Ichthyology Exam 1
1/182
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
183 Terms
Chordata
Notochord, dorsal hollow nerve cord, pharyngeal slits, post-anal tail
Olfactores
share ability to smell
cephalochordates
subphylum of chordata; no vertebral column, but notochord and pharyngeal slits
urochordata
subphylum of chordata; invertebrates that have a larval phase with chordate characteristics
Craniata
subphylum of chordata
Vertebrata
Infraphylum under Craniata
Gnathostomata
superclass under subphylum craniata; jaws are present and derived from gill arches
Agnatha
jawless fishes; two different lineages - hagfishes and lampreys
Dipnoi
Lungfishes; Sarcopterygii
What do Elasmobranchii include
Selachimorpha (sharks) and Batoidea (skates and rays)
Holocephali
chimeras
Actinistia
Coelocanths
Actinopterygii
ray-finned fishes (30,000)
Elopiformes
tarpon, ladyfishes
Anguilliformes
Eels
Elopomorpha
eels, tarpon, ladyfishes
Leptocephalus
tarpon larva
Clupeomorpha
herring, anchovies, filter feeders, most numerous fishes
Chondrichthys
cartilaginous species
Teleostii
genome duplication; huge diversity of fishes
Ostariophysi
minnows, tetras, catfishes
Cypriniformes
minnows; includes giant barb
Characiformes
tetras, pirahnas
Siluriformes
catfishes
Salmoniformes
order for salmon, trout; genome duplicated again (tetraploid)
Acanthomorpha
spiny-finned fishes (17,500 species); 80% of marine fishes
endochondral bone
replaces cartilage precursor
Petromyzontiformes
Order for native lampreys
Petromyzontidae
family for native lampreys
Lampetra tridentata
Pacific Lamprey
Acipenseriformes
Order for native sturgeons
Acipenseridae
family for native sturgeons
Acipenser transmontanus
white sturgeon; largest fish in North American waters
Salmoniformes
order for salmon, trout, whitefish, and grayling
Oncorhynchus nerka
sockeye salmon
Oncorhynchus gorbuscha
pink salmon
Oncorhynchus keta
chum salmon
Prosopium coulteri
Pygmy whitefish (native)
Introduced Atlantic salmon
Salmo salar
Introduced brown trout
Salmo trutta
Osmeriformes
order for native smelts
Osmeridae
family for native smelts
Thaleichthys pacificus (native smelt)
Eulachon
Esociformes
order for native mudminnows
Umbridae
family for native mudminnows
Novumbra hubbsi
Olympic Mudminnow; only fish endemic to WA
Cypriniformes
order for native minnows
cyprinidae
family for native minnows
Gila bicolor
Tui chub (native minnow)
Couesius plumbeus
Lake Chub (native minnow)
Mylocheilus caurinus
Peamouth (native minnow)
Catostomidae
family for native suckers
Catostomus catostomus
Salish sucker
Siluriformes
order for catfishes
Ictaluridae
family for introduced catfishes
Ameiurus melas
Black Bullhead
Cyprinodontiformes
order for livebearers
Poeciliidae
family for introduced livebearers
Gambusia affinis
Mosquitofish (livebearers)
Perciformes
order for sunfishes
Centrarchidae
introduced sunfishes
Lepomis macrochirus
Bluegill
Lepomis cyanellus
Green Sunfish
Percidae
family for introduced perches
Perca flavescens
Yellow perch
Scorpaeniformes
order for sculpins
Cottidae
family for native sculpins
Cottus asper
prickly sculpin (native)
Cottus gulosus
Riffle sculpin
Aristotle’s History of Animals
first European biology text
Zoarcidae
eelpouts
Stichaeidae
Pricklebacks
Pholidae
Gunnels
Embiotocidae
Surfperches
Scorpaenidae
rockfishes
Hexagrammidae
Greenling
Agonidae
Poachers
Pleuronectidae
Righteye flounders
How many fishes in the Salish sea
253
WA has —— marine fishes and —— freshwater fishes
403 and 89
Eel grass, bull kelp forest, salt marsh, rocky reefs, intertidal, soft bottom, and open water
What are the main Salish Sea habitats?
Admiralty inlet, deception pass, and swinomish channel
What are the three Salish Sea connections?
intramembranous bone(dermal bones)
form within a membrane
perichondral bone
forms when bone ossifies around cartilage without replacement
What bone type makes up fish skeletons?
intramembranous bone
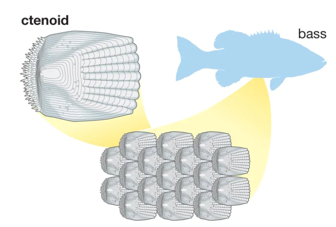
ctenoid scales
most species of fish; overlapping scales; spines on posterior marigins
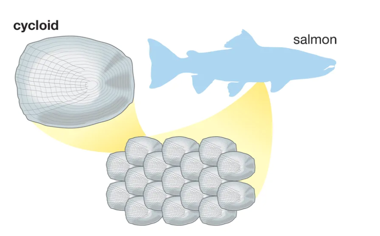
cycloid scales
simple version of ctenoid scales; salmon
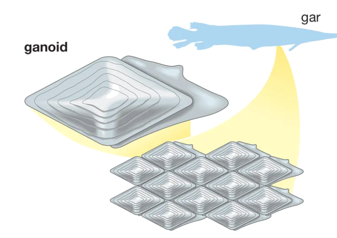
ganoid scales
older scale pattern; lots of mineralization; gars
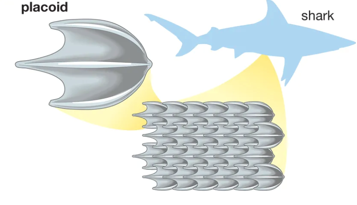
placoid scales
incredibly rough; sharks; dermal denticle
odontode
refers to scales or teeth; any epidermal structure that contains enamel or dentine
Hydrolagus colliei
Spotted ratfish; has second set of teeth for mating
cosmoid scales
present in sarcopterygian fishes (coelacanths and lungfishes)
skeletal, cardiac, and smooth (gut)
types of fish muscle tissues
white muscle
strong but fatigues quickly
red muscle
not as strong as white, but operates for long periods
biting muscles
adductor mandibulae
viscous (fictional) drag
friction between fish’s body and water; heavily influences body and fin shape
inertial (pressure) drag
pressure differences that result from displacement of water as fish moves; also influences body shape
physics of water, ecological niche, ancestry, present circumstances, and developmental stage
Swimming style is influenced by
how much trunk of body oscillates and which fins are being used
Two factors that describe swimming style