UWORLD Neurology Step 2 CK
1/98
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
99 Terms
Lacunar syndromes
Cause
#1 Hypertension
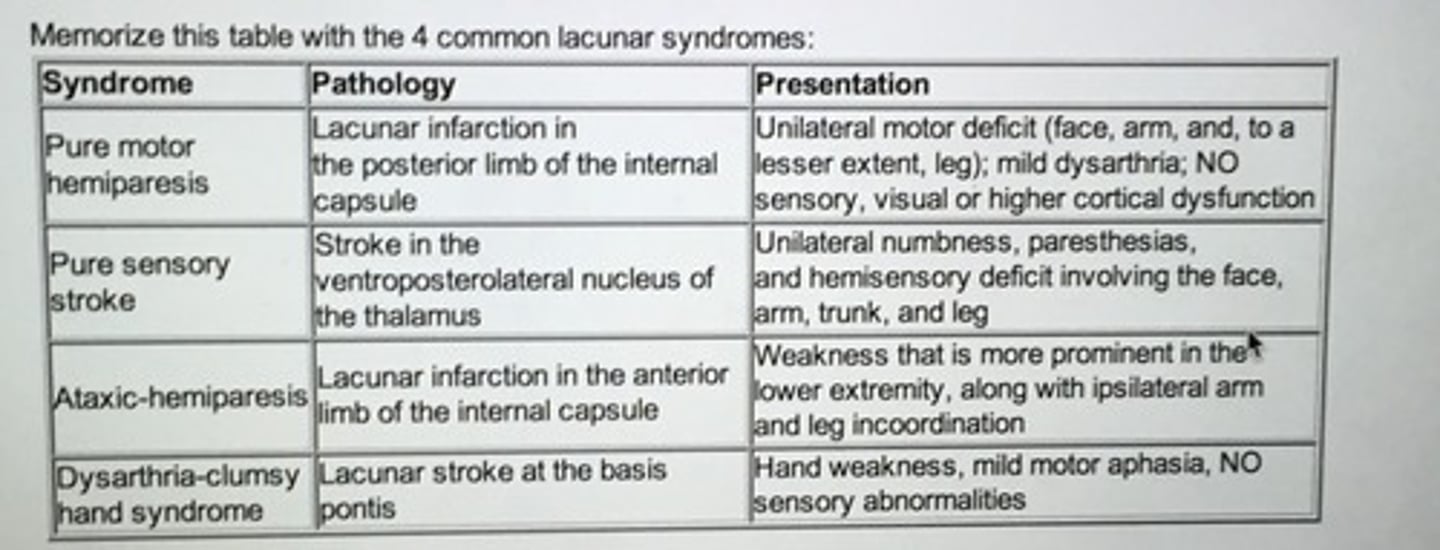
Pure Motor Hemiparesis
@ Posterior Limb of Internal Capsule
Unilateral Motor Deficit
Mild Dysarthria
Infarct @ Posterior Limb of Internal Capsule
Pure Motor Hemiparesis
Unilateral Motor Deficit
Mild Dysarthria
Pure Sensory Stroke
@ Ventroposterolateral Nucleus (VPN) of the Thalamus
Unilateral numbness, paresthesia
Hemisensory deficit—face, arm, trunk, leg
Infarct @ Ventroposterolateral Nucleus (VPN) of the Thalamus
Pure Sensory Stroke
Unilateral numbness, paresthesia
Hemisensory deficit—face, arm, trunk, leg
Ataxic-Hemiparesis
@ Anterior Limb of the Internal Capsule
Weakness more prominent in LOWER extremity
Ipsi-lateral arm and leg incoordination
Infarct @ Anterior Limb of the Internal Capsule
Ataxic-Hemiparesis
Weakness more prominent in LOWER extremity
Ipsi-lateral arm and leg incoordination
Essential Tremor
PX
bilateral action Tremor of the hands—⦸ leg involvement
Relieved by alcohol
Essential Tremor
TX
Propanolol
Primidone—Barbiturate
Parkinson's disease
Resting tremor (4-6 Hx)—@ legs & hands
improves—voluntary movement
___ is currently approved for use in pts with ALS.
Riluzole
- glutamate inhibitor
First line treatment for idiopathic intracranial HTN.
Acetazolamide (inhibits choroid plexus carbonic anhydrase) +/- furosemide
- optic nerve sheath decompression or LP shunting is recommended for pts refractory to medical tx
___ are benign suprasellar tumors that presents with visual defect, HA, and symptoms of pituitary hormonal deficiencies.
Craniopharyngiomas
- Rathke's pouch common children, but can presents in adults
- confirm MRI/ CT scan
- Tx: Sx or radiotherapy
MMSE score of less than ___ is suggestive of dementia (total maximum is 30).
24 points
- Neuro imaging shows atrophy which is more prominent in the temporal and parietal lobes
Myasthenia Gravis
TX
1. Acetylcholinesterase inhibitors (anticholinesterases) - Pyridostigmine or neostigmine
- SE: abd cramps, fasciculations, muscular weakness
2. Immunosuppressive agents
- prednisone, azathioprine, cyclosporine
3. Thymectomy
__ is a prokinetic agent used to tx N/V, gastroparesis. Pts taking this med should be monitored closely for the development of drug-induced extrapyramidal symptoms.
Metoclopramide
= dopamine receptor antagonist
- tx nausea/vomiting/gastroparesis
- SE: agitation, loose stools, tardive dyskinesia, dystonic rxns, parkinsonism
tx dystonic rxn: Benztropine or Diphenhydramine
Subdural hematoma are common in ___.
Older patients
Alcoholics due to brain atrophy + vessel fragility
Blunt or shearing trauma tears bridging veins, causing them to bleed into the subdural space
Brain death characteristic findings.
Absent cortical and brain stem functions
Spinal cord may still function, DTR may be present
Site of hemorrhage
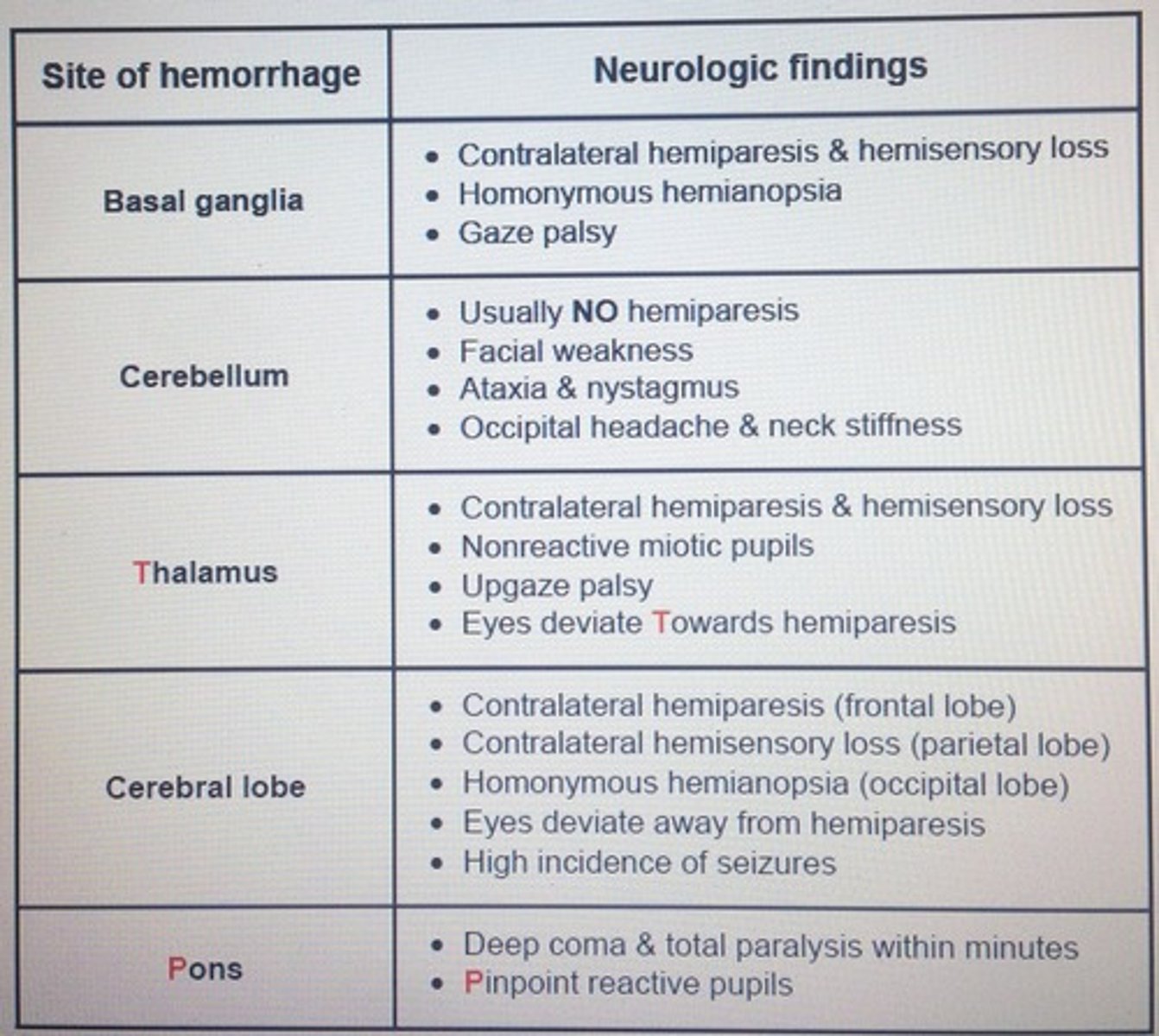
Hemorrhage
@ Basal Ganglia
CONTRA-lateral Hemiparesis & Hemisensory loss
Homonoymous hemianopsia
Hemorrhage
@ Cerebellum
Facial weakness
Ataxia & Nystagmus
Occipital Headache & Neck Stiffness
Hemorrhage
@ Thalamus
CONTRA-lateral hemiparesis & Hemisensory loss
Miotic pupils, non-reactive
Upgaze palsy
Eyes deviate TOWARD hemiparesis
Hemorrhage
@ Cerebral Lobe
Eyes deviate AWAY from hemiparesis
↑ incidence of seizures
CONTRA-lateral hemiparesis—Frontal Lobe
CONTRA-lateral hemisensory loss—Parietal Lobe
Homonymous Hemaninopsia—Occipital Lobe
Hemorrhage
@ Pons
Deep Coma
Total paralysis w/in minutes
Pinpoint, reactive pupils
B/L action tremor of the hands, usually w/o leg involvement.
Isolated head tremor w/o dystonia.
No other neuro signs.
Essential tremor
- relieved with alcohol
- Propranolol (useful also if pt has coexisting HTN)
- second line: primidone, topiramate
Parkinson's disease
Resting tremor (4-6 Hz) that decreases with voluntary movement.
Involves legs & hands.
Facial involvement less common.
A few hours or days after mild TBI pt has HA, confusion, amnesia, difficulty concentrating, vertigo, mood alteration, sleep disturbance, and anxiety. Dx.
Postconcussive syndrome
- resolve weeks to up to 6 months or more
Risk factors for Alzheimers dementia.
Age
Female gender
Positive family history
Head trauma
Down's syndrome
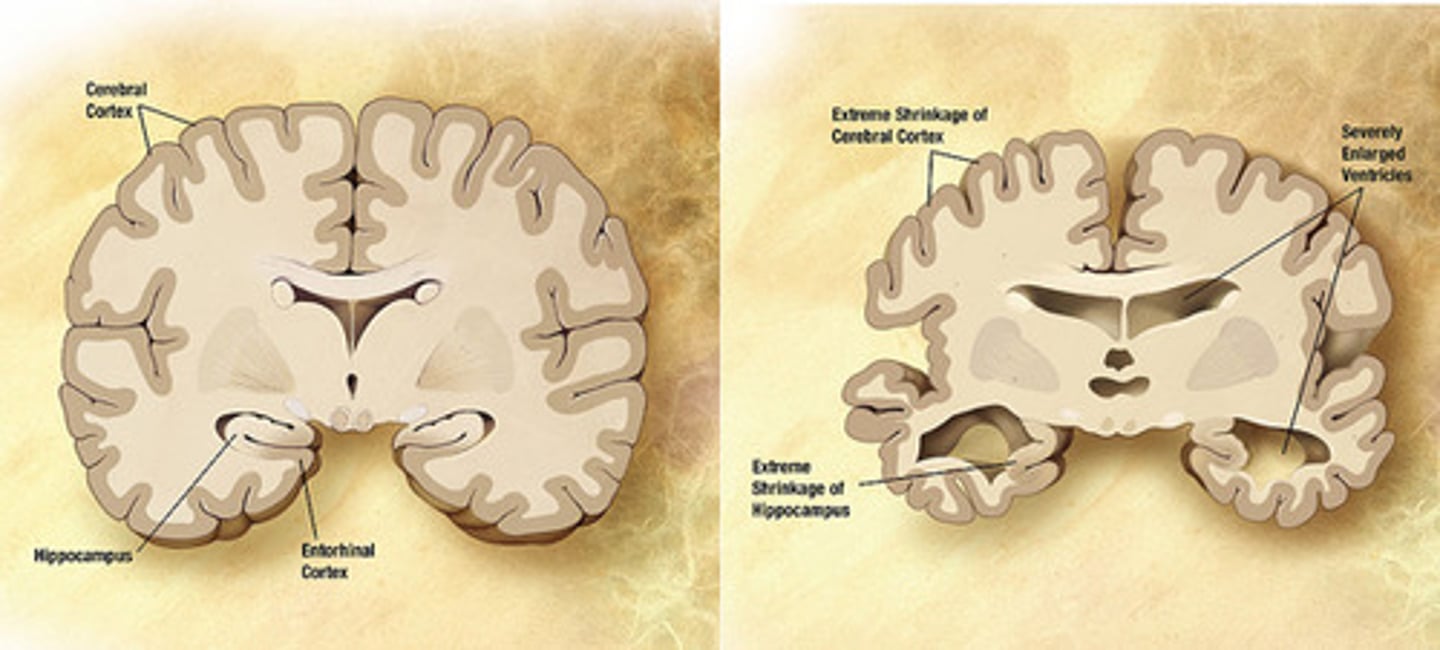
Dementia with Lewy bodies (DLB)
Fluctuating cognitive impairment and bizarre, visual hallucinations.
Vascular dementia
Stepwise decline
Early executive dysfunction
Cerebral infarction & or deep white matter changes on neuroimaging
Frontotemporal dementia
Early personality changes
Apathy, disinhibition & compulsive behavior
Which dementia?
Normal pressure hydrocephalus
Ataxia early in the disease
Urinary incontinence
Dilated ventricles on neuroimaging
Causes of chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy (CIPN)?
Vinca alkaloid (vincristine)
Platinum based meds (cisplatin)
Texanes (paclitaxel)
Weeks after tx, symmetrical paresthesias in stocking-glove pattern, loss ankle jerk reflex and loss P and T sensation
Gradual worsening severe low back pain
Pain worse in the recumbent position/at night
Early signs: symmetric LE weakness, hypoactive, absent DTR
Late signs: B/L Babinski reflex, DEC rectal tone, paraparesis/paraplegia with INC DTR, sensory loss.
Spinal cord compression
- injury (MVA)
- malignancy (lung, breast, prostate cancer, myeloma)
- infection (epidural abscess)
Sensory ataxia
Lancinating pains
Neurogenic urinary incontinence
Associated with Argyll Robertson pupil.
Tabes dorsalis
- INC incidence syphilis in men who have sex with men & HIV infected patients
- Treponema pallidum spirochetes directly damage the dorsal sensory roots
Enlargement of blind spot with momentary vision loss that varies according to changes in head positioning.
Can lead to rapid permanent vision loss and requires urgent dx evaluation.
Papilledema
- INC ICP transmitted to the optic nerve sheath, swelling of the optic nerve head
- HA worse in the morning due to INC ICP
Young age, obesity, due to idiopathic intracranial HTN (pseudo tumor cerebri)
Next step get CT/MRI to exclude underlying mass lesion
Meds used for Parkinson's disease that can lead to anticholinergic excess.
Trihexyphenidyl, Benztropine
- flushing, anhidrosis/dry mouth, hyperthermia, mydriasis/vision changes, delirium/confusion, urinary retention/constipation
Progressive proximal muscle weakness & atrophy w/o pain or tenderness.
LE muscles are more involved.
ESR and CK normal.
Dx the myopathy.
Glucocorticoid induced myopathy
Muscle pain & stiffness in the shoulder and pelvic girdles.
Tenderness with DEC ROM at shoulder, neck and hip.
Responds rapidly to glucocorticoids.
INC ESR, normal CK
Dx the myopathy.
Polymyalgia rheumatica
Muscle pain, tenderness & proximal muscle weakness
Skin rash and inflammatory arthritis may be present
ESR and CK INC
Dx the myopathy.
Inflammatory myopathy
Prominent muscle pain/tenderness w/ or w/o weakness
Rare rhabdomyolysis
Normal ESR, CK INC
Dx. the myopathy.
Statin-induced myopathy
Muscle pain, cramps, weakness in the proximal muscles, delayed DTR and myoedema
Occasional rhabdo
ESR normal, CK INC
Dx. the myopathy.
Hypothyroid myopathy
Clinical presentation:
- HA
- Focal neuro deficit
- Solitary ring-enhancing lesion on brain CT scan
- Fluid collection in the ethmoid sinus
Dx.
Brain abscess 2/2 ethmoid sinusitis
- Head and neck infections: Viridans streptococcus (most common) and other anaerobic (prevotella, bacteroides)
- distant infections lung or endocarditis (staph aureus)
tx: surgical draining and aspiration, prolonged abx therapy (4-8 weeks)
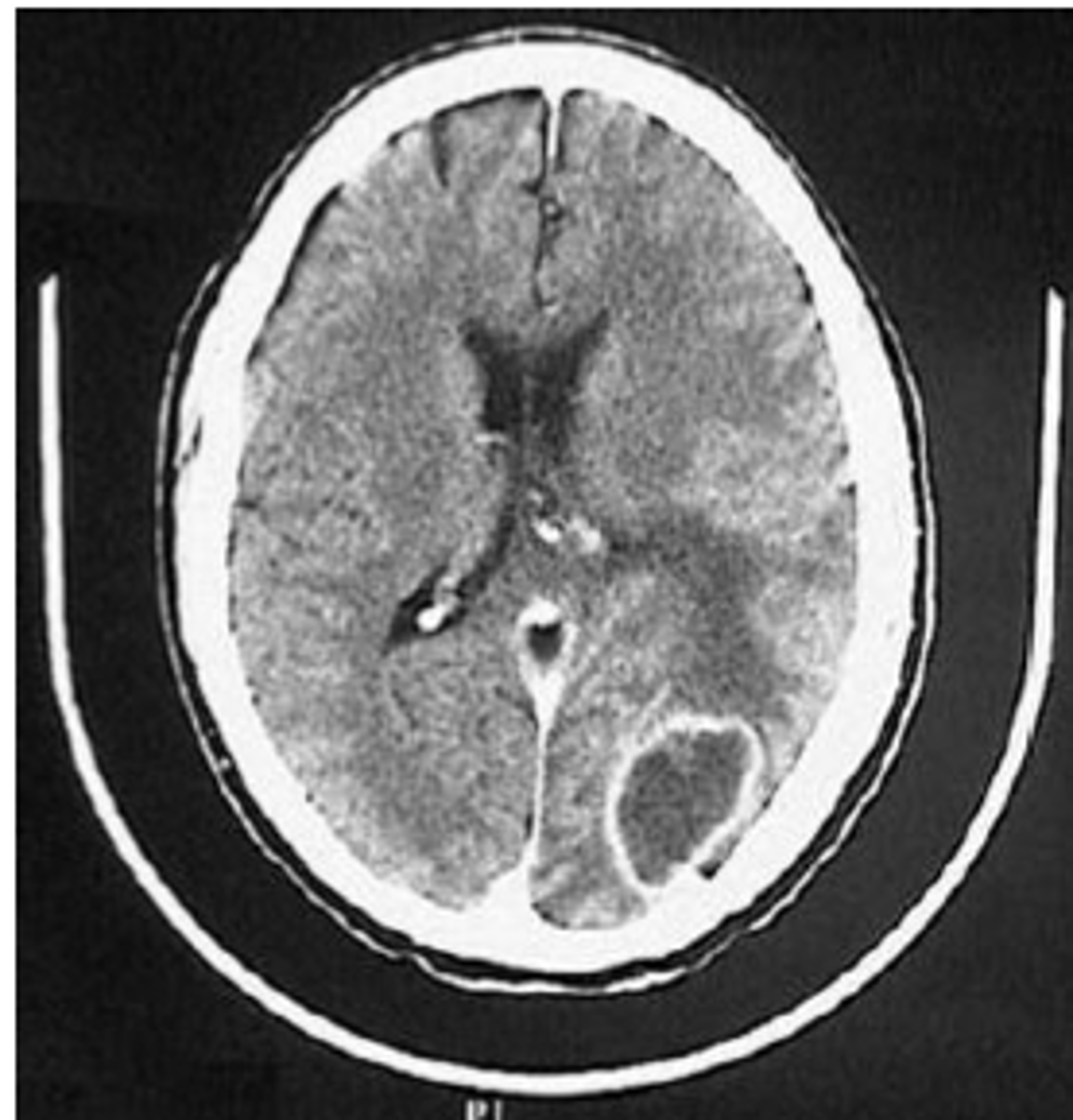
Dx:
- HA (worse at night)
- N/V
- Mental status changes
- Papilledema
- Focal neuro deficits
Cushing reflex.
Intracranial HTN
- Cushing reflex (HTN, bradycardia, respiratory depression) worrisome finding for brainstem compression
What is the monotherapy for acute migraine attacks, patients with N/V?
IV antiemetics (chlorpromazine, prochlorperazine, metoclopramide)
CSF in Guillain-Barre syndrome.
CSF shows high protein with normal WBC (albuminocytologic dissociation)
INC permeability blood-nerve-barrier
Tx: IVIG or plasmapheresis
Bacterial Meningitis
CSF
↑↑ WBC
↓ Glucose
↑ Protein
Tuberculosis Meningitis
CSF
↑ WBC
↓↓ Glucose
↑ Protein
Viral Meningitis
CSF
↑ WBC
Glucose normal
Guillain-Barre
CSF
WBC normal
Glucose normal
↑ Protein
Complications post Subarachnoid hemorrhage.
- Rebreeding (first 24 hours)
- Vasospasm (after 3 days - CT angiography detects vasospasm and prevented with Nimodipine)
- Hydrocephalus/INC ICP
- Seizures
- Hyponatremia (usually from SIADH)
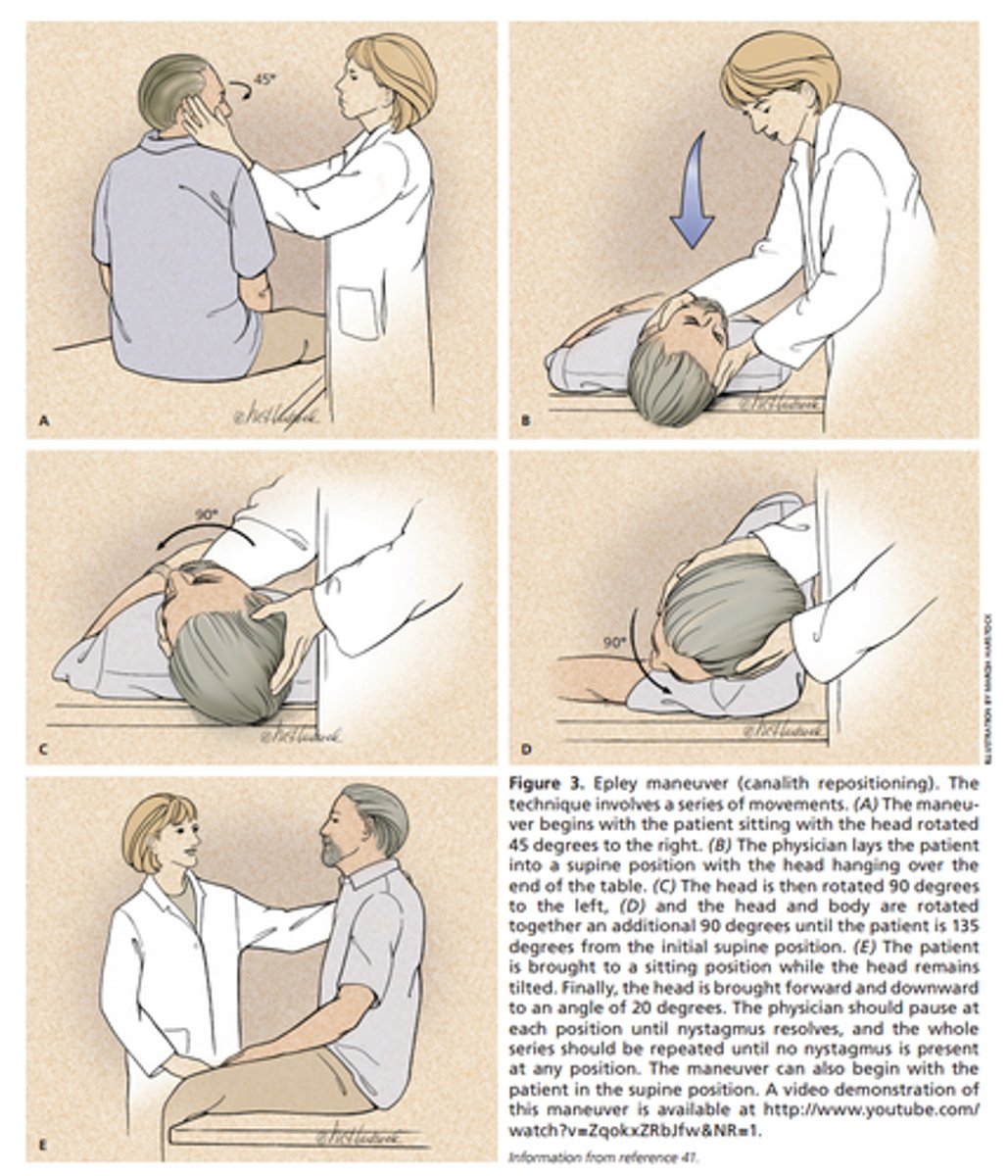
Recurrent, brief episodes brought on by predictable head movts or position change
No neuro or auditory symptoms
Dix-Hallpike maneuver causes nystagmus.
BPPV
- crystalline deposits (canaliths) in the semicircular canals that disrupt the flow of fluid in the vestibular system
- canalith repositioning maneuver (Epley maneuver)
Meniere's disease/syndrome
Recurrent episodes of vertigo
Preceded by ear fullness/pain
Unilateral hearing loss & tinnitus
Vestibular neuritis
Usually due to viral syndrome
Acute onset of single episode that can last days
Severe vertigo but no hearing loss, patient falls down toward side of lesion
Abnormal head thrust test.
Once confirmed the dx of myasthenia gravis what test should be ordered next?
CT chest look for thymoma if pt is younger than 60
Diabetic mononeuropathy often involved CN ___. Nerve damage is often ___, and only somatic nerve fibers are affected.
CN III
- Ischemic
- Parasympathetic fibers retain function
- ptosis + down and out gaze
___ DEC the risk of embolic events in pts with native valve infective endocarditis.
IV abx
- Sx is considered in pts with significant valve dysfunction, persistent/difficult to treat infection, or recurrent embolism
What is the most important risk factor for stroke?
HTN—4x the risk
Treatment of restless leg syndrome.
Mild/intermittent sxs:
- Supplementation iron when serum ferritin < 75
- use supportive measures (leg massage, heating pads, exercise)
- avoid aggravating factors (sleep deprivation, meds)
Persistent/moderate severe sxs:
First line: Dopamine agonists (pramipexole)
Alternate: Alpha-2-delta calcium channel ligands (gabapentin enacarbil)
The majority of embolic stories are due to ___ that develop 2/2 to ___.
Mural thrombi
A. fib
* Pts with infective endocarditis can form septic emboli when parts of valvular vegetations break off and travel to the brain
___ is commonly associated with burst fracture of the vertebra and is characterized by total loss of motor function below the level of lesion with loss of pain and temperature on both sides below the lesion.
Anterior cord syndrome
- MRI
- intact proprioception
When a patient has pronator drift, this finding is relatively sensitive and specific for ___ disease.
UMN disease
- weakness in supination causing the pronator muscles to be dominant
Sxs of cerebellar dysfunction.
Common among chronic alcohol abusers
- gait instability
- truncal ataxia
- difficulty with rapid alternating movements
- hypotonia
- intentional tremor
Hemorrhages are seen as [hyper/hypo]dense areas on CT scan, while infarcts are [hyper/hypo]dense parenchymal areas on CT scan.
Hemorrhages = Hyperdense
Infarctions = Hypodense
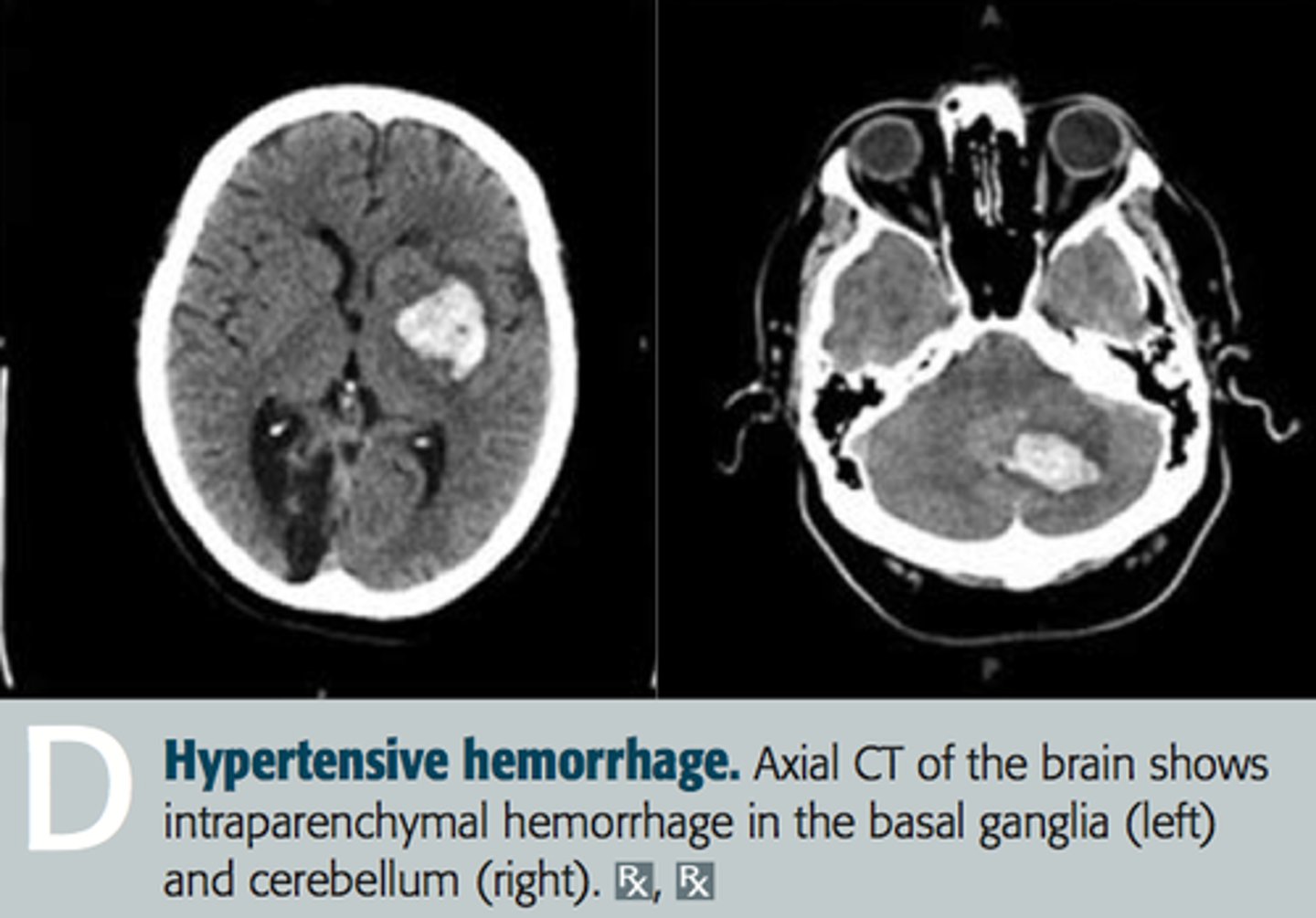
Suspect ___ in a young female with bilateral trigeminal neuralgia.
Multiple Sclerosis
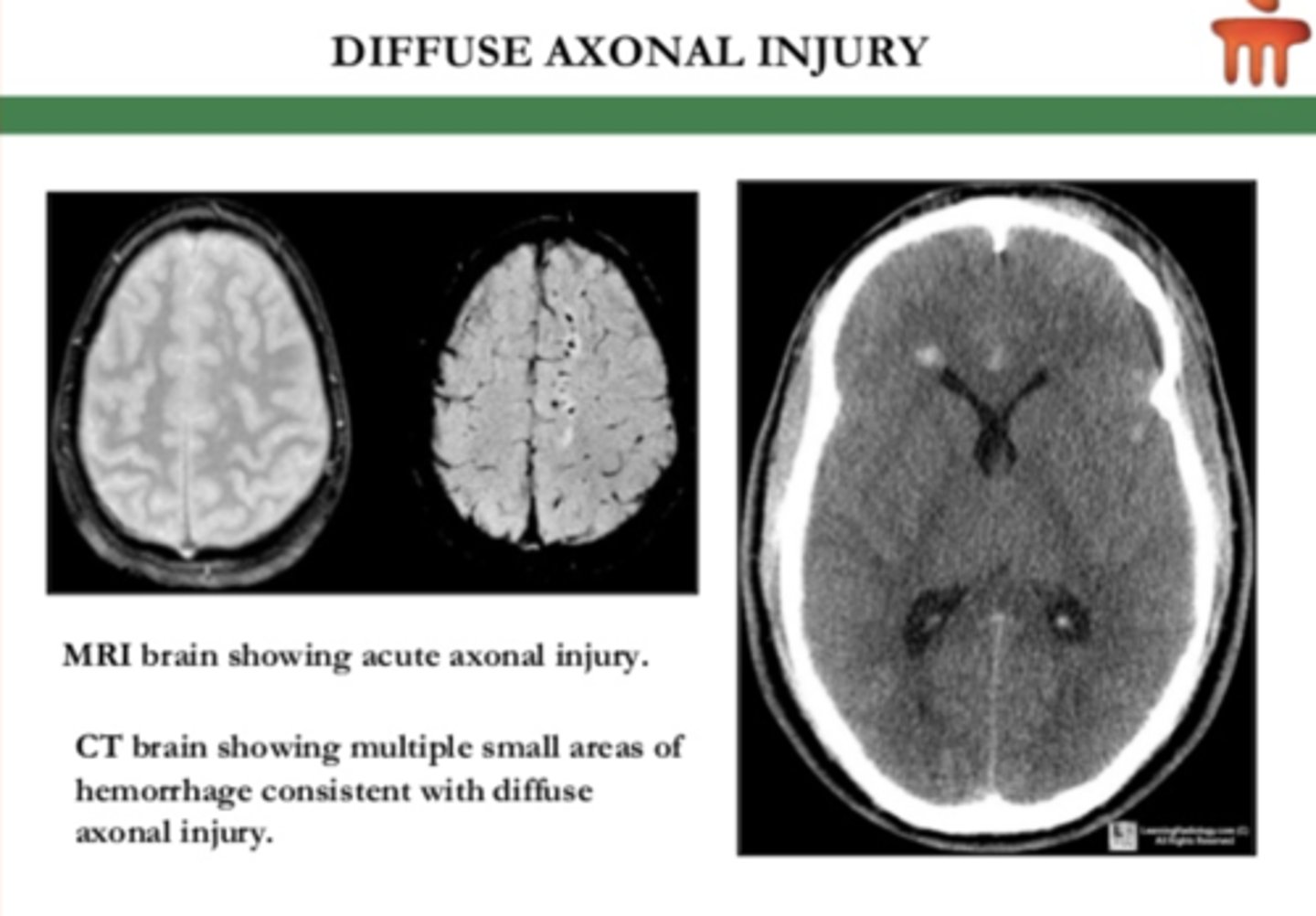
CT scan of ___ shows numerous minute punctate hemorrhages with blurring of grey-white interface.
Diffuse axonal injury
- most significant cause of morbidity in patients with TBI
- traumatic deceleration
What is the gold standard in dx herpes encephalitis?
PCR analysis of HSV DNA in CSF (highly sensitive and specific)
___ may result from hyperextension injuries, particularly in elderly patients with spondylosis.
Central cord syndrome
- weakness in the UE
- localized deficit in pain and T sensation
Delirium
Risk Factors
Dementia
Parkinson’s Disease
Prior Stroke
Adv. Age
Sensory Impairment
Delirium
Precipitating Factors
Drugs—Narcotics, Sedatives, Antihistamines, Muscle Relaxers, Polypharmacy
Infections—Pneumonia, UTI, Meninigitis
Electrolytes—Hyponatremia, Hypercalcemia
Metabolic—Volume depletion, Vit. B12 deficiency, Malignancy
Systemic Illness—CHF, Hepatic Failure, Malignancy
Central Nervous System—Seizure, Stroke, Head Injury, Subdural Hematoma
The treatment of choice for agitation in the elderly is ___.
Low-dose haloperidol
Ischemic Stroke—TX
< 4.5 hours after onset
IV Alteplase
Ischemic Stroke—TX
⦸ prior Anti-platelet therapy
Aspirin
Ischemic Stroke—TX
pt. on Aspirin therapy
Aspirin + Clopidogrel
Recommended prophylactic meds for cluster HA.
Verapamil
Lithium
Ergotamine
Hemi-sensory loss of severe dysesthesia of the affected area is typical for a ___ stroke.
Thalamic (Dejerine-Roussy syndrome)
- stroke in the VPL nucleus
- CL hemianesthesia, transient hemiparesis, athetosis, or ballistic movements
- dysesthesia in the sensory loss, thalamic pain phenomenon
Normal pressure hydrocephalus thought to result from ____.
DEC CSF absorption or transient INC in ICP that cause permanent ventricular enlargement w/o chronically INC ICP
Dementia, gait disturbance, and urinary incontinence
Lumbar spine stenosis is most commonly caused by ___.
Degenerative joint disease (DJD)
- pain relief flexion of the spine
- spinal MRI
Causes of pseudotumor cerebri.
Glucocorticoids
Vitamin A
OCPs
causes by impaired absorption of CSF by the arachnoid villi
tx: wt reduction and acetazolamide, shunting or optic n. sheath fenestration may be performed to prevent blindness
Lewy body dementia
___ is characterized by fluctuating cognitive impairment, recurrent visual hallucinations, and motor features of Parkinsonism.
primary CNS lymphoma
Suspect ___ in an HIV-infected patient with an AMS, EBV DNA in CSF, and solitary, weakly ring-enhancing periventricular mass on MRI.
Myasthenic Crisis
Precipitating Factors
Infection or Surgery
Pregnancy or Childbirth
Tapering Immunosuppressive drugs
Drugs—Aminoglycosides, Beta-blockers
Myasthenic Crisis
TX
Intubation for deteriorating respiratory status
Plasmapheresis or IVIG
Corticosteroids
Suspect neurofibromatosis type II in a young patient with acoustic neuroma and multiple cafe-au-lait spots. Best dx method for acoustic neuroma.
MRI with gadolinium
- acoustic neuroma (gradual developing tinnitus and hearing loss)
Wallenberg Syndrome
PX
Vertigo
⦸ pain & temperature—IPSI-lateal Face, CONTRA-lateral trunk & limbs
Hoarseness
IPSI-lateral Horner’s Syndrome
Lacunar Stroke
Risk Factors
#1 Hypertension
Diabetes Mellitus
Adv. Age
↑ LDL
Smoking
Ascending Paresthesia
Paresthesia @ Hands & Feet
Guillain-Barre Syndrome
Cluster Headache
PX
Recurrent episodes lasting 15-90 mins.
Periorbital pain, Severe
ANS—Lacrimation, Ptosis, Rhinorrhea
Cluster Headache
TX
100% Oxygen
Intracranial HTN
PX
Headache, N/V
Pulsatile tinnitus
Retrobulbar, Neck, or Back pain
Vision changes
Intracranial HTN
DX
1. CT scan of Head—If normal
2. Lumbar Puncture—↑ opening pressure
Intracranial Hypertension
Risk Factors
Women of childbearing age
Recent weight gain/obesity
Medications
Retinoids/vitamin A
Tetracyclines
Growth hormone
Intracranial Hypertension
TX
Weight Loss
Acetazolamide, Topiramate
Carbonic anhydrase inhibitor
Cryptococcal Meningitis
TX
3 successive phases
1. Induction Therapy
liposomal Amphotericin B + Flucytosine
given for ≥2 weeks until acute symptoms resolve and/or cerebrospinal fluid becomes sterile
2. Consolidation therapy
high-dose oral Fluconazole
given for ≥8 weeks
prevent disease relapse
Maintenance therapy
low-dose oral Fluconazole
Given:
Indefinitely
until CD4 counts rise to >100/mm3 for >3 months on antiretroviral therapy (ART)
Pituitary Apoplexy
PX
Thunderclap Headache
Menstrual irregulaties
bilateral visual field defects—optic chiasm
Ophthalmoplegia—impaired right eye adduction consistent with oculomotor nerve [CN III] compromise
Pituitary Apoplexy
TX
Glucocorticoids
Replace ACTH loss with anterior pituitary hormone loss
Sign most indicative of a Seizure?
Tongue Biting
Brain MRI
Indications
Red Flag symptoms
Focal weakness
Bowel dysfunction
Bladder dysfunction
Fever
Brain CT
⦸ red flags
Focal weakness
Bowel dysfunction
Bladder dysfunction
Fever