Final Exam Review: Bacteria and Pathogenesis
1/130
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
131 Terms
Nucleoid
Large circular chromosome in bacterial cells.
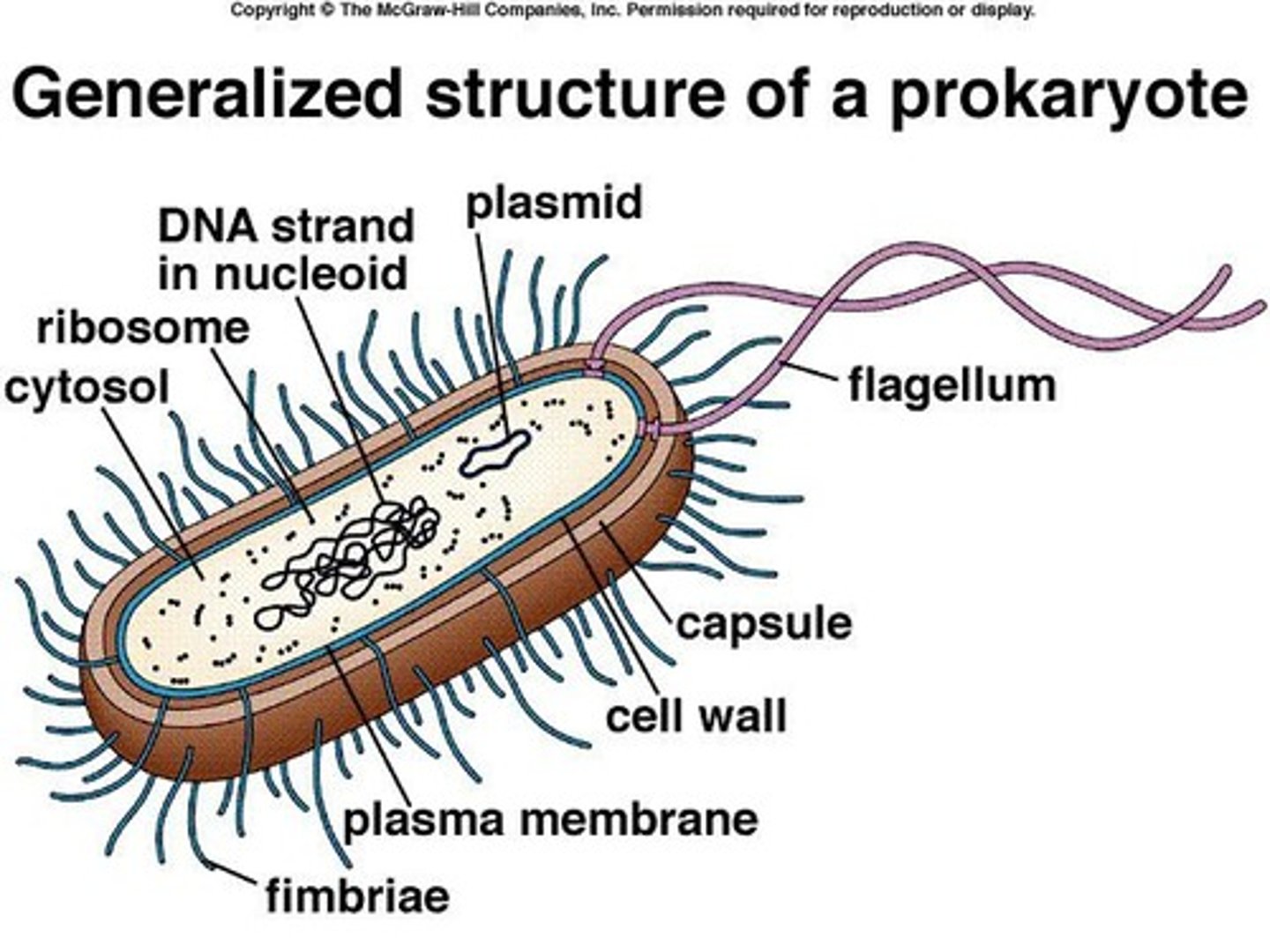
Plasmids
Small DNA molecules often carrying virulence genes.
Cocci
Bacterial shape that is round.
Bacilli
Bacterial shape that is rod-like.
Spiral
Bacterial shape that is twisted.
Gram Positive
Retains stain, thick cell wall, one membrane.
Gram Negative
Does not retain stain, thin cell wall, two membranes.
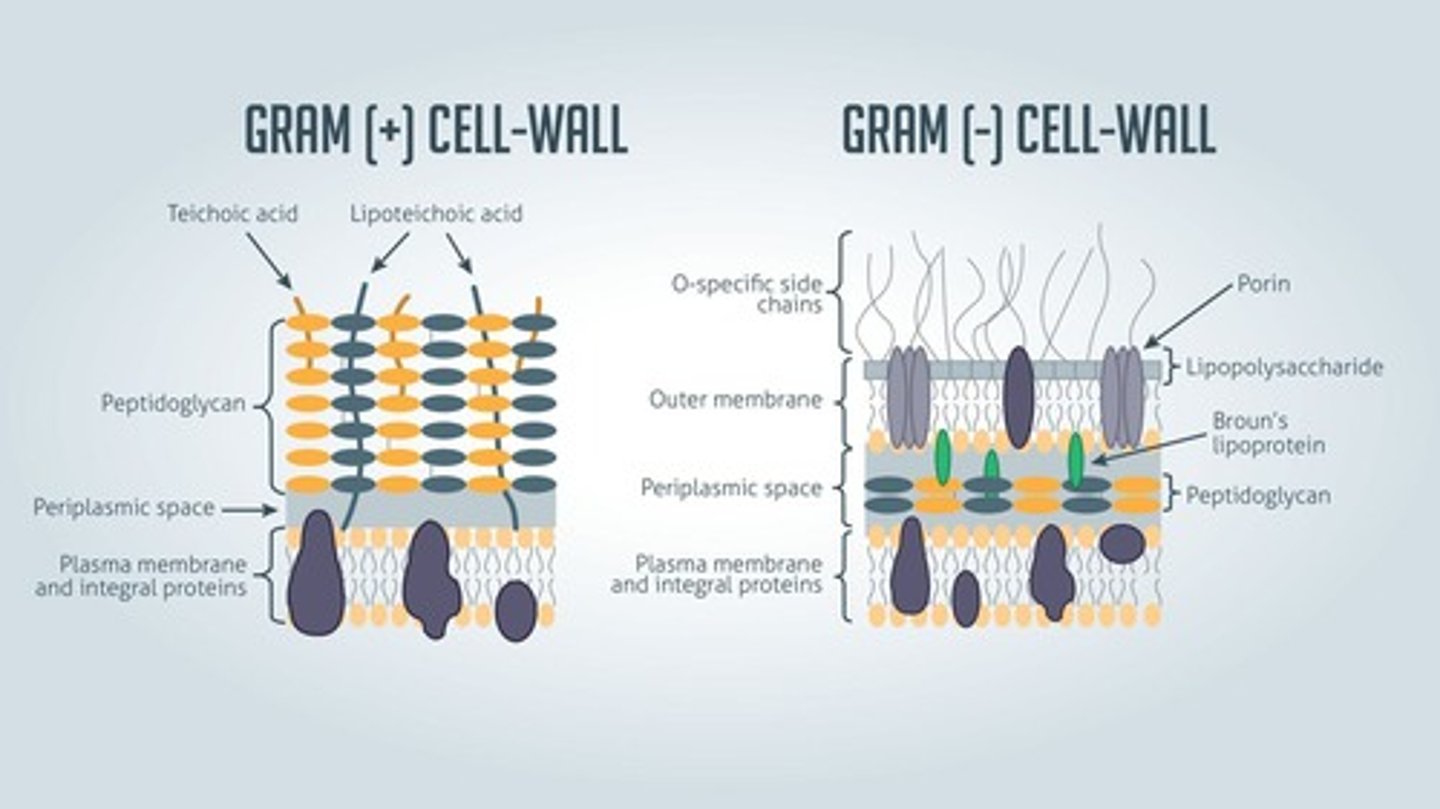
Peptidoglycan
Polymer that affects bacterial cell shape.
Teichoic Acid
Polymers affecting Gram-positive cell development.
Obligate Aerobes
Require oxygen for metabolic activity.
Facultative Anaerobes
Can use both aerobic and anaerobic respiration.
Obligate Anaerobes
Oxygen is toxic; use fermentation.
Spores
Non-active, resistant structures formed by bacteria.
Pathogenicity
Ability of an organism to cause disease.
Pathogen
Organism capable of causing disease.
Virulence
Degree of pathogenicity of a bacterium.
Primary Pathogens
Always harmful bacteria to hosts.
Opportunistic Pathogens
Harmful only under certain conditions.
Commensal Bacteria
Generally beneficial bacteria in the body.
Antiphagocytosis
Capsule prevents immune system from attacking.
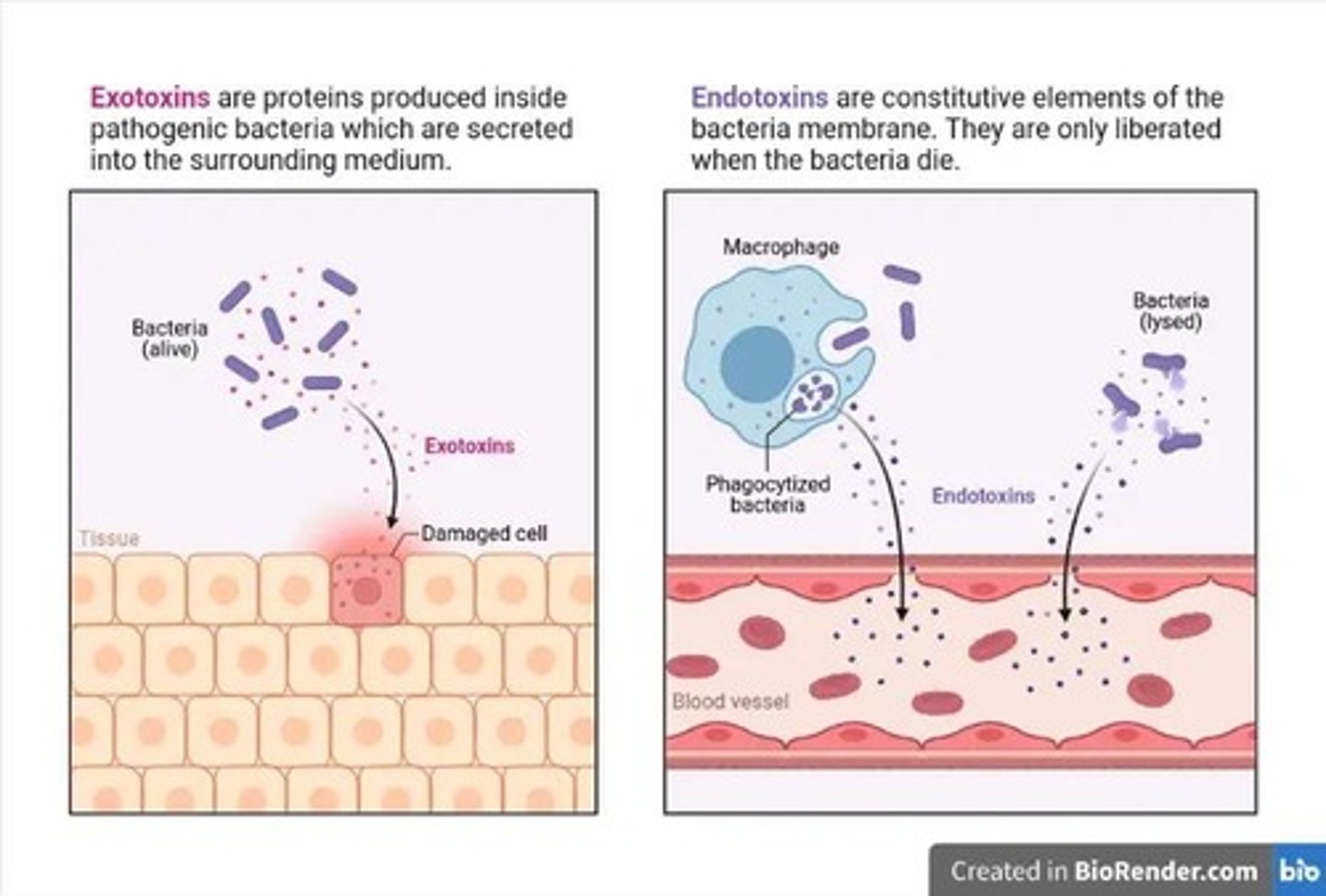
Exotoxins
Toxins secreted by bacteria affecting host cells.
Endotoxins
Part of Gram-negative bacteria, activates immune response.
Antimicrobial
Substances that kill or inhibit microbes.
Bactericidal
Antibiotics that kill bacteria.
Bacteriostatic
Antibiotics that inhibit bacterial growth.
Minimal Inhibitory Concentration
Lowest antibiotic concentration preventing bacterial growth.
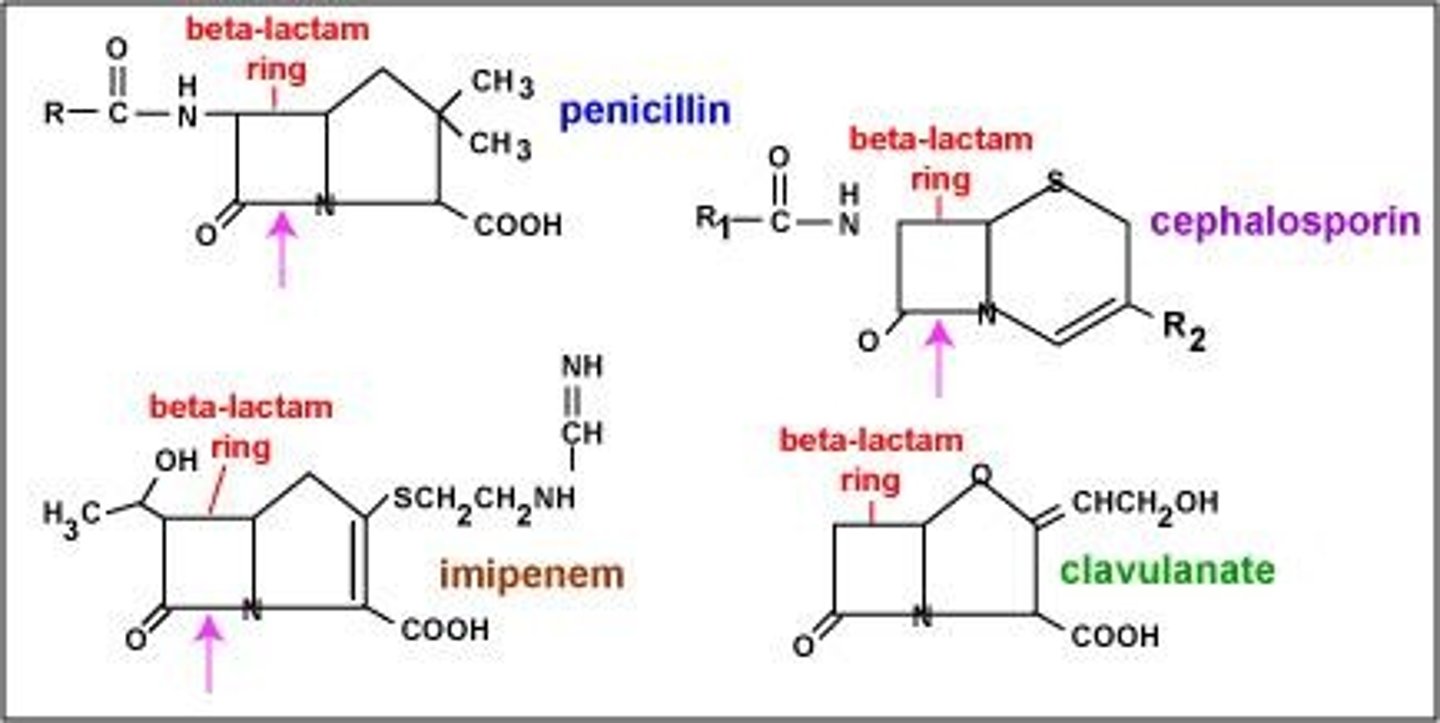
Beta-lactams
Antibiotics interfering with peptidoglycan cross-linking.
Glycopeptides
Inhibit peptidoglycan synthesis; last resort antibiotics.
Aminoglycosides
Bind to bacterial ribosomes, blocking protein synthesis.
Tetracyclines
Bacteriostatic antibiotics with broad-spectrum activity.
Fluoroquinolones
Inhibit DNA topoisomerase, broad-spectrum antibiotics. (blocks topoisomerase which helps bactier unwind to copy their DNA; block them, the bacteria can’t divide = bacterial death)
Beta-lactamase
Enzyme that destroys beta-lactam antibiotics.
Staphylococcus Aureus
Pathogenic bacteria producing various harmful toxins.
Alpha-toxin
Pore-forming toxin affecting cell membranes.
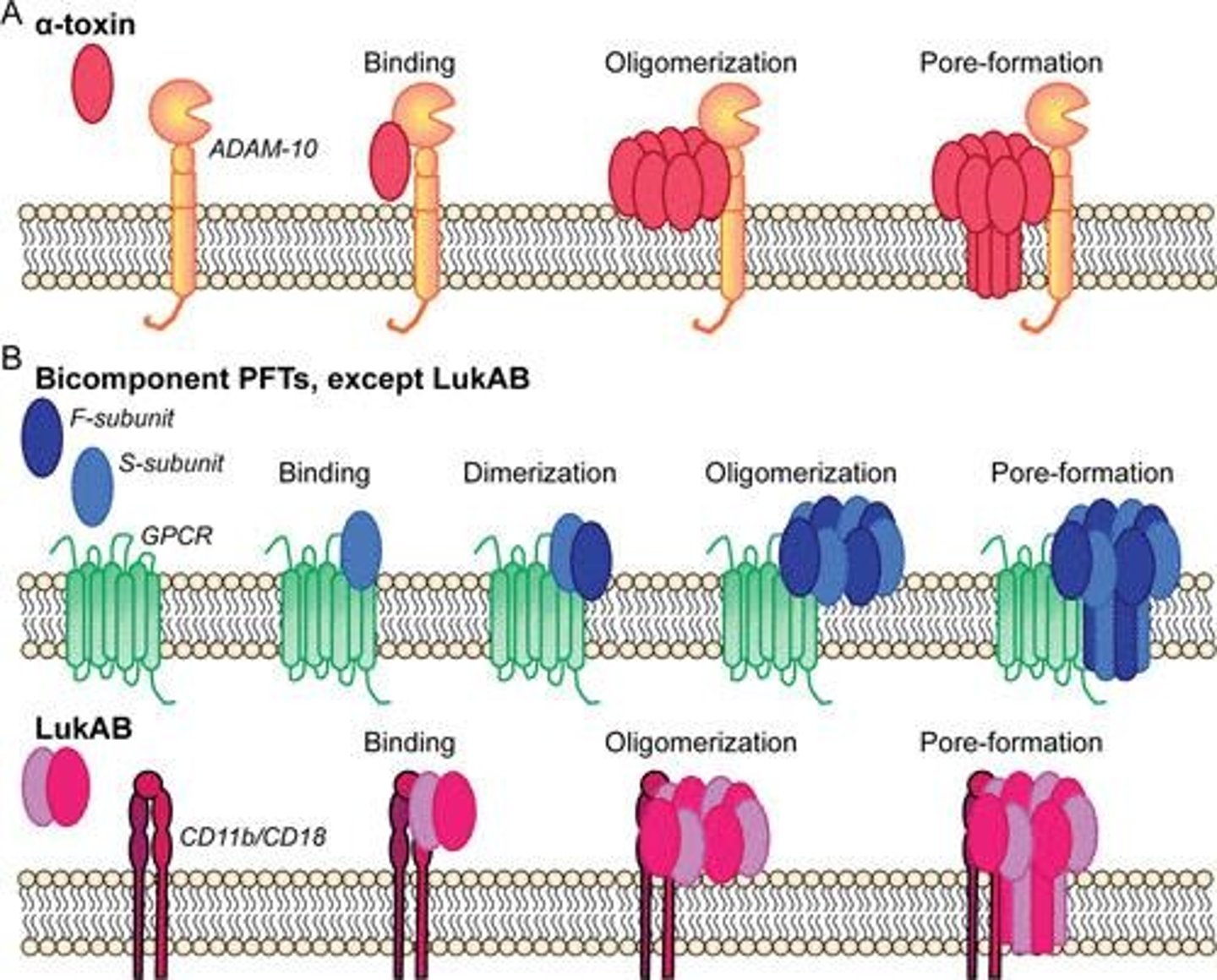
Superantigens
Toxins causing massive cytokine release.
Enterotoxins
Toxins causing food poisoning symptoms.
Gram-positive
Bacteria that retain crystal violet stain.
Facultative anaerobes
Can grow with or without oxygen.
Catalase positive
Produces enzyme that breaks down hydrogen peroxide.
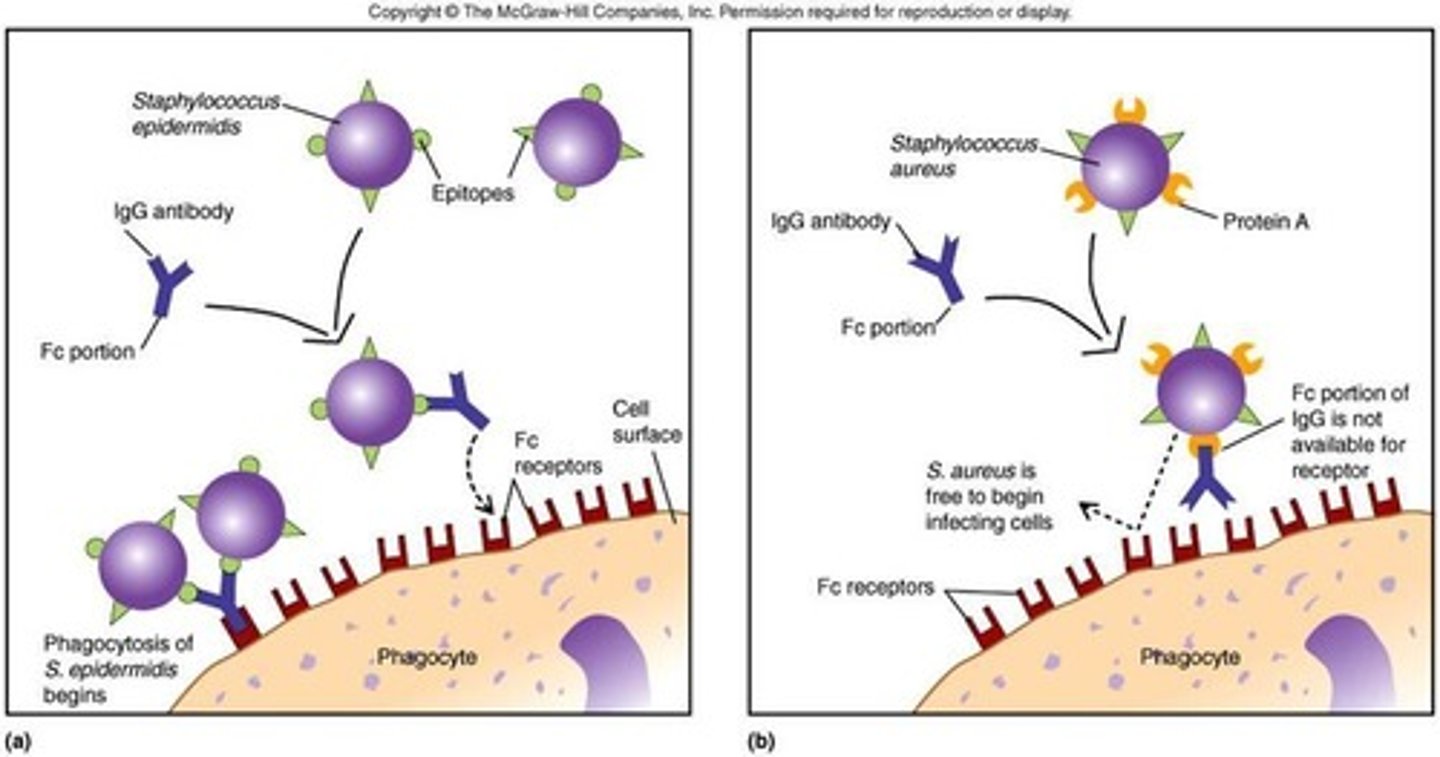
Protein A
Binds to Fc region of antibodies.
Clumping factor
Coagulase that promotes bacterial clumping.
Fibronectin-binding proteins
Facilitates bacterial adhesion to host cells.
Toxin-mediated disease
Diseases caused by bacterial toxins.
Bullous impetigo
Skin infection with blisters caused by toxins.
Exfoliative toxin
Causes skin peeling in infections.
Scalded skin syndrome
Severe skin condition from exfoliative toxin.
Toxic shock syndrome
Severe illness caused by superantigens.
Coagulase-negative staph
Bacteria lacking coagulase, often form biofilms.
S. Saprophyticus
Causes urinary tract infections, especially in women.
Streptococcus
Small, round bacteria found in chains.
Alpha-hemolytic
Partial lysis of red blood cells.
Beta-hemolytic
Complete lysis of red blood cells.
Group A strep
Causes pharyngitis and skin infections.
Scarlet fever
Rash and fever from Group A strep infection.
M protein
Helps bacteria evade immune response.
Corynebacteria
Gram-positive rods causing diphtheria.
Diphtheria toxin
A-B toxin causing cell death.
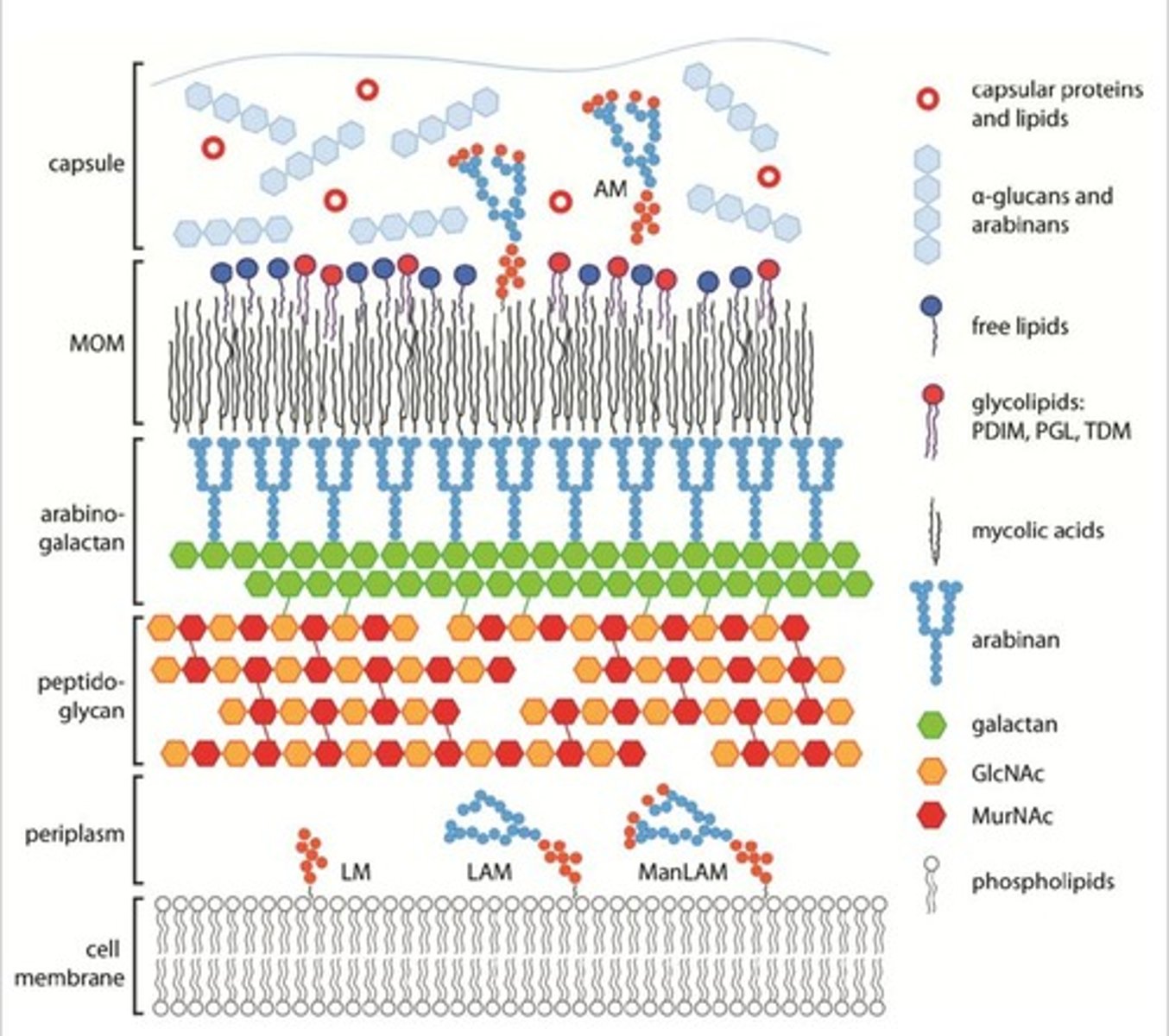
Mycobacteria
Bacteria causing tuberculosis and leprosy.
Acid-fast
Resistant to decolorization by acid-alcohol.
Mycolic acid
Component of thick cell wall in mycobacteria.
Lipoarabinomannan
Similar to LPS, found in mycobacterial cell wall.
Niacin
Vitamin used for tuberculosis testing.
Granulomas
Immune response causing localized inflammation.
M. Tuberculosis
Bacteria causing tuberculosis, infects lungs.
Tuberculin test
Skin test for tuberculosis exposure.
Acid-fast smears
Microscopy technique for detecting mycobacteria.
Reactivation
Return of tuberculosis due to stress.
Necrosis
Tissue death due to infection.
Isoniazid
Antibiotic used to treat tuberculosis.
Ethambutol
Antibiotic targeting tuberculosis bacteria.
BCG vaccine
Vaccine derived from M. Bovis for TB.
Leprosy
Infection caused by M. Leprae.
Schwann Cells
Nerve cells infected by leprosy.
Tuberculoid leprosy
Localized leprosy with strong immune response.
Lepromatous leprosy
Widespread leprosy with extensive damage.
Enterobacteriaceae
Family of gram-negative bacteria, includes E. coli.
Pili
Hair-like structures for bacterial attachment.
Alpha Hemolysin
Toxin causing red blood cell damage.
Shiga toxin
Cytotoxic toxin modifying ribosomes.
Enterotoxigenic E. coli
Causes traveler's diarrhea via toxins.
Type III secretion system
Bacterial syringe for injecting virulence factors.
Enterohemorrhagic E. coli
Causes bloody diarrhea, linked to food.
Shigellosis
Dysentery caused by Shigella bacteria.
Virulence factors
Molecular traits enhancing bacterial pathogenicity.
Coli
No flagella; very low infectious dose.
M cells
Targeted by pathogens for invasion and uptake.
Salmonella
Complex antigens; causes systemic infections.
Typhoid fever
Chronic infection; spreads through blood.
Yersinia
Slow-growing; causes plague and pseudotuberculosis.
Invasin
Protein aiding Yersinia in cell invasion.
Vibrio Cholerae
Causes cholera; linked to contaminated water.
Cholera toxin
A-B toxin causing massive diarrhea.
cAMP
Cyclic AMP; regulates chloride secretion.
El Tor strain
More resilient; causes subclinical cholera infections.
Helicobacter
Curved, gram-negative; causes stomach ulcers.
CagA
Protein disrupting normal cell functions.
Clostridium
Gram-positive; spore-forming; obligate anaerobes.
C. Perfringens
Causes gas gangrene; hemolytic alpha-toxin.
Gas gangrene
Wound infection; muscle destruction from toxins.
C. Botulism
Neurotoxin causing flaccid paralysis.