Water Pollution and Wastewater Treatment Overview
1/197
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
198 Terms
Water Pollution
Contamination of water bodies from human activities.

Water Bodies
Includes lakes, rivers, aquifers, and groundwater.
Contaminants
Substances introduced into water in excess concentrations.
Physical Characteristics
Includes solids, temperature, color, odor, turbidity.
Chemical Characteristics
Includes organics, inorganics, and gases in water.
BOD
Biochemical Oxygen Demand; measures organic matter in water.
COD
Chemical Oxygen Demand; measures total oxygen required.
TOC
Total Organic Carbon; measures organic compounds in water.
Point Source Pollution
Single large source of water pollution.
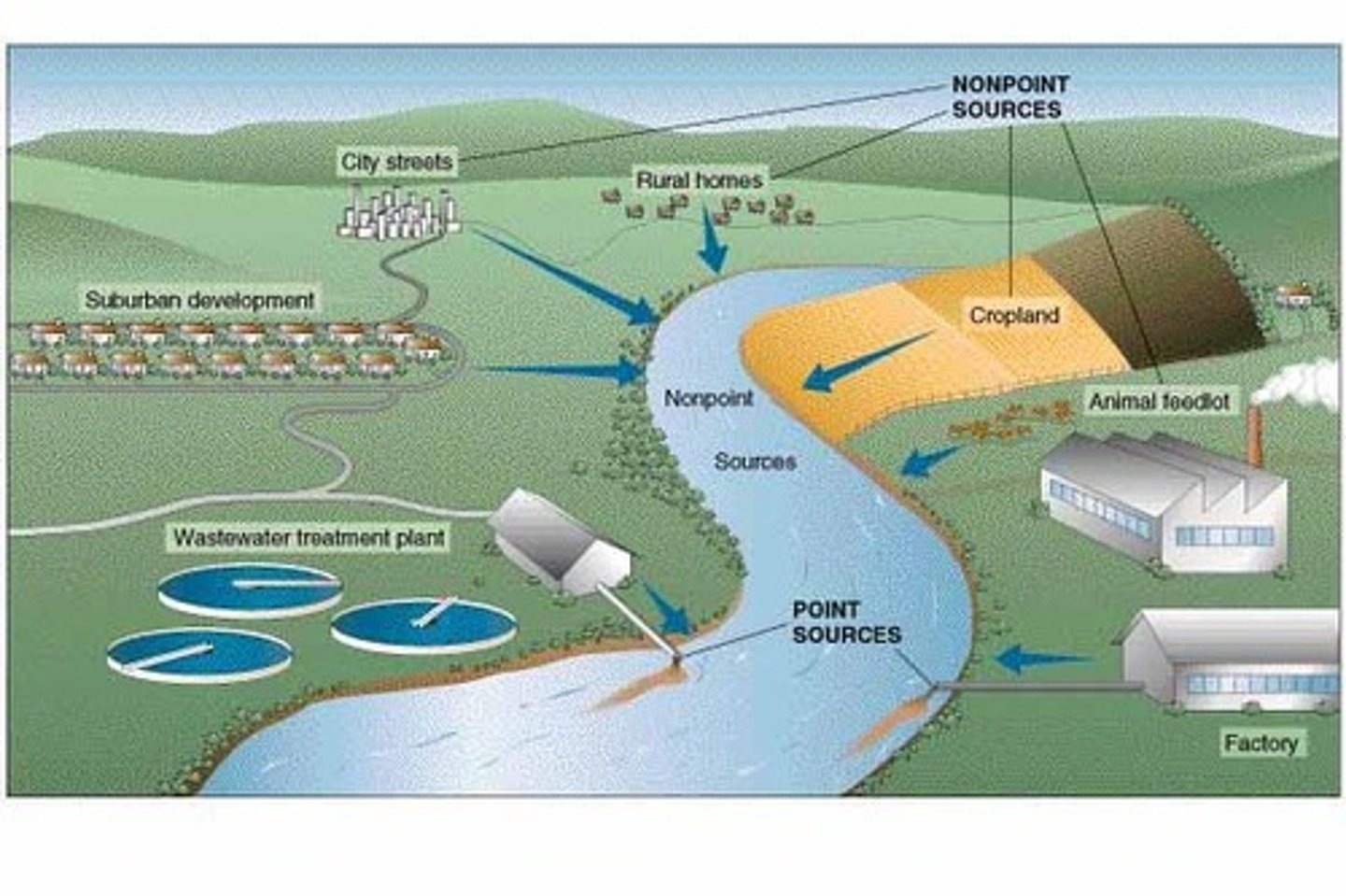
Non-point Source Pollution
Diffuse pollution without a specific identifiable source.
Organics in Water
Includes proteins, carbohydrates, lipids, and pesticides.
Inorganics in Water
Includes pH, chlorides, nitrogen, phosphorus, heavy metals.
Gases in Water
Includes oxygen, hydrogen sulfide, and methane.
Biological Characteristics
Includes pathogens, indicators, viruses, and invertebrates.
Emerging Organics
Newly recognized organic pollutants in water.
Alkalinity
Water's ability to neutralize acids.
Heavy Metals
Toxic metals like lead, mercury in water.
Turbidity
Cloudiness or haziness of water due to particles.
Pathogens
Microorganisms causing diseases in water.
Water Cycle
Natural process of water movement through environment.
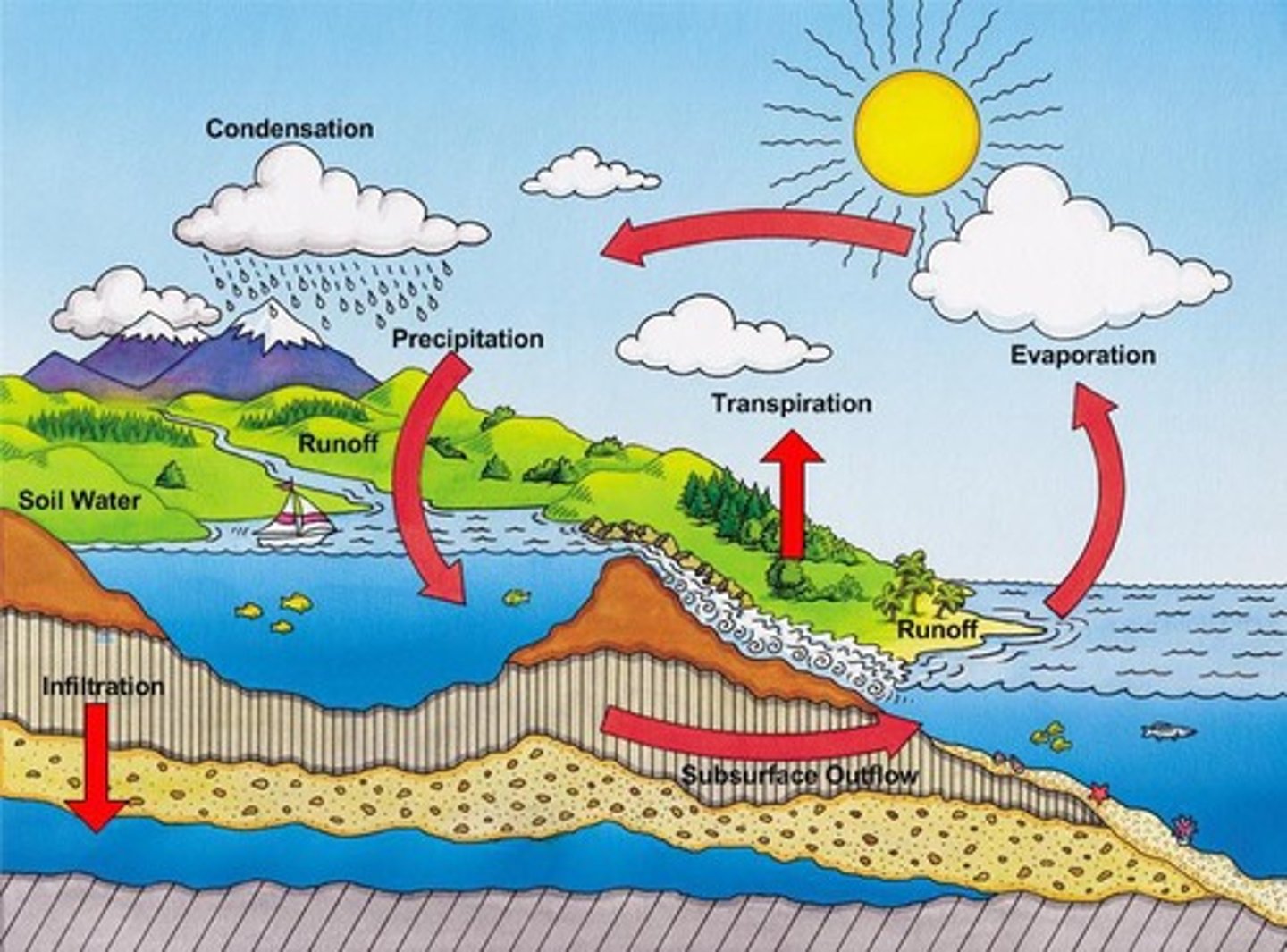
Runoff
General movement of sediments into water bodies.
Pesticide Spraying
Application of chemicals to control pests.
Fertilisers
Nutrients from farms that can pollute water.
Point Sources
Identifiable sources of water pollution.
Non-Point Sources
Diffuse sources contributing to water pollution.
Biodegradable Organic Matter
Decomposable waste by bacteria in water.
Suspended Solids
Particles floating in water affecting clarity.
Colloidal Solids
Tiny particles that remain suspended in water.
Dissolved Solids
Substances dissolved in water affecting quality.
Nutrients
Essential elements like nitrogen and phosphorus.
Acidic Species
Substances lowering water's pH level.
Basic Species
Substances raising water's pH level.
Ionic Species
Charged particles affecting water chemistry.
Soaps and Detergents
Surfactants causing pollution in water bodies.
Volatile Organics
Organic compounds that evaporate easily.
Recalcitrant Organics
Chemicals resistant to degradation in water.
Thermal Pollution
Increase in water temperature affecting ecosystems.
Radioactive Material
Substances emitting radiation contaminating water.
Fund Pollutants
Pollutants with some environmental absorptive capacity.
Degradable Pollutants
Organic waste broken down by bacteria.
Eutrophic Conditions
Excessive nutrients causing overgrowth of plants.
Persistent Pollutants
Chemicals not easily broken down by nature.
Stock Pollutants
Pollutants with little to no absorptive capacity.
Dissolved Oxygen (DO)
Measure of oxygen available in water.
DO Maximum
10 mg/L at 16°C for dissolved oxygen.
Oxygen Sources in Water
Diffusion, aeration, and photosynthesis introduce oxygen.
DO Stress Level
Below 5 mg/L, aquatic life is stressed.
Water Quality Ratings
Good (8-9), Slightly Polluted (6.7-8), etc.
Total Organic Carbon (TOC)
Measure of organic compounds in water.
Chemical Oxygen Demand (COD)
Amount of oxygen required to oxidize pollutants.
Biochemical Oxygen Demand (BOD)
Oxygen needed by bacteria to decompose organic matter.
Physio-Chemical Characteristics
Physical and chemical properties of water quality.
Physical Properties
Characteristics like temperature, colour, and odour.
Turbidity
Cloudiness or haziness in water due to particles.
Conductivity
Measure of water's ability to conduct electricity.
Sampling Methods
Techniques include grab, composite, and flow weighted.
ThOD
Total oxygen needed to oxidize a compound.
Stoichiometric Principles
Calculations based on the ratios of reactants.
C6H12O6
Chemical formula for glucose, a simple sugar.
Molecular Weight
Mass of a molecule, e.g., C6H12O6 is 180.
Oxygen Demand Ratio
1.067 g O2 per g of glucose.
Chemical Oxygen Demand (COD)
Measures pollution potential of organic matter.
Biochemical Oxygen Demand (BOD)
Indicates organic matter concentration in wastewater.
Potassium Dichromate
Oxidant used in COD testing.
Oxidation Reaction
Organic matter reacts with oxidant to produce CO2.
FAS Titration
Used to determine remaining potassium dichromate.
COD Calculation Formula
COD = (Blank-Test)M8*1000/Volume of sample.
Titration
Process to determine concentration of a substance.
Ferrous Ammonium Sulphate (FAS)
Used in titration for COD measurement.
Incubation Conditions
Sample held in dark at 20°C for BOD.
BOD5
BOD test over a five-day period.
Dissolved Oxygen (DO)
Oxygen available in water for organisms.
Sewage Sample Volume
Example used was 35 ml for COD calculation.
Blank Sample
Control sample used for comparison in titration.
Turbidity Measurement
Indicates water clarity and potential pollutants.
Organic Matter
Substances containing carbon, significant in water quality.
Environmental Engineering
Field focused on improving environmental quality.
Biochemical Oxygen Demand (BOD)
Oxygen needed by microorganisms for organic matter decomposition.
BOD5
BOD test over 5 days at 20°C.
BOD3
BOD test over 3 days at 20°C.
Exponential decay curve
Describes the rapid oxidation of BOD substances.
Dilution Factor (D)
Ratio of sample bottle volume to sample volume.
BODt
BOD at time t, measured in mg/L.
DOi
Initial dissolved oxygen in sample, mg/L.
DOf
Final dissolved oxygen in sample, mg/L.
Ultimate BOD (UBOD)
Maximum biochemical oxygen demand of a sample.
BOD rate constant (k)
Rate of BOD decay at specific temperature, day-1.
Temperature
Affects microbial activity and BOD measurements.
Time
Duration for BOD tests, influencing results.
Light
Environmental factor affecting microbial activity.
Sodium Thiosulfate
Used for titration in BOD testing.
Starch indicator
Used to indicate endpoint in titration.
BODt formula
BODt = UBOD (1-e^(-kt)).
BOD calculation
BODt = (DOi - DOf) * D.
Sample volume (Vs)
Volume of wastewater sample in mL.
Sample bottle volume (Vb)
Typically 300 mL for BOD tests.
BOD at 30°C
Calculated using temperature correction factor.
θ (theta)
Temperature correction factor, typically 1.047.
BOD test procedure
Involves titration and incubation of samples.
BOD significance
Indicates organic pollution level in water.