chapter 12: forces and motion
5.0(1)
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/57
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
58 Terms
1
New cards
force
a ______ is a push or pull that acts on an object
2
New cards
motion
a force can cause a resting object to move, or it can accelerate/decelerate a moving object by changing the object’s _______ and/or direction
3
New cards
newton
force is measured in _____ abbreviated as N
4
New cards
kg times m/s2
1 N = 1 ________
5
New cards
add
forces in the same direction ______ together
6
New cards
subtract
forces in opposite directions ______ from each other
7
New cards
net
the _____ force is the overall force acting on an object after the forces are combined
8
New cards
0
when the net forces on an object are balanced, the net force is _____, and there is no change in the object’s motion
9
New cards
unbalanced
an ______ force results when the net force is NOT zero
10
New cards
moves
when an unbalanced force acts on an object, the object ________ in a specific direction
11
New cards
friction
_______ is a force that opposes the motion of objects that touch as they move past each other
12
New cards
static
________ friction is the friction force that acts on objects that are not moving
13
New cards
stationary
static friction exists on ______ objects
14
New cards
opposite
static friction always acts in the direction _______ to that of the applied force
15
New cards
sliding
________ friction is a force that opposes the direction of motion of a moving object as it slides over a surface
16
New cards
less
because it is easier to move an already moving object, sliding friction for an object is always ______ that static friction
17
New cards
rolling
________ friction is the friction force that acts on rolling objects
18
New cards
100-1000
for a given set of material, the force of rolling friction is about ___________ times less than the forces of sliding or static friction
19
New cards
fluid
______ friction opposes the motion of an object through fluid
20
New cards
air resistance
fluid friction acting on an object moving through the air is known as ____ ______
21
New cards
gravity
_______ is a force that acts between any two masses
22
New cards
attractive
gravity is an _____ force that pulls objects together
23
New cards
terminal velocity
eventually, the force of air resistance equals the force of gravity, and an object reaches ____________
24
New cards
curved
when you throw an object forward, you’ll notice that it actually follows a _______ path
25
New cards
projectile
this curved path is an example of ______ motion
26
New cards
gravity
the combination of a forward velocity plus ______ causes an object to follow a curved path
27
New cards
aristotle
_________ was a greek scientists and philosopher that lived in 384 bc-322 bc
28
New cards
galileo
________ was an italian scientist from 1564-1642
29
New cards
newton
______ started his work in 1665 on the basis of galileo
30
New cards
first
newton’s _______ law of motion states that the motion of an object does not change as long as the net force acting on the object is zero
31
New cards
law of inertia
newton’s first law of motion is often referred to as the ____________
32
New cards
resist
inertia is the tendency of an object to ______ a change in motion
33
New cards
mass
inertia is based on the _____ and the speed of an object
34
New cards
mass
newton’s second law of motion states that the acceleration of an object is equal to the net force acting on it divided by the object’s ________
35
New cards
a=f/m
newton’s second law equation
36
New cards
9\.8m/s2
acceleration can also be due to gravity: _______
37
New cards
mass
_______ is the amount of matter in an object of the measure of the inertia
38
New cards
weight
_______ is the force of gravity acting on an object
39
New cards
w=mg
weight forumla
40
New cards
third
newton’s _____ law of motion states that whenever one object exerts a force on a second object, the second object exerts an equal and opposite force on the first object
41
New cards
reaction
whenever there is an action, there is an equal and opposite _______
42
New cards
direction
the reaction force is equal in size, but opposite in ______ to the action force
43
New cards
momentum
_______ is the product of an object’s mass to its velocity
44
New cards
more
the ______ the momentum something has, the harder it will be for that object to come to a stop
45
New cards
conservation
the law of _______ of momentum states if no outside force acts on the system, then the total momentum of the system does not change
46
New cards
when bat hits ball
when brushing your hair with a hairbrush
when brushing your hair with a hairbrush
describe examples of force
47
New cards
newton (N)
identify appropriate SI units used to measure force
48
New cards
the forces acting on an object have equal strength and act in opposite directions, they are balanced. These forces cancel out one another, and the motion of the object they are acting on remains unchanged. When the forces acting on an object are unbalanced, they do not cancel out one another.
explain how the motion of an object is affected when balanced and unbalanced forces act upon it
49
New cards
Static, sliding, and rolling friction occur between solid surfaces. Static friction is strongest, followed by sliding friction, and then rolling friction, which is weakest. Fluid friction occurs in fluids, which are liquids or gases
compare and contrast the four kinds of friction
50
New cards
Gravity causes objects to accelerate downward, whereas air resistance acts in the opposite direction and reduces acceleration
describe how earth’s gravity and air resistance affect falling objects
51
New cards
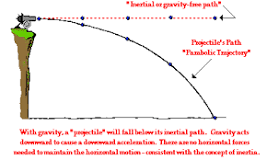
there is one force applied at the beginning on the trajectory, after which the only interference is from gravity
describe the path of a projectile motion
52
New cards
projectile is an object upon which the only force is gravity
identify the forces that produce projectile motion
53
New cards
every object will remain at rest or in uniform motion in a straight line unless compelled to change its state by the action of an external force. This tendency to resist changes in a state of motion is inertia
describe newton’s first law of motion and its relation to inertia
54
New cards
the acceleration of an object depends upon two variables – the net force acting on the object and the mass of the object. acceleration of the body is directly proportional to the net force acting on the body and inversely proportional to the mass of the body
describe newton’s second law of motion and its use to calculate acceleration, force, and mass values
55
New cards
Weight is equal to the mass of the object (m) x the acceleration due to gravity (g)
relate the mass of an object to its weight
56
New cards
forces always act in equal but opposite pairs. Another way of saying this is for every action, there is an equal but opposite reaction. This means that when you push on a wall, the wall pushes back on you with a force equal in strength to the force you exerted
explain how action and reaction forces are related according to newton’s third law of motion
57
New cards
momentum(p) = mass(m)x velocity(v)
calculate the momentum of an object
58
New cards
the total momentum of the two objects before the collision is equal to the total momentum of the two objects after the collision
describe what happens when momentum is conserved during a collision