Foreign exchange market (FOREX)
1/19
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
20 Terms
Exchange rate
the value of a currency in one country compared with the value in another
Balance of payments
Measures all the monetary exchanges between one nation and all other nations. Includes the current account and the capital account.
Balance of trade
Net exports= Exports-Imports
Trade surplus
when a country exports more than it imports
trade deficit
when a country imports more than it exports
Interest rates and capital flow
Interest rates increase= Inflow increases, outflow decreases
net capital outflow
the difference between the purchases of foreign assets by domestic residents and the purchases of domestic assets by foreign residents
net capital inflow
the total flow of funds into a country minus the total flow of funds out of a country
Current account
net exports, investment incomes, net transfers
Financial (capital) account
stocks & bonds, Foreign Direct Investment, net capital outflow
Deapreciation
the loss of value of a country's currency with respect to the foreign currency
Appreciation
The increase of value of a country's currency with respect to a foreign currency
FOREX graph
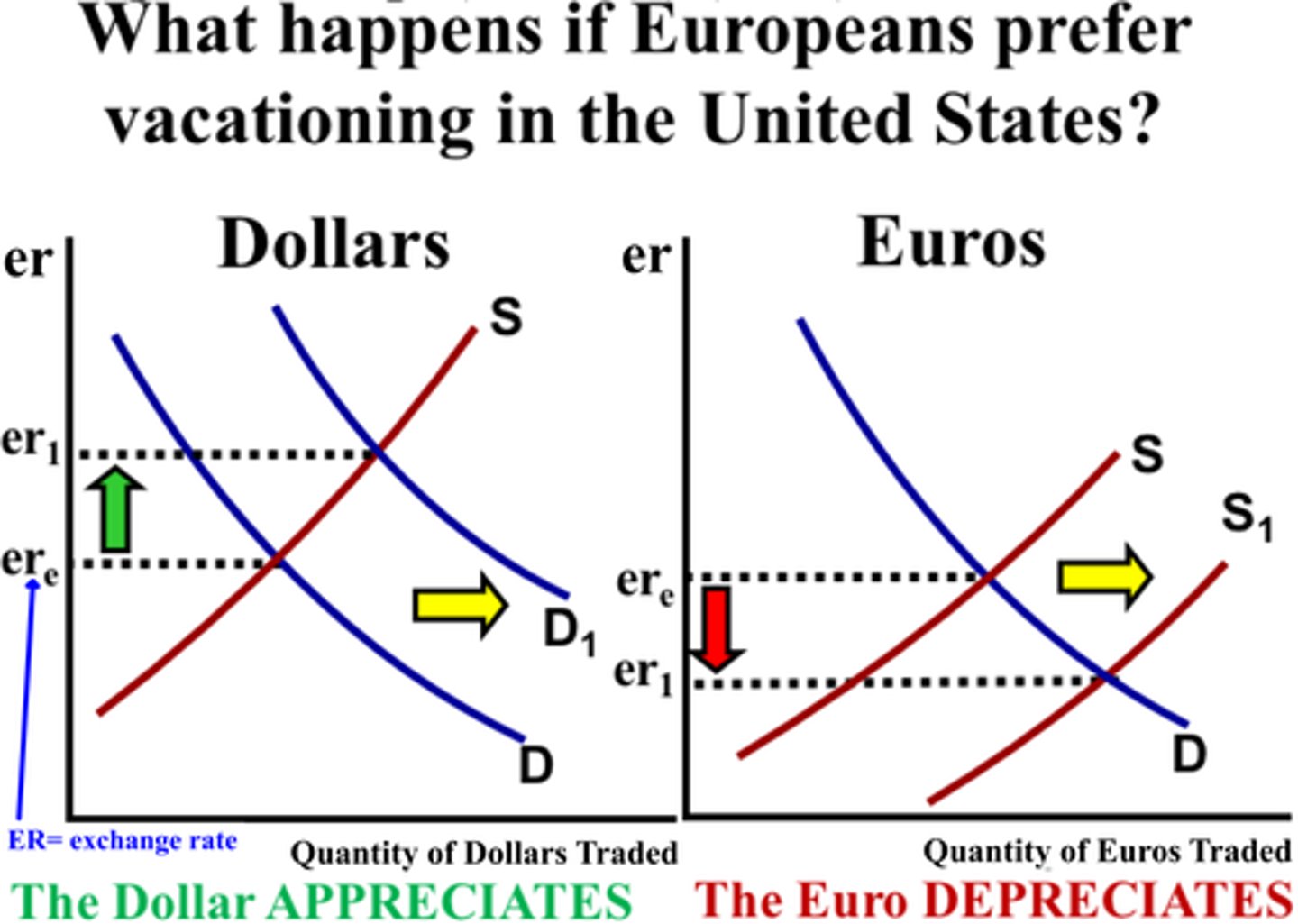
Foreign exchange shifters
1. Change in taste (ex: British flock to U.S.)
2. Change in relative income, (resulting in more imports) ex: U.S. growth increases U.S. increases
3. Change in relative price levels (resulting in more imports) ex: U.S. prices increase relative to Britain.
4. Change in relative interest rates, ex: if the U.S. has a higher interest rate than Britain.
fiscal policy
Government policy that attempts to manage the economy by controlling taxing and govt spending.
monetary policy
Government policy that attempts to manage the economy by controlling the money supply and thus interest rates.
expansionary fiscal policy
An increase in government purchases of goods and services, a decrease in net taxes to increase aggregate demand and expand real output (during periods of recession)
contractionary fiscal policy
Fiscal policy is used to decrease aggregate demand or supply—deliberate measures to decrease government expenditures, increase taxes, or both during periods of inflation.
expansionary monetary policy
Federal Reserve system actions to increase the money supply, lower interest rates, and expand real GDP (increase aggregate demand)
contractionary monetary policy
the Federal Reserve's policy of increasing interest rates and decreasing supply of money to reduce inflation