Unit 1 Ap Psychology
1/211
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
212 Terms
Psychology
The science of mental and behavioral processes.
Epigenetic
How the environment affects your gene expression(on/off).
Interaction
How different factors effect an outcome.
Fraternal (Dizygotic) Twins
Twins from separate fertilized eggs *DO NOT HAVE IDENTICAL DNA.
Identical (Monozygotic) Twins
Twins from the same egg that split *HAVE IDENTICAL DNA.
Environment
The non-genetic influences on our psychology.
Hereditary
The transfering of characteristics and genes from parents to offspring.
Genes
The traits parents pass down.
Genome
The complete set of genes in an organism.
Mutation
Errors in gene replication that leads to a change in the organism.
Natural Selection
Survival of the fittest-only the good traits get passed on.
Evolutionary Psychology
How evolution affects our psychology as a species.
Behavior Genetics
How our genes and environment affect our psychology on a personal level.
Nature-Nurture Issue
Is our psychology because of our biology or because of how we were raised?
Family Studies
Analyze traits that might be shared biologically in families.
Twin/Adoption Studies
Analyzes traits that might be because of shared genes and/or environments.
Reflexes
Automatic responses to stimuli.
Nervous System
The body’s electrochemical communication network(all the nerves in the peripheral and central nervous system)-takes in/sends information, makes decisions.
Central Nervous System(CNS)
The brain and spinal cord-makes decisions.
Peripheral Nervous System(PNS)
Sensory and motor neurons that connect CNS to the rest of the body.
Nerves
Bundled axons connecting the CNS to muscles, glands, and sensory organs.
Sensory(Afferent)Neurons
Carries incoming information from the body’s tissues and sensory receptors to the brain and spinal cord.
Motor(Efferent)Neurons
Neurons that carry information out of the brain into the body.
Interneurons
Neurons in the brain/spinal cord-they communicate internally and process the info coming from the sensory inputs and outputs.
Somatic/Skeletal Nervous System
The PNS system that controls the skeletal muscles.
Autonomic Nervous System(ANS)
Controls the glands and muscles of internal organs; sympathetic division arouses, parasympathetic calms.
Sympathetic Nervous System
The part of the ANS that stimulates and uses energy to move the body.-Fight or Flight
Parasympathetic Nervous System
The part of the ANS that cals the body and preserves its energy.
Why is the spine a part of the CNS?
It acts as a two way street for information inputs and outputs/reactions with neutral fibers.
Neuron
A nerve cell-building blocks of the nervous system.
Cell Body
The part of the neuron that has it’s nucleus.
Dendrites
The little “hairs” receiving messages.
Axon
Connects a neuron to other neurons, muscles, or glands, and passes messages.
Myelin Sheath
Covers the axon and helps speeds up messages.
Glial Cells(Glia)
Nourishes, supports, and protects neurons; also play a role in thinking, learning, and memory.
Action Potential
Impulses.
Threshold
How much of a trigger is needed to set off an impulse.
All-Or-None-Responses
If stimulation becomes too high, the neuron either completely fires or not at all.
Refractory Period
A break for a neuron after it fires off-needs to regenerate axon first.
Synapse
A small gap where electrical signals are being sent from the neuron.
Neurotransmitters
Chemical messengers that go between neurons-binds to the receptors of the other neuron and makes the decision to act or not.
Reputake
Excess neurons being disposed of(either absorbed or broken down).
Endorphins
Natural-pain control and pleasure.
Agonist
A molecule that increases the neurotransmitter’s action.
Antagonist
A molecule that blocks a neurotransmitter’s action
Endocrine System
A set of glands and fats that secrete hormones into the bloodstream.
Hormones
Chemical messengers created by the endocrine glands that affect other tissues.
Endocrine System in a Nutshell
Hypothalamus→Pituitary Gland→Other Glands→Hormones
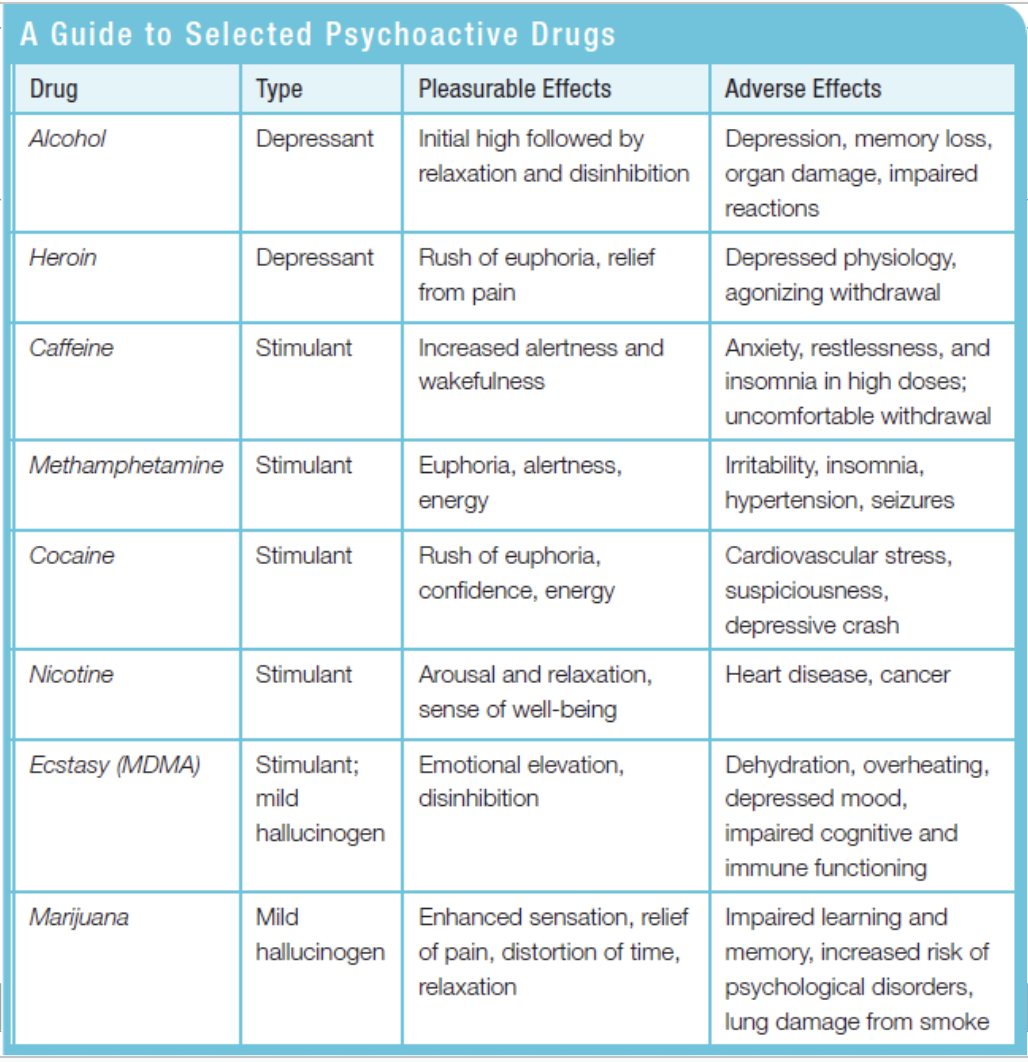
Hallucinogens
Psychedelic drugs that affect perception.
Near-Death-Experience
A state of consciousness near death.
Stimulants
Drugs that excite neural activity and speeds up bodily functions. Ex: Caffeine(An antagonist of adenosine receptors, and nicotine, Agonist for nicotinic acetylcholine receptors")
What are some examples of stimulants?
Nicotine, Caffeine, Cocaine, Molly
Barbiturates(Tranquilizers)
Depressants that lower CNS activity. They bring down anxiety, but also judgement and memory-AFFECTS GABA.
Opioid
Opium and Co. Depresses neural activity, lessens pain and anxiety.(Fentanyl, Oxycotin, Morphine-too much makes the brain stop producing its own opium)
Tolerance
How much of a substance your body needs to feel the effects.
Addiction
A dependency on a substance to feel normal.
Withdrawal
Feeling uncomfortable without a substance.
Depressants
Drugs that lessen neural activity and body functions.
Psychoactive Drugs
Chemicals that alter the brain, leading to changes in perceptions and moods
What are the 3 of psychoactive drugs?
Depressant, Stimulant, Hallucinogen.
What are some examples of depressants?
Alcohol.
What are some examples of hallucinogens?
LSD, Marijuana.
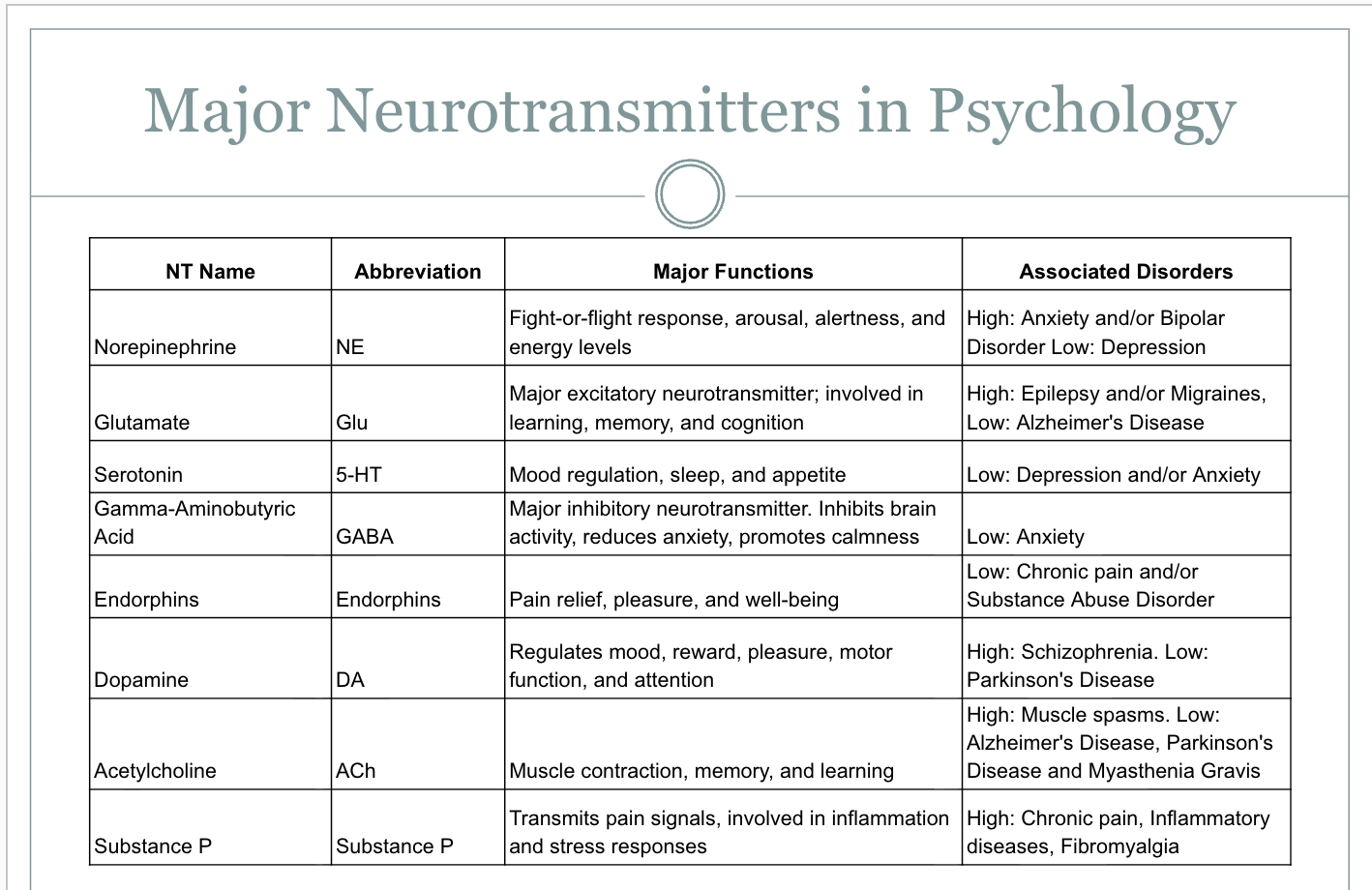
Seretonin
Sleep regulation, Emotional stability/mood regulation, Appetite control, Nausea reduction, Energy-Too little=Sleep problems and depression.
Dopamine
Movement, Motivation, Drive, Energy. Too little=Depression, Mood Issues.
Norepinephrine
Fight for Flight, Energy levels, Alertness-too much=anxiety, too little=depression
Acetylcholine
Muscle movements and contractions, memory/learning, Emotions and
GABA
Inhibits brain activity,reduced anxiety, makes you calm-low=anxiety.
Endorphins
Pain relief, pleasure, well-being(exersize)-too little=substance abuse and chronic pain.
Glutamate
Learning, memory, cognition-too much=epilepsy/ migraines, too little=alzheimer’s.
Substance P
Pain receptors.
Types of Drugs+Effects
Steps of Firing a Neuron
Chemical is resting at -70 Mv-Stimulus happens, Mv is -55-depolarization until 40 Mv(N is in, then action potential, then repolarization(K out)-Hyperpolarization, Refractory period, repeat.
Breakdown of Major NTmitters
Nodes of Ranvier
Gaps in the Meylin Sheath.
Terminal branch
Tunnels at the end of the axon.
Terminal Button/Synaptic Knob
Structure at the end of an axon terminal branch.
Synaptic vesicles
Sacs that hold the chemicals then burst.
Synaptic Space/Cleft
The tiny gap between the axon terminal of one neuron and the dendrites of the next neuron.
Biological Psychology
The study of the link between biology and psychology.
Biopsychosocial Approach
The study of how our biology, psychology, and sociology influence our mental processes.
Levels of Analysis
The different lenses of viewing psychology(ex. sociocultural).
Neuroplasticity
The brain’s ability to change by building new pathways.
Lesion
Tissue destruction in the brain.
EEG(Electroencephalogram)
A hat is placed over the subject and electrodes measure the electrical activity in the brain.
MEG(Magnetoencephalography)
Measures the magnetic fields around the brain.
CT (Computed Tomography) Scan
Pictures of the brain taken at different angles to represent a part of the brain.
PET (Positron Emission Tomography)
A display that shows where radioactive glucose goes every time the brain does something.
MRI (Magnetic Resonance Imaging)
A technique that measures magnetic fields and radio waves to make an image of soft tissue and brain anatomy.\
fMRI (functional MRI)
An MRI that reveals the blood flow.
Neural Measures Review
Name | How Does It Work? | Sample Finding |
|---|---|---|
Electroencephalography (EEG) | Electrodes placed on the scalp measure electrical activity in neurons. | Symptoms of depression and anxiety correlate with increased activity in the right frontal lobe, a brain area associated with behavioral withdrawal and negative emotion (Thibodeau et al., 2006). |
Magnetoencephalography (MEG) | A head coil records magnetic fields from the brain’s natural electrical currents. | Soldiers with posttraumatic stress disorder (PTSD), compared with soldiers who do not have PTSD, show stronger magnetic fields in the visual cortex when they view trauma-related images (Todd et al., 2015). |
Computed Tomography (CT) | X-rays of the head generate images that may locate brain damage. | Children’s brain injuries, shown in CT scans, predict impairments in their intelligence and memory processing (Königs et al., 2017). |
Positron Emission Tomography (PET) | Tracks where in the brain a temporarily radioactive form of glucose goes while the person given it performs a task. | Monkeys with an anxious temperament have brains that use more glucose in regions related to fear, memory, and expectations of reward and punishment (Fox et al., 2015). |
Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) | People sit or lie down in a chamber that uses magnetic fields and radio waves to provide a map of brain structure. | People with a history of violence tend to have smaller frontal lobes, especially in regions that aid moral judgment and self-control (Glenn & Raine, 2014). |
Functional Magnetic Resonance Imaging (fMRI) | Measures blood flow to brain regions by comparing continuous MRI scans. | Years after surviving a near plane crash, passengers who viewed material related to their trauma showed greater activation in the brain’s fear, memory, and visual centers than when they watched footage related to the 9/11 terrorist attacks (Palombo et al., 2015). |
Brainstem
Beginning of brian-automatic survival functions-Pons(sleep/movement) , midbrain(controls movement and sends out information, medulla(heart rate/blood pressure/swallowing), reticular formation(secretary for thalamus)/
Hindbrain
Medulla,Pons,Cerebellum-direct actions like breathing and sleeping, coordination+balance.
Midbrain
On top of brain stem, connects hindbrain and forebrain, controls motor movements+transmits auditory and visual info.
Forebrain
Cerebral cortex, thalamus, hypothalamus-manages complex activities, senses, functions, and voluntary movements.
Medulla
Base of brainstem-controls heartbeat and breathing.
Thalamus
Top of brainstem-takes sensory input and sends to medulla and cerebellum*DOES NOT DO SMELL!!!
Reticular Formation
Connects the brainstem and thalamus-filters information and alertness.
Cerebellum
“Little brain”-back of brainstem, processes sensory input, coordinating movements and balance, enabling non-verbal learning and memory.
Limbic System
Neural system in the forebrain below the cerebral cortex that controls emotions and drive-Amygdala, Hippocampus, Thalamus, Hypothalamus, Pituitary gland.
Amygdala
2 clusters in the limbic system-basic emotions.