Optics II: Refraction & Lenses
1/86
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
87 Terms
Refraction (definition )
Refraction is the bending of a ray of light as it passes from one transparent substance to another of a different density. Speed of light is different in substances with different densities. Denser substance=slower light travels
Draw diagram of refraction explanation (Fig.1) in sketchbook app
...
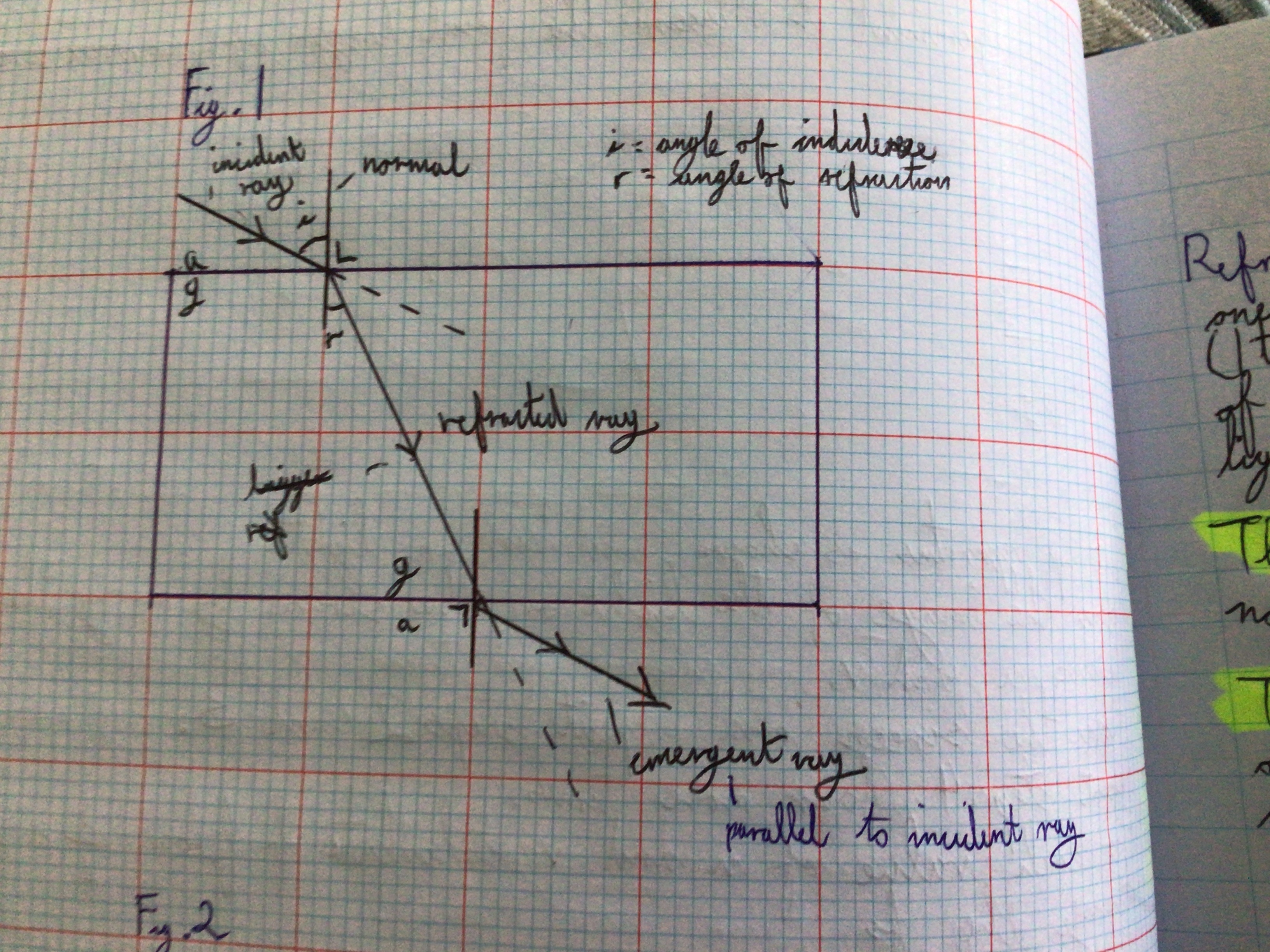
The First Law of Refraction
States that the incident ray, the normal, and the refracted ray are co-planer
The Second Law of Refraction
States that the sine of the angle of incidence is directly proportional to the sine of the angle of refraction
What is The Second Law of Refraction also known as?
Snell's Law
Refraction ray bending (note)
If a ray of light travels from a less dense medium to a more dense medium, it gets bent TOWARDS the normal. When a ray of light travels from a more dense medium to a less dense medium, it gets bent AWAY from the normal
What half of the normal is it bending away or to?
The half of the normal in the medium the ray of light is entering
Why does refraction happen (diagram)?
...
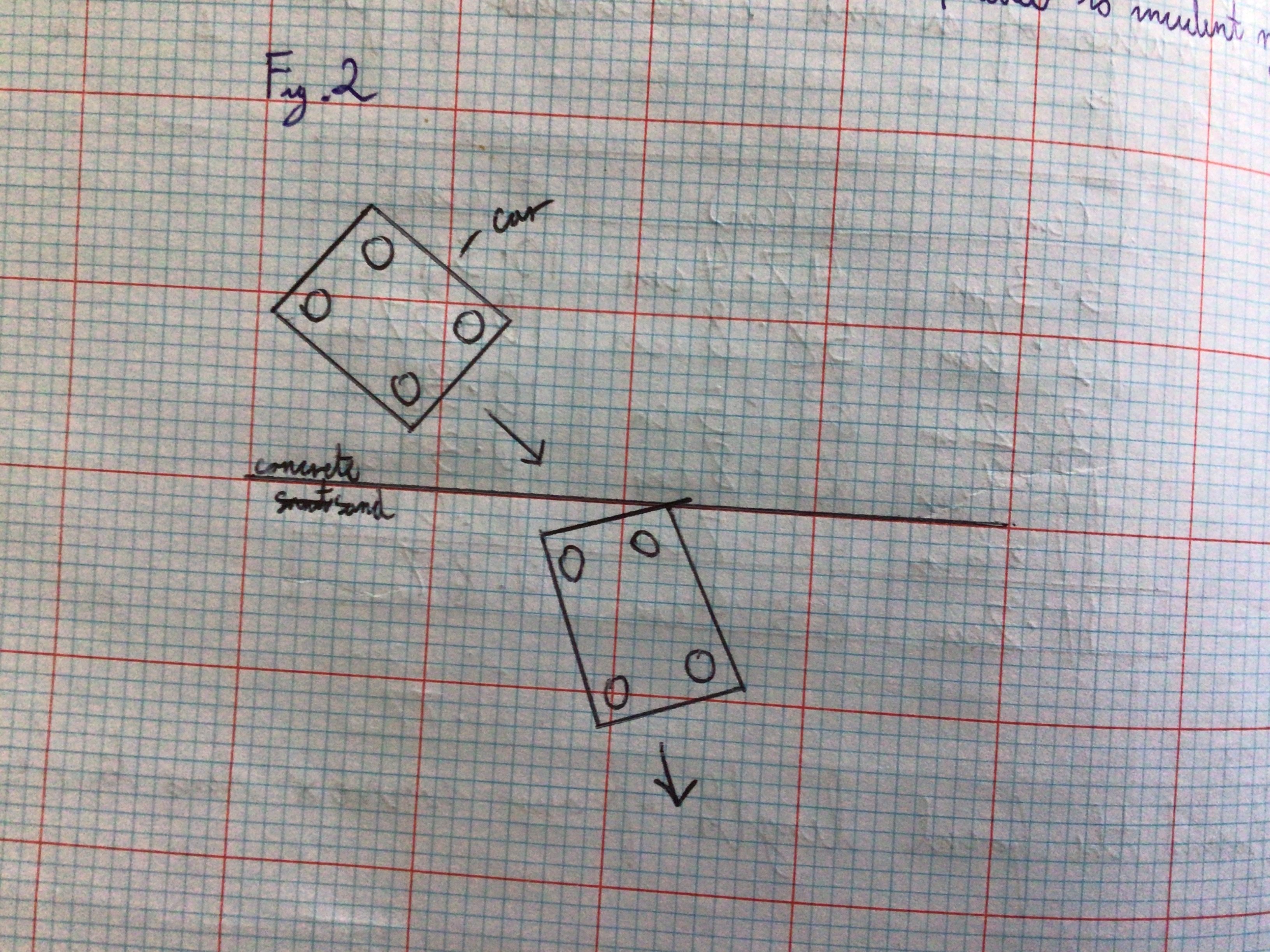
Why does refraction happen (explanation)?
If a car is travelling from concrete onto sand at an angle, for a brief period the right front wheel is travelling on sand (more slowly) than the left front wheel which is travelling on concrete (more quickly). This causes the car to veer to the right. Same thing happens with light
Write symbol for "directly proportional to" in Sketchbook
...
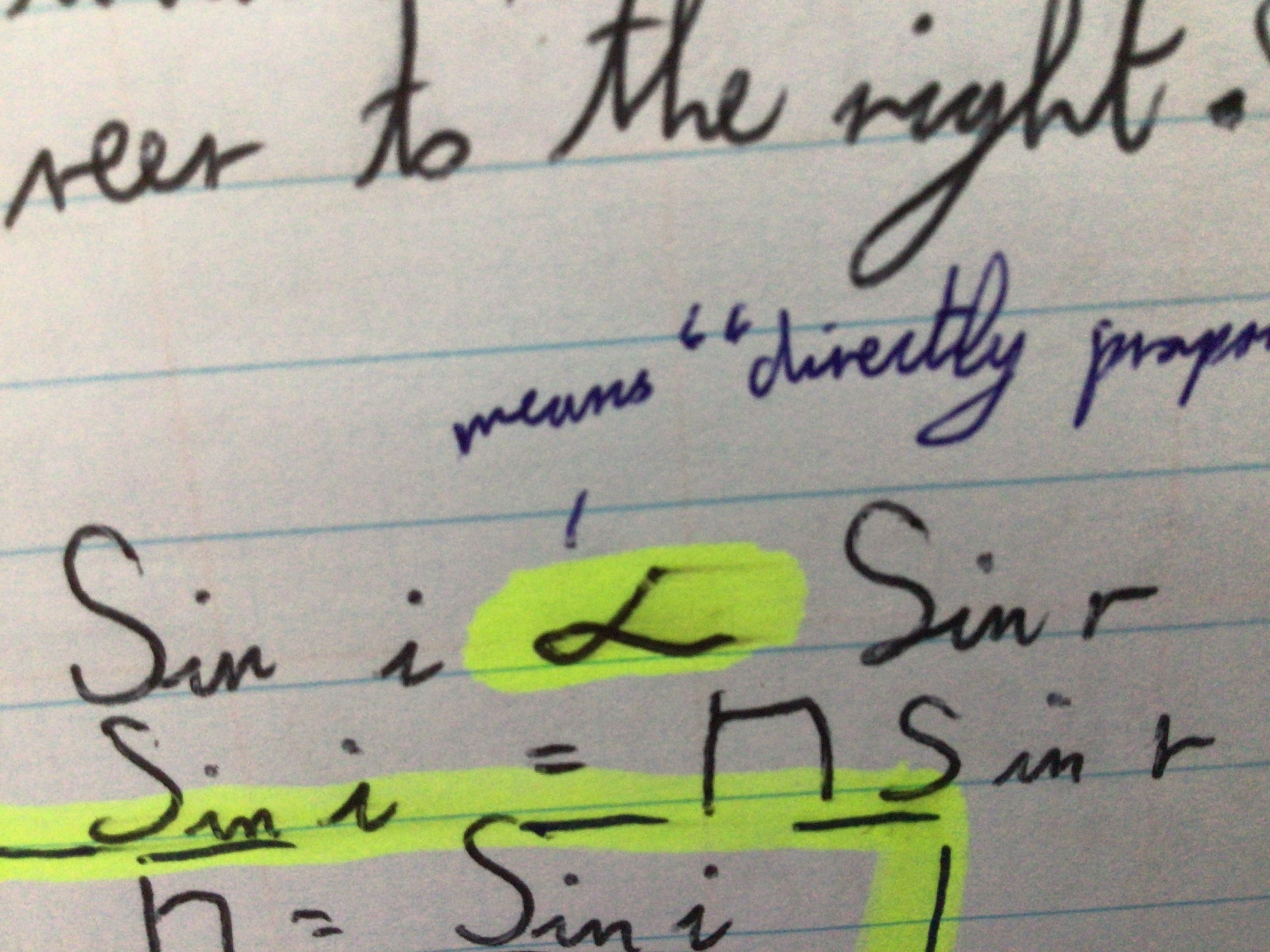
Snell's law formula
N= Sin (i)/Sin(r)
What does "N" mean in the Snell's Law formula?
refractive index
What does "i" mean in the Snell's Law formula?
angle of incidence
What does "r" mean in the Snell's Law formula?
angle of refraction
Refractive Indices (formula 1)
xNy= 1/yNx
Refractive Indices (formula 2)
xNy= xNz.zNy
What does the "." mean in the second refractive indices formula
multiply by
Can you hide a diamond in a fish tank? Why? Why not?
No, because the refractive index isn't 1
How do you make something invisible?
Make glass that has a refractive index of 1
Formula for calculating the refractive index when given the speeds of light
1N2=C1/C2
What does the "n" stand for?
refractive index
What does the "C" stand for in the speed of light/refractive index formula?
Speed of Light
Refractive index (note)
The more the light bends, the greater the refractive index
Draw Real Depth & Apparent Depth Diagram (Fig.3) in Sketchbook
...
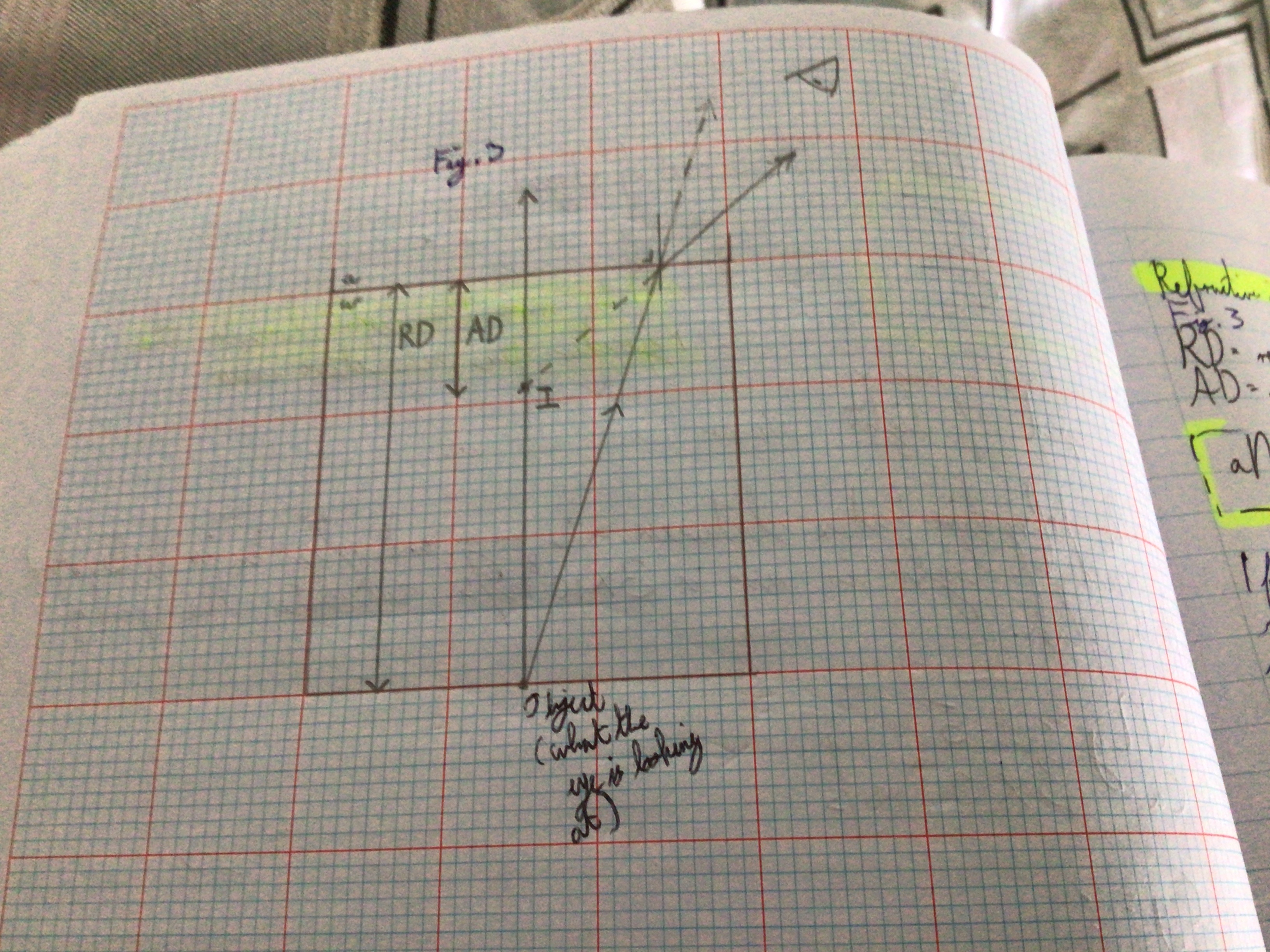
Real Depth & Apparent Depth Formula
aNx=RD/AD
What does "AD" stand for in the Real Depth & Apparent Depth Formula?
Apparent Depth
What does "RD" stand for in the Real Depth & Apparent Depth Formula?
Real Depth
First Rule for Drawing Raw Diagrams for Convex/Converging Lenses
A ray of light enters the lens parallel to the principal axis, it will be refracted through the principal focus
Second Rule for Drawing Raw Diagrams for Convex/Converging Lenses
A ray of light which enters the lens through the principal focus will be refracted parallel to the principal axis
Third Rule for Drawing Ray Diagrams for Convex/Converging Lenses
A ray that enters the lens through the centre of the lens will be undeviated
Draw the Ray Diagram for a Convex lens for u>2f
...
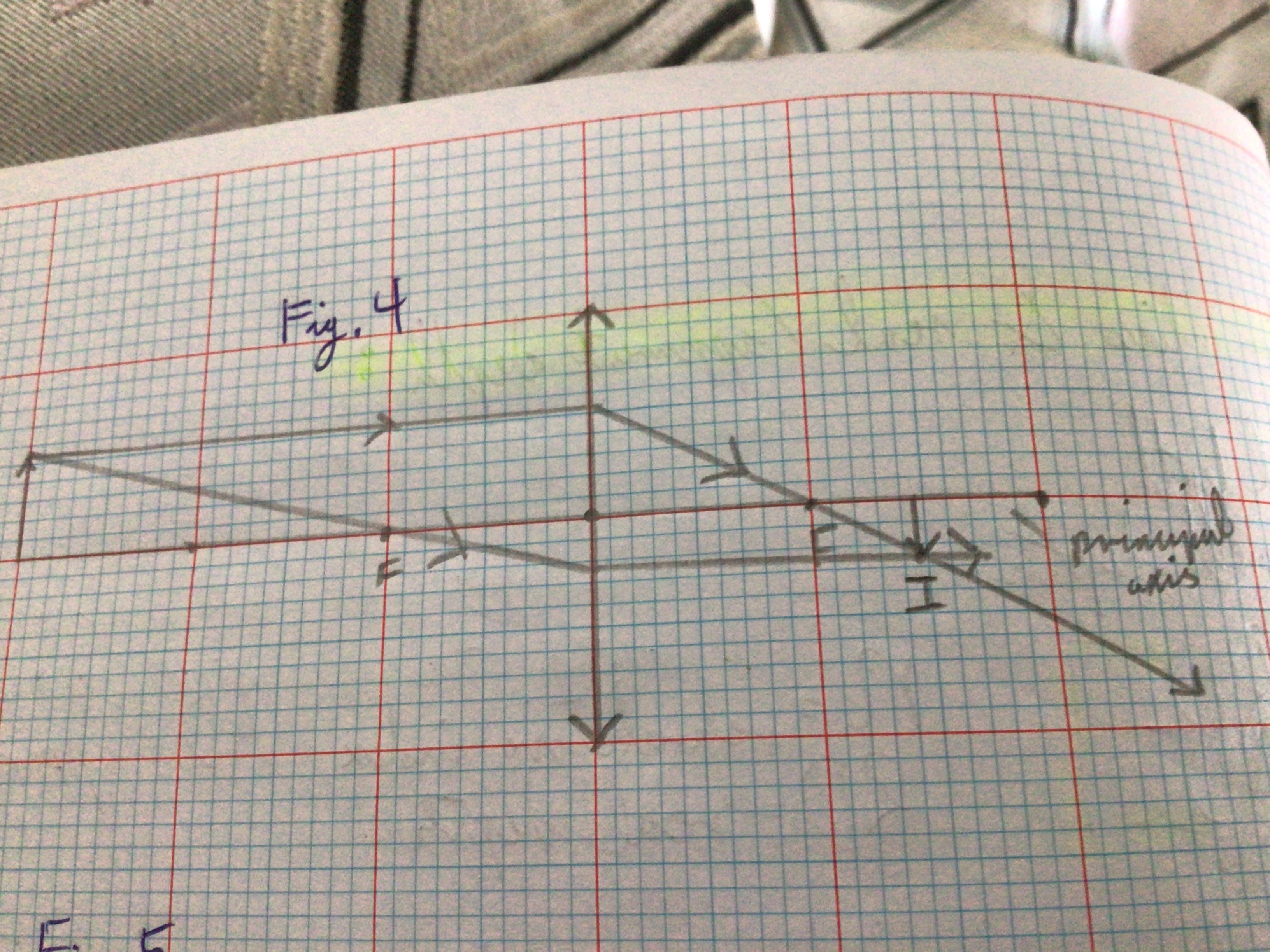
Draw the Ray Diagram for a Convex lens for u=2f
...
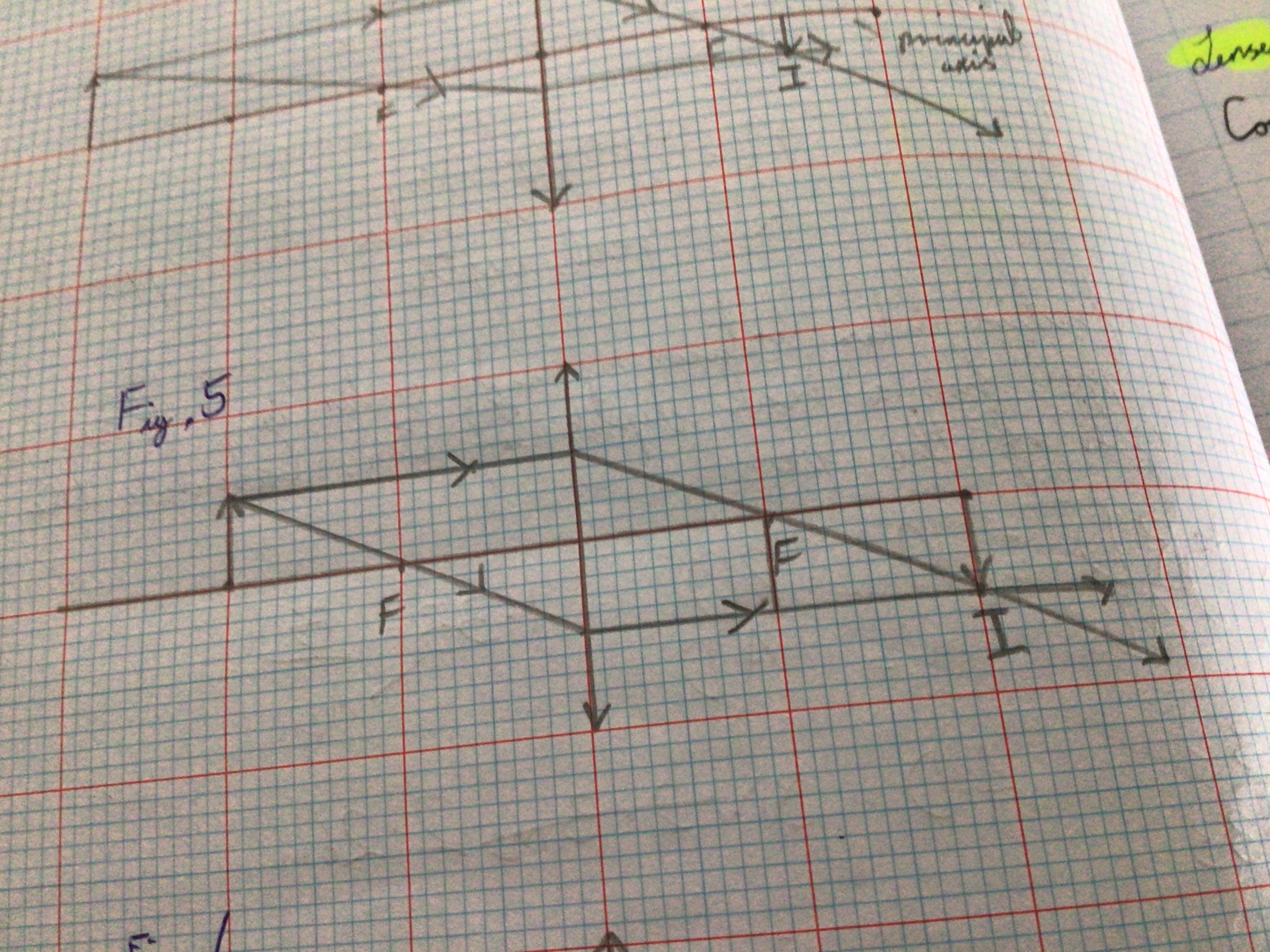
Draw the Ray Diagram for a Convex lens for 2f>u>f
...
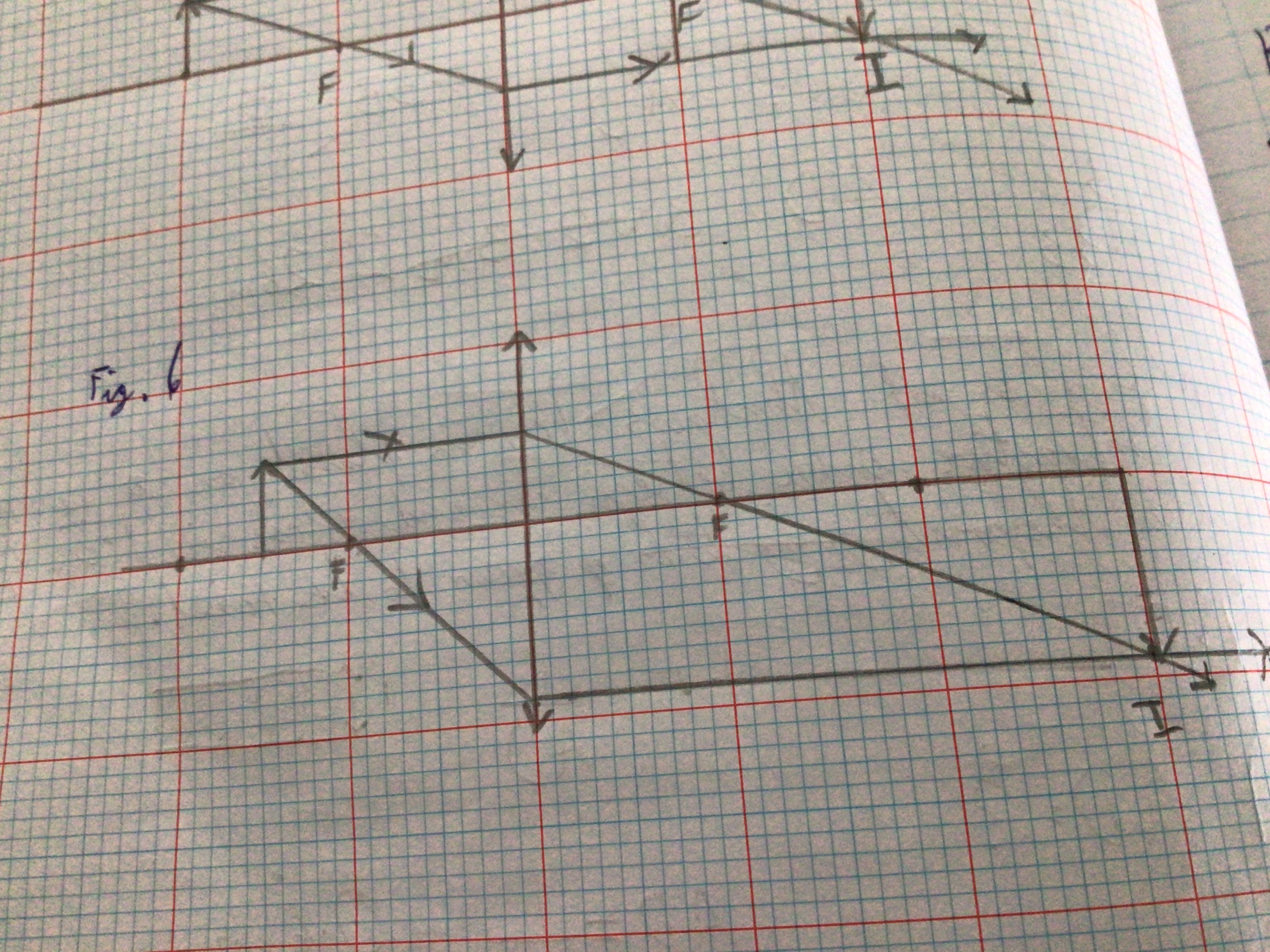
Draw the Ray Diagram for a Convex lens for u=f
...
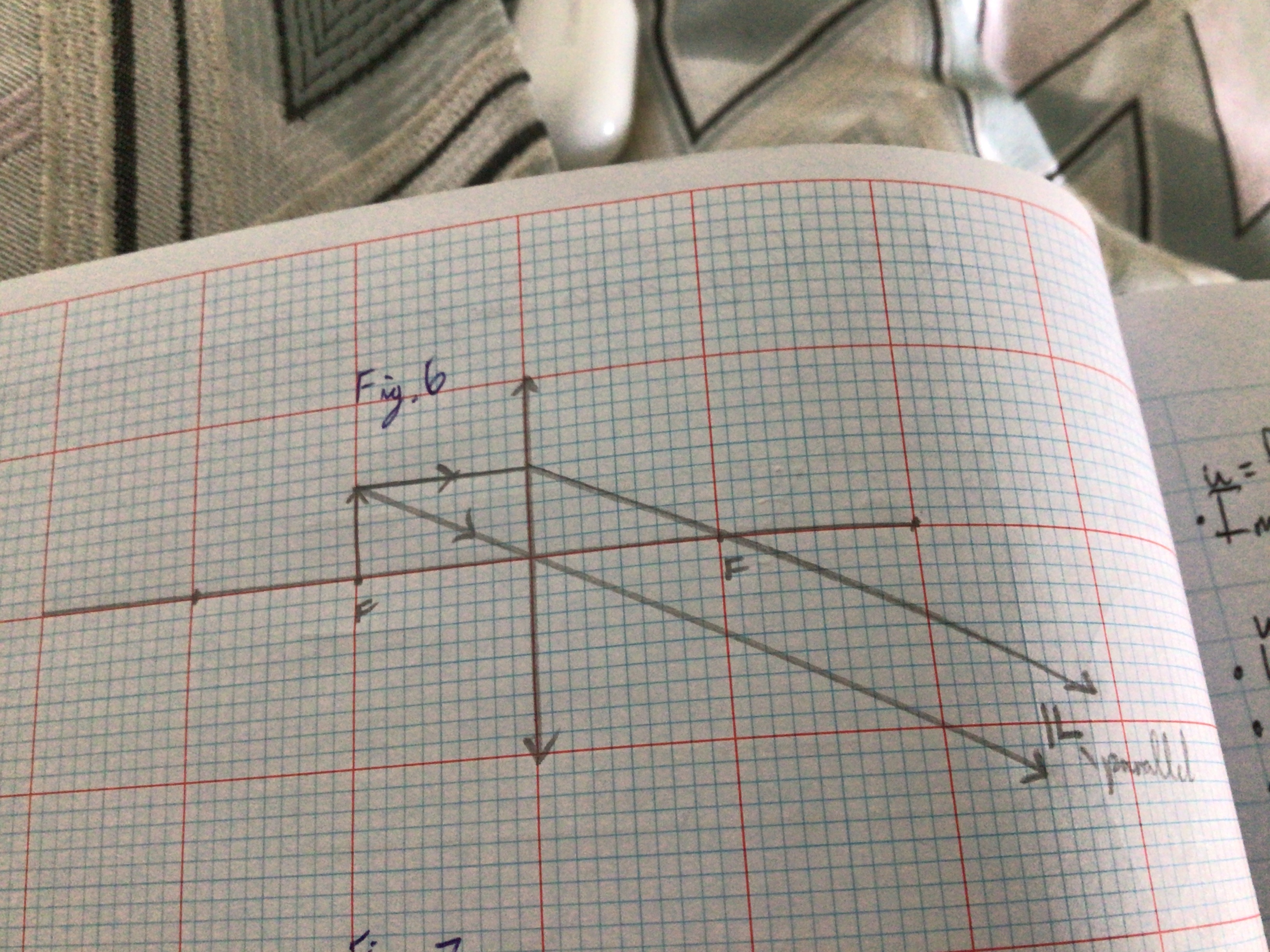
Draw the Ray Diagram for a Convex lens for u<f
...
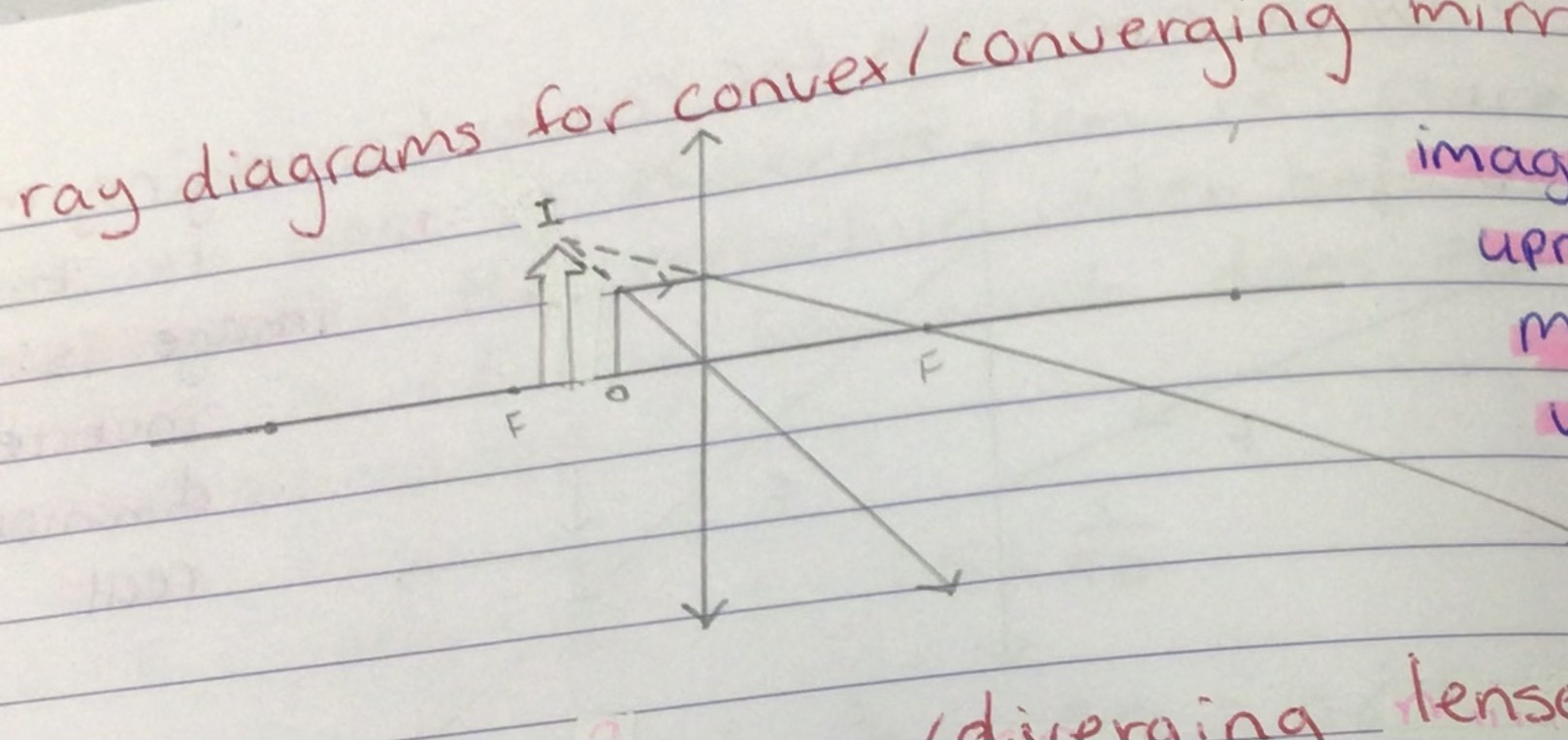
Image characteristics for convex lens u>2f
Inverted. Diminished. Real
Image characteristics for convex lens u=2f
Inverted. Same Size. Real
Image characteristics for convex lens 2f>u>f
Inverted. Magnified. Real
Image characteristics for convex lens u=f
Image is at infinity. Silver sheen visible
Image characteristics for convex lens u<f
erect/upright. magnified. Virtual
Convention of signs for lenses (u)
u is always +VE
Convention of signs for lenses (v)
v is +VE for real images but negative for virtual images
Convention of signs for lenses (f)
f is +VE for convex/converging lenses, but -VE for concave/diverging lenses
Convention of signs for lenses (m)
m is +VE for inverted images but -VE for upright/erect images
Formula for focal length (lenses)
1/f=1/u + 1/v
Formula for magnification (lenses)
m = v/u
Power formula (lenses)
P=1/f
Power formula for when you have two lenses
P= P1 + P2
What does "f" stand for?
Focal length
What does "u" stand for?
object distance
What does "v" stand for?
image distance
What does "m" stand for?
magnification
What does "P" stand for?
Power
What is Power?
How much a lens/a material converges/diverges light
Draw the 1 Ray Diagram for Concave/ Diverging lenses in Sketchbook
...
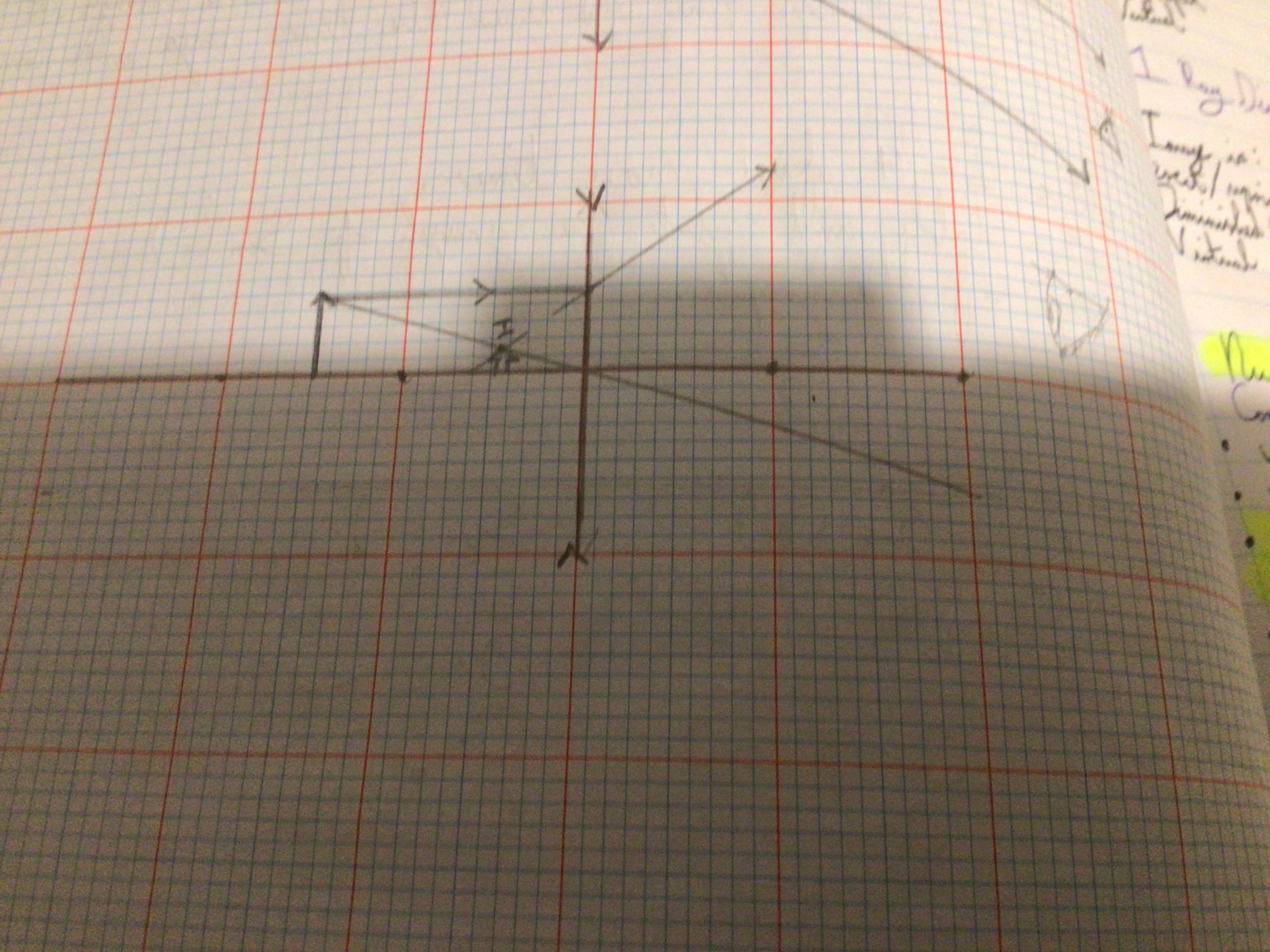
Image characteristics for a concave lens
erect/upright. Diminished. Virtual
Draw a diagram for a critical angle
...
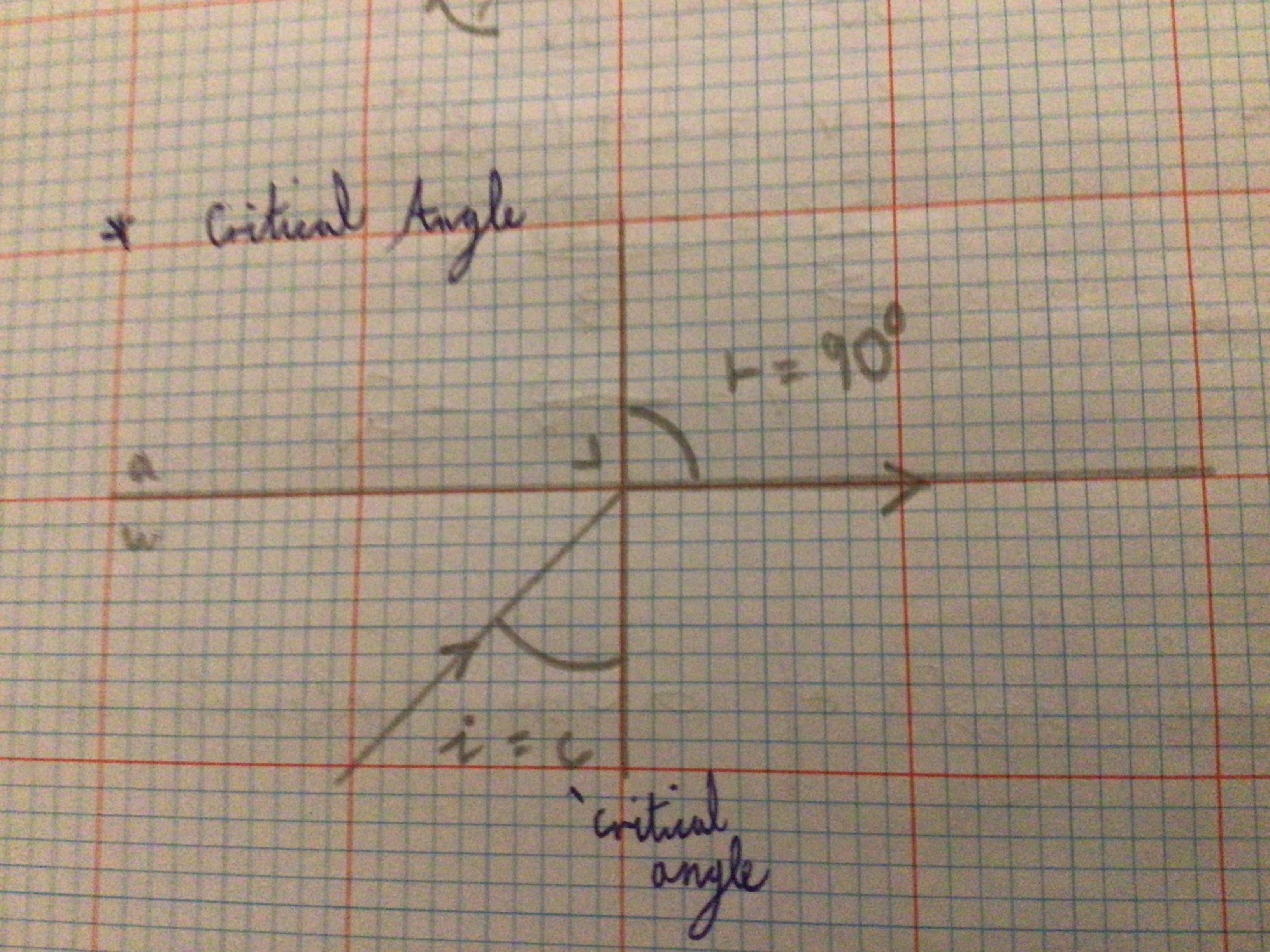
Critical angle (definition)
The angle of incidence in the more dense medium which causes an angle of refraction of 90 degrees in the less dense medium
Draw the diagram for total internal reflection
...
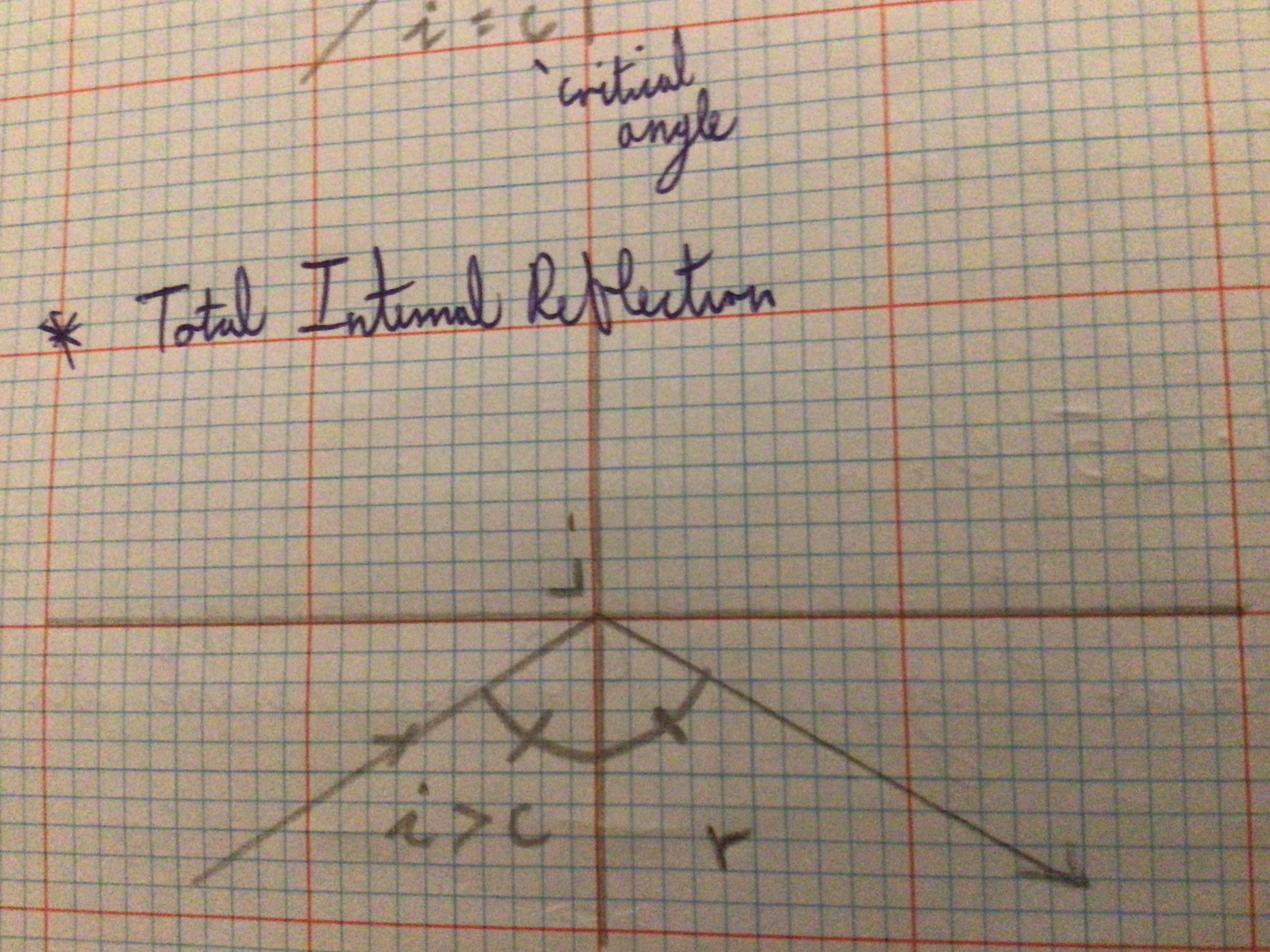
Total Internal Reflection (definition)
Occurs when the angle of incidence in the more dense medium is greater than the critical angle.
Draw diagram of Optical Fibres
...
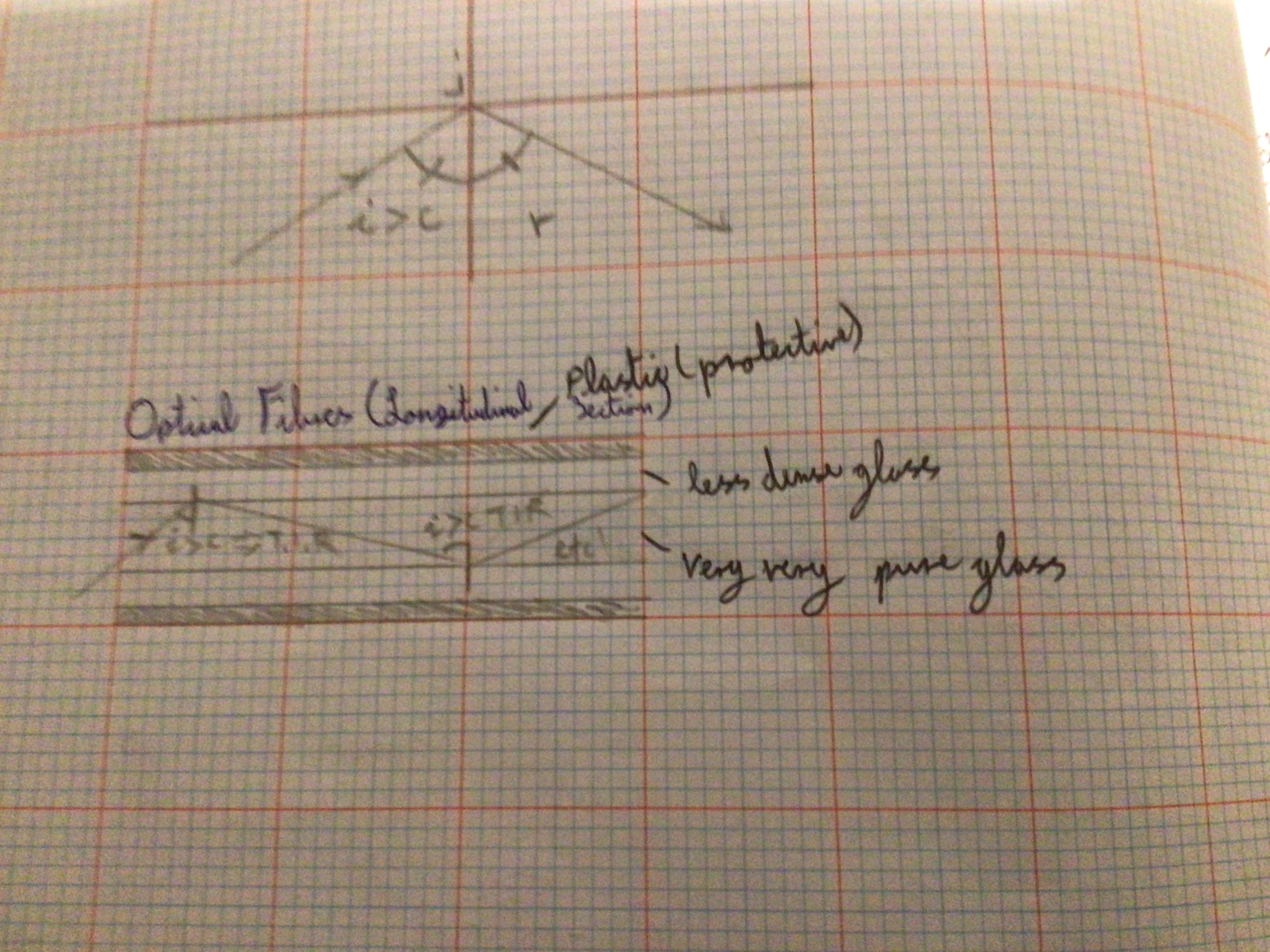
Optical Fibres (definition)
If a ray of light enters an optical fibre with an angle of incidence greater than the critical angle, total internal reflection will occur. This continues to occur all the way along the fibre due to the laws of reflection and symmetry, even if it's bent
First Advantage of Optical Fibres over Copper Wires for Carrying info
£ for a lb: Optical Fibres can carry more information than copper wires
Second Advantage of Optical Fibres over Copper Wires for Carrying info
Silica (sand) is cheaper than copper
Third Advantage of Optical Fibres over Copper Wires for Carrying info
Optical fibres are much harder to tap (listen to) than copper wires
Fourth Advantage of Optical Fibres over Copper Wires for Carrying info
Signal needs to be boosted less often
What is the role of the outer less dense layer of glass in an optical fibre?
Total internal reflection needs light to travel from a more dense substance (the pure glass) to less dense (outer layer of glass)
Name two uses of Optical Fibres
Telecommunications (Broadband). Endoscopy + Colonoscopy
Draw the diagram for a Mirage
...
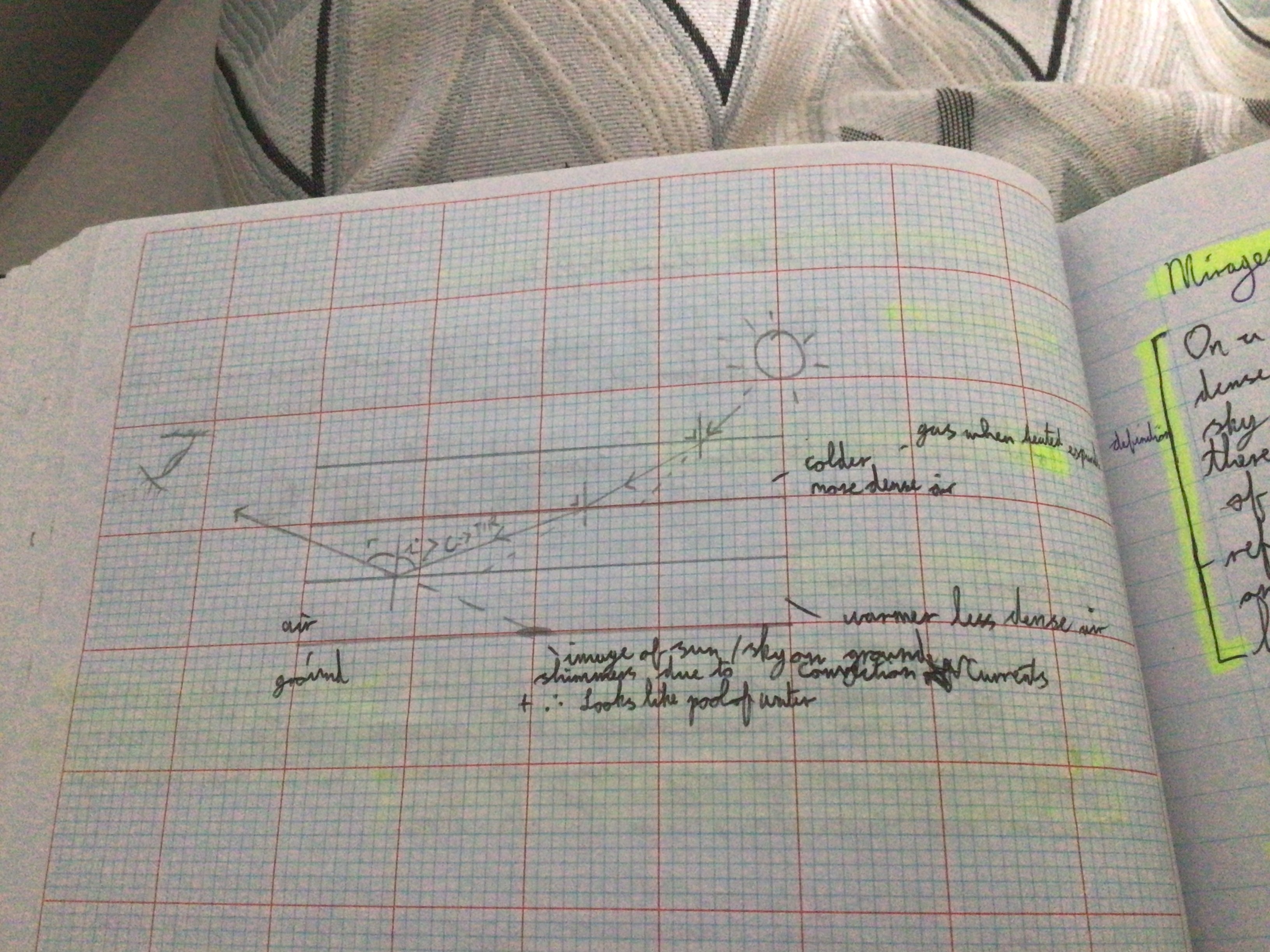
Mirage diagram notes
Colder air more dense, hotter air less dense. Image of sun/sky on ground shimmers due to convection currents and looks like a pool of water
Mirage (definition/explanation)
On a hot day, the air near the ground is warmer and less dense than the air higher up. Therefore the light from the sun is constantly travelling from more dense to less dense and therefore gets refractive upwards. If the day is hot enough the angle of incidence will exceed the critical angle and total internal reflection will occur. This produces an image of the sun/sky on the ground which shimmers due to Convection Currents and looks like a pool of water
Why does the air near the ground warmer than the air higher up on a warm day?
Ground absorbs heat
Critical angle problems formula
C = Sin -1 (1/n)
What does "C" stand for in the critical angle formula?
critical angle
What does "N" stand for in the critical angle formula?
refractive index
Why do diamonds sparkle more than identically cut glass?
Because the critical angle of diamond is smaller than the critical angle of glass, you get more total internal reflection in diamond and this is what causes sparkle
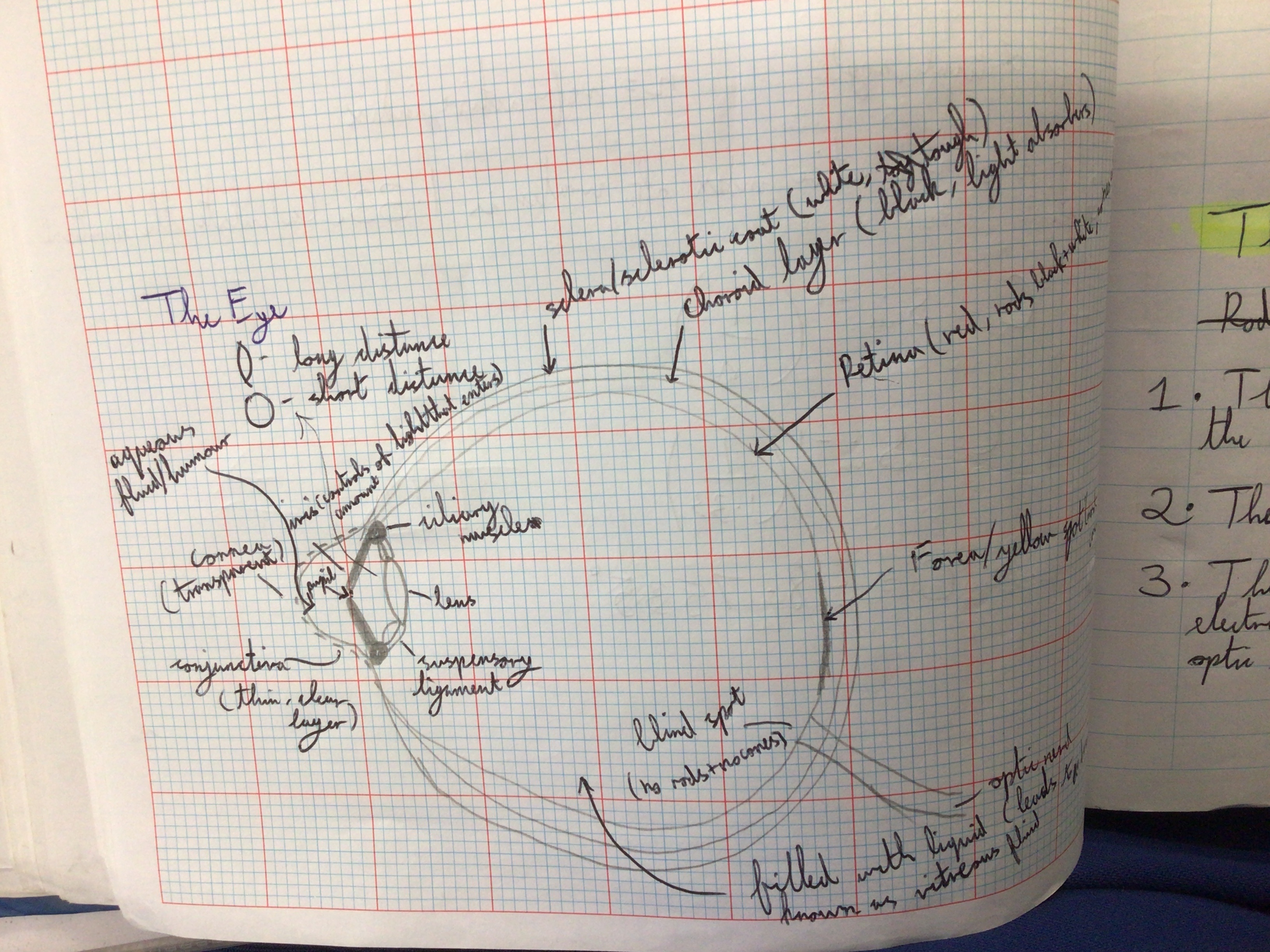
The Eye
The ciliary muscles pull on the suspensory ligaments to change the shape of the lens
Iris controls the amount of light that enters the eye.
Retina contains rods and cones. When light hits these electricity is generated which is sent to the brain via the optical nerve and is interpreted as sight
How does the eye bring objects at different distances into focus?
Ciliary muscles pull on the suspenseful ligaments which changes the lens’s shape and changes the focus of the eye
Draw a diagram with the optical structure of the eye
…
Why can’t a diverging lens be used as a magnifying glass?
Diverges light causing the image to always be smaller, making it impossible for it to be used as a magnifying glass
Draw diagram for near-sightedness (myopia)
...
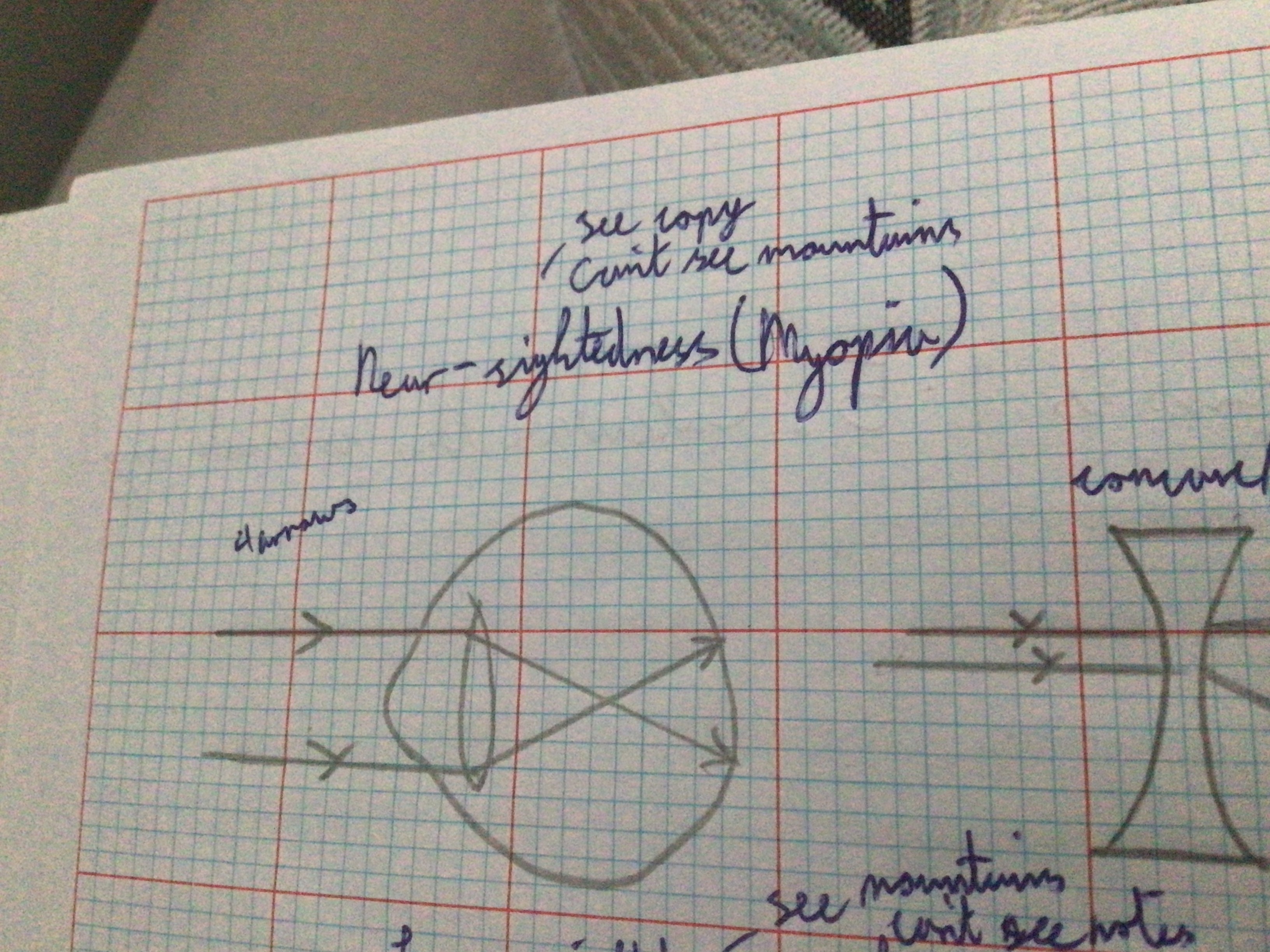
Draw diagram for near-sightedness (myopia) correction
...
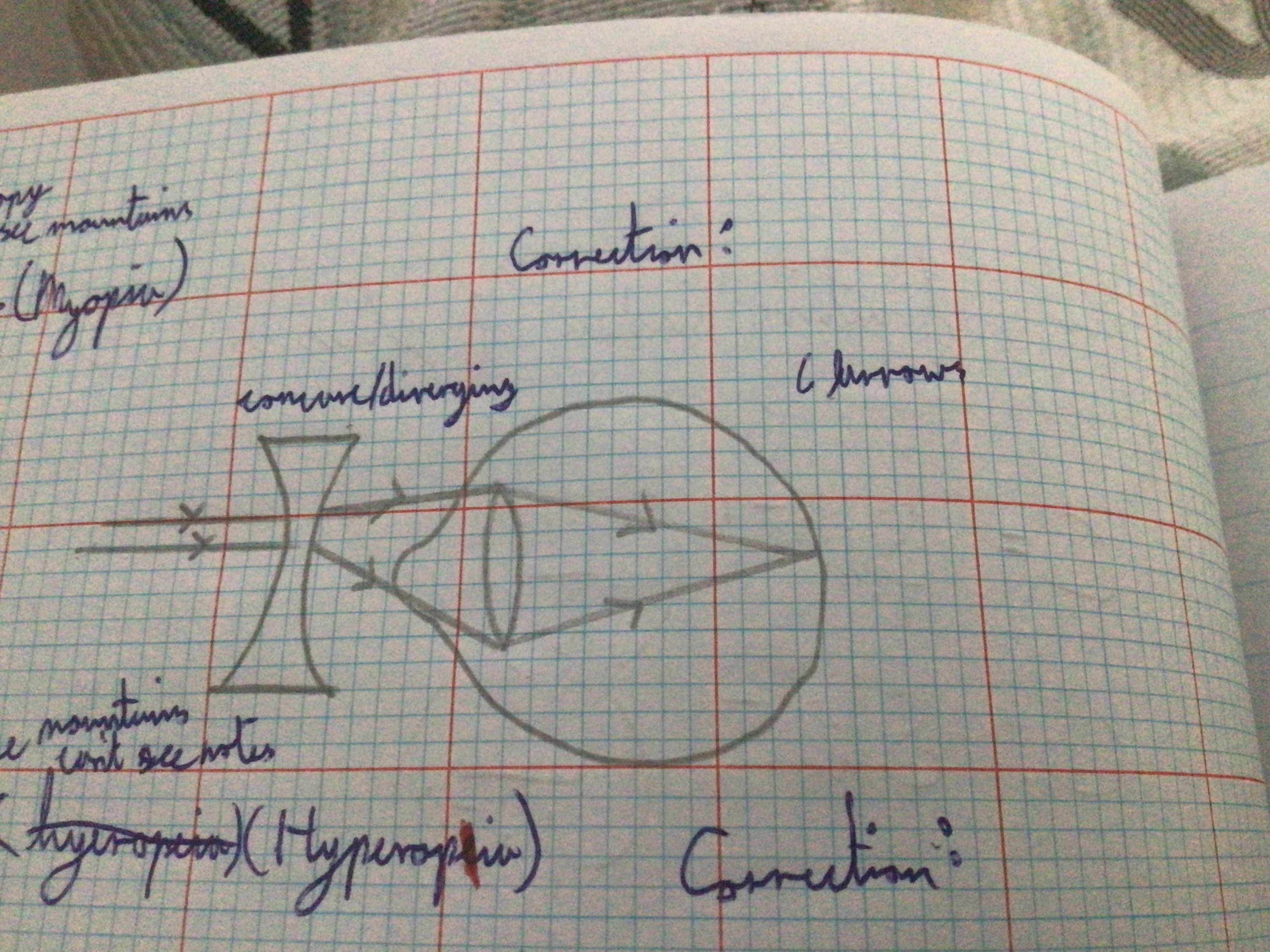
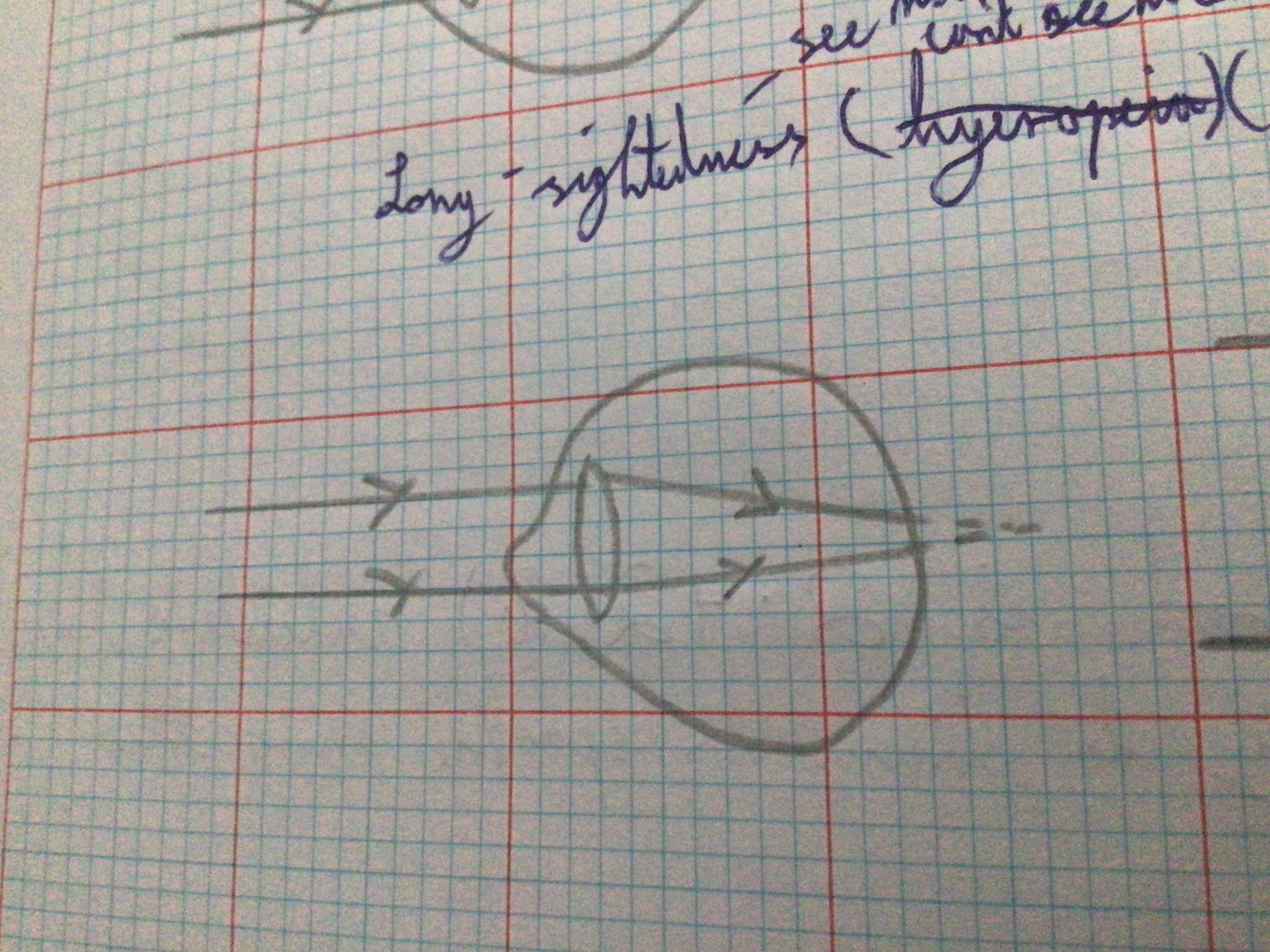
Draw diagram for far-sightedness (hyperopia)
...
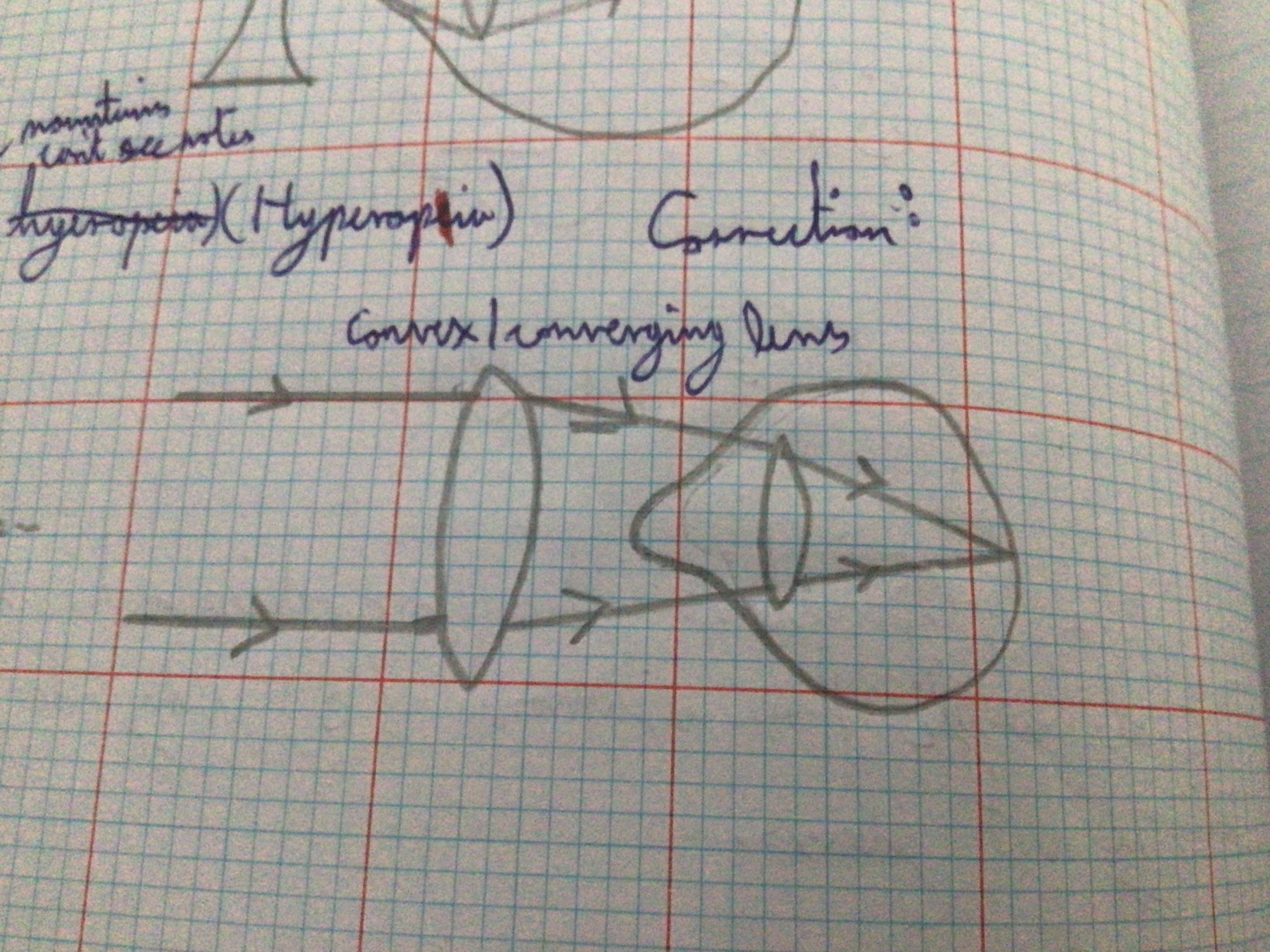
Draw diagram for far-sightedness (hyperopia) correction
...
Uses of lenses
Spectacles, monocles, contact lenses, cameras, microscope, telescope, eyes, magnifying glasses, binoculars
Unit for power
/cm
Why is the cornea not a lens?
Because it doesn’t refract light