regulating blood pressure urinary system
1/10
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
11 Terms
juxtaglomerular cells
The cells of the afferent artery at the juxtaglomerular apparatus. They are baroreceptors that sense pressure change
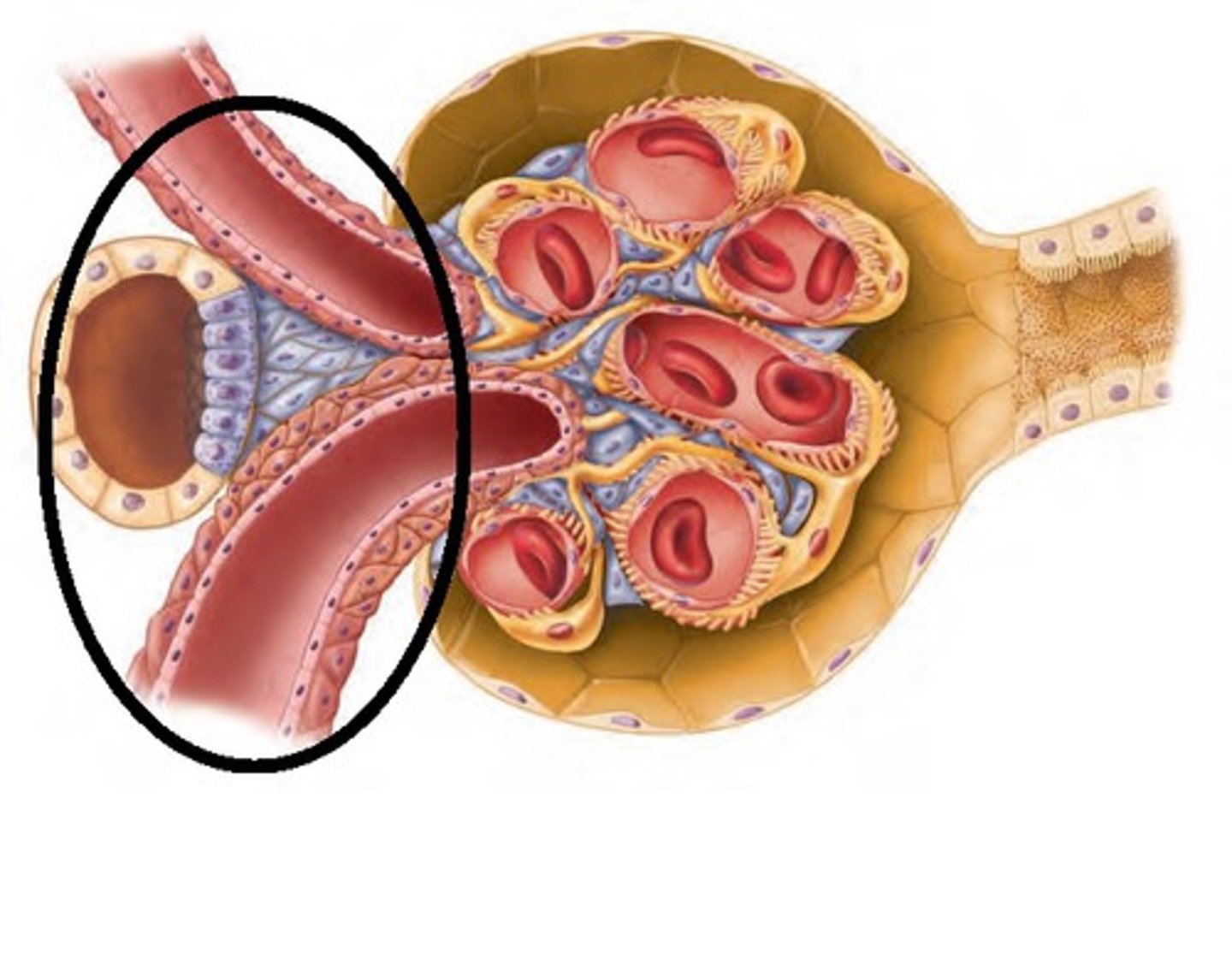
macula densa cells
Specialized cells in the ascending limb which monitor the NaCl content of the filtrate entering the DCT. When it senses that there isn't enough NaCl it inhibits nitric oxide (nitric oxide causes vasodilation)
high blood pressure
smooth muscles in the walls of the arterioles stretch (increase GFR, decreasing reabsorption- it's moving too fast)
myogenic mechanism
Smooth muscle cells in afferent arterioles contract in response to elevated blood pressure ( reaction of muscles to contract when stretched)
juxtaglomerular apparatus
in the nephron, the complex of cells from the distal tubule and the afferent arteriole which helps regulate blood pressure by secreting renin in response to blood pressure changes in the kidney; located near the glomerulus
acute stress
1) the myogenic mechanism is triggered which stretches the arterioles
2)the little amount of NaCl in the DCT (from not enough filtration) is sensed by the macula densa cells which inhibits nitric oxide (a vasodilator) from the juxtaglomuler apparatus which causes vasoconstriction
chronic hypertenstion leads to:
-can cause damage to renal vessels (prolonged stretching)
-nephrons don't recieve enough oxygen
-less blood is filtered
-fluid is retained
-blood pressure rises (positive feedback)
low blood pressure
the juxtaglomerular cells don't stretch, meaning blood flow is slow and too much reabsorption. The cells release renin in response which is a catalyst for angiotensin 1 which interacts with ACE in the lungs to turn into angiotensin 2, a powerful vasoconstrictor. brain releases antidiuretic to reclaim water and adrenal gland releases aldosterone to reabsorb sodium and reclaim more water to increase blood pressure
angiotensin 2
potent vasoconstrictor
aldosterone
Hormone that stimulates the kidney to retain sodium ions and water released by the adrenal gland
antidiuretic hormone
hormone secreted by the posterior pituitary gland to prevent the kidneys from expelling too much water (helps retain water)