Chapter 15 Forensic Serology
1/87
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
88 Terms
What significant discovery did Karl Landsteiner announce in 1901?
The typing of blood.
What classification system for blood types did Landsteiner's work lead to?
The A-B-O system.
What factor in blood was demonstrated by 1937?
The Rh factor.
What was the focus of forensic scientists regarding blood factors until the early 1990s?
Linking blood to an individual using A-B-O blood factors.
What change occurred in forensic science with the advent of DNA technology?
The focus shifted from blood factors to characterizing biological evidence by DNA.
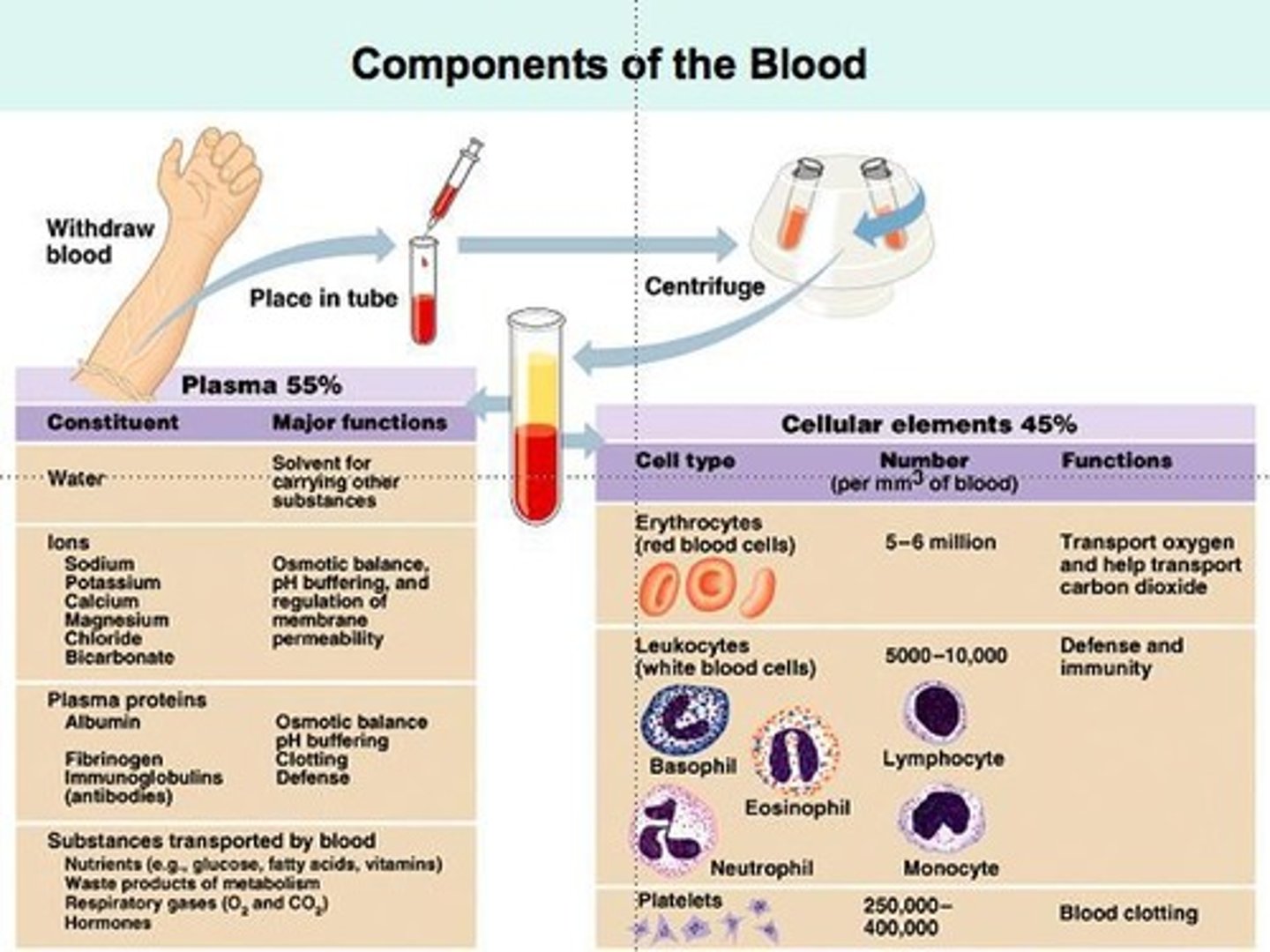
What is blood composed of?
A highly complex mixture of cells, enzymes, proteins, and inorganic substances.
What is the fluid portion of blood called and what does it primarily consist of?
Plasma, which is principally composed of water and accounts for 55% of blood content.
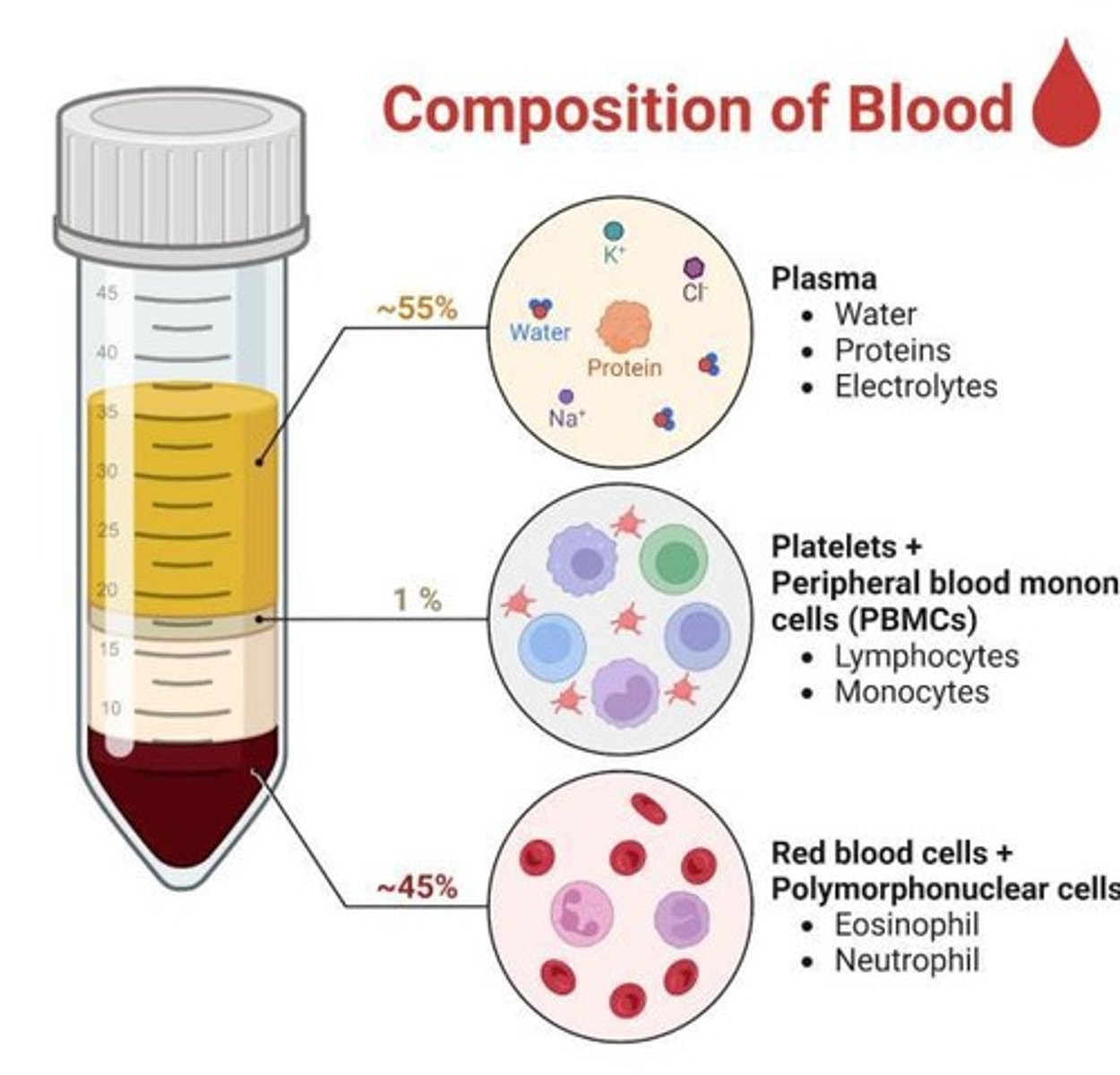
What are the solid materials suspended in plasma?
Red blood cells (erythrocytes), white blood cells (leukocytes), and platelets.
What is the role of fibrin in blood?
Fibrin is a protein that traps and enmeshes red blood cells to form clots.
What is left after removing clotted material from blood?
A pale yellowish liquid known as serum.
What is the primary function of red blood cells?
To transport oxygen from the lungs to body tissues and remove carbon dioxide back to the lungs.
What are antigens?
Substances on the surface of red blood cells that stimulate the body to produce antibodies.
How are blood antigens grouped?
Into systems depending on their relationship to one another, with A-B-O and Rh systems being the most important.
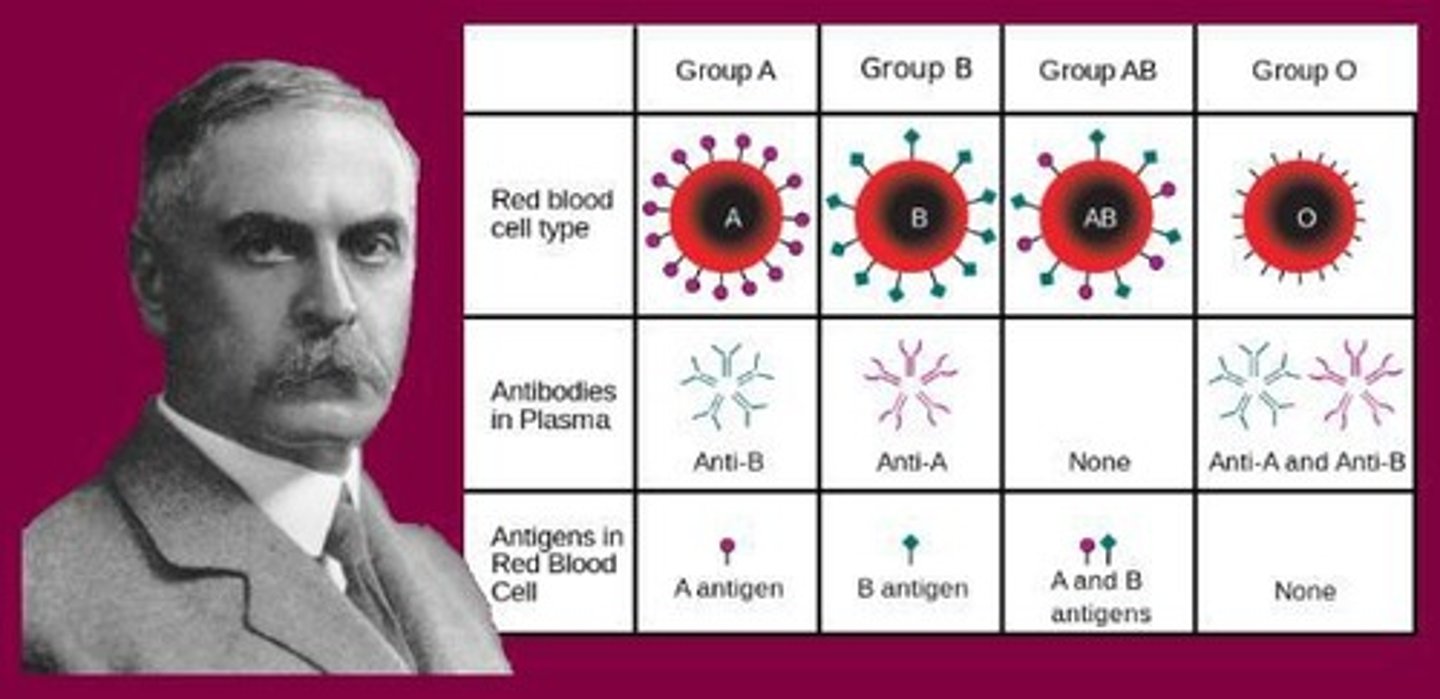
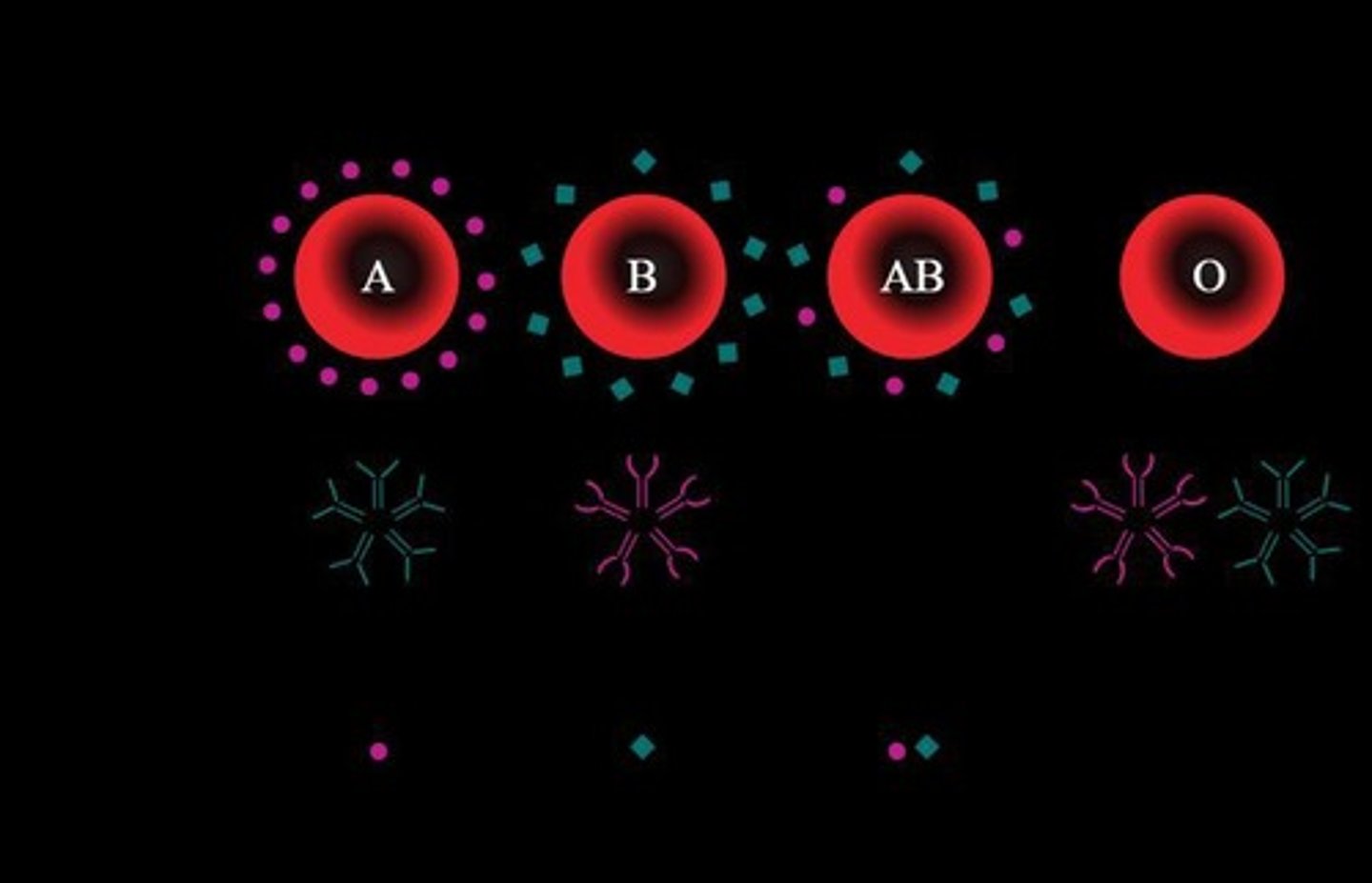
What do type A, B, AB, and O blood types indicate about antigens?
Type A has A antigens, type B has B antigens, AB has both A and B antigens, and type O has neither.
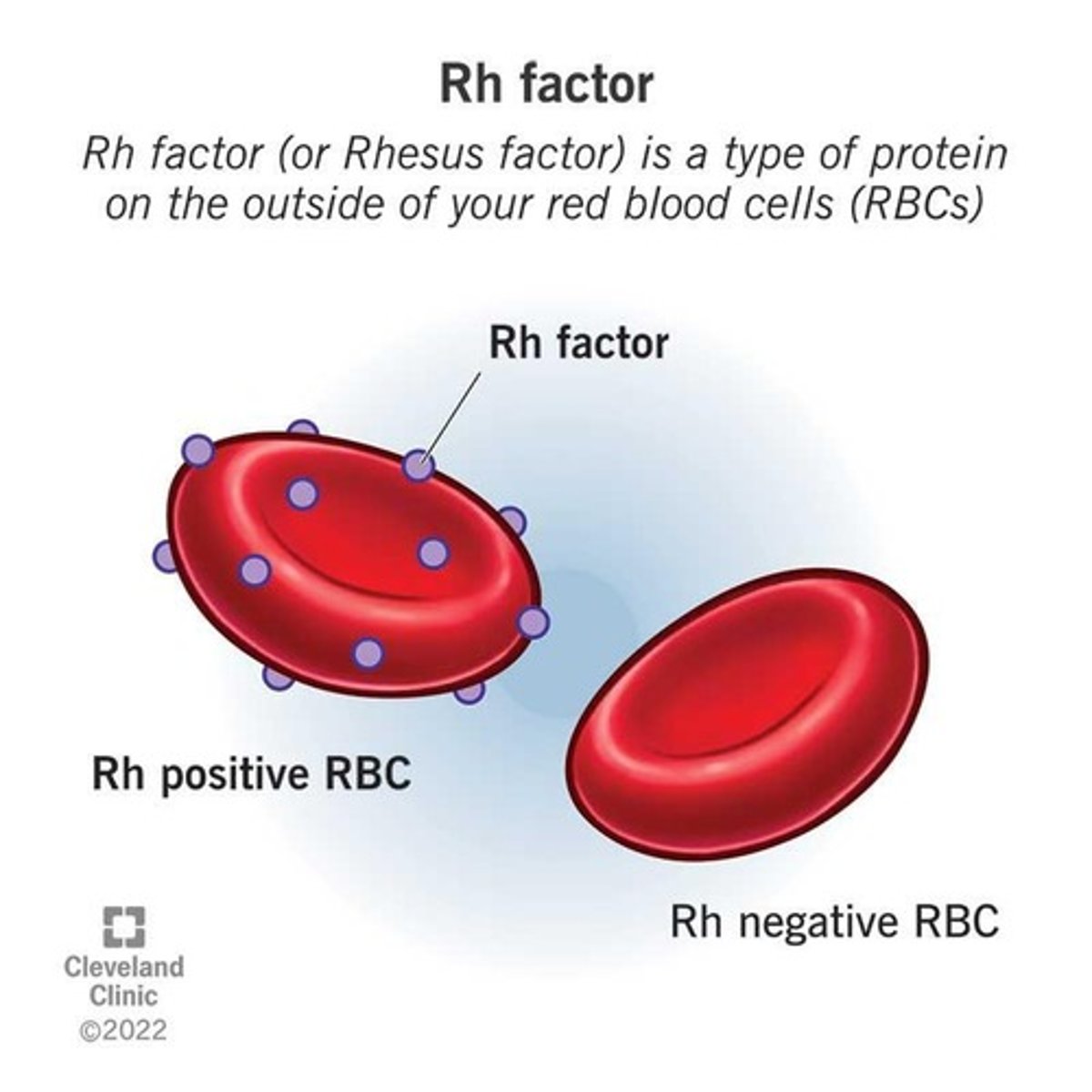
What is the Rh factor?
An important blood antigen also known as the D antigen.
What does it mean to be Rh positive or Rh negative?
Rh positive individuals have the D antigen, while Rh negative individuals do not.
What are antibodies?
Proteins found in blood serum that destroy or inactivate specific antigens.
What is the fundamental principle of blood typing?
For every antigen, there exists a specific antibody.
What is antiserum?
Blood serum that contains specific antibodies.
What are the two main blood antigen systems identified?
The A-B-O system and the Rh system.
What is the role of antibodies in blood typing?
Antibodies are specific to antigens, such as anti-A for A antigen, anti-B for B antigen, and anti-D for D antigen.
What is the significance of the A-B-O blood typing system in forensic science?
It was historically used to link blood to individuals, as no two individuals (except identical twins) were expected to have the same combination of blood factors.
What has been abandoned in favor of DNA technology in forensic science?
The search for genetically controlled blood factors in bloodstains.
What is the relationship between antibodies and antigens?
An antibody reacts only with its specific antigen and no other.
What happens when serum containing anti-B is added to red blood cells with the B antigen?
The two immediately combine, causing the antibody to attach itself to the cell.
What does it mean that antibodies are bivalent?
It means that each antibody has two reactive sites and can attach to antigens on two different red blood cells simultaneously.
What is the result of antibodies binding to antigens on red blood cells?
It creates a vast network of cross-linked cells, usually seen as clumping or agglutination.
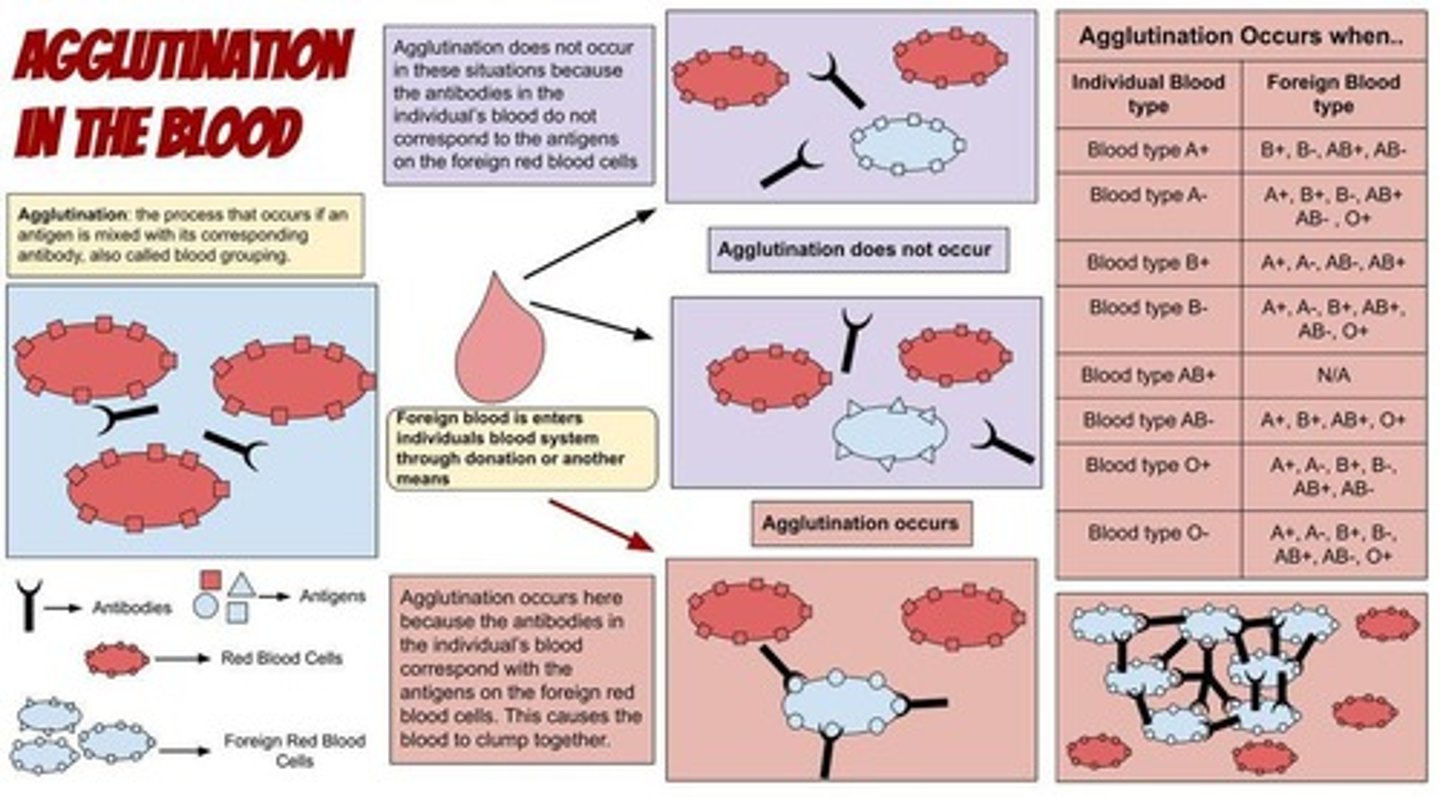
What is serology?
Serology is the study of antigen-antibody reactions.
What is the most widespread application of serology?
The typing of whole blood for its A-B-O identity.
What antiserums are needed to determine A-B-O blood type?
Only two antiserums are needed: anti-A and anti-B.
How does Type A blood react to anti-A serum?
Type A blood is agglutinated by anti-A serum.
How does Type B blood react to anti-B serum?
Type B blood is agglutinated by anti-B serum.
How does Type AB blood react to both anti-A and anti-B serums?
Type AB blood is agglutinated by both anti-A and anti-B serums.
How does Type O blood react to anti-A and anti-B serums?
Type O blood is not agglutinated by either anti-A or anti-B.
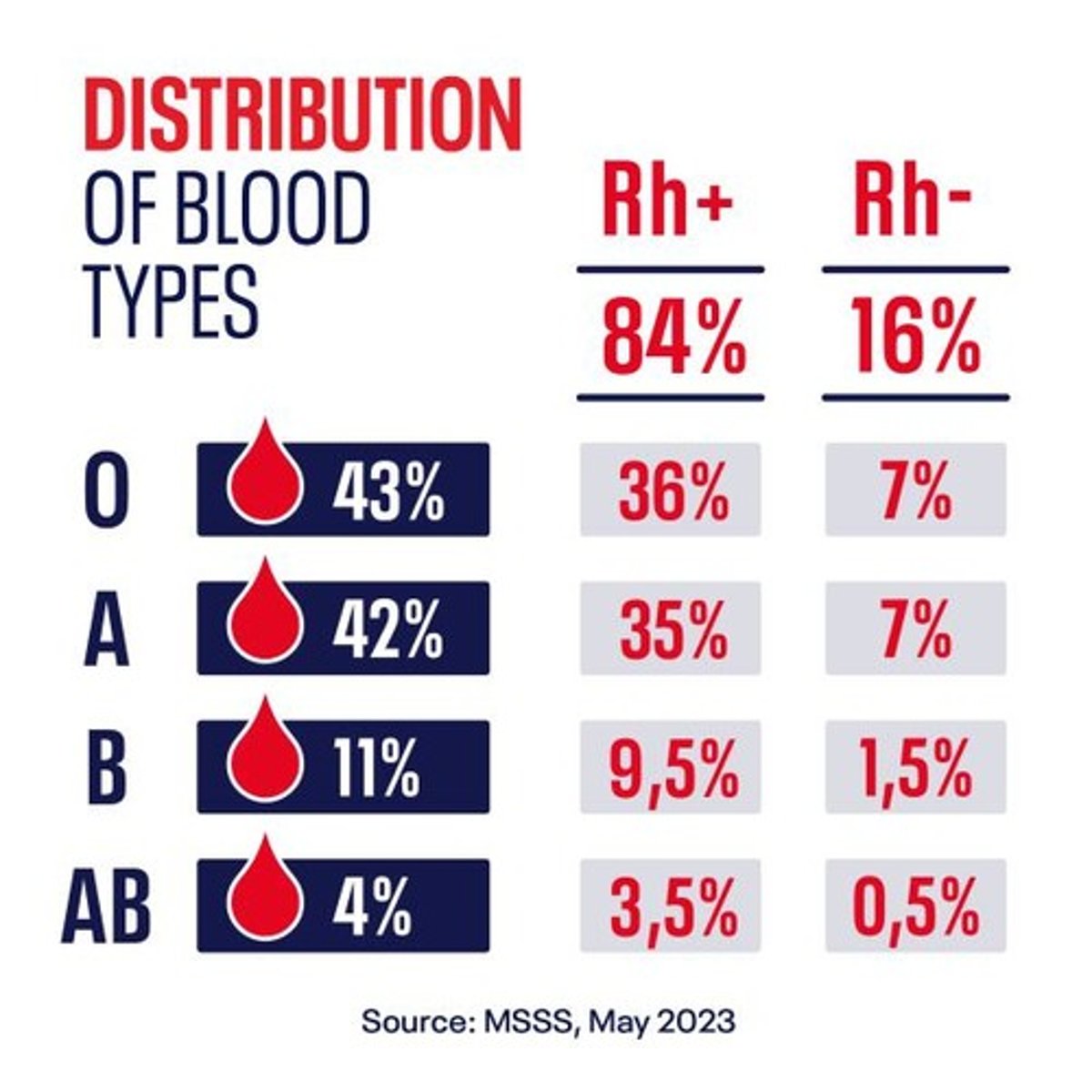
What is the population distribution of blood types in the U.S.?
O - 43%; A - 42%; B - 11/12%; AB - 3/4%.
What are the three questions to answer when examining dried blood?
1. Is it blood? 2. From what species did the blood originate? 3. If human, can it be associated with a particular individual?
What is the best method for determining if a sample is blood?
A preliminary color test.
What was the most used test for blood determination that has been discontinued?
The benzidine color test.
What test is currently used instead of the benzidine color test?
The Kastle-Meyer test or phenolphthalein test.
What is the principle behind the Kastle-Meyer test?
It is based on the observation that blood hemoglobin possesses peroxidase-like activity.
What color indicates a positive result in the Kastle-Meyer test?
A deep pink color.
What are some substances that can also turn pink in the Kastle-Meyer test?
Some vegetable materials like potatoes and horseradish.
What are Luminol and Bluestar used for?
They are preliminary/presumptive tests for blood.
How do Luminol and Bluestar differ in their application?
Luminol requires complete darkness, while Bluestar does not.
What is the sensitivity of Luminol and Bluestar tests?
Both are extremely sensitive, detecting blood at a ratio of 1:100,000.
Do Luminol and Bluestar interfere with DNA testing?
No, neither interferes with DNA testing.
What are microcrystalline tests used for in forensic science?
To make the identification of blood more specific.
What are the two most popular microcrystalline tests for blood?
Takayama and Teichmann tests.
How do Takayama and Teichmann tests work?
They depend on the addition of specific chemicals to blood, forming characteristic crystals with hemoglobin derivatives.
What is the purpose of the precipitin test in forensic science?
To determine if a blood stain is human or animal.
How does the precipitin test work?
It is based on the formation of antibodies when animals are injected with human blood.
What is the significance of the acid phosphatase test in forensic characterization of semen?
It is the best way to locate and characterize a seminal stain.
What is acid phosphatase and where is it predominantly found?
An enzyme secreted by the prostate gland, predominantly found in seminal fluid.
How much seminal fluid does a normal male release during ejaculation?
2.5 to 6 ml.
How many spermatozoa are typically found in each ml of seminal fluid?
100 million or more.
What distinguishes seminal fluid from semen?
Seminal fluid is ejaculate without sperm, while semen contains sperm.
What indicates a positive acid phosphatase test on filter paper?
The appearance of a purple color after adding reagents.
What is the concentration of acid phosphatase in seminal fluid compared to other body fluids?
It is 400 times greater in seminal fluid.
How can large fabric areas be tested for seminal stains?
By moistening filter paper with distilled water and rubbing it over the suspect area.
What visual cue indicates the presence of semen under UV light?
Semen stains appear as strongly fluorescent areas.
What can give a positive response to the acid phosphatase test besides seminal fluid?
Vegetable and fruit juices, fungi, contraceptive creams, and vaginal secretions.
What is a definitive way to identify semen microscopically?
By the presence of spermatozoa.
What are the dimensions of spermatozoa?
They are slender, elongated structures 50 - 70 microns long, each with a head and a thin flagellate tail.
What is the first step in the forensic examination of articles for seminal stains?
The stain must be located.
What must be done after locating a stain to confirm its identity?
The stain has to be subjected to tests that will prove its identity.
What is the significance of Bluestar's reaction to blood in forensic science?
It is used to detect blood at crime scenes.
How long can bloodstains remain detectable for testing?
Bloodstains can be dried for 10-15 years and still be tested.
What is the role of antibodies in the precipitin test?
They react with invading human blood to neutralize its presence.
What are sperm?
Male reproductive cells.
How long can sperm remain viable in the vagina?
3-5 days.
What is contained in the head of a sperm cell?
The nucleus with 23 chromosomes.
What is the function of the acrosome in sperm?
It contains lysosome, an enzyme that aids in penetrating the egg.
What is the role of the mid-piece of a sperm cell?
It contains mitochondria responsible for sperm energy.
What is the purpose of the tail in a sperm cell?
For propulsion.
What does the red dye stain in the 'Christmas Tree' staining method?
Nucleic acids in the head of the sperm.
What does the green dye stain in the 'Christmas Tree' staining method?
Lipids in the tail of the sperm.
What does it indicate if no sperm are visualized during examination?
Possible vasectomy, aspermia (no sperm), or oligospermia (low sperm count).
What is the significance of prostate-specific antigen (PSA) in forensic analysis?
It helps to prove the presence of seminal fluid.
What is p30?
A protein produced by the prostate gland, also known as prostate-specific antigen (PSA).
What should be done with clothing during the collection of rape evidence?
All outer and undergarments should be carefully removed and packaged separately in paper bags.
Why is butcher paper used during the collection of rape evidence?
To avoid cross-contamination of physical evidence.
What items are typically collected in a rape kit?
Pubic combings, pubic hair standard, external genital dry-skin area, vaginal swabs and smear, cervix swabs, rectal swabs and smear, oral swabs and smear, head hairs, blood sample, fingerprint scrapings, all clothing, and urine specimen.
How should saliva residues be collected from the skin?
By swabbing the suspect area with a rotating motion using a cotton swab moistened with distilled water.
What is the timeframe for collecting penile swabs after an assault?
Within 24 hours of the assault.
What is the significance of DNA technology in forensic analysis?
DNA levels as low as one-billionth of a gram can be characterized in crime labs.
How long can living or motile sperm survive in the vaginal cavity?
Up to 4-6 hours.
How long can nonmotile sperm be found in a living female after intercourse?
Up to 3 days, occasionally up to 6 days.
When are intact sperm typically not found after intercourse?
16 hours after intercourse, with little chance of identification 48 hours after.