bones and cartilage
1/167
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
168 Terms
How much of body weight do bones make up?
18%
How much of body weight comes from muscles?
36-40%
What percentage of our bones is compact bone/ivory bone/cortical bone?
80%
What percentage of our bones are spongy/cancellated/trabecular bone?
20%
Cartilage does NOT
Have blood (avascular) or nerve (non-innervated) supply
Tendons are made up of
Collagen
What kind of tissue are ligaments and tendons made up of?
Dense regular connective tissue
Function of tendons
Connect muscles to the bones by insertion, can be tight or loose
What are some features of collagen
Strong, flexible, not elastic
Muscle tendons can not
Change in length
Ligaments are made up of
Collagenous tissue
Function of ligaments
Connect bone to bone, soft tissue to bone
Ex: uterus is connected to its bone through ligaments
Functions of bones
Support, protect, movement, mineral storage, hemopoiesis
What are the weight-bearing bones?
Pelvis, femur, tibia, tarsals
What organs does the pelvic bone protect?
Uterus, urinary bladder, prostate, sigmoid colon
What organs does the rib cage protect?
Heart and lungs
What minerals do bones store?
Ca2+ and phosphate
Erythropoiesis occurs when?
There is hypoxia (low oxygen supply)
Erythropoiesis process:
Hypoxia ➡stimulate kidneys ➡ kidneys secrete erythropoietin (hemopoietin) ➡ go to bone marrow and make red blood cells
Where does erythropoiesis take place?
Bone marrow
What percent of cartilage is water and what does it mean?
80%, means cartilage is compressible
Weeping lubrication
Cartilage is compressed and fluid goes to the surface and spreads
What cells make cartilage?
Chondroblasts
What do Chondroblasts do?
Deposit new cartilage, secrete the cartilage matrix
What is the cartilage matrix made out of?
Glucosaminoglycans (GAGs) - chondroitin sulfate, hyaluronic acid
What is the backbone of cartilage matrix?
Hyaluronic acid
Chondrocytes are
Trapped in matrix, living cells, and maintain the cartilage
Layer that surrounds cartilage is
Perichondrium
Chondrocytes are surrounded by
Lacuna
What type of fibers do chondroblasts make?
Collagen fibers, elastic fibers
Elastic fibers are made up of
Elastin
Elastic cartilage features
Has a lot of Chondrocytes and elastic fibers
Where can we find elastic cartilage?
External ear (ear pinna), epiglottis, and larynx
fibrocartilage features
Tough, highly collagenous, can resist pressure
Where can we find fibrocartilage?
Intervertebral discs and pubic symphysis
Pubic symphysis expands at
Parturition
Vertebrae is oriented with
Spinous process, facing backwards and downwards
When intervertebral discs are herniated
The spinal nerve is compressed and the person has pain in the lumbar region
Where is hyaline cartilage found?
Joints, costal cartilages (in rib cage), trachea and bronchial rings, thyroid and arytenoid cartilages (in larynx), nasal cartilage, ends of long bones (epiphyseal plate)
What is the most abundant cartilage in the body?
Hyaline cartilage
Where does bone elongation take place?
Epiphyseal plate
What happens to epiphyseal plate when growth stops?
It turns into epiphyseal line
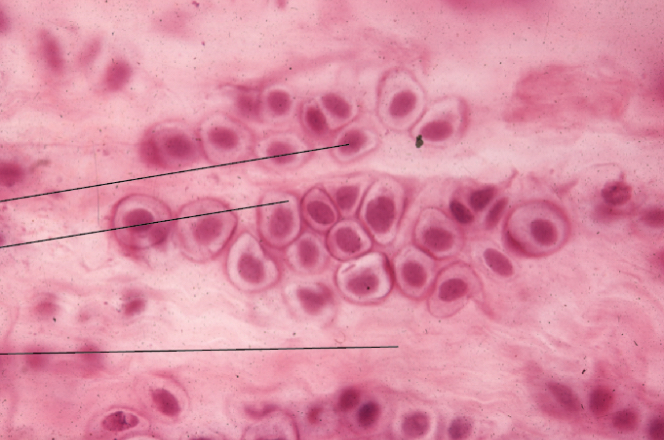
What type of cartilage is this?
Fibrocartilage
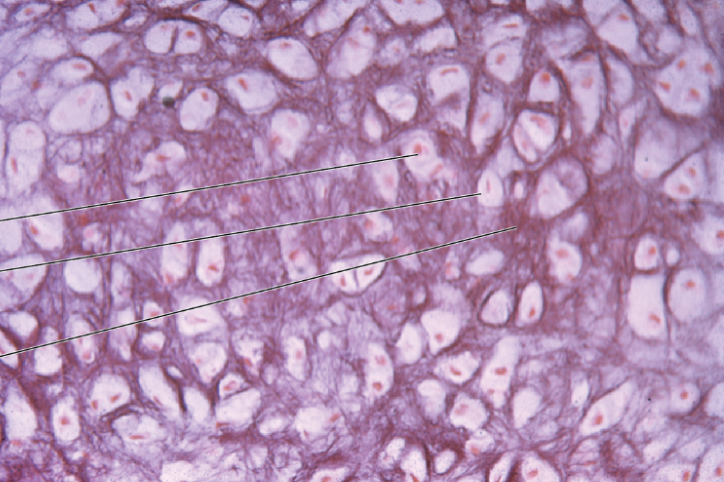
What type of cartilage is this?
Elastic cartilage
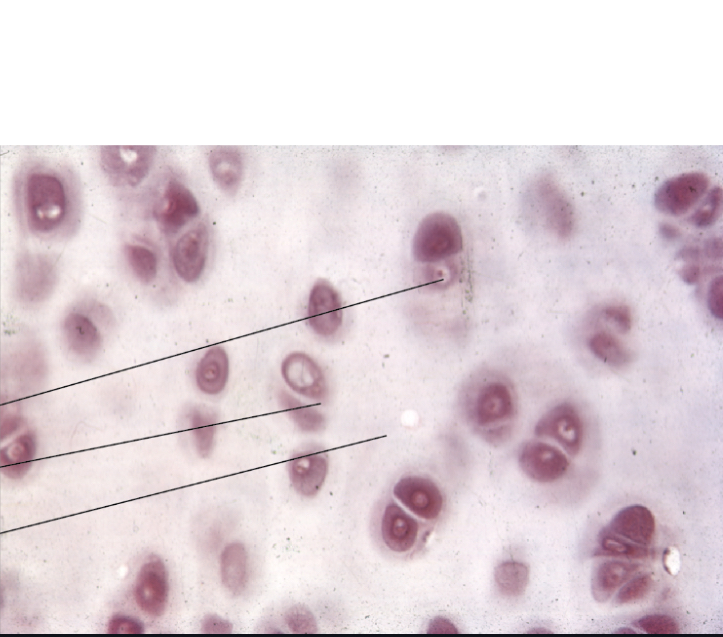
What type of cartilage is this?
Hyaline cartilage
What are the types of growth of cartilage?
Appositional growth and interstitial growth
What is appositional growth?
Cartilage grows from outside ➡ in
What is interstitial growth?
Expansion is from inside ➡out
Compact or ivory bone features
Hard, weight bearing, strong
Spongy or cancellated bone features
Made up of small pieces called trabeculae, easy to remodel (absorption and formation) because the pieces are small
The smallest bone in the body is
In the ear called stapes it is also the innermost in the ear
What are the bones in the middle ear?
Malleus, incus, and stapes
Examples of small bones
Pisiform, stapes
Long bones features and examples
Longer than broad
Ex: Femur, humerus, tibia, phalanges, metacarpals, metatarsals
The largest bone in the body is
In the pelvis, ileum
Flat bones examples
Ribs, sternum, skull bones, scapula
Short bones examples
Carpals and tarsals
Irregular bones examples
Vertebrae
Wormian bones examples
Small sutural bones usually in lamboidal suture
Sesamoid bone features and examples
Muscle tendon becomes ossified (hard and bony)
Ex: quadriceps tendon forms patella, carpi ulnaris forms pisiform
Diploe bones features and example
Contains spongy bone in the middle of compact bone, compact bone gives strength and spongy makes it weigh lighter
Ex: Skull bones
What is the Inca bone
A Wormian bone found in Inca population in lamboidal suture
The two ends of bones are covered with
Joint/articular cartilage
The middle part of the bone is
Compact bone
The bone is covered by the membrane
Periosteum
Spongy bone surrounds the
Epiphyseal plate
Epiphyseal plate is made of
hyaline cartilage
The ends of bones are called
Epiphysis
The middle part of the bone is called
Diaphysis
In between epiphysis and diaphysis is
Metaphysis
Inside the bone it is called
Medullary cavity
Where is the bone marrow
In the medullary cavity
The inside of the bone is lined by
Endosteum
Layers of periosteum
Outer layer: fibrous layer
Inner layer: osteogenic layer
Where are osteoblast and osteoclast found?
Osteogenic layer of periosteum and in endosteum
Sharpey’s fibers
Connect the periosteum with the surface of the bone
Muscle tendon is inserted in
Periosteum
Osteoprogenitor cells
Stem cells that give rise to blood origin hemopoietic cells and mesodermal origin mesenchymal cells
Mesenchymal cells give rise to
Osteoblasts
Function of osteoblasts
Bone formation (mineralization) or bone deposition which makes alkaline conditions
Make bone matrix and trap cells that are now called osteocytes
Osteocytes are
Trapped in matrix, living, communicate with each other via canaliculi, maintain bone health
Canaliculi are
Cytoplasmic connections between osteocytes
Hemopoietic cells give rise to
Osteoclasts
Function of osteoclasts
Large, multinucleated cells with ruffled border
Bone resorption (demineralization) or bone remodeling, secrete acid
Clastogenesis or osteoclastogenesis means
Bone resorption
Osteocytes are formed by
Trapped osteoblasts
Osteoclasts secrete
Hyaluronic acid that dissolves bone
Haversian canal
Vertical canal in compact bone that houses blood vessels and nerves
Lamella
One ring layer of the osteocyte, canaliculi and bone matrix
Osteon is
A collection of lamella
Interstitial lamella
Incomplete lamella in between the osteons
Circumferential lamella
Not formed in rings, on outer surface of bone
Perforating canals or volkmann’s canals
Transverse canals that carry blood vessels
The spongy bone does not have
Haversian system
Spongy bone is made of
Trabeculae
What is osteoid part of bone formation
Organic part where we have proteins
Proteins in osteoid
Osteocalcin, osteopontin, collagen type I (most common)
Collagen type I provides
Pliable-Tensile strength (bone can bend slightly without breaking)
When collagen gene is mutated
COL1A1 (gene) mutation causes osteogenesis imperfecta (brittle bone disease)
What is osteogenesis imperfecta
Inherited condition where there are frequent fractures in bones because they break easily