triggers an immune response, typically a foreign molecule that is recognized as harmful by the immune system.
where are antigens located
on the surface of RBCs
antibody
Y-shaped protein molecule in the blood plasma
purpose of antibodies
to identify and neutralize harmful invaders. antibodies are able to recognize a specific foreign molecule (antigen)
Rh factor is also known as
the rhesus factor
what is the rhesus factor
a protein marker in the blood
people who don't carry the Rh protein are called
Rh-
people who do carry the Rh protein are called
Rh+
Rh+ is
dominant
Rh- is
recessive
over 90% of the world is
Rh-
agglutination
clumping of red blood cells in response to antibodies fending off foreign materials
white blood cells
the defense system of the body; responsible for protecting against harmful, foreign invaders like parasites, viruses, bacteria
red blood cells
responsible for transport of oxygen & carbon dioxide between lungs and other tissues
law of segregation
states that alleles are separated during gamete formation
How does meiosis ensure the law of segregation?
During meiosis, homologous chromosomes are separated into different gametes, ensuring that each gamete receives only one allele for each gene, thus upholding the law of segregation.
law of independent assortment
states that genes for different traits segregate independently of one another during the formation of gametes
How does meiosis ensure the law of independent assortment?
During meiosis, genes for different traits segregate independently because homologous chromosomes align randomly along the metaphase plate, leading to various combinations in gametes.
law of dominance
The dominant allele's trait will mask the effect of the recessive allele in a heterozygous genotype.
heterozygous
having 2 different alleles of a particular gene (ex. Ee)
homozygous dominant
a genotype where an individual inherits 2 copies of a dominant gene ( Ex. EE )
homozygous recessive
a genotype where an individual has 2 copies of a recessive gene (ex.ee)
P generation
parental generation
F1 generation
first filial generation, the kids
F2 generation
second filial generation, the grandkids