Biology: Climate Change - 4.4
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/14
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 1:10 PM on 9/11/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
15 Terms
1
New cards
Measurement of atmospheric gases
1. Satellite Measurements
2. Direct Measurement from Earth by monitoring stations
2
New cards
Why are atmospheric gases measured?
* Data must be collected to evaluate hypotheses and make predictions
* Atmospheric gases have important effects on:
* Photosynthesis rates
* pH of seawater
* Global temperature
* Extent of polar ice sheets
* Sea level and position of coastlines
* Ocean currents
* Distribution of rainfall
* Frequency and severity of extreme weather
\
* Atmospheric gases have important effects on:
* Photosynthesis rates
* pH of seawater
* Global temperature
* Extent of polar ice sheets
* Sea level and position of coastlines
* Ocean currents
* Distribution of rainfall
* Frequency and severity of extreme weather
\
3
New cards
Greenhouse Gas
1. gases in the atmosphere that can
2. absorb and reflect long wave radiation back to Earth
3. trapping heat near Earth’s surface, keeping Earth much warmer than it otherwise would be.
4
New cards
GG: CO2
\
* Added to atmosphere via cell respiration and combustion
* Removed from the atmosphere by photosynthesis and diffusion into the ocean
* Added to atmosphere via cell respiration and combustion
* Removed from the atmosphere by photosynthesis and diffusion into the ocean
5
New cards
GG: H2O
\
* Added to atmosphere via evaporation from ocean and transpiration from plants
* Removed from the atmosphere by rainfall and snow
* Added to atmosphere via evaporation from ocean and transpiration from plants
* Removed from the atmosphere by rainfall and snow
6
New cards
GG: CH4
\
* Added to atmosphere via:
* Methanogenic archaea performing anaerobic respiration
* Melting of tundra (where methane has been trapped in frozen soil)
* Removed from the atmosphere by oxidation to become CO2 and H2O.
* Added to atmosphere via:
* Methanogenic archaea performing anaerobic respiration
* Melting of tundra (where methane has been trapped in frozen soil)
* Removed from the atmosphere by oxidation to become CO2 and H2O.
7
New cards
GG: N2O
* Added to atmosphere whenever combustion occurs in the presence of nitrogen
* (vehicle exhaust, lightning strikes).
* (vehicle exhaust, lightning strikes).
8
New cards
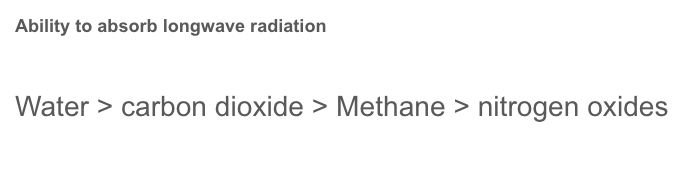
Factors of Capability of GGs
1. **Greater capacity to absorb longwave radiation**
* a greater warming impact per molecule
2. **Concentration within the atmosphere**
* a greater warming impact
* concentration is determined by: rate of release and persistence within the atmosphere
9
New cards
CH4 vs CO2
\
1. carbon dioxide persists longer in the atmosphere as methane is more reactive and breaks down easily.
2. Methane absorbs a narrower range of wavelengths than carbon dioxide
3. Methane is released into the atmosphere at a lower rate than carbon dioxide
\
Therefore CO2 has a greater impact on global warming/greenhouse effect
1. carbon dioxide persists longer in the atmosphere as methane is more reactive and breaks down easily.
2. Methane absorbs a narrower range of wavelengths than carbon dioxide
3. Methane is released into the atmosphere at a lower rate than carbon dioxide
\
Therefore CO2 has a greater impact on global warming/greenhouse effect
10
New cards
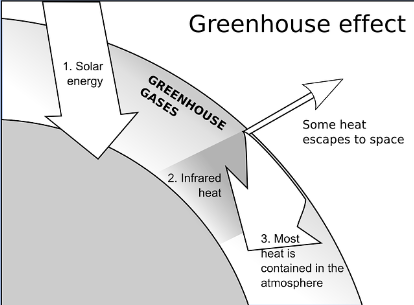
Greenhouse effect
1. process by which radiation from a planet's atmosphere
2. warms the planet's surface to a temperature
3. above what it would be without its atmosphere.
11
New cards
Relative Wavelength sizes
* UV: smallest but most energy
* Visible: middle but middle
* Infrared: largest but least energy
\
* Visible: middle but middle
* Infrared: largest but least energy
\
12
New cards
Short wave radiation
\
* Mainly visible light
* Emitted from the sun
* Peaks at wavelength of 400 nm
* UV, visible and infrared wavelengths
* Mainly visible light
* Emitted from the sun
* Peaks at wavelength of 400 nm
* UV, visible and infrared wavelengths
13
New cards
Long wave radiation
\
* Mainly infrared received from sun
* **Emitted from the Earth**
* Peaks at wavelength of 10,000 nm
* Infrared only
* Mainly infrared received from sun
* **Emitted from the Earth**
* Peaks at wavelength of 10,000 nm
* Infrared only
14
New cards
Absorption & Emission of GG
\
1. Earth absorbs short wave and emits long wave radiation
2. Greenhouse gases capture the long wave radiation
3. Long wave is passed back to Earth, causing warming
1. Earth absorbs short wave and emits long wave radiation
2. Greenhouse gases capture the long wave radiation
3. Long wave is passed back to Earth, causing warming
15
New cards
Ocean Acidification: Effects
1. leads to the death of coral polyps and algae
2. colour of the reef goes from being richly multi-coloured to being as white as bone coral reef death is called bleaching
3. interrupts the food chain, causing many of the organisms that live there to seek food and shelter elsewhere.