Unit 2: Molecular and Ionic Compound Structure and Properties
1/124
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
125 Terms
2 main types of bonding
INTRA and INTER
INTRA meaning
within (inside) compounds,
Ionic bonding
metal plus nonmetal, giant lattice of ions
Covalent bonding
nonmetal plus nonmetal, discrete molecules
Dative or Coordinate bonding
(e- deficient species)
Discrete molecules
INTER meaning
(interactions between covalent molecules)
ALL WEAK, but HB is strongest
interbonding strongest to weakest
HB, dipole dipole, LDF
Hydrogen Bonding
(attached directly to N O F)
permanent dipole
Dipole- Dipole
(polar molecules)
permanent dipoles
London Dispersion Forces
(non-polar molecules)
induced dipoles
Inter bonding is based on…
… the Coulombic attractions between opoosite charges
atoms in a cov bond:
: pair of e- shared by atoms, each atom in the bond as electronegativity
electronegativity
ability of an atom w/in a cov bond to attract e- to itself
most electroneg element
flourine
if pair of atoms that are cov bonded hv same electroneg…
…e- in bonds equally shared, is NONPOLAR
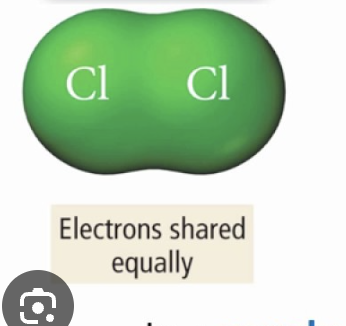
if one atom has much higher electroneg than other…
…e- are more attracted towards the MORE ELECTRONEG atom
e- cloud is distorted, e- charge density is redistributed
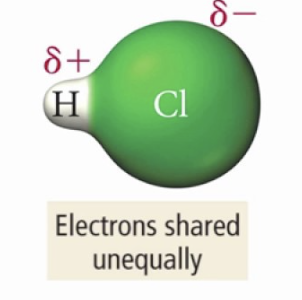
Dipole
Creation of opposite charges at either end of the molecule, bond is POLAR COVALENT
presence/lack of dipoles and intermolecular coulombic attraction between atoms…
…determines type of IMF present in cov bonded compounds
IMF type can influence properties
Discrete molecules
cov bonding, when Ve- are shared
one shared pair of e-
single bond
two shared pairs of e-
double bond
When are atoms attracted to each other?
When outer e- of 1 atom are electrostatically attracted to nuclei of another atom
When attraction between two atoms is stable…
…gives lower potential energies
When is PE raised and atoms become less stable in a bond?
When atoms get too close to each other
nucleis start to repel each other
So when is a bond ofmred?
when the distance between the atoms hv the forces of attraction and repulsion resulting in the lowest most stable potential energy
bond length
a distance where forces of attraction and repulsion= most stable PE
Bond strength
potential energy when bond length distance
the greater the # of e- invlved…
the strongewr the attraction
shorter the bond length=
= stronger bond strength
Bond dissociation energy (BDE)
strength of the bond in a diatomic covalent molecule
“ X kJ of energy put in OR released to break/make the bond”
pos sign in bond energy
addition of energy, endothermic= energy needed to break a bond
neg sign in bond energy
release of energy, exothermic= bond is being made
Ionic bonding involved…
transfer of e- between atoms to form ions
where to find metals on pt?
on the left
where to find nonmetals on pt?
on the right
ionic bond usually formed between…
…. a metal and nonmetal
ionic bonds
strong electrostatic forces between charged particles
ionic bond is strong because…
… electrostatic forces are large
CONCEPT: Coulombs law and ionic bonds
CONCEPT:
C’s law predicts that force INC w/ INC charge and DEC distance between charges, so strongest ionic bonds are formed between ions that are small and highly charged
ions that are highly charged aka…
aka high charge densities
how are ions held in an ionic solid?
rigidly, in fixed position, 3D lattice
ionic solid compound properties
not malleable, ductile, tends to be brittle
cleaves when ordered structure is disrpted
high melting and boiling points, low volatility, low vapor pressures
When are ionic substances able to conduct electricity?
when liquid or in solution (aq)
idea of “like dissolves like”
ionic solid dissolves, polar water molecules attracted to opp charged ions and get into the lattice
forces of attractions formed when ionic solid dissolves
ion to dipole
name when ion to dipole
hydration
ions are HYDRATED, becoming free to move= can conduct electricity
if cation is small and highly charged…
…has ability to distrot charge cloud around anion
Fajans rule
A principle used to predict whether a bond will be covalent or ionic based on the charges and sizes of ions. It states that if a cation is small and highly charged, and the anion is large and polarizable, the bond is more likely to have covalent character. This occurs due to the cation's ability to distort the electron cloud of the anion, leading to shared electron characteristics.
what does fajans rule help with?
assess degree of distortion
degree of distortion
polarization
distortion at a max when:
cation is small and highly charged (high charge density)
anion is large and highlyu charged (e- more loosely held)
less electroneg symbol
Delta ( not triangle but S) +
more electroneg symbol
Delta (S) -
Pauling scale of electronegativities
Developed by Linus Pauling, this scale assigns values to elements, with higher numbers indicating stronger electronegativity. The range typically goes from 0.7 (for cesium) to 4.0 (for fluorine), helping predict bond types and molecular behavior.
CONCEPT: greater diff in electroneg…
…more like ionic compound!
CONCEPT: a diff of 1.7 approc marks…
boundary betweeen predominately ionic or covalent
gen rule for expanded octet:
only avaible to those in the third period, Expanding the octet is possible whenever the molecule has a 3p subshell.
IF there is an extra ion when drawing LS…
… put it on the more ELECTRONEG element
If cannot determine central atom…
… usually least electroneg atom but NEVER hydrogen
non-bonding e-/e- pairs
any e- pairs that occur in valence shell of an atom but do not form a bond w another atom
dative/ co-ordinate bonding
(e- deficient species only)
a new shared pair/cov bond made up by using both e- from one species rather than one from each species as in a norm cov bond
What determines a substance’s polarity?
bonds w/in molecules must carry diff charges (dipole moment MUST exist) AND the dipoles that are present MUST NOT cancel out due to symmetry
how to indicate dipole moment
indicated by an arrow that points toward neg charge center, tail of arrow indicating pos charge center, or by using delta+/- to indicate areas of pos/neg charge
Valence Shell Electron Pair Repulsion theory
VSEPR,
shapes of cov bonded molecules and ions can be determines by considering number of e- pairs(e- domains) around CENTRAL atom
A non-bonding pair repels ___ stronglyu than a bonding pair
MORE
when predicting shape, triple and double bond=
= “one” bonding pair
2 0
linear
2 0 bond angle
180
3 0
Trigonal Planar
3 0 bond angle
120
2 1
bent
2 1 bond angle
slightly less than 120
4 0
tetrahedral
4 0 bond angle
109.5
3 1
trigonal pyramidal (lone pair on top, three on bottom
3 1 bond angle
107.5
2 2
Bent (the second one)
2 2 bond angle
104.5
5 0
trigonal byramidal (like a diamond)
5 0 bond angel
120 in plane, 90 perp to plane
4 1
SEESAW !!!!! (lone pair on top)
4 1 bond angle
complex (lol)
3 2 (Three to…)
T-shaped
(three to T)
3 2 bond angle
approx 90 for T
2 3
linear (second one)
2 3 bond angle
180
6 0
octahedral (6=8=oct)
6 0 bond angle
90 (oct)
5 1
square pyramidal (lone pair on bottom)
5 1 bond angle
approx 90 (sqPy)
4 2
square planar
4 2 bond angle
90 (sqPl)
# of e- domains (bond and lone pair)=
sum of s and p orbitals
weird not right but works rule for finding hybridization:
count totall number of e- domains then subtract one to get spX or sp3d (if 4 e- domains)
hybridize/hybridization
process of mixing
type of bonds used to form final molecule when terminal atom joins central atoms hybridizedd orbitals:
simple sigma bonds
hybdrization nummber tupes
sp, sp², sp³, sp³d
sigma covalent bond
when two dumbell 2p orbistals that are incomplete overlap their heads tgt
pi bond
when sideways overlap of other p orbitals
only sigma bonds…
…single bonds