the animal kingdom (#14)
1/46
Earn XP
Description and Tags
🍂
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
47 Terms
diversity
refers to when animals range from insects to mammals, adapting to various environments
invertebrates & vertebrates
2 classification of animals
adaptations
include unique traits like camouflage & migration help animals survive
invertebrates
animals without a backbone;
no backbone allows flexibility;
body structures may include exoskeletons or soft bodies;
reproduce asexually (ex. coral polyps)
ex. giant clams, golden orb-weaver spider
vertebrates
animals with a backbone;
backbone protects the spinal cord and provides support
complex organ systems;
higher mobility due to skeleton;
ex. Philippine tarsiers, monitor lizards
Porifera (sponges)
Cnidaria (jellyfish)
Platyhelminthes (flatworms)
Nematoda (roundworms)
Annelida (segmented worms)
Mollusca (clams)
Arthropoda (insects)
Echinodermata (sea stars)
Chordata (vertebrates)
8 invertebrate phyla
Mammalia
Aves (birds)
Reptilia
Amphibia
Osteichthyes (bony fish)
Chondrichthyes (cartilaginous fish)
6 vertebrate classes
bilateral, radial, and asymmetrical
3 types of body symmetry in animals
triploblastic animals
these animals develop from three germ layers allowing for complex structures;
endoderm, mesoderm, ectoderm
ex. coelomates, frog, flatworms, & humans
dipoblastic animals
these animals’ body wall develop from two embryonic germ layers;
endoderm/mesendoderm & ectoderm
ex. phylum cnidaria (generally regarded), phylum ctenophores (comb jellies)
biodiversity
refers to the variety of life forms contributing to ecosystems;
suggests that each species plays a crucial role in its ecosystem
predators
herbivores
pollinators
seed dispersers
decomposers
roles of animals in the ecosystem
Least Concern, Vulnerable, Endangered, Critically Endangered, & Extinct
5 categories of conservation status
True
TRUE OR FALSE:
Biodiversity plays a crucial role in ecosystem balance and function, with various animal.
coral polyps
give an example of an invertebrate that reproduce asexually
radial symmetry
ANIMAL SURVIVAL & ADAPTATION:
in finding food, they used _____ _____ to interact w/ their environment from all sides;
this helped them capture food more easily as they are sessile
cepehalization
ANIMAL SURVIVAL & ADAPTATION:
to protect themselves from predators, they used _______ which allowed them to detect threats & food faster;
allowed for movement
bilateral symmetry, cohabitation
ANIMAL SURVIVAL & ADAPTATION:
in adpating to changing environments, immobile organisms adapted through ______ _____ & _____ which helped them move efficiently and survive in diverse environments
radial symmetry
3 TYPES OF SYMMETRY:
body that can be divided equally around a central point
ex. cnidaria
bilateral symmetry
3 TYPES OF SYMMETRY:
allowed for efficient movement: streamined body organization;
enhanced coordination;
survival benefit: better mobility is essential for finding food, escaping predators, & navigating environments
assymetrical
3 TYPES OF SYMMETRY:
body w/ no pattern or symmetry
ex. sponges, narwhale, snails
segmentation
refers to when body is organized into definite regions or segments;
each segment is called a metamere/somite
metamerism
2 TYPES OF SEGMENTATION:
animals who experience this has similar morphology throughout their body
ex. centipede
tagmatization
2 TYPES OF SEGMENTATION:
animals who experience this has different segments throughout their body;
each segment is called tagmata
ex. mantis
coelom
this is the fluid-filled body cavity
coelomate
ANIMAL CHARACTERIZATION BASED ON COELOM PRESENCE:
these have a true coelom fully lined by mesoderm
ex. annelids & verterbratex
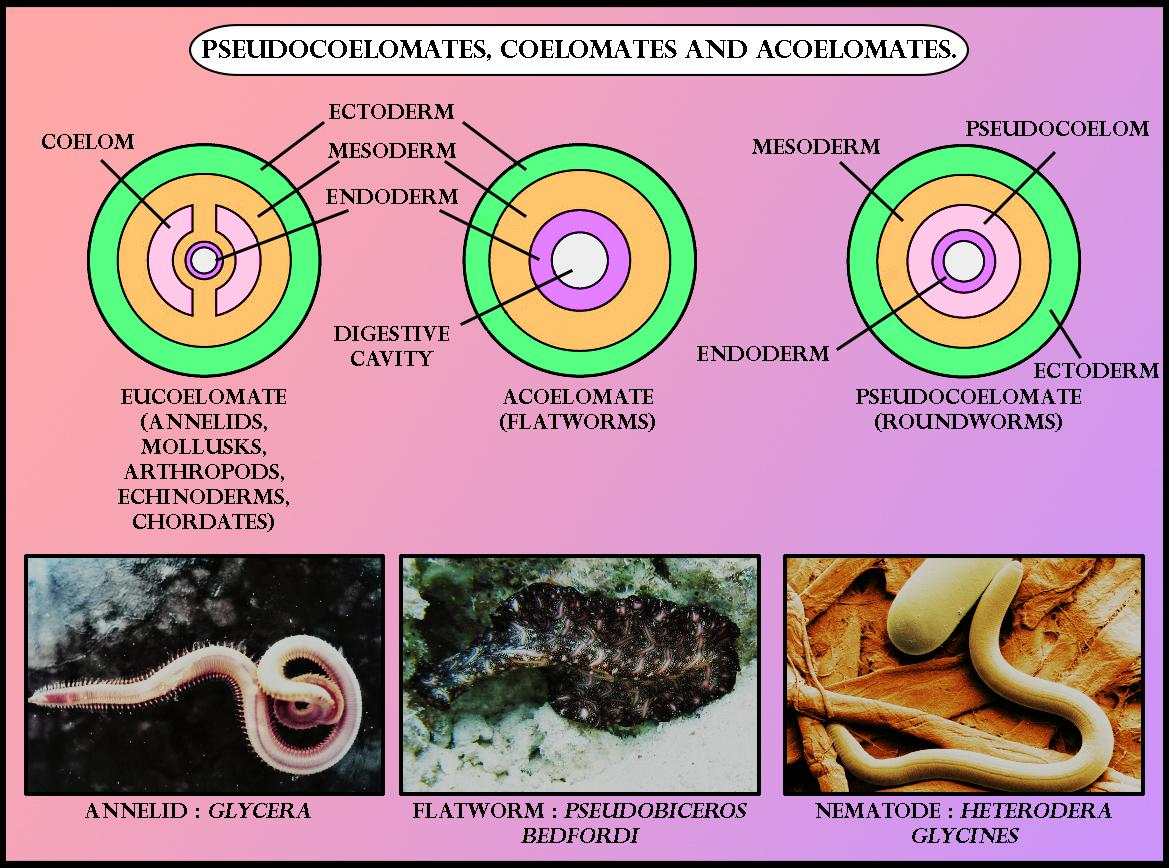
pseudocoelomate
ANIMAL CHARACTERIZATION BASED ON COELOM PRESENCE:
annelids w/ a body cavity partially lined by mesoderm
ex. roundworms
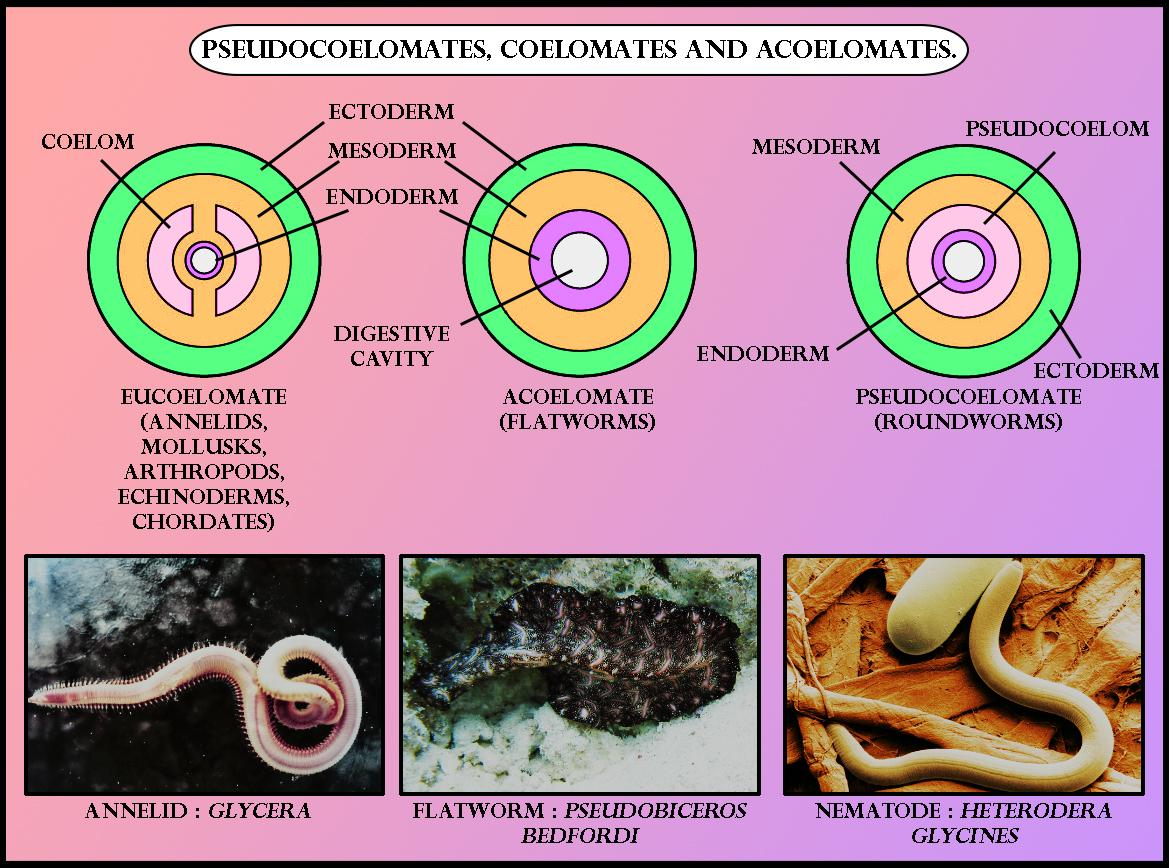
acoelomate
ANIMAL CHARACTERIZATION BASED ON COELOM PRESENCE:
animals without coelom
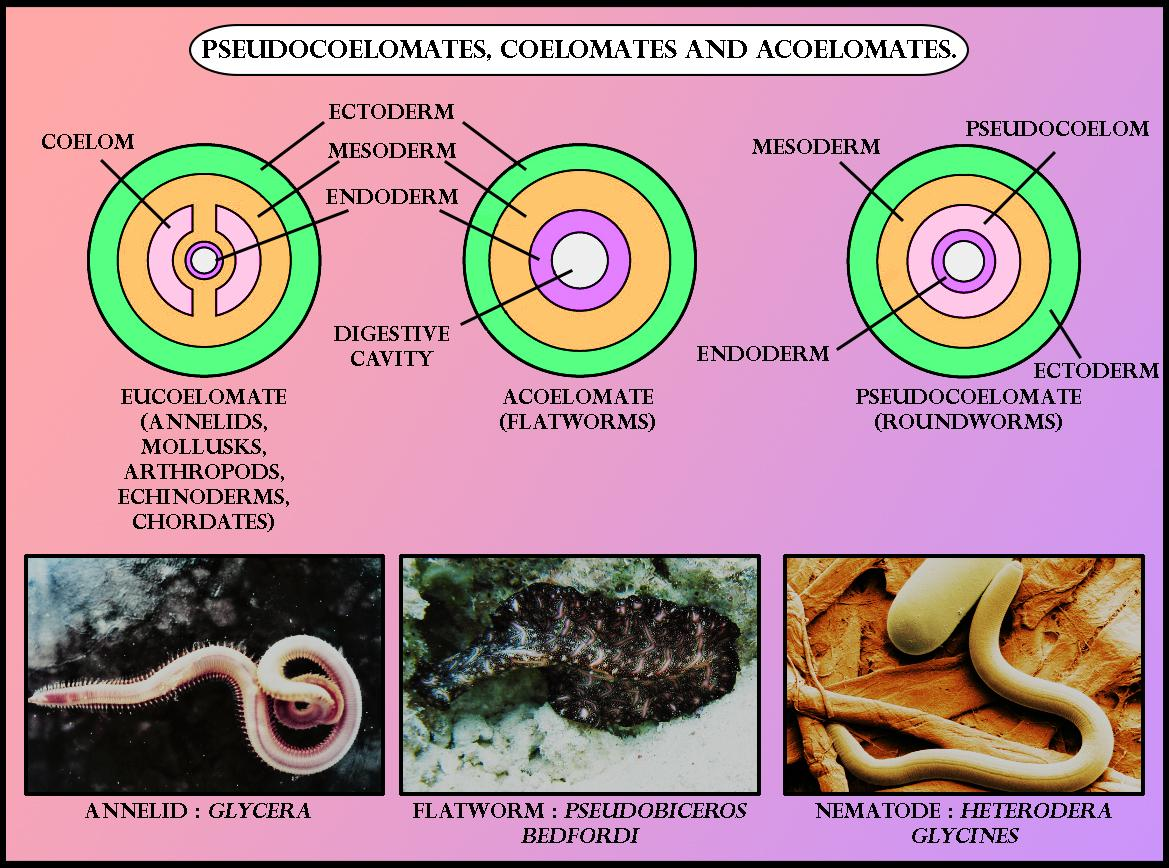
porifera
9 INVERTEBRATE PHYLA:
filter feeder;
cellular level;
sessile (adult), free swimming (larvae)
ex. Aplysina fistularis (Yellow tube sponge)
acoelomate, asymmetrical /radially symmetrical, both sexual & asexual
PORIFERA:
coelom:
symmetry:
mode of repro.:
cnidaria
9 INVERTEBRATE PHYLA:
no distinct internal organs but w/ tissue layers;
polyp: body shaped like a hollow cylinder of bag that opens & closes at the top
medusa - umbrella shaped w/ mouth 1 tentacles hanging down in the water
ex. jellyfish
polyp
in cnidarians, this refers to the body shaped like a hollow cylinder of bag that opens & closes at the top
medusa
in cnidarians, this refers to the umbrella shaped w/ mouth & tentacles hanging down in the water
acoelomate, diploblastic, radial
CNIDARIA:
coelom:
germ layer:
symmetry:
sexual & asexual reproduction
platyhelminthes (flatworms)
9 INVERTEBRATE PHYLA:
simplest phylum at organ level;
has digestive, reproductive, muscular, & excretory organs
dorsoventrally flattened
ex. planaria
triploblastic acoelomate, bilateral, sexual & asexual
PLATYHELMINTHES:
coelom:
symmetry:
mode of repo.:
nematoda (roundworms)
9 INVERTEBRATE PHYLA:
complete digestive system;
round & slender bodies that taper at both ends;
has tough cuticle;
parasitic
ex. Ascaris lumbricoides
triploblastic pseudocoelomate, bilateral, sexual & asexual
NEMATODA (ROUNDWORMS):
coelom:
symmetry:
mode of repro.:
annelida (segmented worms)
9 INVERTEBRATE PHYLA:
round & slender segmented bodies, divided internally by septa;
complete digestive system;
body divided into segments
ex. Hirudinaria granulosa (leech)
through skins, gills, or parapodia
In annelids (segmented worms), where does there respiration occur?
triploblastic coelomate, sexual & asexual
ANNELIDA (SEGMENTED WORMS):
coelom:
mode of repro:
mollusca
9 INVERTEBRATE PHYLA:
soft-bodied animals, w/ a shell
mantle: tissue that secretes the shell
foot: used for movement or anchoring
radula: tongue-like organ w/teeth for feeding
ex. snails
triploblastic coelomate, bilateral and asymmetrical, sexual & asexual
MOLLUSCA:
coelom:
symmtery:
mode of repro.:
arthropoda
9 INVERTEBRATE PHYLA:
segmented body;
exhibit tagmatization;
chitinous exoskeleton
largest phylum
insects
triploblastic coelomates, bilateral, sexual reproduction
ARTHROPODA (JOINT-LEGGED ANIMALS):
coelom:
symmetry:
mode of repro.:
echinodermata (spiny-skinned animals)
9 INVERTEBRATE PHYLA:
exclusively marine;
has water vascular system;
no cephalization & tube feet
ex. starfish, sea urchin
triploblastic coelomates, radial & bilateral, sexual & asexual
ECHINODERMATA (SPINY-SKINNED ANIMALS):
coelom:
symmetry: ______ (adults) & ______ (larvae)
mode of repro.: