PDA IB Lecture 19: Receptors of the Autonomic Nervous System
1/35
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
36 Terms
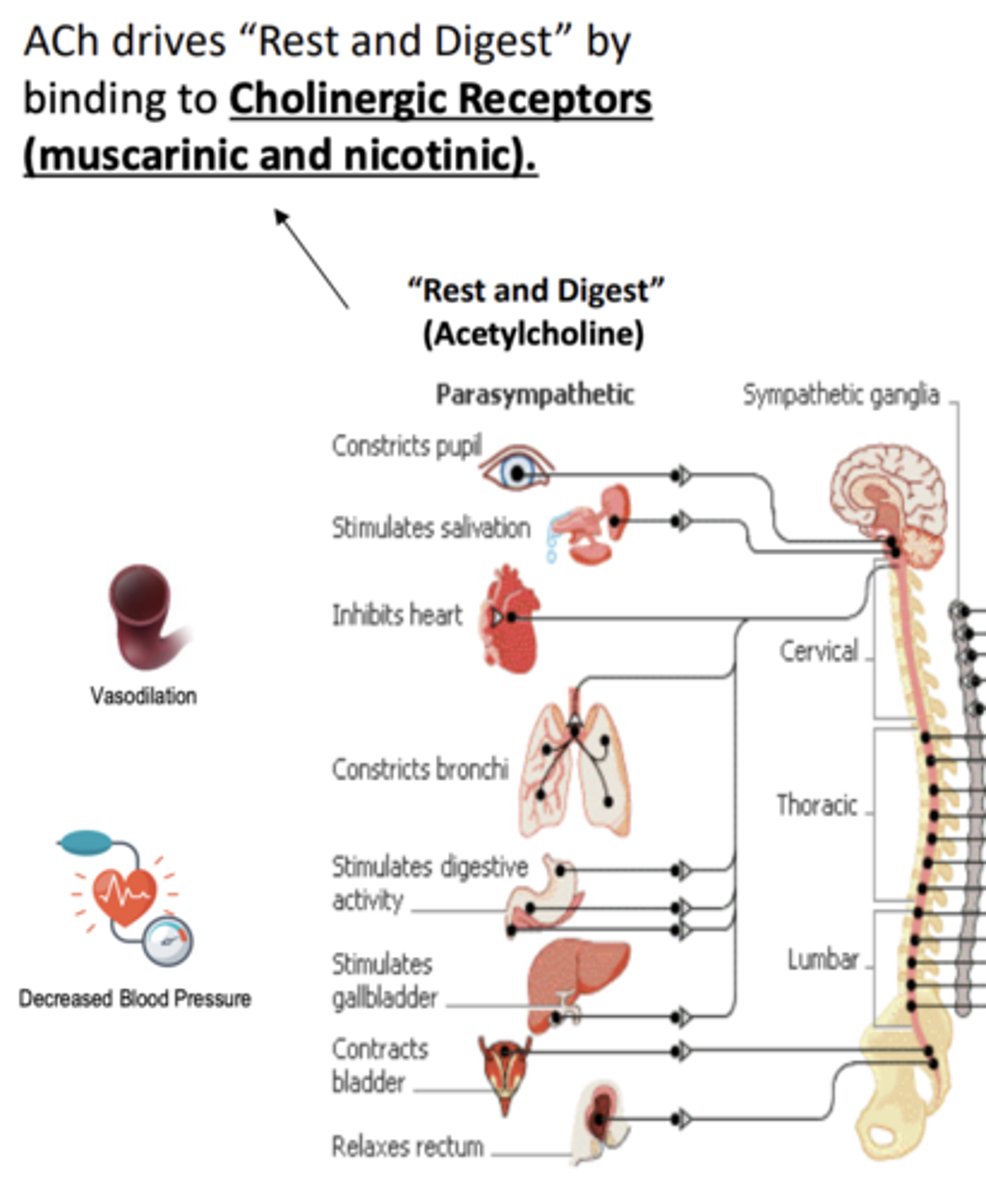
ACh drive "______ and ________" by binding to _______________________________________
- "Rest and Digest"
- Cholinergic receptors (muscarinic and nicotinic)
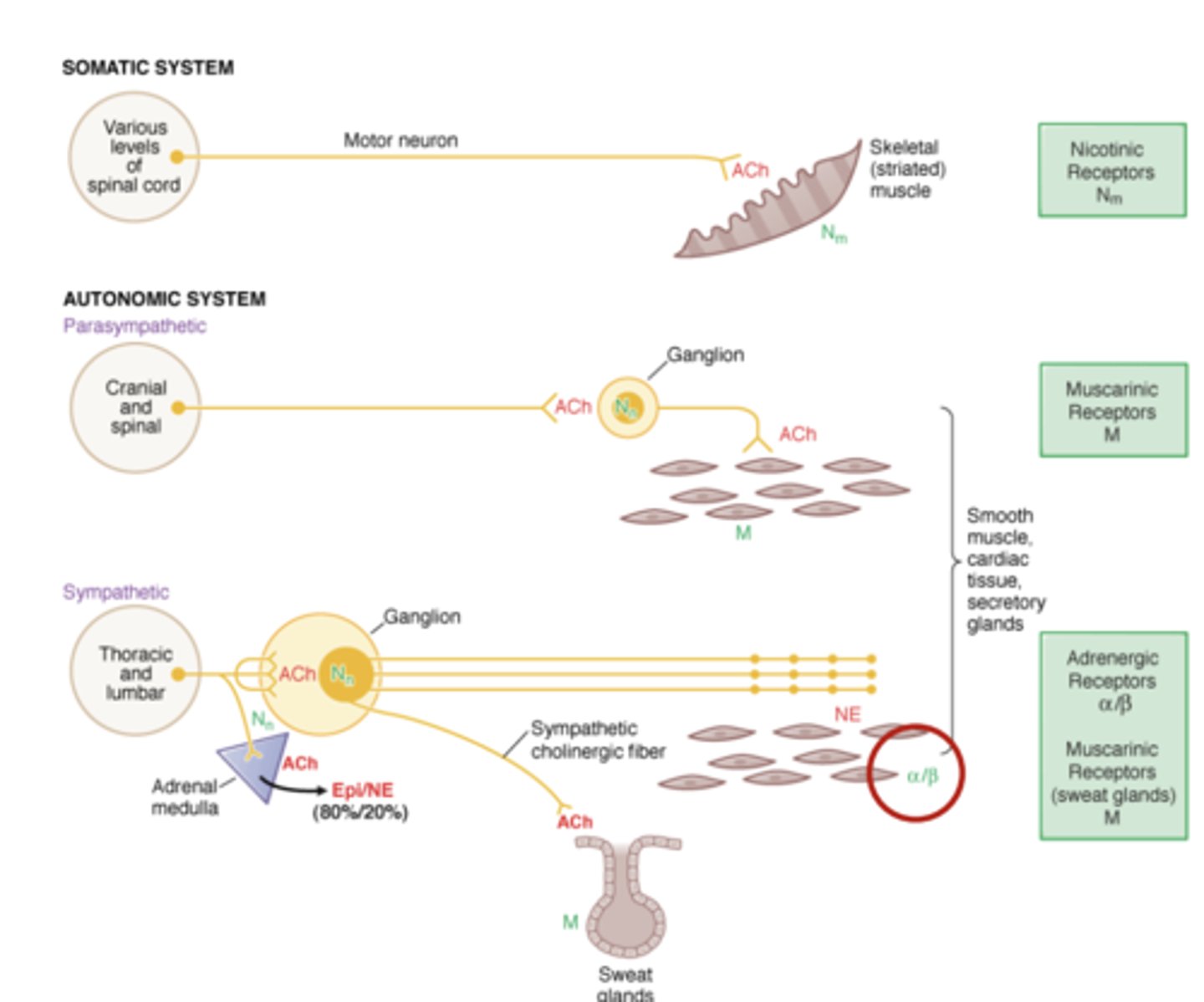
Cholinergic receptors (2)
- Nicotinic receptors
- Muscarinic receptors
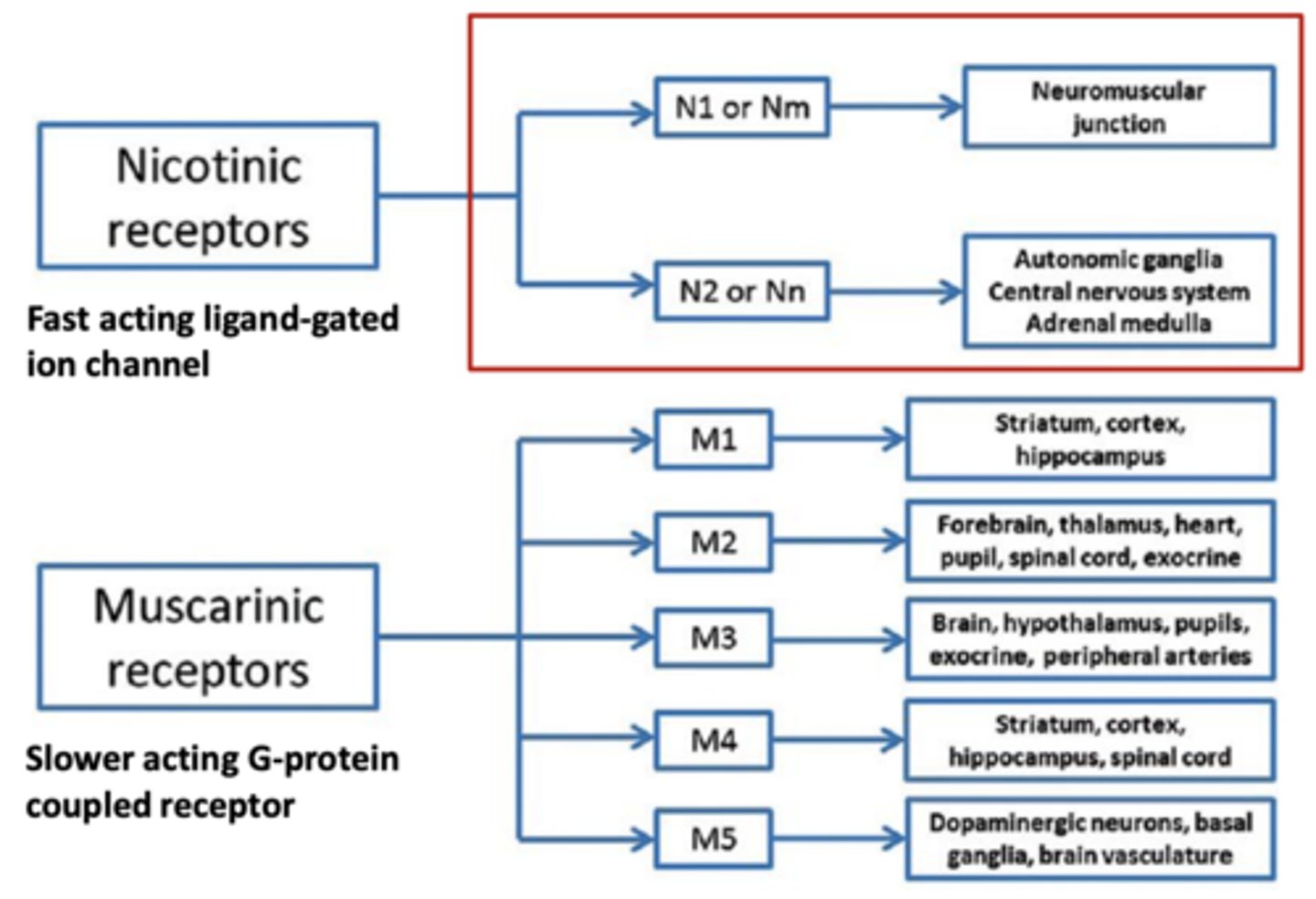
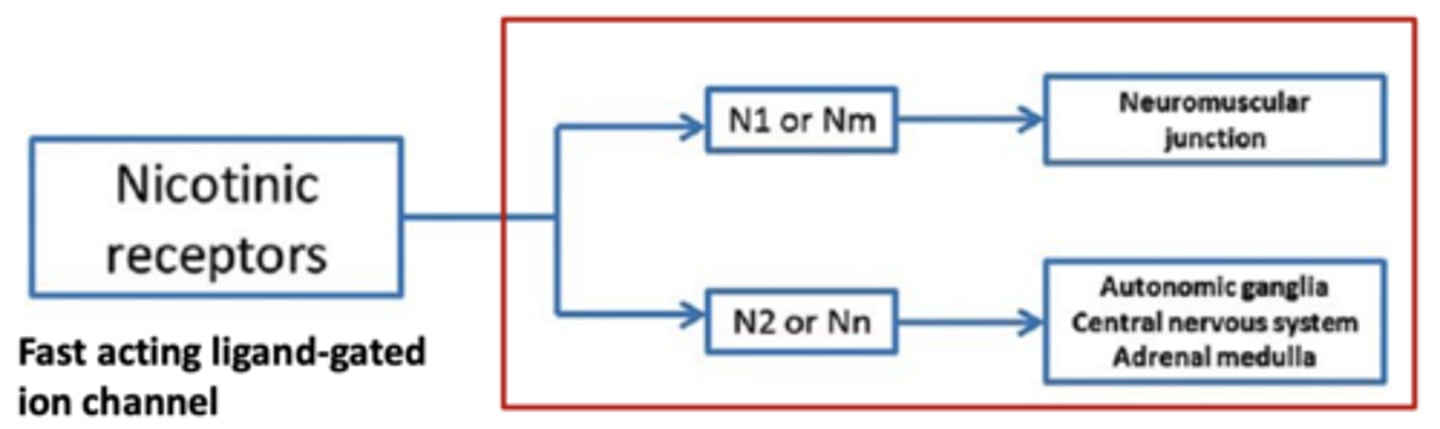
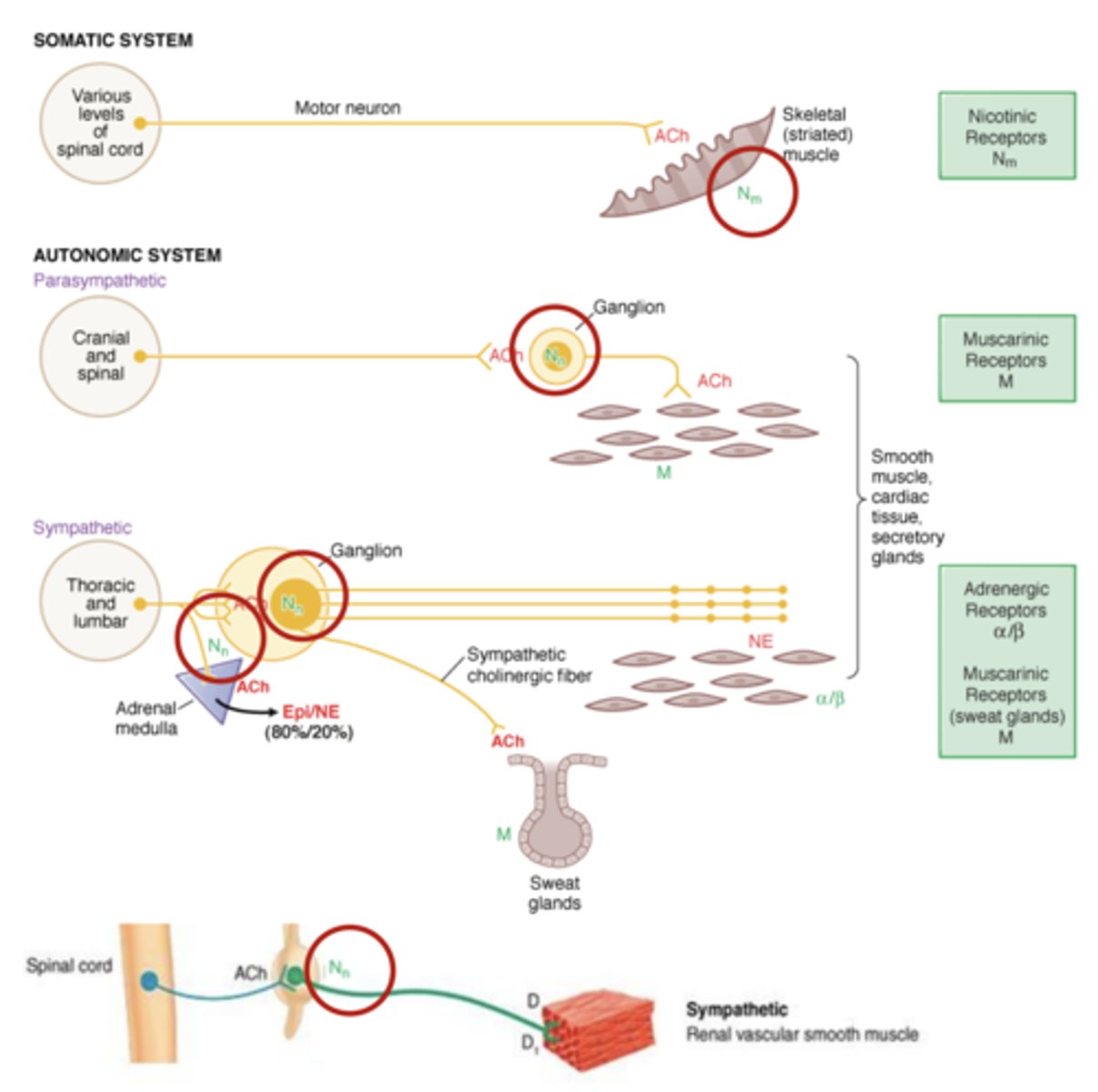
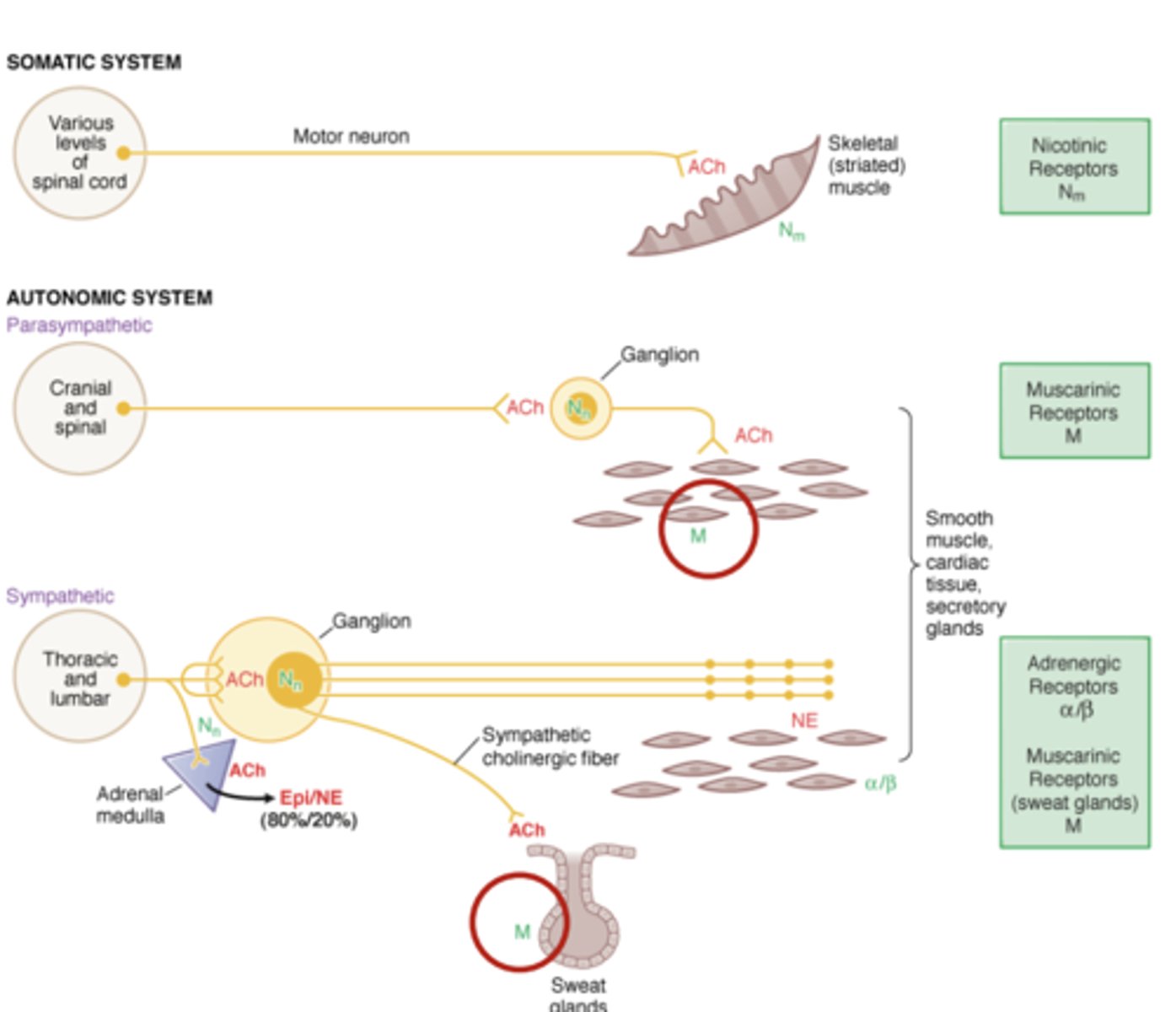
Nicotinic receptors
fast acting ligand-gated ion channel
- N1 or Nm--> neuromuscular junction
- N2 or Nn--> autonomic ganglia, CNS, adrenal medulla
Muscle type nicotinic receptors (Nm) is found on....
skeletal muscle of the somatic system
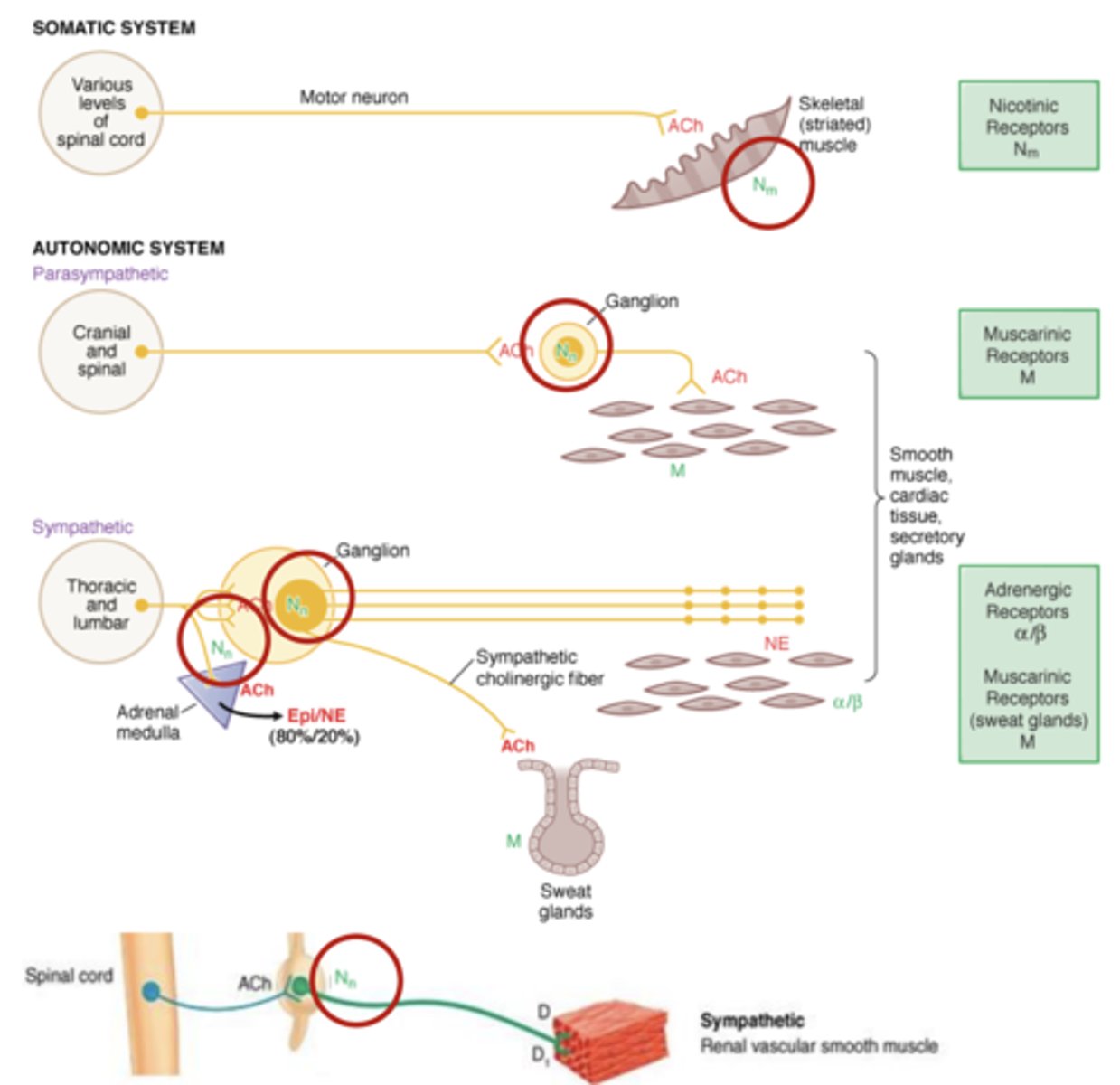
Neuronal type nicotinic receptors (Nn) is found on...
neurons, including ganglion of ANS
- parasympathetic ganglion
- sympathetic ganglion
- also found on certain tissues- adrenal medulla
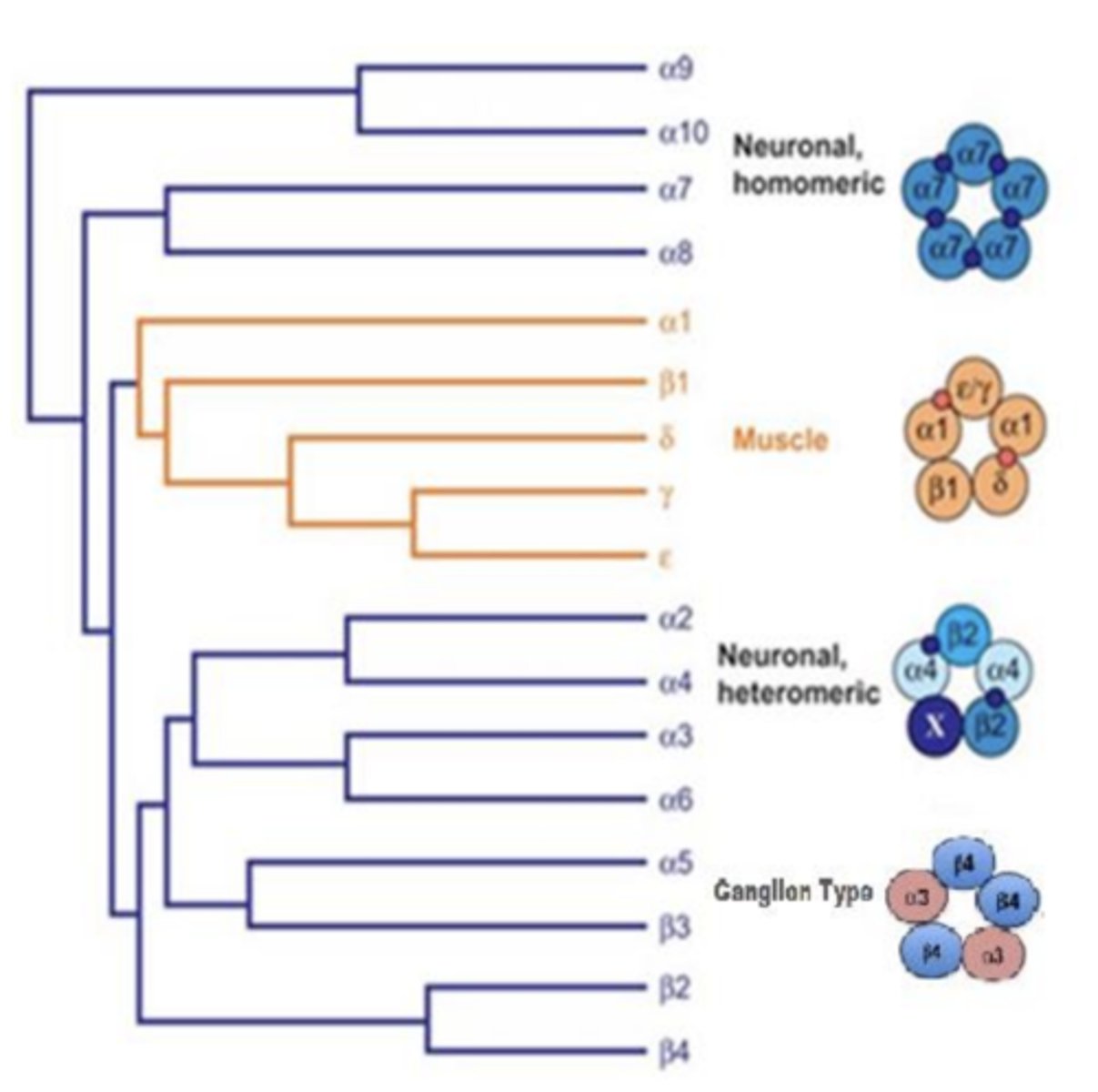
Nicotinic receptor subtypes (5)
- fast acting ligand-gated ion channel activated by Ach
- pentamers (5 sybunits)
- 2 or more ACh binding sites
- 17 vertebrate nAChR subunits identified
- activation is excitatory as a result of increased Na+, K+, or Ca++ permeability
Activation of nicotinic receptor subtypes is __________________ as a result of _____, ____, or _________ permeability
- excitatory
- Na+, K+, or Ca++ permeability
Muscarinic receptors
slower acting G-protein coupled receptor
- M1--> striatum, cortex, hippocampus
- M2--> forebrain, thalamus, heart, pupil, spinal cord, exocrine
- M3--> Brain, hypothalamus, pupils, exocrine, peripheral arteries
- M4--> striatum, cortex, hippocampus, spinal cord
- M5--> dopaminergic neurons, basal ganglia, brain vsaculature
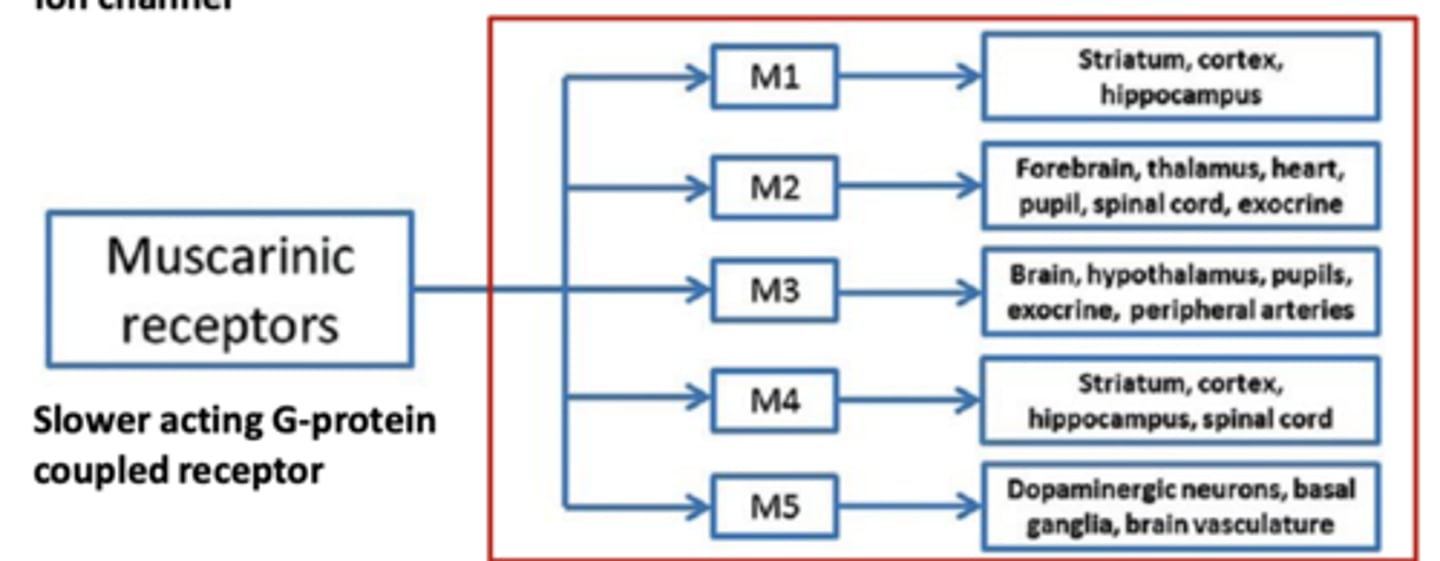
Where are muscarinic receptors (M) found?
- on smooth muscle tissue, allowing for parasympathetic system regulation of smooth muscle organs with ACh
- also found on sweat glands controlled by ACh release from the sympathetic system (1 of 3 exceptions to sympathetic regulation of smooth muscle organs with NE)
Muscarinic receptor subunits*****
- ________-acting _____________ activated by Ach
- Which receptors activate Gq? What does this lead to?
- Which receptors activate Gi/o? What does this lead to?
- Which receptors can be found pre- and post-synaptically?
- Which receptors are implicated in ANS function?
- slower acting G-protein coupled receptors activated by Ach
- M1, M3, M5: activate Gq --> activates phospholipase C, generally excitatory
- M2, M4,: activate Gi/o--> inhibits adenylate cyclase, generally inhibitory
- M2 and M4 can be found pre- and post-synaptically (as auto-recepotrs)
- M1, M2, and M3 are implicated in ANS function
NE drives "_____ or ______" by binding to ______________________
- "fight or flight"
- adrenergic receptors
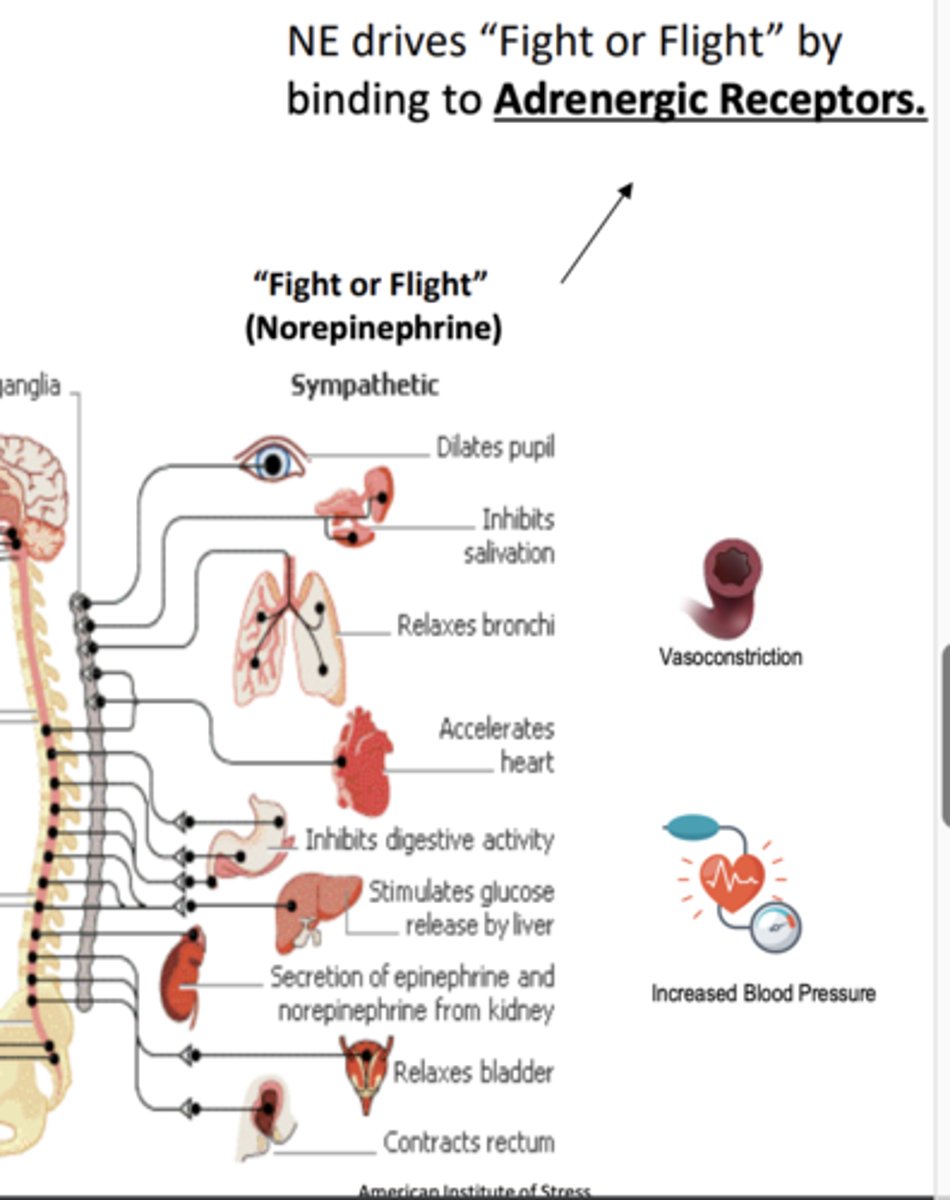
Adrenergic receptor distribution in ANS: Alpha and Beta adrenergic receptors (α/β): Where are they found? What does this allow for?
Alpha and beta adrenergic receptors (α/β) are found on smooth muscle tissue
- allows for sympathetic system regulation of smooth muscle organs with NE
Adrenergic receptors; are they faster or slower acting?
slower acting G-protein coupled receptors activated by norepinephrine and epinephrine
Adrenergic receptors: what does α1 activate?***
α1 activates Gq---> activates phospholipase C
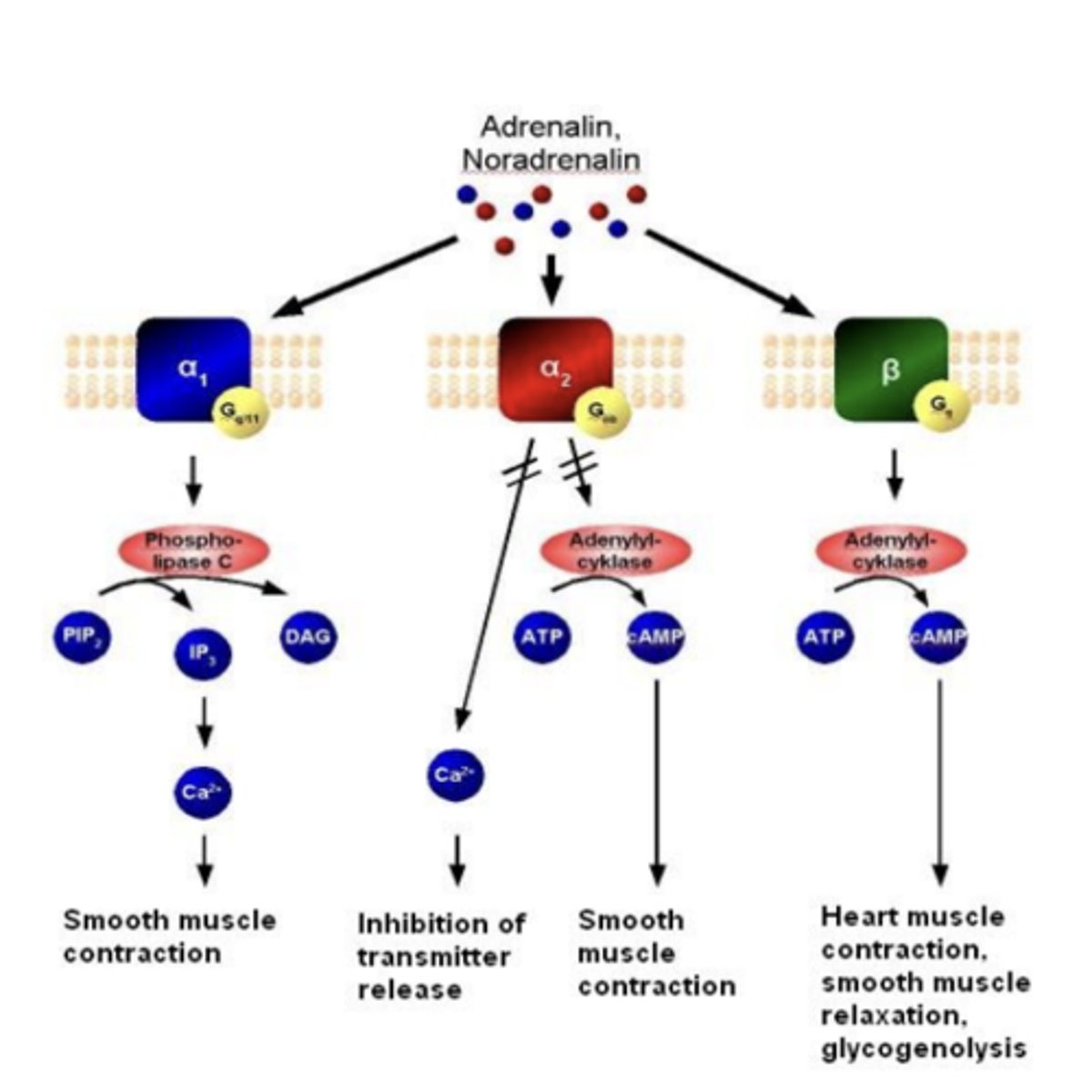
Adrenergic receptors: what does α2 activate?***
α2 activates Gi/o ---> inhibits adenylate cyclase
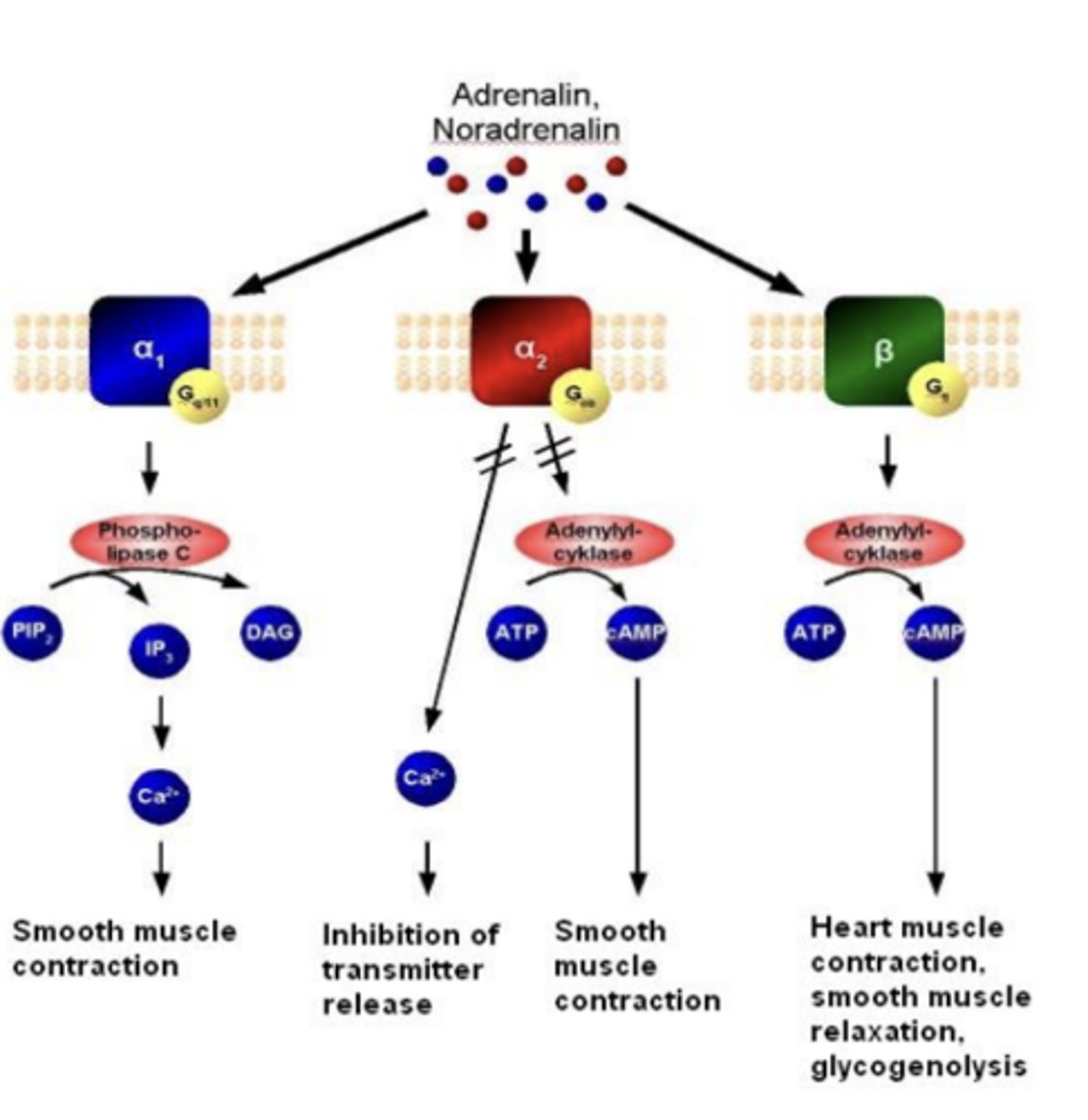
Adrenergic receptors: what do β1 and β2 activate?***
β1, β2 activate Gs ---> activates adenylate cyclase
All adrenergic receptors: α1, α2, β1, β2 are all generally...
all generally excitatory
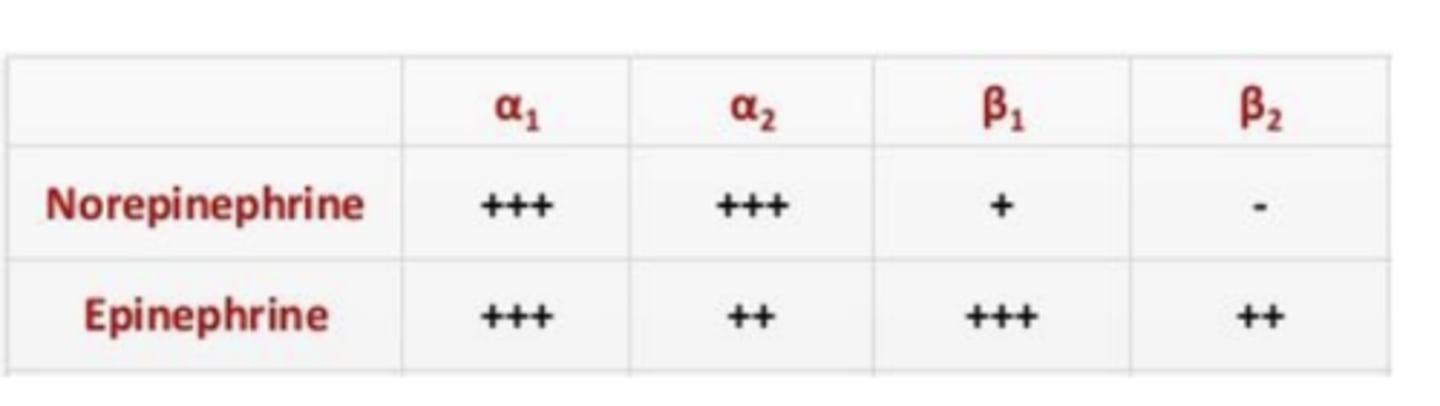
T/F: Adrenergic receptors have varying sensitivities to norepinephrine and epinephrine
TRUE
Norepinephrine and epinephrine bind to all adrenergic receptors except....
β2
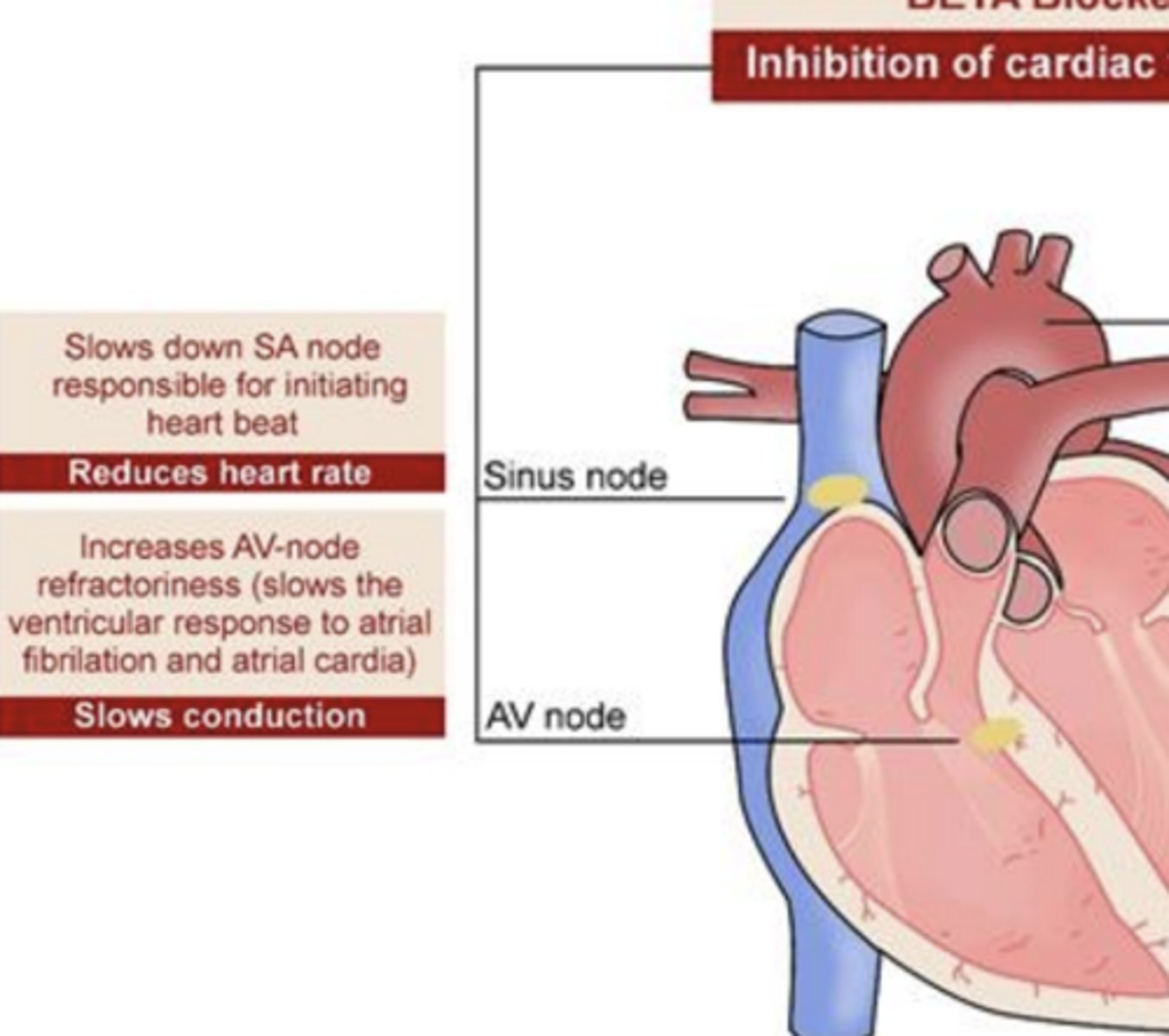
BETA Blockers- Inhibition of cardiac functions:
Sinus node
slows down SA node responsible for initiating hear beat
- reduces heart rate
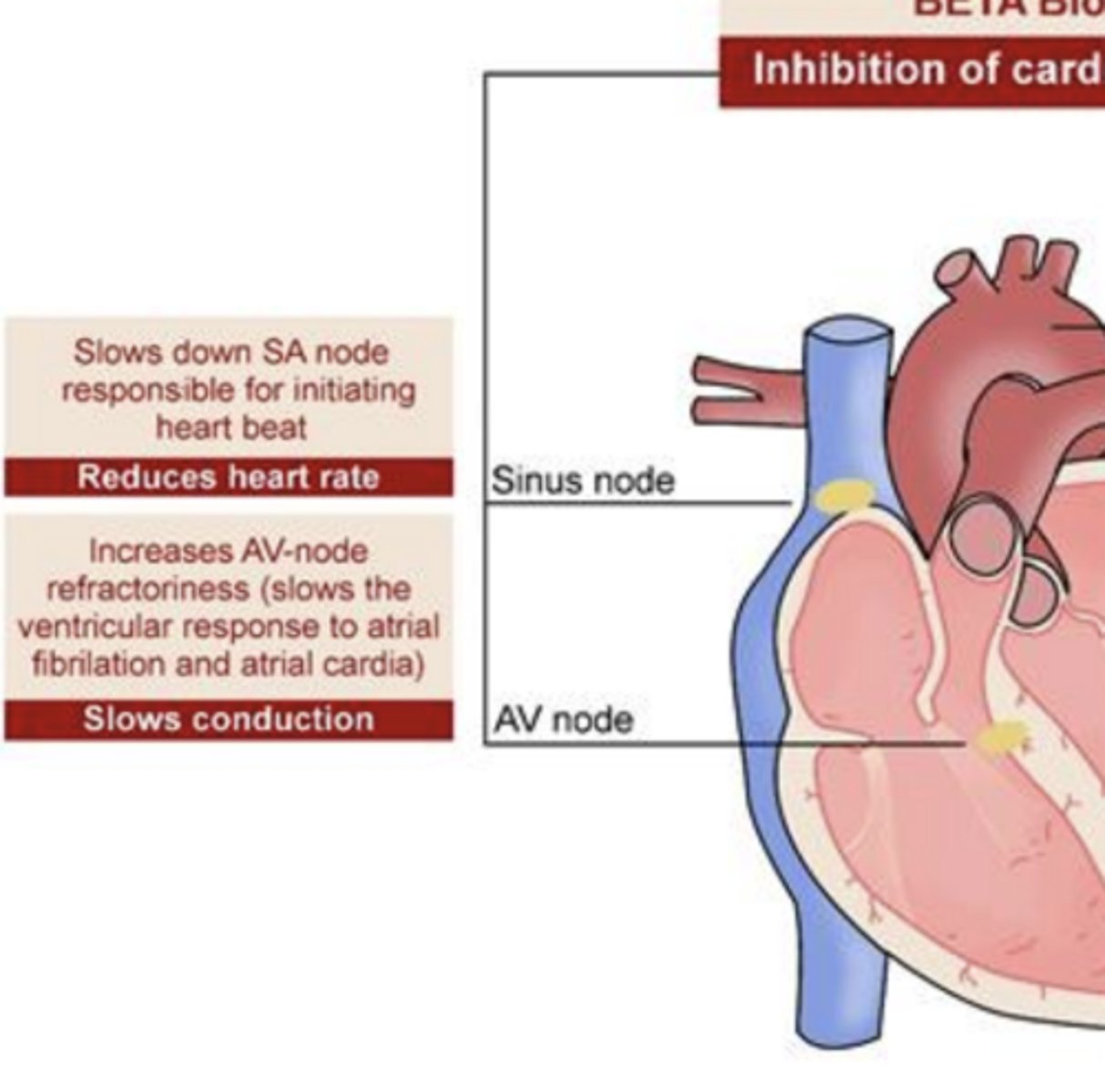
BETA Blockers- Inhibition of cardiac functions:
AV node
increases AV-node refractoriness (slows the ventricular response to atrial fibrillation and atrial cardia)
- slows conduction
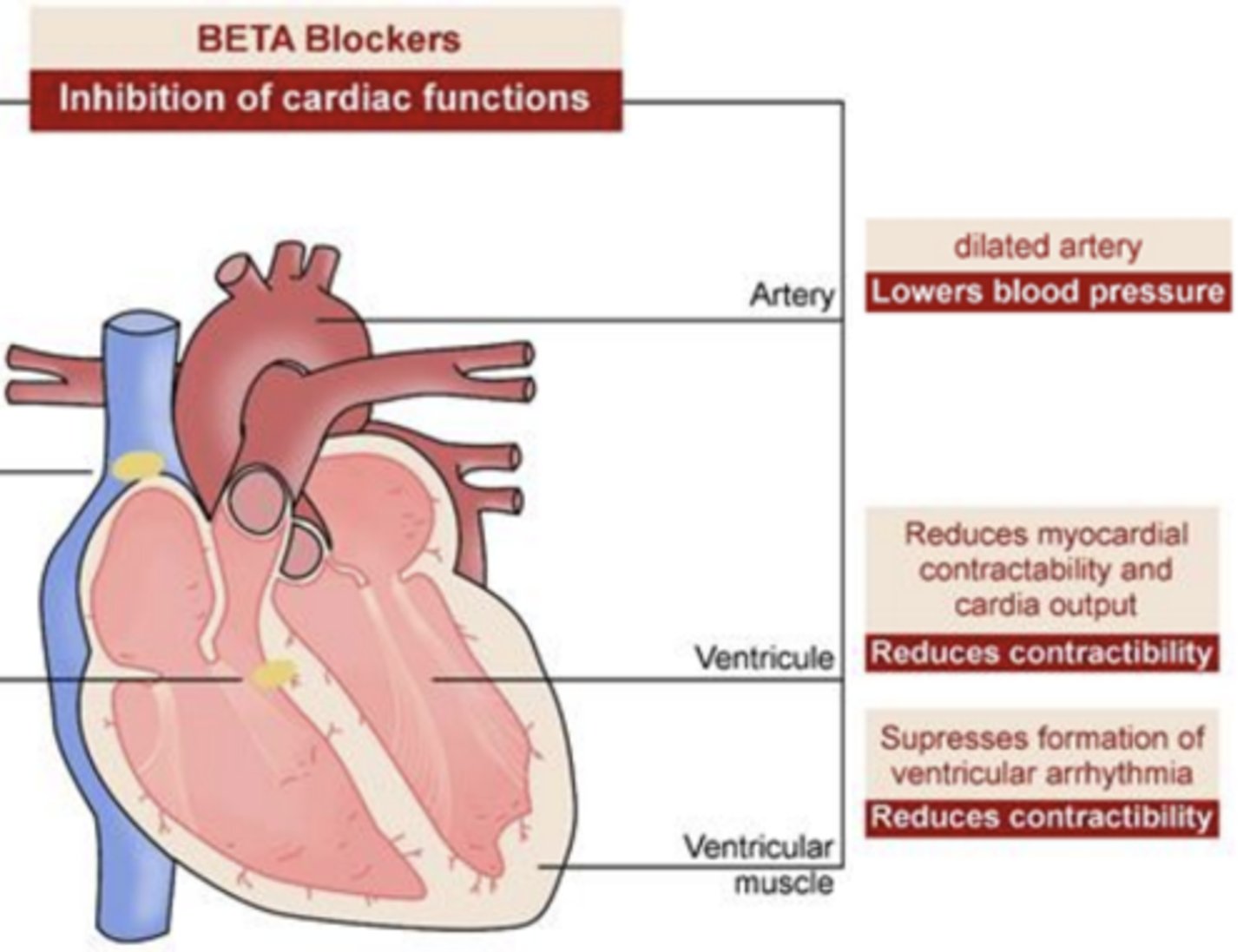
BETA Blockers- Inhibition of cardiac functions:
Artery
dilates artery
- lowers BP
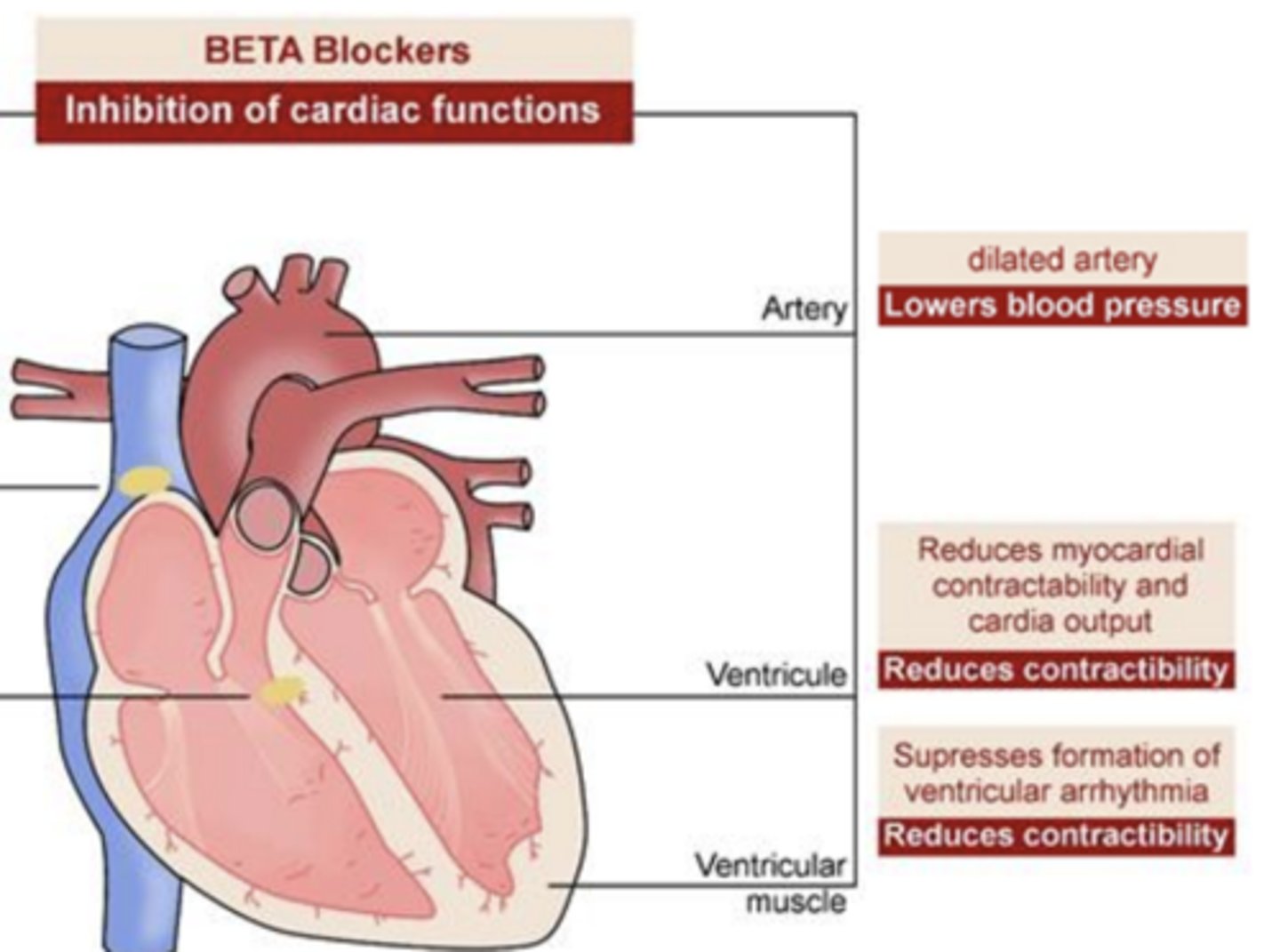
BETA Blockers- Inhibition of cardiac functions:
Ventricule
reduces myocardial contractibility and cardia output
- reduces contractibility
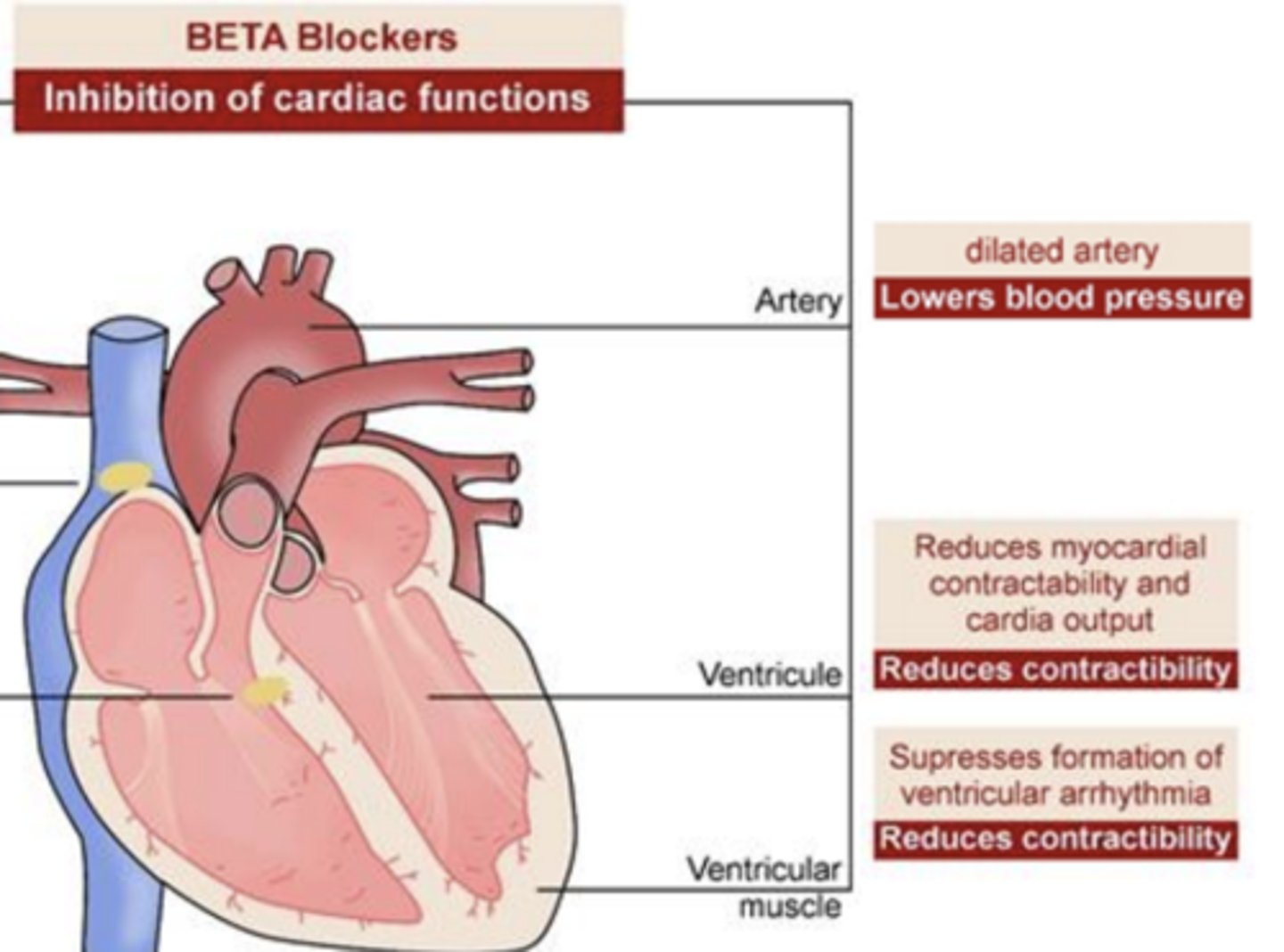
BETA Blockers- Inhibition of cardiac functions:
Ventricular muscle
supresses formation of ventricular arrhythmia
- reduces contractibility
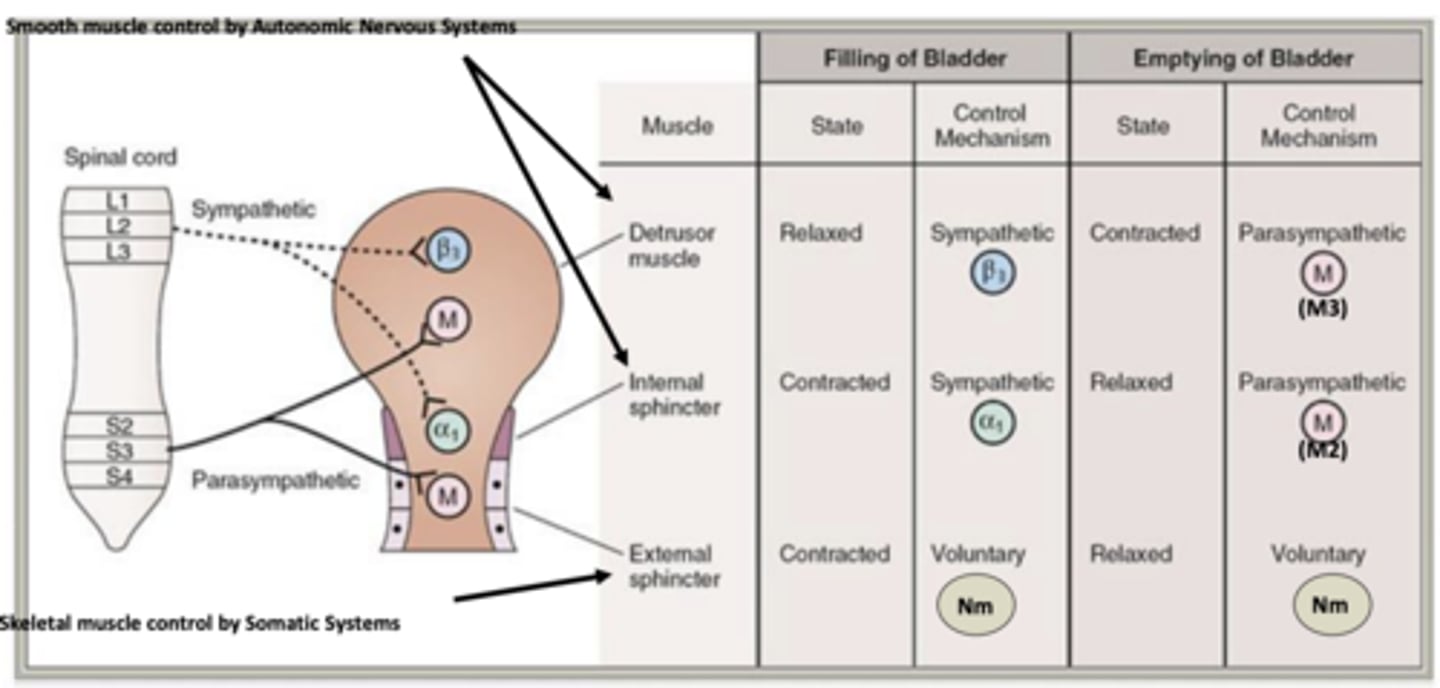
There are actually _____ autonomic muscles that work together to control bladder function
What are they?
- 2 autonomic muscles
- detrusor muscle and internal sphincter muscle
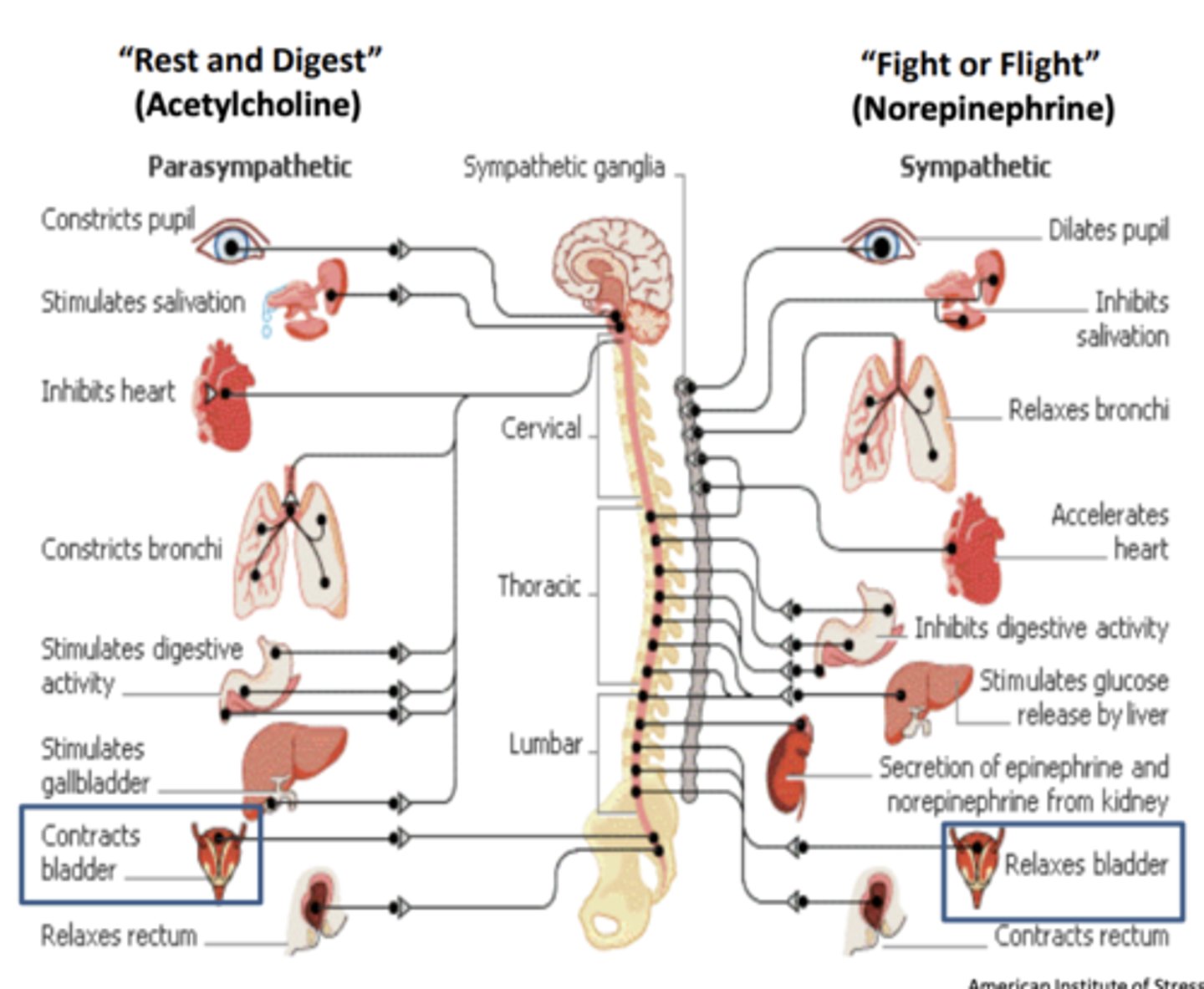
Which system fills the bladder?
What occurs? What is released and what does it activate in the detrusor muscle and in the internal sphincter? What does this allow for?
- sympathetic system fills bladder
- NE is released and activates β3 adrenergic receptors in the detrusor muscle and α1 adrenergic receptors in internal sphincter
- β3 adrenergic receptors- relaxes and allows bladder to fill
- α1 adrenergic receptors- contract to prevent urination

Which system empties the bladder?
What occurs? What is released and what does it activate in the detrusor muscle and in the internal sphincter? What does this allow for?
- parasympathetic system empties bladder
- ACh is released and activates M3 muscarinic receptors in detrusor muscle and M2 muscarinic receptors in internal sphincter
- M3 muscarinic receptors- contract to empty bladder
- M2 muscarinic receptors- relax to allow urination
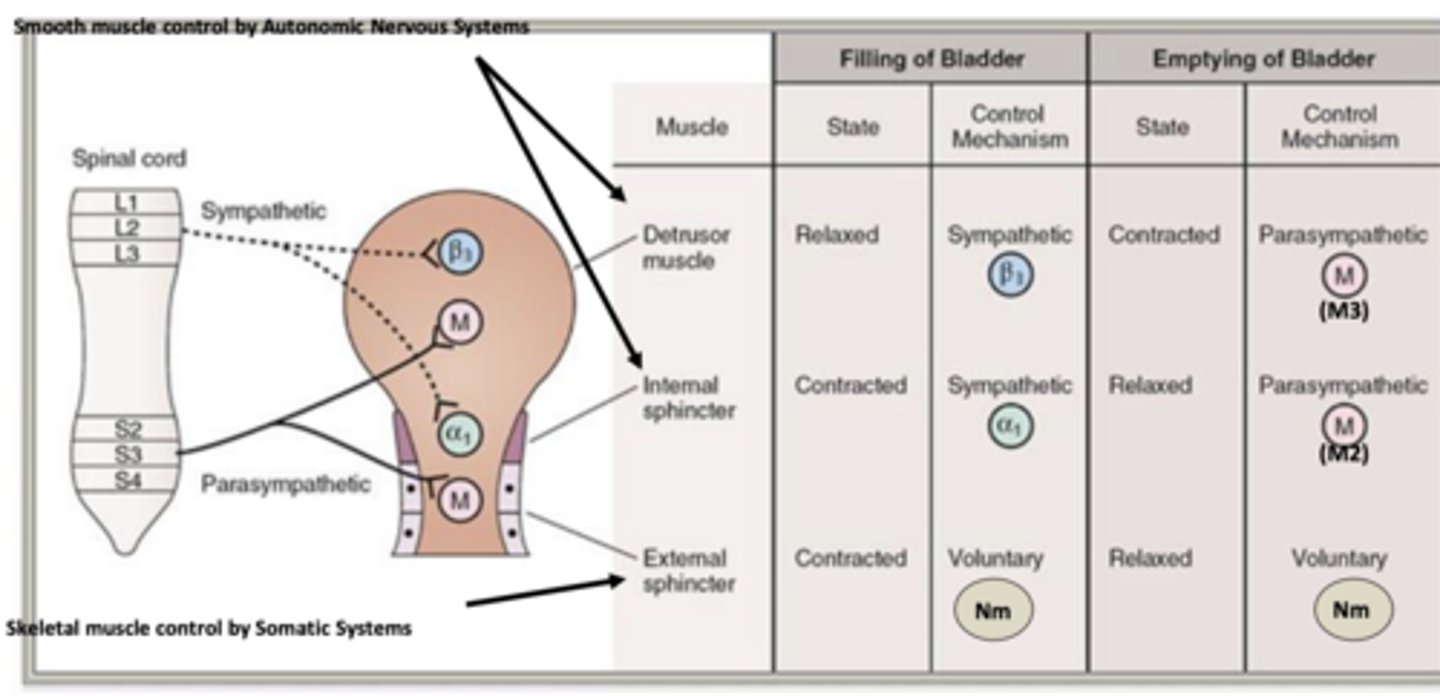
- Somatic system provides ___________________ of bladder.
- what is released? what does it activate?
- voluntary control
- ACh is released and activates muscle-type nicotinic receptors (Nm) in external sphincter, which contracts or relaxes for voluntary bladder control
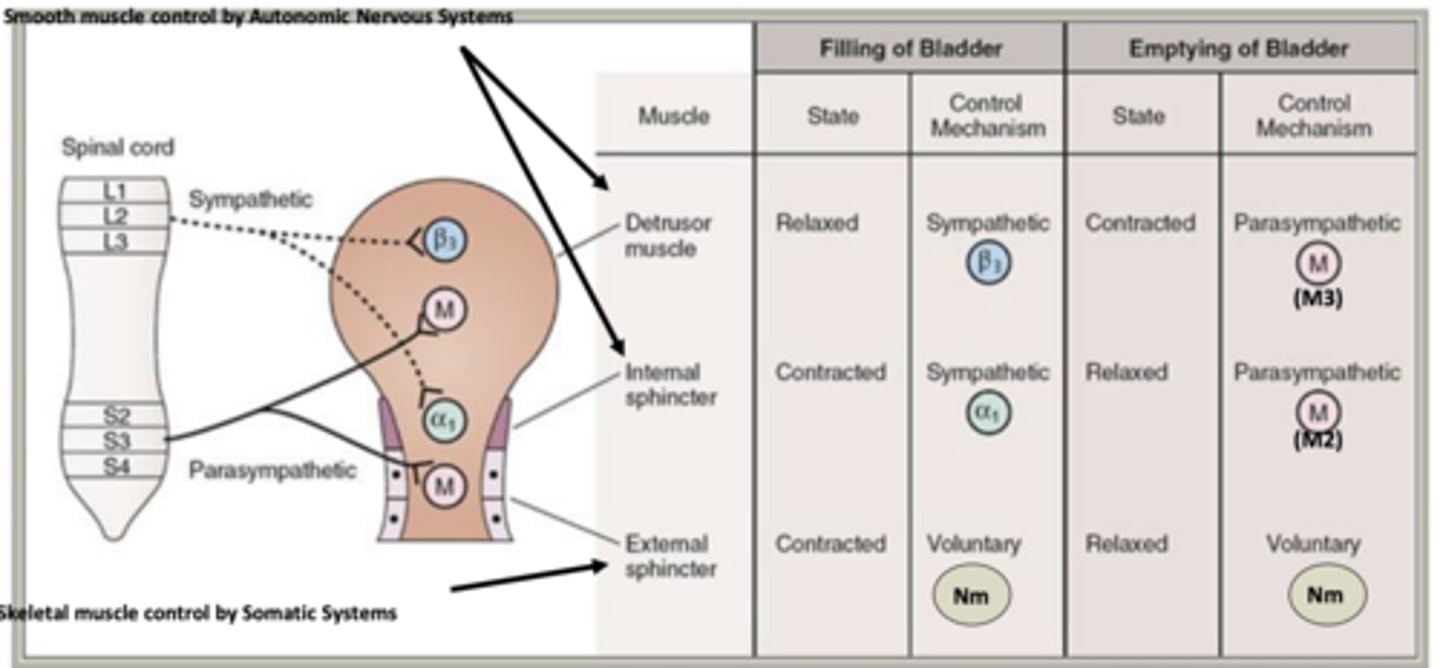
Smooth muscle control of bladder is done by....
autonomic nervous system
Skeletal muscle control of bladder is done by...
somatic systems
Which receptors are used in the filling of the bladder control mechanisms?
- Sympathetic:
- Voluntary:
Sympathetic: α1 and β3
Voluntary: Nm
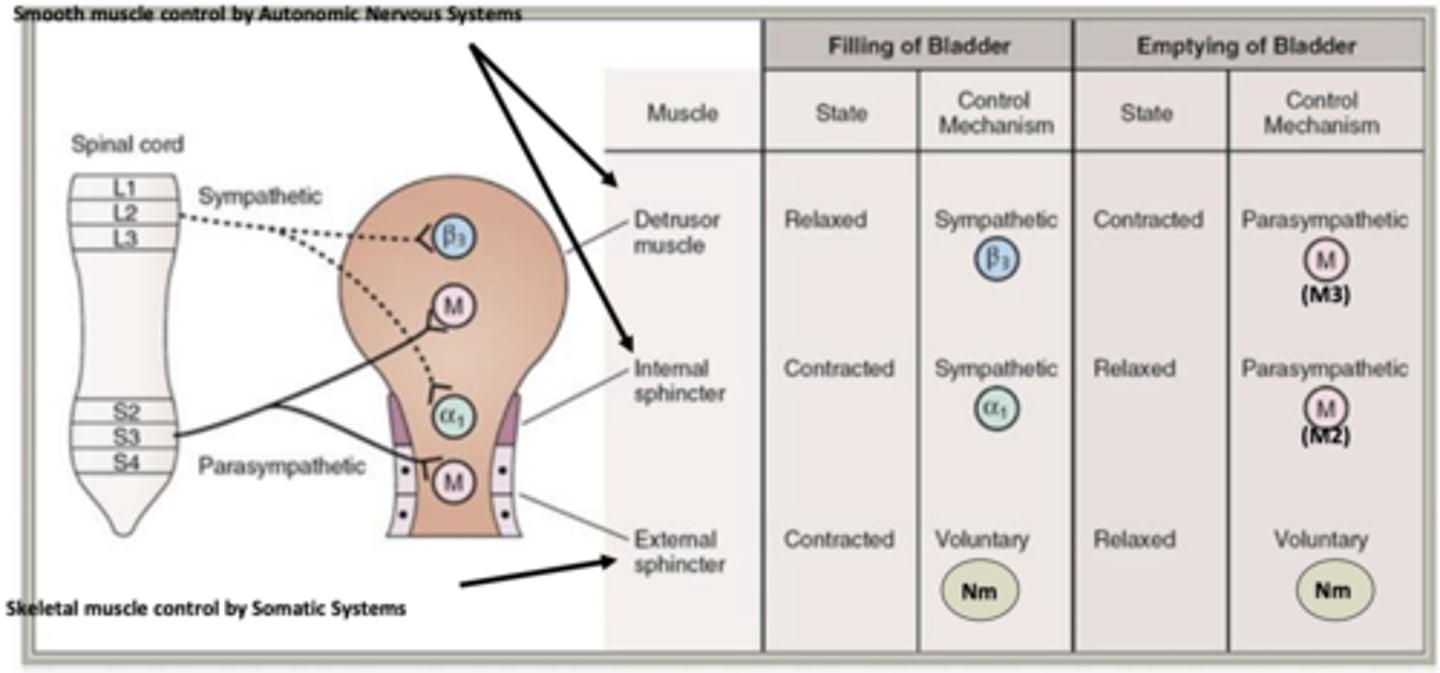
Which receptors are used in the emptying of the bladder control mechanisms?
- Parasympathetic:
- Voluntary:
Parasympathetic: M3 and M2
Voluntary: Nm
Nicotinic receptors consist of how many subunits?
A. 4
B. 6
C. 3
D. 5
D. 5
T/F: Nicotinic ionotropic receptors are fast acting receptors that when activated, allow Na+, K+, and Ca++ to cross the cell membrane
TRUE
Which muscarinic receptors are implicated in processes controlled by the autonomic nervous system?
A. M4 and M5
B. M1, M2, and M3
C. M1, M3, and M5
D. M2 and M4
E. All muscarinic receptors
B. M1, M2, and M3
Which of the following adrenergic receptors can inhibit the release of neurotransmitters?
A. α1
B. α2
C. β1
D. β2
B. α2