B7
1/99
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
100 Terms
what is the endocrine system
system made of endocrine glands that release chemical substances known as hormones into the blood stream
difference between nuerones and hormones
nuerone’s have faster action. Hormones are longer lasting. Hormones act more generally .
list all endocrine glands
pituitary gland, thyroid glands, adrenal gland , pancreas, ovaries, testes
adrenal gland hormones and function
produces adrenaline which stimulates the flight or fight response when in a dangerous situation
pituitary gland function
known as master gland. releases hormones to regulate body conditions and acts on other glands
thyroid gland hormone and function
thyroxine which regulates metabolism
pancreas hormone and function
insulin to regulate blood glucose levels
testes hormones and function
testosterone which controls puberty and sperm production
ovaries hormones and function
produces oestrogen and progesterone which are involved in menstrual cycle
negative feedback
homeostatic mechanism to maintains body conditions and return the body to normal after a change
negative feedback cycle when thyroxine levels are low
hypothalamus detects change and releases more TRH. This stimulates release of more TSH from the pituitary which stimulates more thyroxine to be produced by the thyroid
negative feedback cycle for when thyroxine levels are high
hypothalamus detects change and releases less TRH which inhibits TSH production from pituitary gland which inhibits thyroxine production from thyroid.
adrenaline
released from adrenal gland , prepares body for fight or flight in scary or stressful situations.
how does adrenaline affect the body
pupils dilate to let more light enter retina
glycogen reserves break down increasing blood glucose concentration for increased respiration in muscle cells
increased heart rate and breathing rate so glucose and oxygen can be delivered to cells and co2 can be taken away more quickly
blood flow diverts from non-essential parts such as the digestive system
comparison of thyroxine and adrenaline against time
thyroxine increases and decreases as an example of negative feedback whilst adrenaline increases to a peak and then decreases
homeostasis
controlling a constant internal environment
examples of homeostasis
osmoregulation , thermoregulation , blood glucose regulation
importance of homeostasis
ensure the reactions in body cells can function at optimum
label the skin cell
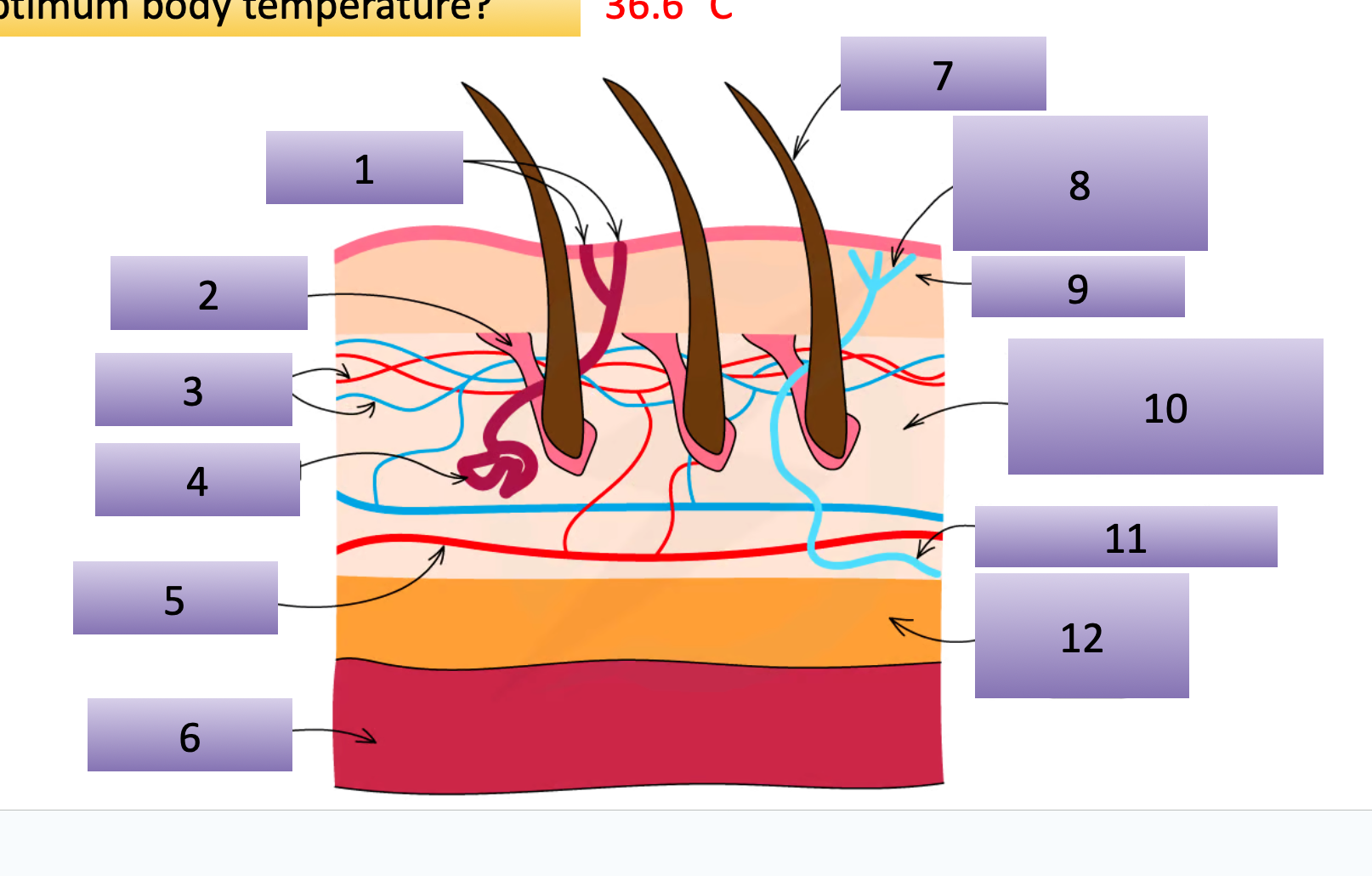
sweat pores
erector muscles
capillaries
sweat gland
arteriole
muscles
hair
temperature receptors / nerve endings
epidermis
dermis
sensory nuerone
fat
body response to an increase in temperature
sweating, vasodilation, erector muscles relax / pilorelaxation
body response to a decrease in temperature
vasoconstriction , shivering, erector muscles contract / piloerection
how does the thermoregulatory centre detect temperature change
it has receptors that are sensitive to the blood temperature in the brain. It also receives impulses from receptors in the skin that provide information about external temperature
where is the thermoregulatory centre
hypothalamus
how does sweating decrease body temperature
when sweat evaporates off the skin , heat energy its lost to the environment
how does shivering increase body temperature
it requires more energy from respiration which releases heat energy. the rapid contraction of muscles can also heat the body due to the friction
how does pilorelaxation / piloerection affect body temperature
when the erector muscles contract, the hairs stand trapping an Insulating layer of air which warms you. When the erector muscles relax, no insulating air is trapped
how does vasodilation / vasoconstriction affect body temperature
when the blood vessels dilate , they are closer to skin surface so heat is lost by radiation. When they constrict , less energy is lost by radiation
what does the body do to regulate blood glucose levels when its too high
the pancreas releases insulin which stimulates the liver and muscle cells to store excess glucose from the blood stream and store it as glycogen
what does the body do to regulate glucose levels when they are too low
the pancreas releases glucagon which stimulates the liver to break down glycogen into glucose and release it into the blood
what is type 1 diabetes and how is it treated
the pancreas produces little or no insulin . It is treated with insulin therapy
what is type 2 diabetes and how is it treated
cells no longer respond to insulin. It is treated with a low sugar diet and exercise
what is a risk factor for type 2 diabetes
obesity
why is osmoregulation important
as the cytoplasm of all cells and the blood plasma is largely composed of water , osmoregulation is important to prevent harmful changes to cells as a result of osmosis like cell shrinking or bursting.
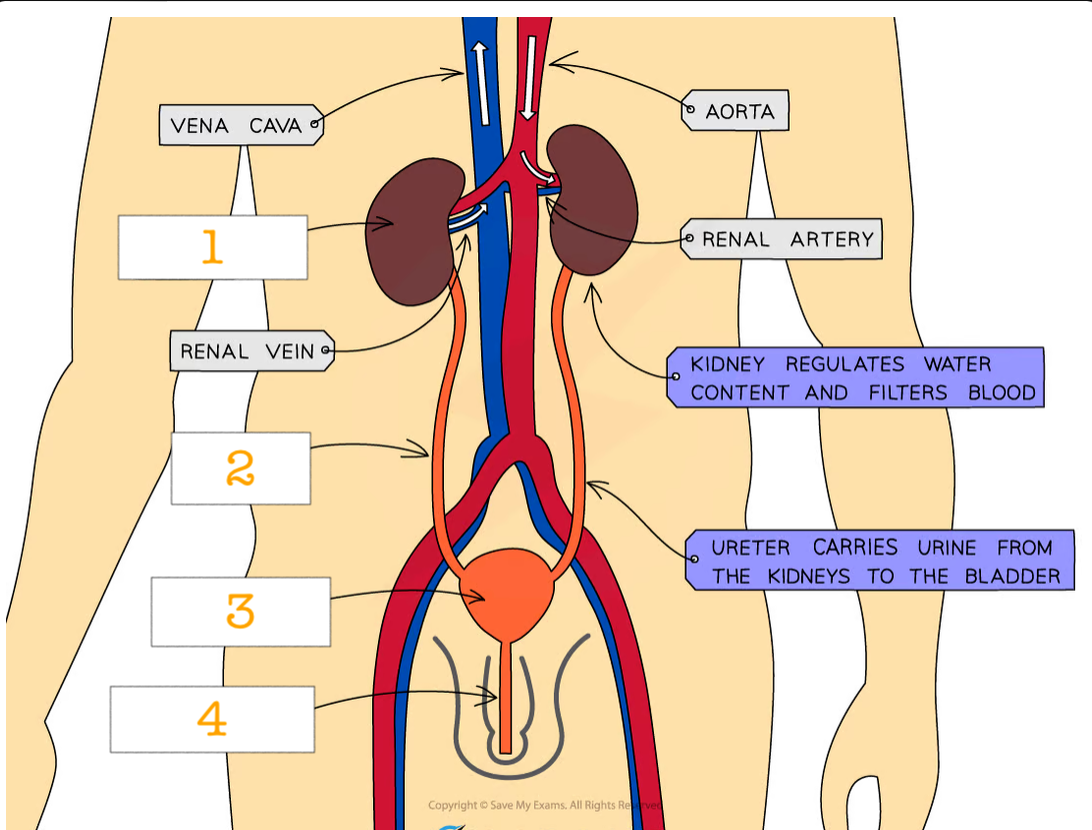
label 1-4 and explain
kidney = organs that filter the blood
ureter - tube connecting kidney to bladder
bladder- organ that stores urine
urethra - tube that connects bladder to the exterior - where urine is released
urinary system steps
liver produces urea which enters kidney via renal artery. it is filtered and the clean blood leaves via renal vein. the remaining waste products are sent to bladder via ureter and excreted via urethra
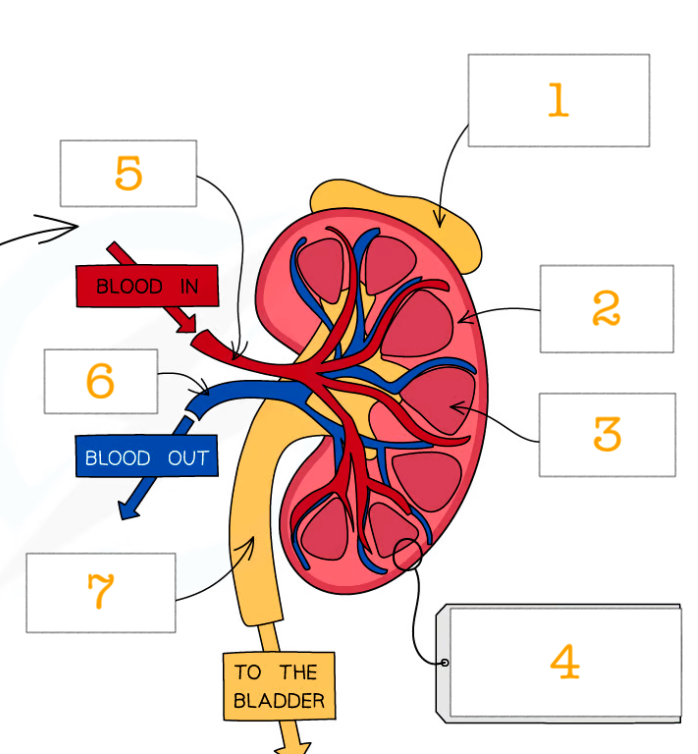
label kidney structure 1-7
adrenal gland
cortex -outermost region
medulla - intersection of the kidney
nephrons
renal artery
renal vein
ureter
label the nephron structure
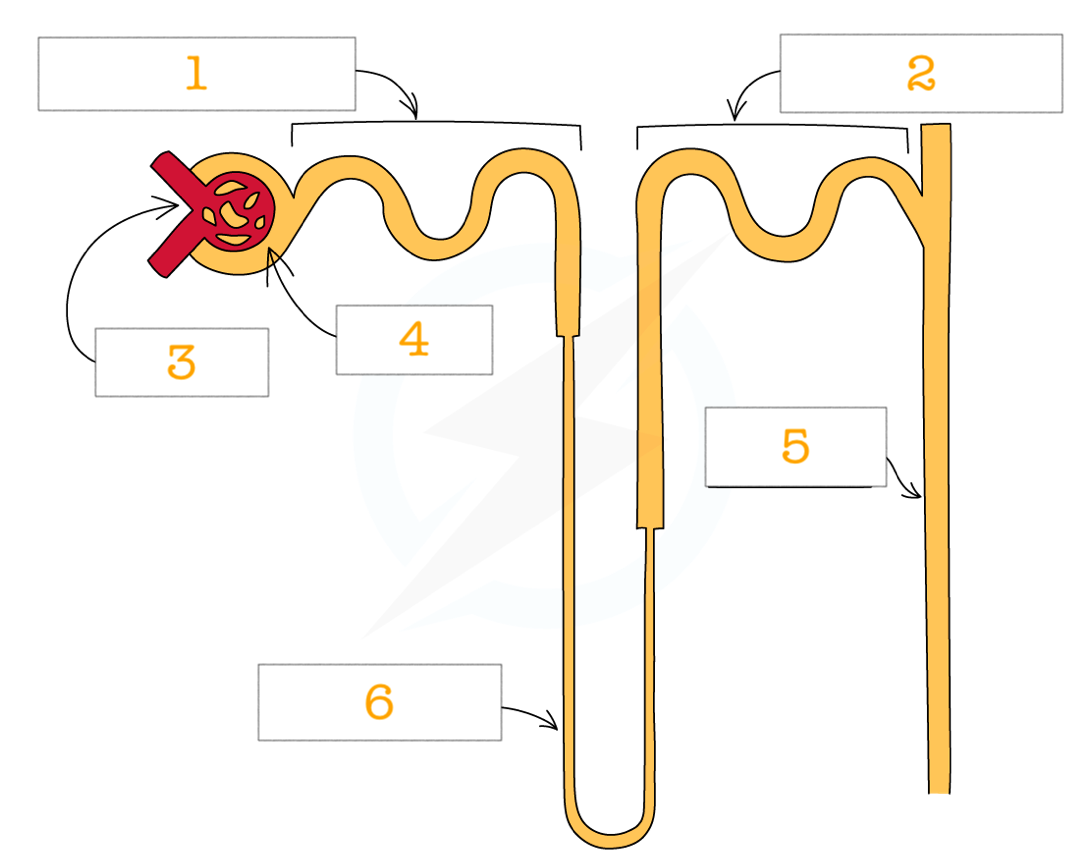
Proximal convoluted tubule
distal convoluted tubule
glomerulus
bowman’s capsule
collecting duct
loop of henle
3 processes in the nephron
ultrafiltration , selective reabsorption, excretion
ultrafiltration steps
high pressure blood is forced from the capillaries of the glomerulus into the bowman’s capsule past a partially permeable membrane . large molecules like proteins and red blood cells are forced out
where does selective reabsorption happen
in the PCT , DCT, Loop of Henle and part of the collecting duct
reabsorption of glucose in selective reabsorption in the kidney
only occurs at the PCT , takes place by active transport. The nephron has many mitochondria to provide enough energy for the active transport
reabsorption of water and salts in selective reabsorption
in the loop of henle , DCT and collecting duct. Water is reabsorbed into the blood by osmosis and any salts by diffusion
excretion steps
whatever isn’t reabsorbed continues out the nephron via the collecting duct and then passes through the ureter into the bladder
what does ADH do
makes the kidney tubules in collecting duct more permeable
what is the response in the body when there is water loss
brain detects less water content in the blood and instructs the pituitary gland to release ADH into the blood . ADH makes the collecting ducts more permeable so more water is reabsorbed .
what is the body’s response if there’s water gain
the brain detects more water content in the blood and instructs the pituitary gland to release less ADH. The collecting ducts are now less permeable so less water is reabsorbed
how does water content affect pee colour
more water = more dilute pee = clear colour.
less water = more concentrated pee = yellow colour due to more urea
how does the dialysis machine work
patients blood is pumped into machine. It flows in a tube with a partially permeable membrane. The waste products like urea and excess ions diffuse into the dialysis fluid from blood and glucose and water could diffuse back into blood. The blood is now filtered from harmful waste
what is specific about the dialysis fluid
it has to have the same concentration of salts and glucose as the blood plasma
what is added to blood in dialysis machine to stop clotting
anti-coagulant
what is a benefit of dialysis treatment
can filter your blood and keeps you alive until a transplant. It is also readily available
what is a negative of dialysis treatment
time consuming and expensive. Restrictive diet
positive of kidney transplant
long term solution for kidney failure. Less restrictive diet
negative of kidney transplant
risk of rejection . Have to take immunosuppressant drugs for life
where does deamination occur and what is it?
In the Liver. It is when excess amino acids are broken down. carbon is broken down into glycogen and nitrogen into ammonia. ammonia breaks down to urea
what happens to the urea produced by the liver
it dissolves in the blood and is taken to the kidney to be excreted.
FSH function
causes a follicle ( an egg ) to mature
oestrogen
causes the lining of the uterus to thicken and grow
Luteninsing hormone function
stimulates the release of an egg
progesterone purpose
maintains the lining of the uterus
where is FSH and LH released
pituitary gland
where is progesterone released
corpus luteum
FSH and Oestrogen relationship
FSH stimulates oestrogen production. Oestrogen inhibits FSH production
LH and progesterone relationship
LH stimulates progesterone production. Progesterone inhibits LH production
describe stages of menstrual cycle
menstruation
lining starts to thicken
ovulation
lining is maintained ( luteal phase )
menstruation
loss of lining from the uterus, occurs at the start of the cycle if no fertilisation has occurred
ovulation
egg matures and is released from ovary to the uterus down the oviduct
name 2 chemical contraceptives
IUD , contraceptive pill / implant / injection
how do contraceptive pills , implants or injections work
they release progesterone or a mixture of progesterone and oestrogen to prevent egg maturation and egg release
how does the IUD work
releases hormones that thicken lining making it difficult for sperm to travel to egg. The copper also acts as a spermicide
barrier methods of contraception
condom , diaphragm - rubber cap over cervix entrance
surgical contraception
cutting sperm ducts
tying off oviducts
clomifene therapy
women who don’t ovulate or don’t ovulate regularly are given clomifene. this releases more FSH and LH
In-Vitro fertilisation- IVF
women given FSH and LH to stimulate maturation of several eggs
eggs are collected from the mother ovaries and fertilised by sperm from father in lab
fertilised eggs develop into embryos and are inserted in the uterus
why is thermoregulation important
most of cellular processes use enzymes. too high of a temp means they denature, too low of a temp means they are not working as efficiently .
how do blood vessels dilate/constrict
muscles in walls of arterioles relax/ constrict
what happens to blood glucose regulation in a person w type 1 diabetes
no insulin released after blood glucose rises to dangerous levels. need insulin therapy
how does controlling your diet help with type 2 diabetes
by having a diet with less sugar means that blood glucose doesn’t rise too quickly so that insulin can cope
why is dialysis fluid constantly pumped inside
maintain the concentration gradient
what happens to blood glucose regulation in a person w type 2 diabetes
pancreas produces insulin. liver receptors do not respond and do not convert glucose to glycogen
what happens to blood glucose during exercise
decreases as it is used in respiration
what happens to ADH levels when someone is sleeping
increase, body becomes dehydrated during sleep
what happens to adh levels when exercising
increase as water is lost by sweating
how does caffeine and alcohol effect adh and pituitary gland
they act on pituitary gland and inhibit adh . kidneys reabsorb less water and there is more urine
when should a woman avoid sexual intercourse if she doesn’t want to be pregnant
when ovulation happens. 13-15 days as that Is when they are the most fertile
does ovulation always happen on the 14th day
no , factors like stress and illness contribute to varying times
hyperthyroidism
overactive thyroid gland
hypothyroidism
underactive thyroid gland
why would an underactive thyroid cause someone to feel tired and have increased body mass and feel cold
not enough thyroxine is produces so a reduced basal metabolic rate so less heat generated and less calories used from food.
when is IVF used over clomifene therapy
unhealthy sperm , blocked oviducts
why would hyperthyroidism cause people to lose weight, have increased energy and feel warmer
more thyroxine and higher metabolic rate. more heat generated from respiration and more calories used from food meaning less fat stored.
symptoms of hyperthyroidism
weight loss, increased BMR and protein synthesis, feel warmer, increased energy
symptoms of hypothyroidism
weight gain, decreased BMR and protein synthesis, feel colder, more tired, nerve and heart problems
how can progesterone reduce fertility
stimulate production of thick mucus preventing sperm from reaching egg.
how can adrenaline restore heart function
cause blood vessels to other organs to constrict increasing blood pressure and restores blood flow to coronary arteries
what does high levels of oestrogen stimulate
release of LH
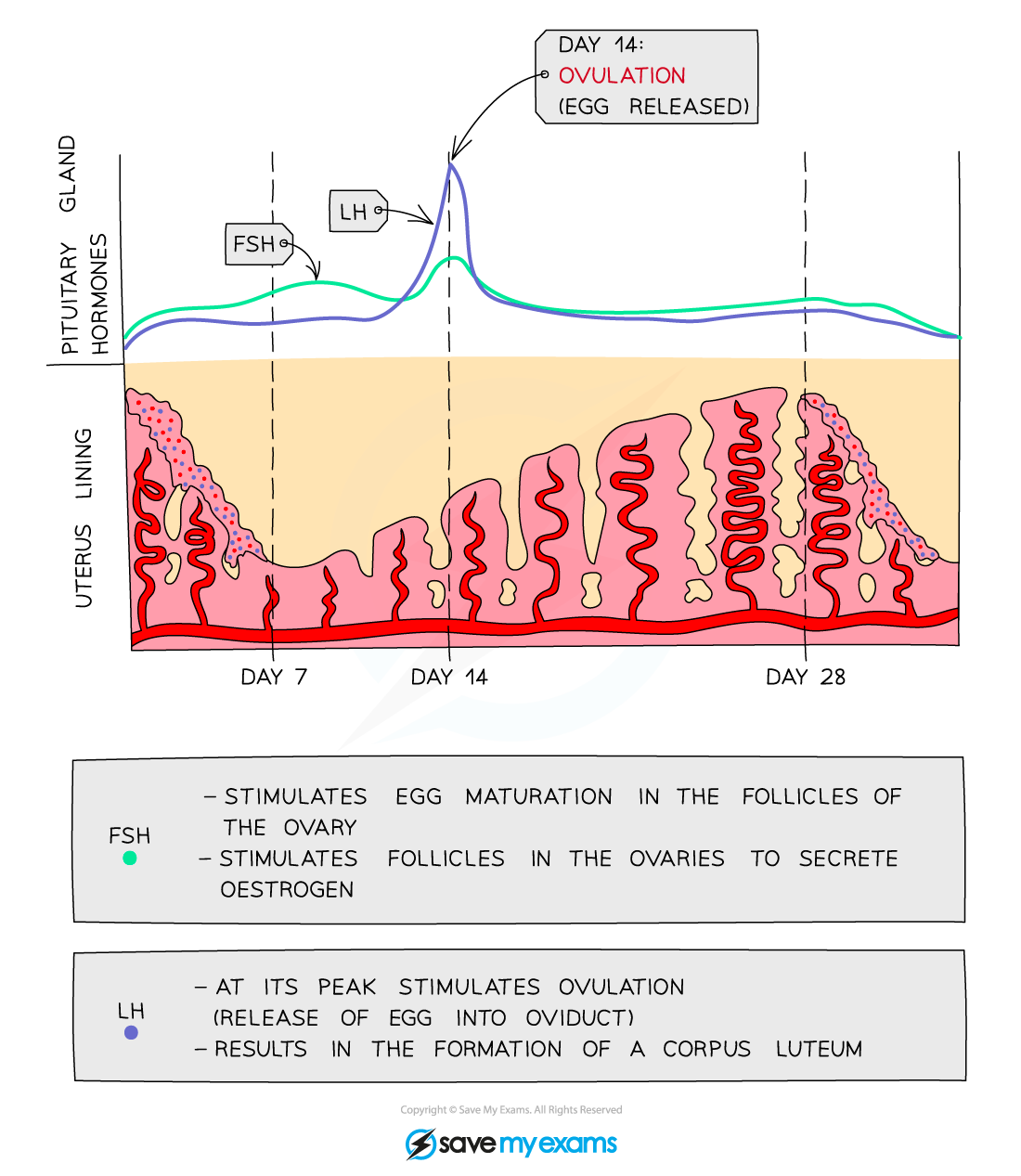
FSH levels in the stages of menstrual cycle
high at start then decreasing
increasing
peaks before ovulation
low
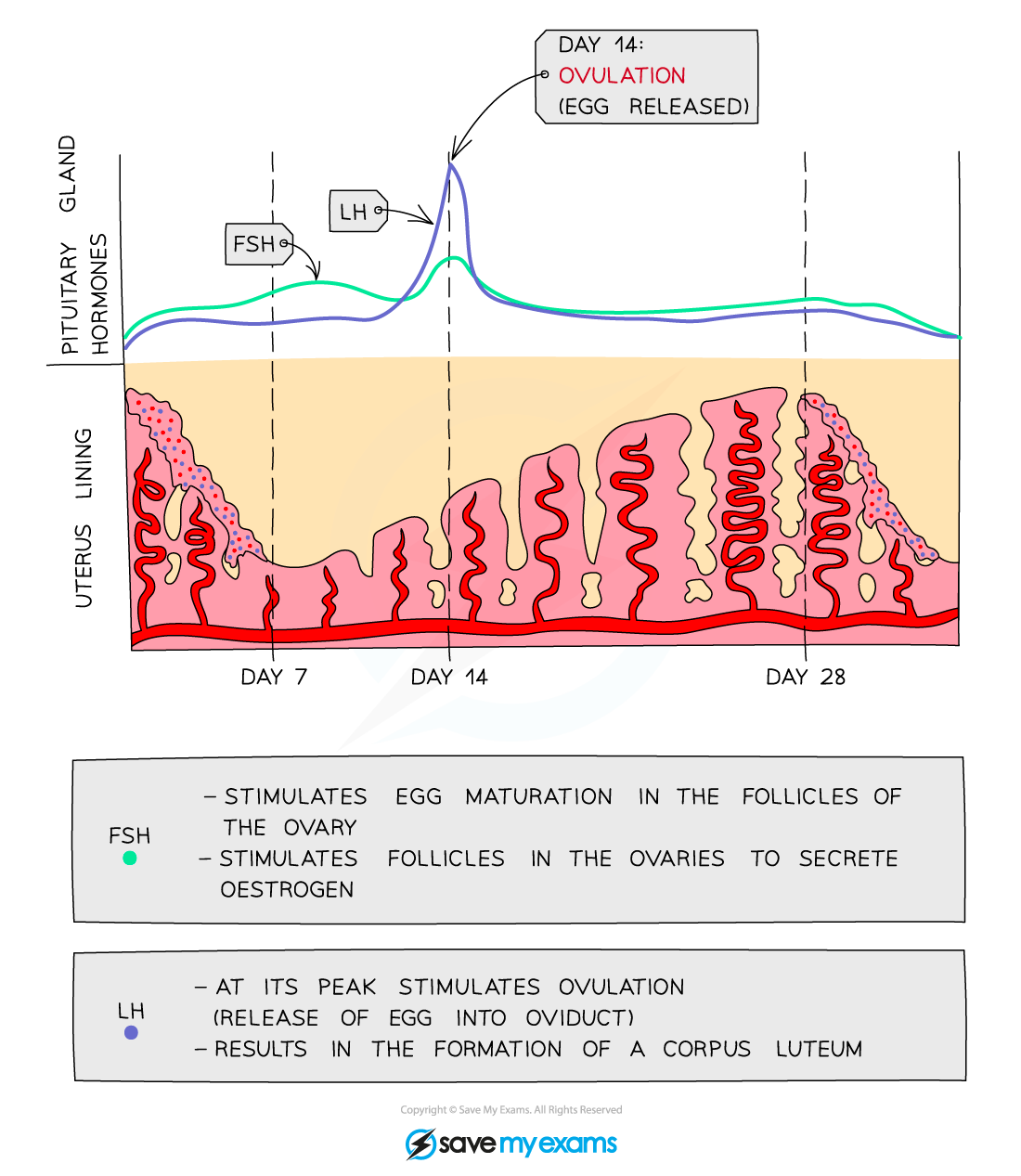
LH levels in menstrual cycle
low
low but slightly increasing
peaks sharply
low
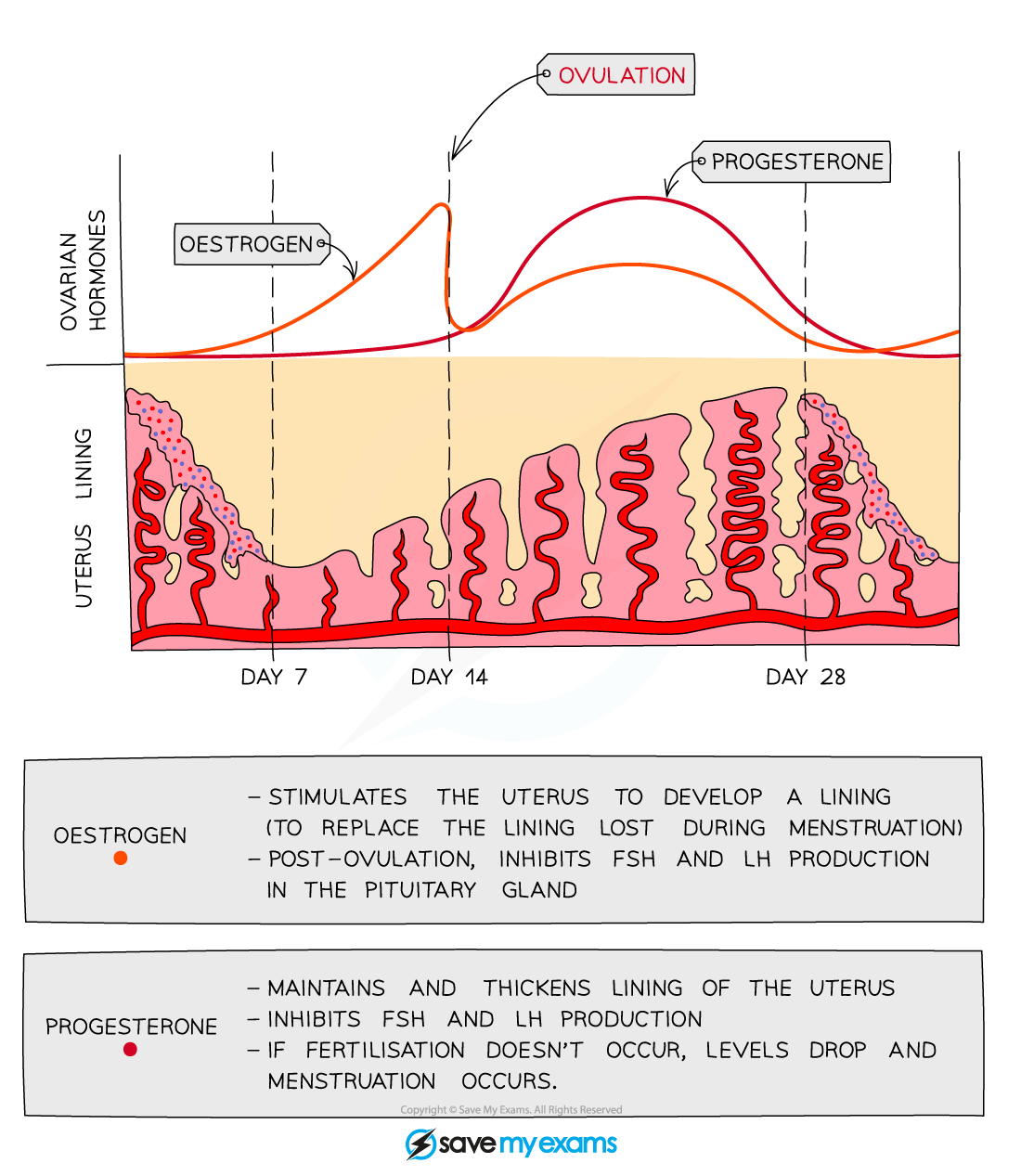
oestrogen levels in menstrual cycle
low
increasing and peaks before ovulation
very high
high then decreasing if no pregnancy
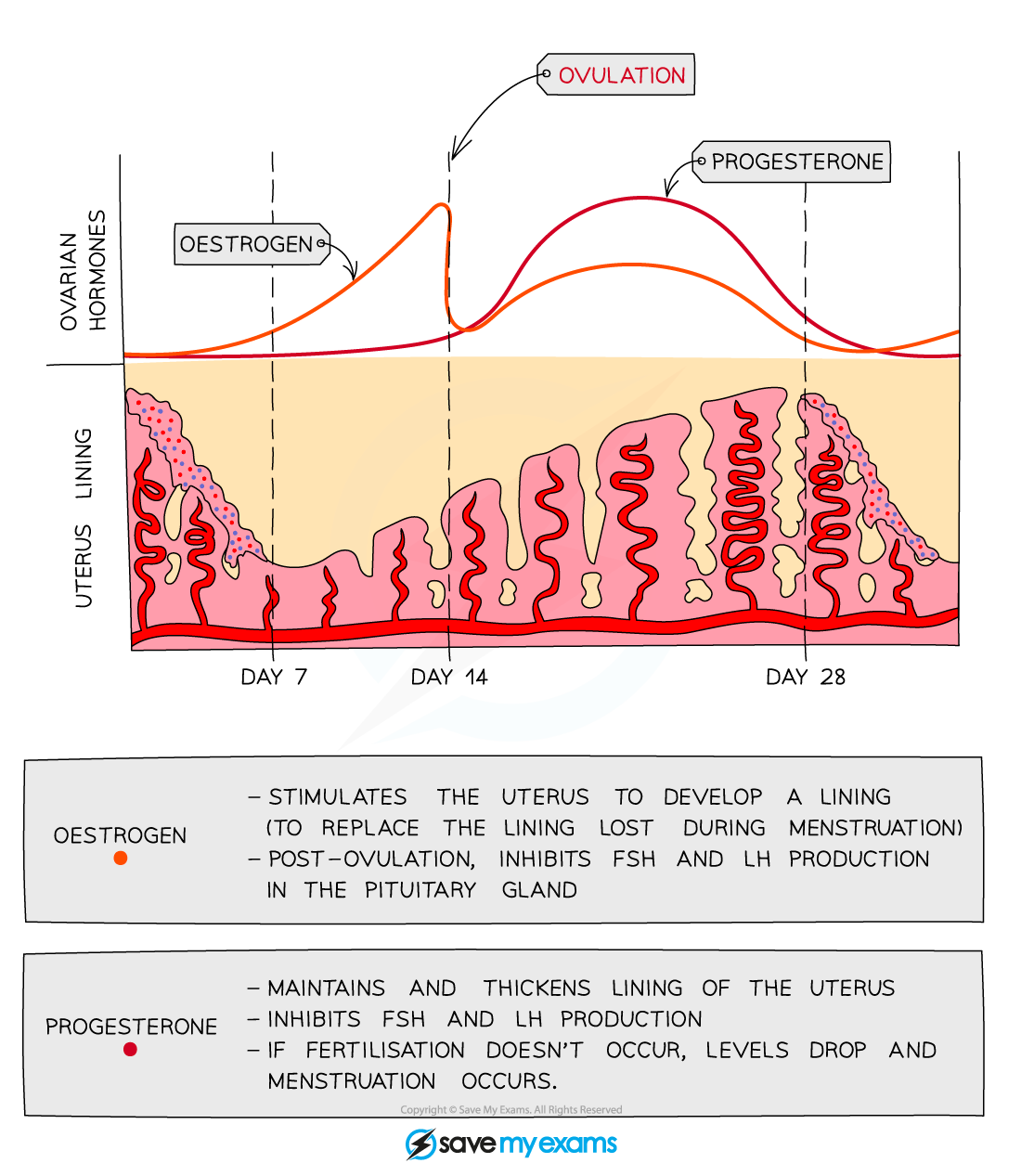
progesterone levels in menstrual cycle
low
low
low
high, peaks then decreases if no pregnancy