CEM 141 - Exam 2
1/211
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
212 Terms
What is electromagnetic radiation?
a wave that is oscillating in two perpendicular fields (light)
What are some examples of electromagnetic radiation?
radio waves
microwaves
infrared
visible
ultraviolet
x-rays
gamma rays
What are the 3 ways that we characterize electromagnetic radiation?
wavelengths
frequency
energy
What is different about radio waves and x-rays?
their wavelengths, frequencies, and energies differ
What is a light?
A. a wave
B. a particle
C. both
D. neither
C - both
True or false: electrons are both particles and waves
true
What makes light a wave?
Light doesn’t contain mass, yet it can transfer energy
When characterizing waves, what is the amplitude?
amplitude is the height of the wave (peak) or depth of the trough.
What is amplitude related to in light?
the intensity of the light
True or false: the lower the amplitude the higher the intensity (brightness) of light
False - the higher the amplitude the higher the intensity of light
When characterizing waves, what is wavelength?
The distance between any two identical points on the wave.
What greek letter is the symbol for wavelength?
lambda (wishbone & measured in m)
True or false: the type of light depends on its wavelength
true
What is the greek letter for frequency?
nu (squiggly v)
When characterizing waves, what is frequency?
The number of wave fronts that pass through a point in a given amount of time (typically 1 second).
What is the unit of frequency?
1 Hz = 1 1/s OR 1 s^-1
True or false: there is not an inverse relationship between wavelength and frequency
false - when you double frequency, wavelength is halved
How are wavelength and frequency related?
speed of light (c)
Energy of light
increases as frequency increases (and wavelength decreases)
True or false: energy of light is not related to amplitude
true
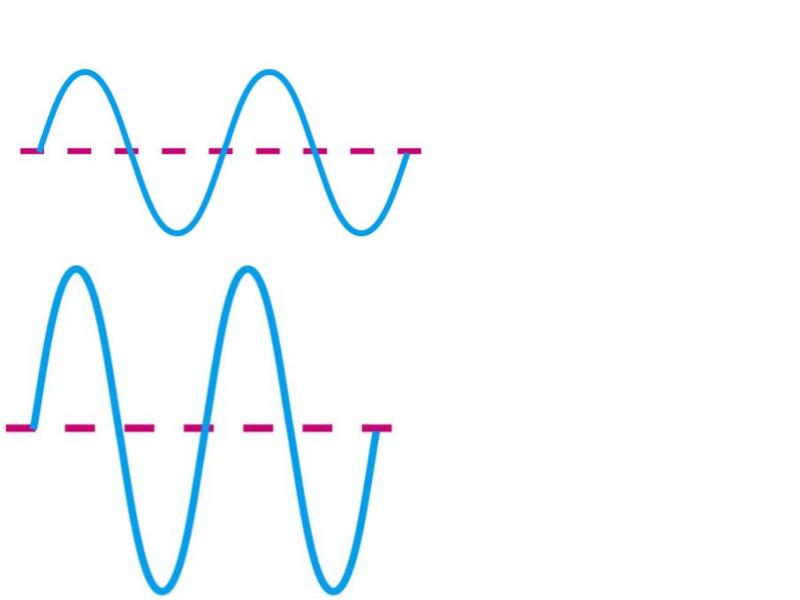
Which has higher intensity?
B
Which has higher frequency?
B
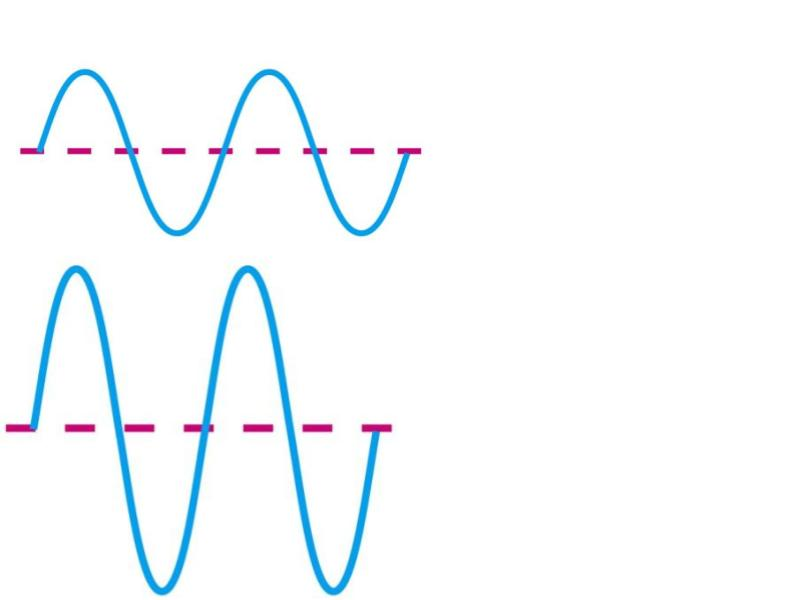
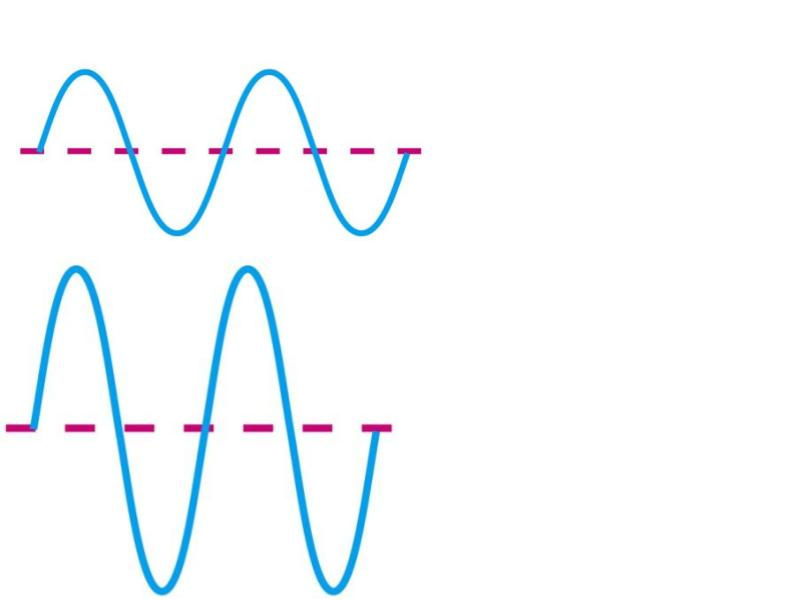
Which has a longer wavelength?
A
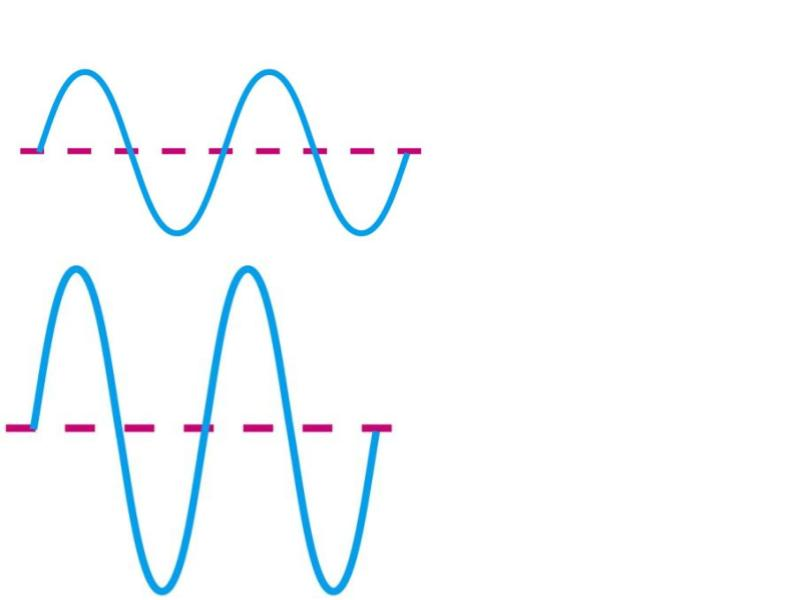
Which one is more likely to be red light (as opposed to blue)?
A
True or false: the violet/blue end of the electromagnetic spectrum has long wavelengths
false - the violet end has short wavelengths
What level of energy (high or low) does the violet end of the electromagnetic spectrum have?
high
What level of frequency (high or low) does the violet end of the spectrum have?
high
True or false: the red end of the electromagnetic spectrum has long wavelengths
true
What is the level of frequency (high or low) for the red end of the electromagnetic spectrum?
low
What level of energy (high or low) does the red end of the electromagnetic spectrum have?
low
List all of the light from right to left on the electromagnetic spectrum.
long radio waves
radio, TV
microwave
infrared rays
visible light
UV rays
x-rays
gamma rays
How many nanometers is the violet light on the electromagnetic spectrum?
~400 nm
How many nanometers is the red light on the electromagnetic spectrum?
~700 nm
True or false: the higher the logarithmic scale, the shorter the wavelength.
true - gamma rays (10^-12 = 10^-16 & 10^20 - 10^24)
Which electromagnetic radiation has wavelengths about the size of an atom?
x-rays (measured in nanometers)
What are the properties that provide evidence that light is a wave?
diffraction & interference —> shown in double-slit experiment
Diffraction
When the wave hits the barrier with the slit, it begins to spread out as they go through the opening.
True or false: particles diffract
false - only waves have the ability to diffract
If waves are in-phase (their peaks and troughs line up), does constructive or destructive interference occur?
constructive interference
constructive interference
crests and troughs reinforce (brighter light); only occurs if waves are in-phase
True or false: if waves are out of phase, destructive interference occurs.
true
destructive interference
crests and troughs cancel (darker light); only occurs if waves are out of phase
Double Slit Experiment
The marbles hitting a slit will strike the back wall and create a band of hits. If we have a double slit and aim a line of marbles at them, then we would expect to see a duplicate band of the first initial line. In the single slit, the waves hit the slit and radiate out, striking the back wall with the most intensity directly in line with the slit. When we add a double slit, the top of one wave will meet the bottom of another wave which causes them to cancel out and create an interference pattern of many bands on the back wall.
Which has the longest wavelength?
A. x-rays
B. visible
C. infrared
C - infrared
Why can’t we just classify light as a wave?
According to the wave model, energy should increase with the intensity but that does not occur in light (higher frequency & shorter wavelengths = higher energy).
Which has the highest frequency?
A. x-rays
B. visible light
C. infrared
A - x-rays
Which has the highest energu?
A. x-rays
B. visible
C. infrared
A - x-rays
What are the properties that provide evidence that light is a particle?
photoelectric effect
Photoelectric Effect
many metals emit electrons when electromagnetic radiation shines on the surface (garage door openers)
How does the photoelectric effect work?
the light is transferring energy to the electrons at the metal surface where it is transformed into kinetic energy that gives the electrons enough energy to “leave” the atoms in the metal.
Why are electrons stuck on atoms?
the electrostatic attraction between the negatively-charged electrons and positively-charged nucleus (protons).
If you increase the intensity of UV light does….
A. the number of electrons emitted increase
B. the number of electrons emitted decreases
C. no change
D. zero electrons are emitted
A - the number of electrons emitted increases
If you keep the intensity the same and increase the wavelength to blue light does…
A. the number of electrons emitted increase
B. the number of electrons emitted decreases
C. no change
D. zero electrons are emitted
C - no change in the number of electrons but they move slower
If you keep the intensity the same and increase the wavelength to yellow light does…
A. the number of electrons emitted increase
B. the number of electrons emitted decreases
C. no change
D. zero electrons are emitted
D - zero electrons are emitted
If you keep the yellow light and increase the intensity does….
A. the number of electrons emitted increase
B. the number of electrons emitted decreases
C. no change
D. zero electrons are emitted
C - no change (zero electrons are still emitted)
True or false: as you move towards long wavelength colored light (yellow, orange, red) no electrons are emitted
True - electrons are emitted as frequency increases and the length of the wavelength decreases
True or false: if the frequency of the light is above the threshold frequency, then electrons are not emitted from the metal
False - electrons are emitted and the amount of electrons depends on the intensity of the light (current)
True or false: if the frequency of the light is below the threshold frequency, no electrons are emitted
true - intensity of light has no impact (no current)
Photons
a little packet of energy; light
True or false: the energy of a photon is not quantized
False - photons can only have certain values
True or false: the photoelectric effect allows us to conclude that the energy of light depends on frequency and not the intensity
true - this is evidence for why light is also a particle
True or false: if a photon has enough energy, it will cause an electron to be ejected
true
True or false: you can add photons together to create enough energy to eject an electron
false - photons cannot be combined. a singular photon must have enough energy to eject an electron
What are the two ways energy can be transferred to molecules to break covalent bonds?
collisions with other molecules
collision with a photon
how many nm are gamma rays?
0.001 nm
how many nm are x-rays?
0.1 nm
how many nm is UV light?
10 nm
How many nm is visible light?
1000 nm
how many nm is infrared light?
1 × 10³ nm
how many nm are microwaves?
1 × 10^7 nm (1 centimeter)
how many nm are radio waves?
1 × 10^9 nm (1 meter)
how many nm are long radio waves?
1 × 10^11 nm
How is a sunburn formed?
if the photons emitted by the sun (UV rays) contain enough energy , then they can damage biological molecules by breaking their internal bonds.
True or false: electromagnetic radiation can be described as either a particle or a wave
true
True or false: matter and energy behaves the same at a small scale and in the macroscopic world
false - the wave-particle duality is important at small scales and the wavelength of the macroscopic objects is much smaller than the object and does not affect its properties.
True or false: white light contains every visible color in the spectrum
true
True or false: light from the sun can be separated into their varying wavelengths with a prism
true (can view full visible spectrum)
True or false: atoms can not emit light
false - atoms can emit light but they will not contain all the colors of the spectrum because specific elements only have a few wavelengths
True or false: atoms can absorb light
true
Why does the atomic absorption spectrum contain black lines?
The black lines represent light that did not pass through the atoms because those wavelengths were absorbed by the atom.
True or false: the wavelengths of an atom's emission lines are different then the wavelengths of its absorption lines
FALSE - the black lines on the absorption spectrum appear as colored lines on the emission spectrum
Can each element absorb or emit every wavelength of light in the visible spectrum?
A. Yes
B. No
B - no
True or false: the spectrum of an element is the same whether that element is on Earth, in the sun, or in a galaxy light years away
true
Why did we alter Rutherford’s model?
the model does not explain the atomic absorption & emission spectrum. not sustainable because the atom would have imploded.
Bohr’s model
electrons move in orbits around the nucleus
the orbits have definite energies and are at definite distances from the nucleus (quantized)
explained the emission & absorption spectrum with discrete energy levels
photons are emitted or absorbed by atoms as electrons move from one energy level to another
energy of photons corresponds to the difference in energy between orbits
True or false: an electron moves to a higher energy orbit when a photon is absorbed
true (electron moves to lower energy orbit when photon is emitted)
What is the only element that the bohr model works for?
hydrogen
What were the problems with Bohr’s model?
only works for hydrogen
transition of electrons upon absorption and emission of photons is better demonstrated with energy diagrams
Energy diagrams
each energy level has a quantum number
higher number = higher energy
energy levels are not orbits
electrons transition between energy levels by absorbing or emitting photons with energies equal to the exact difference in energy between two levels
True or false: when an emission spectrum is produced, the energy diagram shows the atoms moving down energy levels
true
True or false: when determining which electron will release the largest amount of energy from a diagram, it is more important to look at the number of energy levels than the difference in energy.
False - only look at the difference in energy
Why can a specific element only absorb or emit certain wavelengths of light in the visible spectrum?
Electrons can only have the energies of the levels. Basically, only certain colors are emitted because they are equivalent to the amount of energy required by each level.
How are absorption and emission different from the photoelectric effect?
In the photoelectric effect, you are shining a beam of light on a piece of metal and the atom absorbs a photon resulting in the ejection of an electron. The electron completely leaves the atom (ionization). In absorption and emission, electrons remain on the atom but change energies.
de Broglie
all matter has wave properties and, therefore, a wavelength.
True or false: de Broglie is for light only, not matter
FALSE - de Broglie is for matter only; not light
True or false: wavelength is much smaller than macroscopic objects and is about the same size as atomic-scale objects
true - this means that the wavelength impacts atomic-scale objects but not macroscopic objects
What is wavelength measured in?
meters
What is the evidence that electrons are waves?
when electrons are used in the double slit experiment, they show an interference pattern.
Heisenberg Uncertainty Principle
we cannot measure accurately both the energy and position of an electron
What must our model of the atom include?
electrons have wave-like properties
electrons in an atom can only have certain energies
since we know the energy of the electron, we can’t know its exact position