Inorganic and Organic Chemistry
1/199
Earn XP
Description and Tags
For test, im scared this sucks everything hurts
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
200 Terms
The four fundamental types of inorganic compounds:
acids, bases, salts, and oxides
Acids and bases are normally dissolved in —
Water
acids dissociate in an aqueous solution to yield hydrogen ions; bases yield hydroxide ions
Hint: What theory is this statement referring to?
Arrhenius theory
Acids that yield one hydrogen ion per molecule in solution
monoprotic
Acids that dissociate into more than one hydrogen ion
polyprotic
Acids composed of hydrogen and one other element
Binary
Acids that contain oxygen in addition to hydrogen and another nonmetallic element
ternary or oxyacids
yield a large number of hydrogen ions in the solution; examples include hydrochloric, hydrobromic, nitric, and sulfuric acid
Strong acids
neither high nor low; examples include phosphoric acid and sulfurous acid
Hint: This is a type of acid
Moderate acids
yield a low number of hydrogen ions; includes acetic acid, boric acid, carbonic acid, and nitrous acid
Weak acids
Strengths of bases are determined by the percent dissociation of the compounds into — ions and — ions
Positive and hydroxide
Noted for a sour taste
Changes litmus paper red
Reacts with metals above hydrogen liberate hydrogen gas
Acids

Is Associated with the term “alkali”
Noted for a bitter, metallic taste
Changes litmus paper blue
Bases

An acid is a proton donor
A base is a proton acceptor
What theory states this?
BRØNSTED-LOWRY THEORY
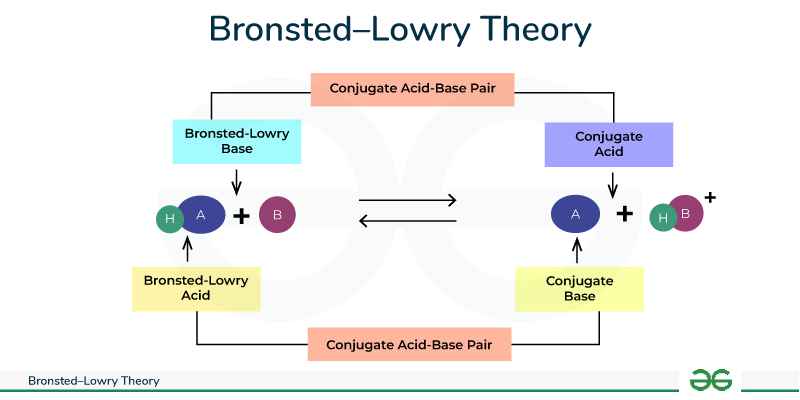
Water is — meaning is can act as either an acid or a base
amphoteric
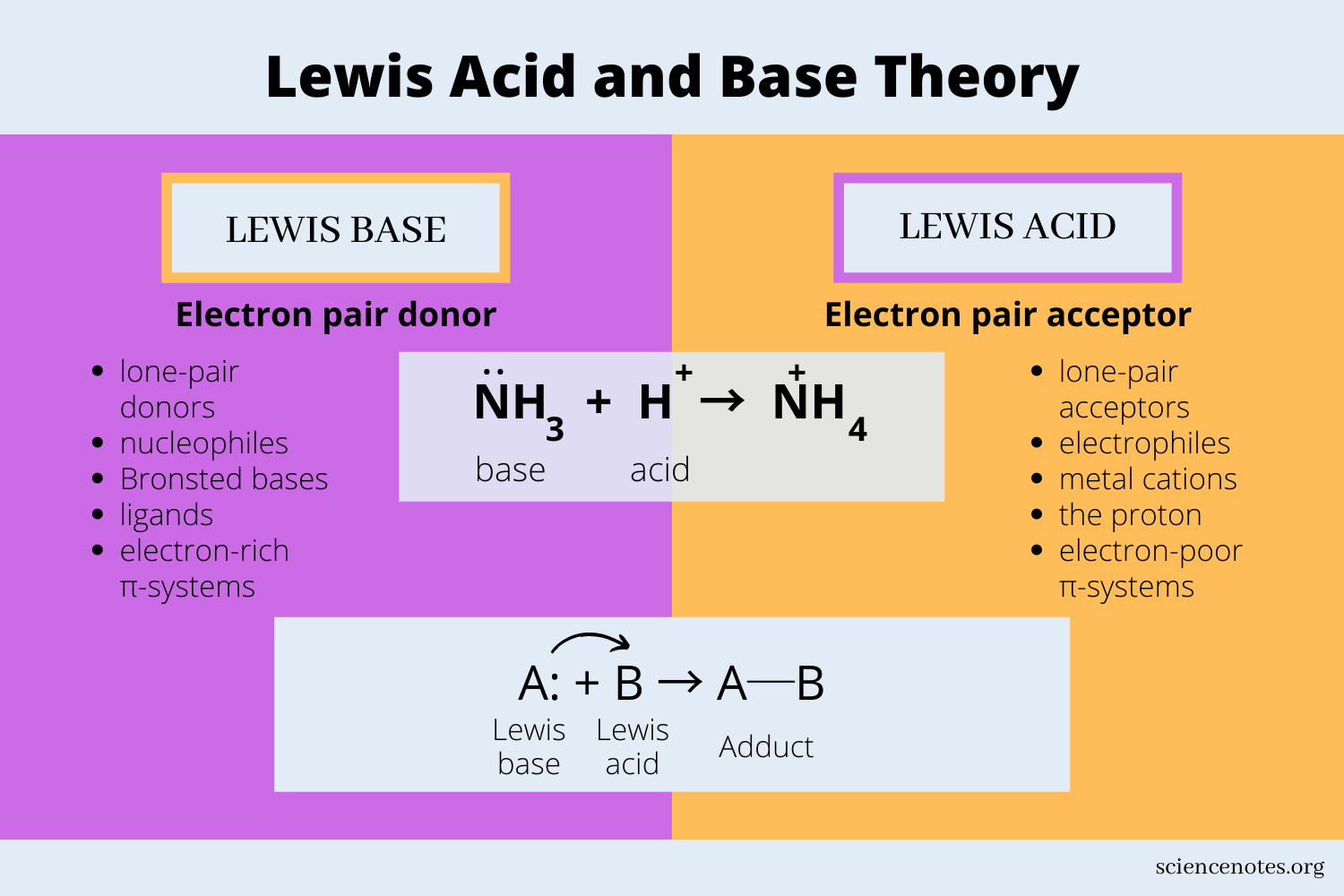
An acid accepts a pair of electrons
A base donates a pair of electrons
What theory is this?
Lewis theory
Literally means “without water”
Includes oxides of metals and nonmetals
Nonmetallic oxides react to form acids
Metallic oxides react to form bases (remember bases have a metallic taste)
Anhydrides

compounds formed between a positive ion other than H+ and a negative ion other than OH-
Salts

chemical reaction of salts
Hydrolysis
the property of dissociating a substance into charged species that may be atoms or groups of atoms
Ionization
positively charged ions
Cations

negatively charged ions
Anions
the passage of an electric current through a solution
Electrolysis
Solutions that allow electrolysis are called
electrolytes
It is necessary to buffer embalming fluids to have a pH approximately equal to that of normal blood
What is this PH?
7.35-7.45
After death, pH of the blood in the body changes from slightly basic to
Acidic
As decomposition sets in, the pH again becomes
Basic
The action of formaldehyde on body proteins is pH dependent and works most effectively in the range of:
Hint: This is a pH value
7.35-7.45
Typical buffers added to embalming fluids:
borax, sodium phosphates, and citrates
a compound, typically a crystalline one, in which water molecules are chemically bound to another compound or an element:
Hydrate
Anhydrous means
Without water
Whenever water is removed from a substance, — occurs
Dehydration
traditionally used as a method of closing the back of the skull in the case of a cranial autopsy
Plaster of Paris

This term means “water-loving”
Hydrophilic
Chemists use — to refer to hydrates that are able to attract additional moisture
hygroscopic
hydrates that are capable of absorbing additional water
Deliquescence
(Note: The image is sodium chloride, which is a salt)

This terms means to give up their water of crystallization to the air
(I dont why its worded like this)
Efflorescent
A process by which water is split by other compounds
The principal chemical property of salts
Hydrolysis
What is the most abundant compound on Earth?
Water
How much of the Earth’s surface does water cover?
Hint: This is not a %
3/4
What percent of the human body is water?
70%
What percent of bacterial cells is water?
85%
Inorganic compounds do not contain both of these elements
Hydrogen and carbon
What is the freezing point of water?
32 F
0 C
What is the boiling point of water?
212 F
100 C
What is the universal solvent?
Watuh

An electrically positive atom because it has a deficiency of electrons:
(Hint: What element is this?)
Hydrogen
This is formed when the positive end of one molecule is attracted to a negative end of another:
Hydrogen bond
The surface film of a liquid caused by the attraction of the particles in the surface layer by the bulk of the liquid, which minimizes surface area:
Surface tension
An example shown was raindrops

How is surface tension lowered?
Adding surfactants
What is the role of surface tension in embalming?
It helps facilitate the fluid through the tissues.
Helps retain moisture in emaciated bodies
What is the primary vehicle used in embalming?
Water
Types of substances considered to be impurities in water:
Soluble solids
Insoluble solids
Bacteria
Gases
Liquids
This type of water contains certain minerals (calcium, magnesium, and sometimes iron) that destroy the cleansing action of soap
Hard water
(This water sucks for curly hair)
Can be removed by boiling and is due to the presence of bicarbonate salts of calcium and magnesium
Hint: Is this temporary or permanent?
I will have to go back and figure out what this is asking. Water slides.
Temporary
Caused by chloride and sulfate salts of calcium and magnesium, can only be removed with addition of chemicals
Hint: Is this temporary or permanent?
I will have to go back and figure out what this is asking. Water slides.
Permanent hardness
How can you remove hardness from water?
Adding sodium carbonate
Adding soap
Ion exchange systems
Simple distillation
These are homogeneous mixtures of two or more substances:
True solutions

A solution that has ethanol as its solvent:
Tincture
A solution with water as its solvent:
Aqueous solution
A solid solution is called:
Alloy
(brass, bronze, stainless steel, and sterling silver)
This is what does the dissolving:
Solvent
This is what is dissolved:
Solute
This is a synonym for the word “solvent”
Vehicle
The quality of being soluble; the amount of a substance that will dissolve in another substance:
Solubility
A solution that contains all of the solute it can hold is described as:
Saturated
(Note: One example is soda. It holds all the carbon dioxide (solvent) in water (solute).

Factors that influence solubility:
The nature of the solute and solvent – “like dissolves like”
Temperature – the solubility of gases in liquids decreases with an increase in temperature
Pressure – only effects gases; soda going flat after being opened as carbon dioxide escapes
A solution that contains a relatively small amount of solute:
Diluted solution
Contains a relatively large amount of solute:
Concentrated
(Note, honey is a concentrated solution. HIGH amount of SUGAR; LOW amount of WATER)

This is when the solute has not reached saturation:
Unsaturated solution
Contains more solute than it can normally hold; difficult to prepare and maintain:
Supersaturated solution

The concentration of formaldehyde in embalming fluid:
Index
Particles move from regions of higher concentration to lower concentrations to attain a uniform concentration:
Diffusion
a type of diffusion specifically through membranes – diffusion of water is from a region of higher water concentration to lower water concentration
Osmosis
This is when a solute has equal concentration:
Isotonic
(Note, this is an image of 0.9% saline, which is normal saline. This is a isotonic solution. It helps me to be able to think of a real life example)
Saline is considered isotonic because its sodium chloride (NaCl) concentration is similar to that of blood plasma, meaning it doesn't cause cells to shrink or swell when introduced into the body, maintaining fluid balance (thanks google)

This is when a solute has a greater concentration:
Hypertonic
This is when a solute has a lesser concentration:
Hypotonic
Placing a red blood cell in a hypertonic solution causes it to shrink is called:
Crenation
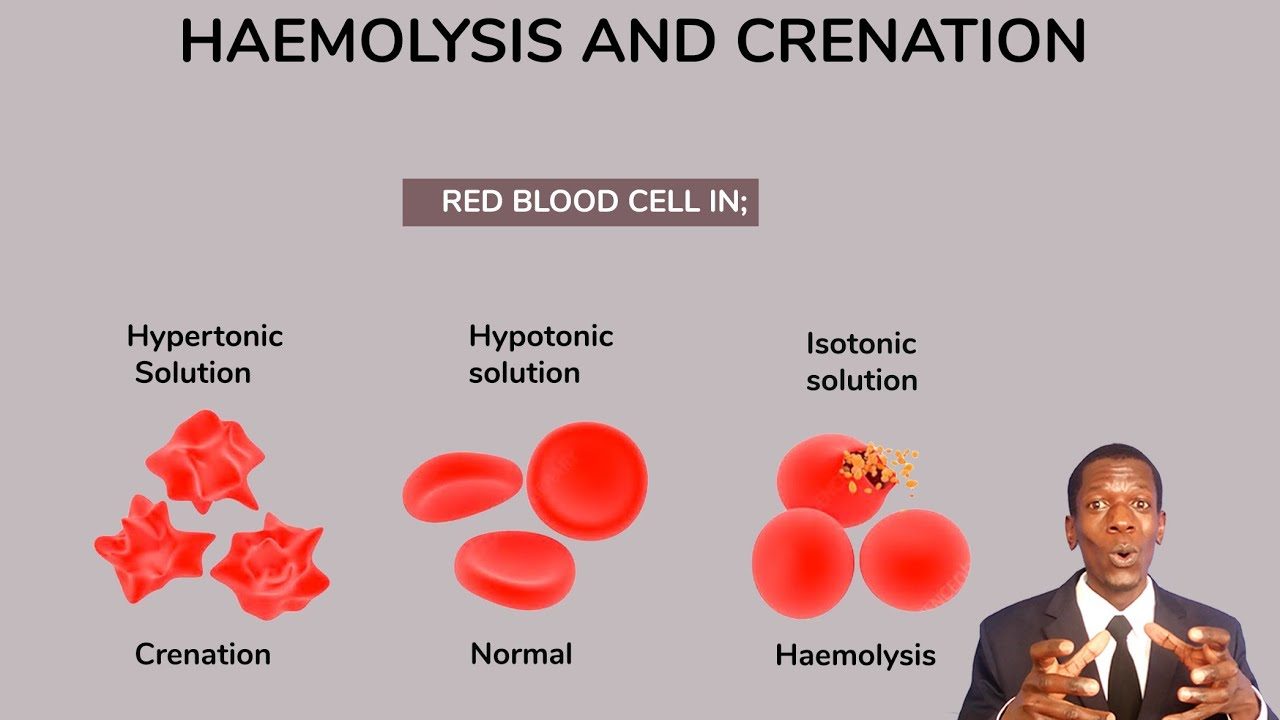
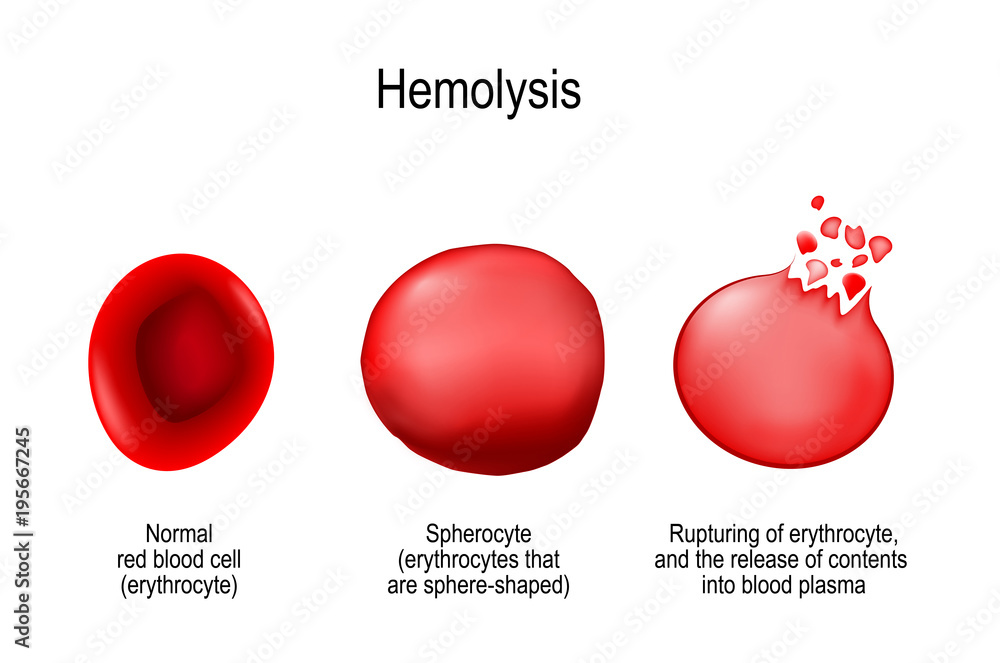
Hypotonic solution can cause the cell to swell and burst. This is called:
Hemolysis
(Note, this is when the red blood cells rupture)
When a body with normal moisture content is embalmed, the injected embalming solution should be — — to the content of the tissues
Slightly hypotonic
Edematous bodies require a — — solution to draw out water
Slightly hypertonic
Dehydrated bodies require a — — solution than normal:
More hypotonic
The study of carbon and substances which contain carbon:
Organic chemistry
Chemical reactions in organic chemistry should produce a minimum of how many types?
Eight
What are the ten types of chemical reactions in organic chemistry?
Acids
Alcohols
Aldehydes
Amides
Amines
Esters
Ethers
Hydrocarbons
Ketone
Mercaptans
Two or more organic substances that contain the same elements and the same number of atoms but have entirely different physical and chemical properties:
Isomers
What is a key factor in identifying an organic substance?
The exact arrangement of atoms
This type of formula usually involves a diagram showing the exact arrangement and bonding patterns of a compound:
The structural/graphic formula
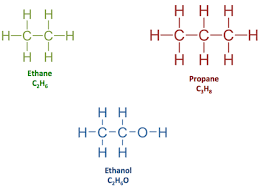
This type of formula is an abbreviation of a structural formula:
Line formula
The simplest organic compounds; contains only the elements carbon and hydrogen
Hydrocarbons
Hydrocarbons only contain these two elements:
Hydrogen and Carbon
Compounds characterized by open-chains of carbon to carbon bonds are considered:
aliphatic/acyclic
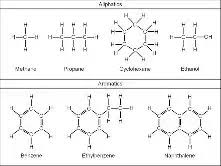
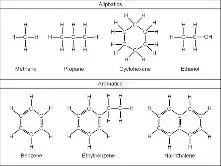
Compounds whose chains of carbons form a ring are
called:
aromatic/cyclic
All carbon to carbon bonds are — covalent bonds
Hint: Single, double, or triple?
Single
Are alkanes aromatic or aliphatic?
Aliphatic
(Remember, alk means aliphatic)
These are considered saturated hydrocarbons because they will not hold any more hydrogens
Hint: This is a group of hydrocarbons
Alkanes
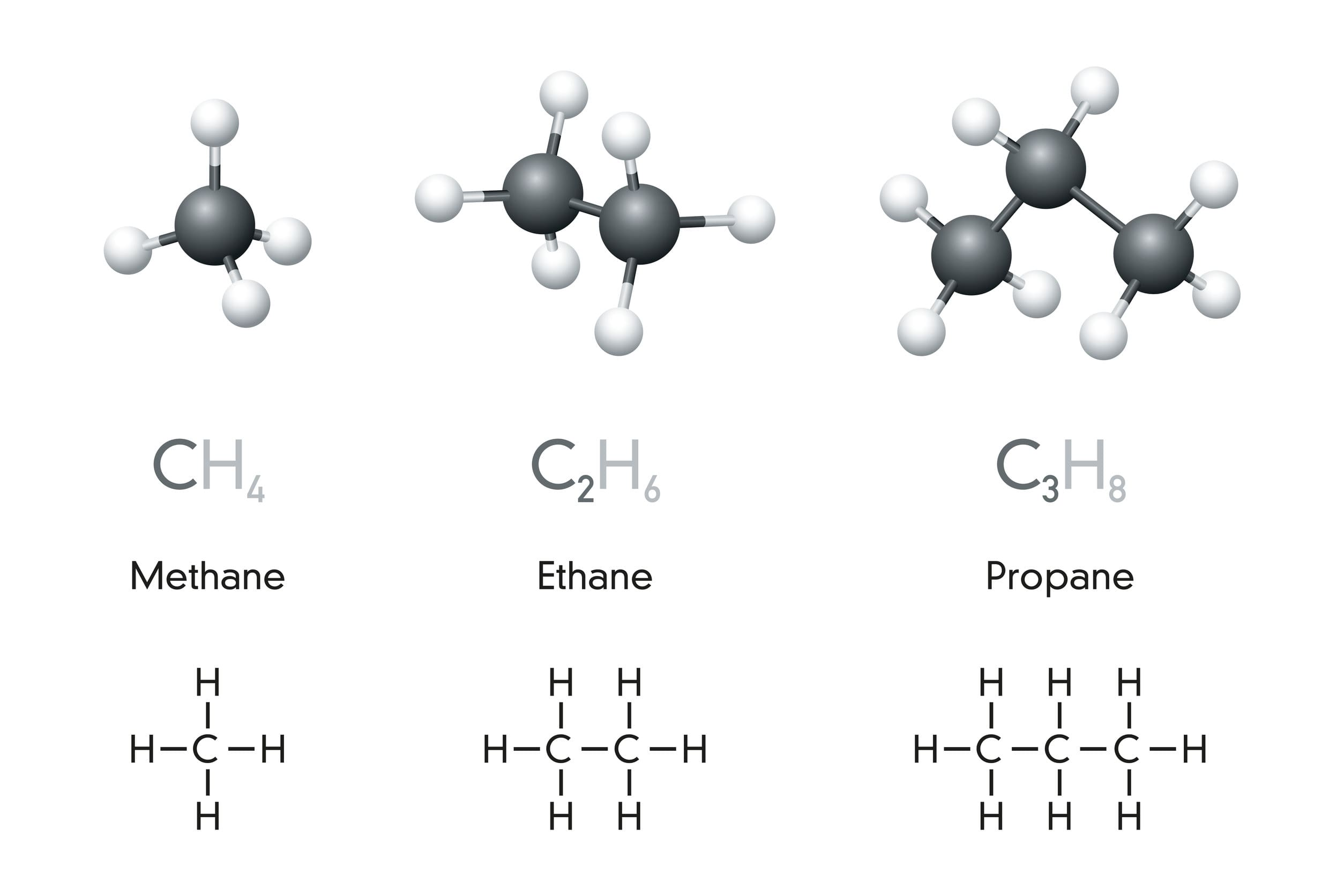
Prefix “alk” means:
Aliphatic
Suffix “ane” means
Single bond
Methane is the first member of its class. This is called the Methane class, another term for this class is:
The Paraffin class
CH4 is…
How many carbon?
How many hydrogen?
Methane
1 carbon
4 hydrogen