ESSC - test 3.1 igneous rocks
1/54
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
55 Terms
What are the three basic types of rocks?
Igneous, sedimentary, and metamorphic
How are the categories of rock determined?
Based on how they form
What are igneous rocks?
These form from the cooling of magma or lava.
What is magma?
Magma is molten rock and dissolved gas. EX: shaken bottle of soda while the cap is still sealed, because it's the liquid and the gas
What does magma form from?
Either decompression melting at ocean ridges, or partial melting of subducting slabs.
What is lava?
Molten rock material from which gas has mostly escaped. EX: once you open the shaken bottle of soda, THAT'S lava.
How does pressure influence melting point?
Increased pressure increases melting point. If there's too much pressure, it can't melt. If the pressure is released, now it can
Adding water (raises/lowers) the melting temperature of rocks
lowers
Who were the two researchers that discovered that putting water inside a rock will lower the melting temperature?
Tuddle and Bowen
Why does adding water to a rock decrease melting temperature?
Because a rock with water in it has a reduced solid liquid boundary.
What is decompression melting?
the upward movement of the earth's mantle to an area of lower pressure
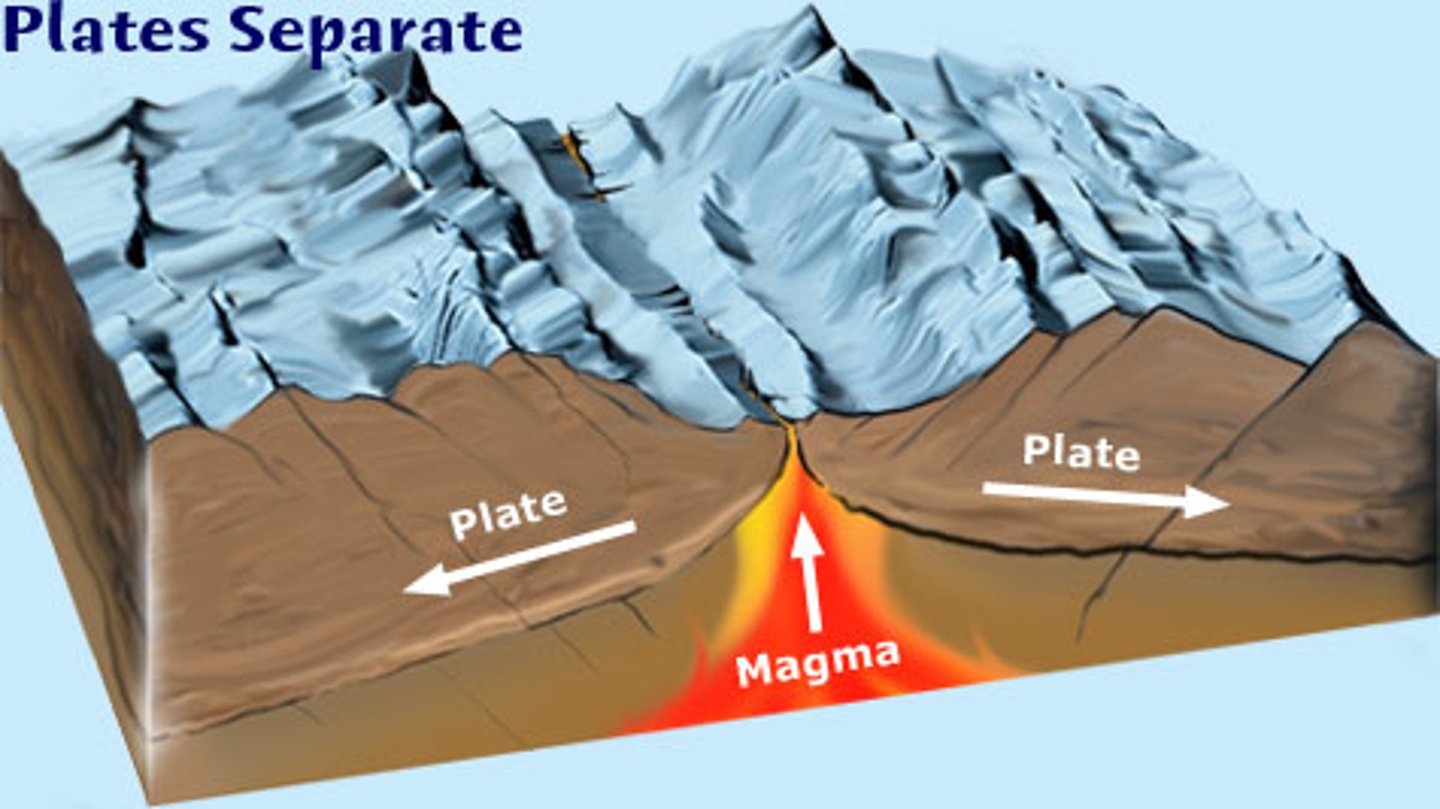
What is the number one way we make lava?
At a divergent boundary. As the magma rises, you get decompression melting.
What are pillow basalts?
eruption of basaltic lava under water. As the magma chamber forms, it creates hydraulic pressure (liquid pressure). The liquid is less dense, so it's trying to rise. If you can generate enough hydraulic pressre, it breaks the rocks above.
The vertical cracks that the gestalt is deposited in are called ______
dikes
What is partial melting?
Some of the minerals hit their melting point, but not all of them.
How does melting occur in a ocean-ocean convergent boundary?
As the plate subducts, both temperature and pressure increase. water supplied by the breakdow of water bearing materials lowers the melting temp, causing melting of the overlying asthenosphere.
When two pieces of ocean crust converge, which one gets subducted?
The older and colder ocean crust, because it's more dense.
How could melting occur along an ocean continent convergent boundary?
Mafic magma melts the crust and adding water melts the mantle
If you only melt continental crust, you get _______ magma
felsic. (low density)
If you melt the mantle, you get ______ magma.
mafic. (more dense, what ocean crust is made of)
If you take a little bit of mafic magma and a little bit of felsic, you get _________ magma.
Intermediate.
How does magma cool?
1. Loses heat to air, water, or underlying rocks
2. Loses gas
3. Conduction into wall rocks
4. Circulating water cools it
Who was N.L Bowen?
He didn't understand how all the different rocks were made from only four "ingredients." So he started to put the different magmas together and let them cool to see what would happen. He found that different minerals crystalize at different temperatures.
What degree is the "curie point"
500 degrees. Once they're cooled to 500 degrees, they're locked into position.
Decompression melting will probably give you _______ magma, while continental melting will probably give you _________ magma.
Decompression / continental
What does Bohen's reaction series tell us?
This tells us the temperature that the magma was at when different rocks form.
Bohen figured out that there are _(#)_ crystalization series. They are...
two. First one is the discontinuous, second is continuous.
What is the discontinuous series?
Structure changes, while chemistry stays the same. Called that because as the temperature decreases, certain minerals are discontinued.
What is the continuous series?
Structure stays the same, while chemistry is altered. With this, we are always makig potassium felspar. But at high temperatures it's calcium rich, and at low it's sodium rich.
basically, it's continuous because it's the same mineral, the only difference is how much sodium and calcium is in it.
What is magma differentiation?
As minerals crystalize, the overall chemistry of the remaining magma changes. So one magma can create different igneous rocks with different chemical signatures
You don't have to memorize this, but what's a good explanation for how the chemistry of magma can change to form different rocks?
We have our magma chamber, which is cooling down in the surface but has some volcanoes. It's going to erupt lava that has the same chemistry as the magma down below, so that's composition A. Some time goes by, some green mineral is crystallized. It's more dense than the surrounding liquid, so it settles. That makes the chemistry of the surrounding liquid different, so the next volcano produces composition B magma. It continues to cool, you start making a different mineral because there was a different chemistry. Now the remaining liquid has yet another chemistry, so that's composition C. This one volcano had lava flows with three completely different chemical compositions, all because in the magma chamber the minerals were crystalizinng and changing the chemistry of the liquid left behind.
What are two other ways to change magma chemistry?
Assimilation
Mixing
What is assimilation?
The magma is passing through other rock types. Those host rocks are called country rocks. So as the liquid moves through the country rocks, they melt and become liquid. Now the chemistry is different, and that process is called assimilation.
What is mixing?
When magma rises, it can run into another magma and intersect. When they intersect, or mix, you get a different chemistry.
What are xenoliths?
Xeno - alien
Lith - rock
The country rocks I mentioned before don't always melt. If they don't melt, they'll just sit. Occasionally these will be trapped as the lava cools. (Diamonds)
Xenoliths are mainly found in ________ rocks.
extrusive
What is useful about xenoliths?
They give us clues to underlying geology. We can't go below a volcano, but this gives us some clues.
What are the three main ways igneous rocks are classified?
Texture
Location formed
mineralogy
What is texture?
The look and feel of the rock surface. Gives us clues of rock cooling history
What are some different textures that rocks can be?
- phaneritic
- aphanetic
- porphyritic
- pregmatic
- glassy
- vesicular
- pyroclastic
What is phaneritic texture?
You can see the different materials with the naked eye. EX: like an oatmeal cookie.
This indicates slow crystalization below the surface.

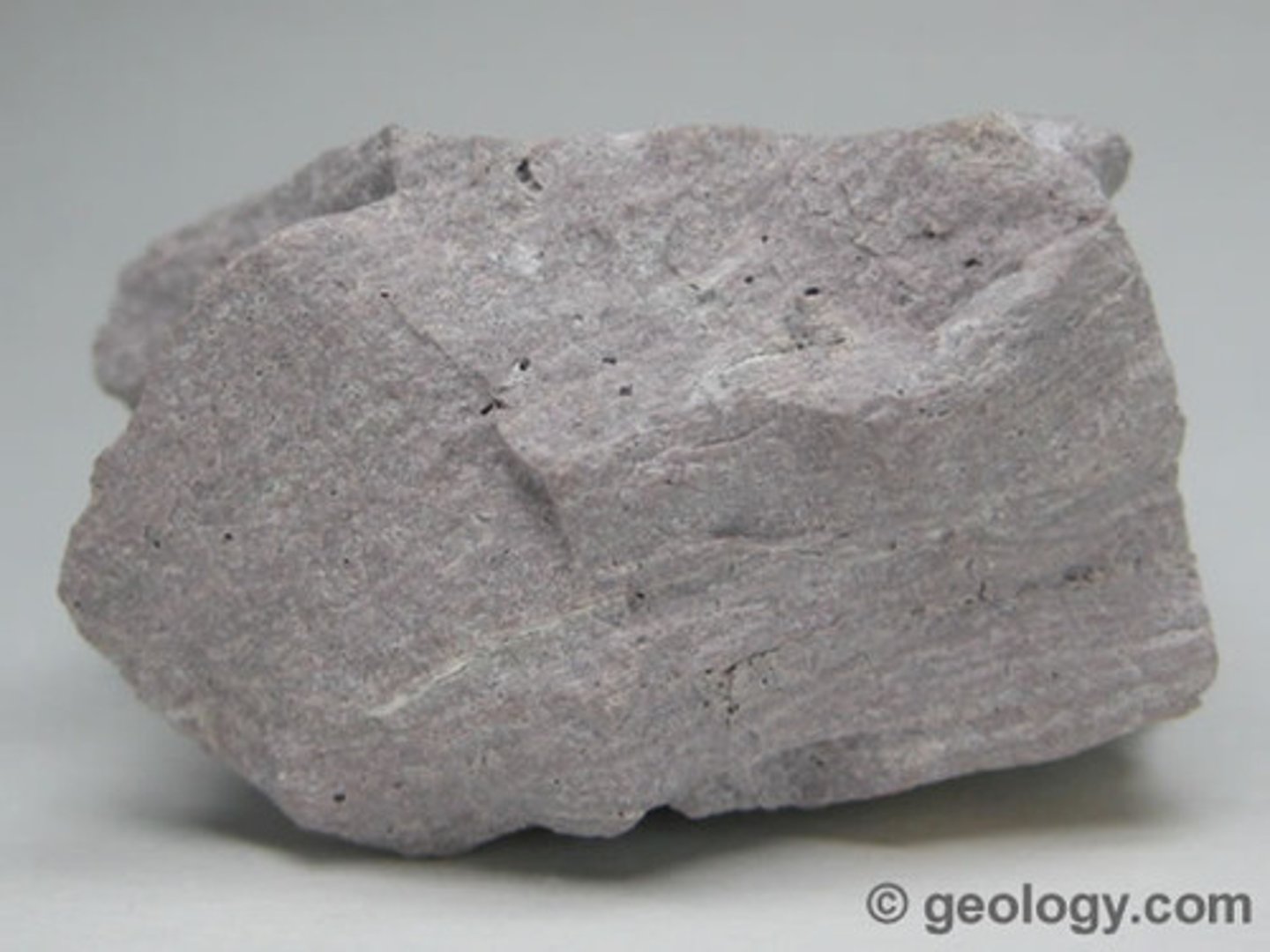
What is aphanetic texture?
"fine grained." The minerals are too small to see without the aid of a microscope. EX: like a sugar cookie
This suggests fast crystalization at the surface (makes sense, because the minerals do not have time to get big)

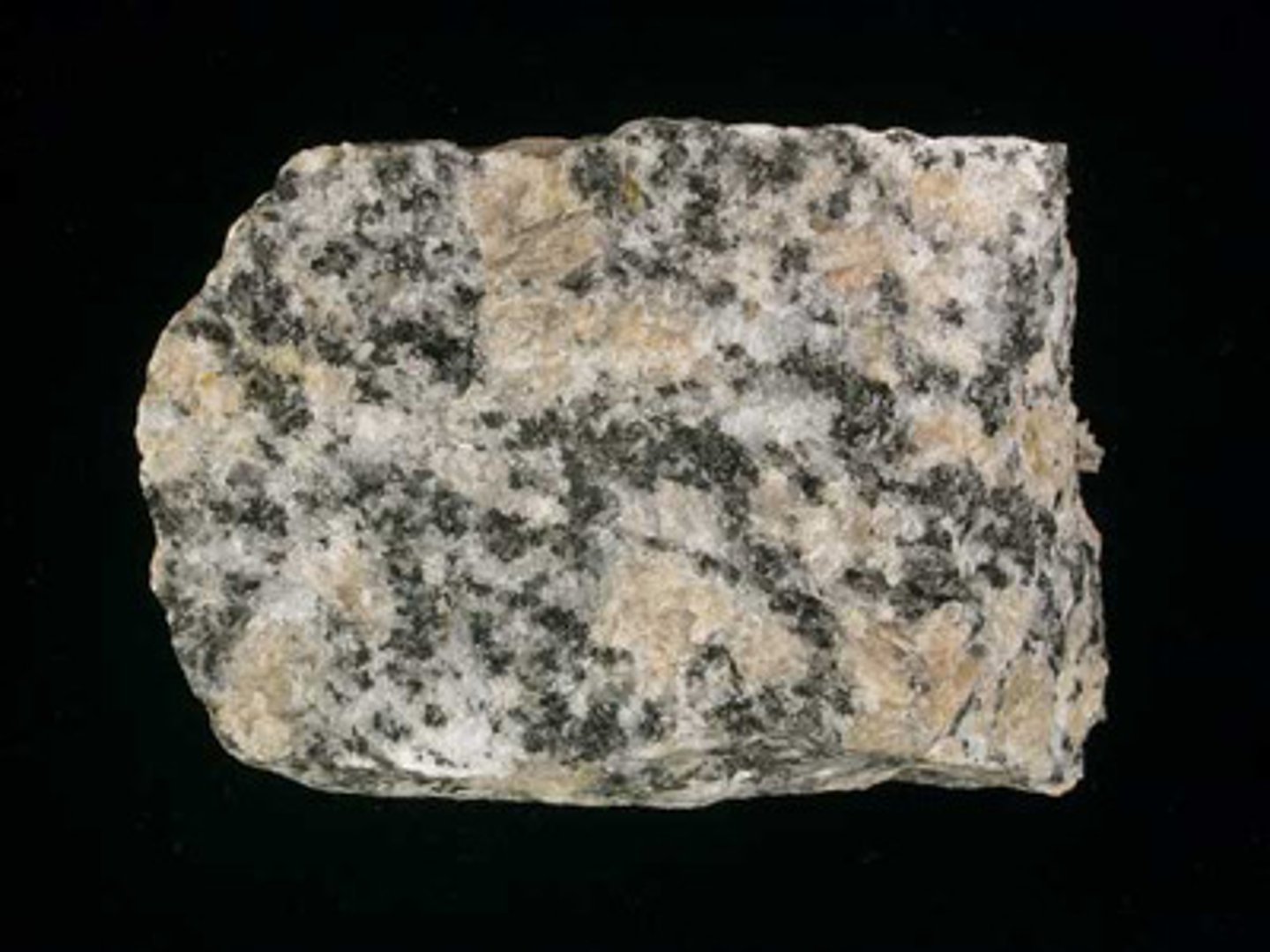
What is porphyritic texture?
Mixed course and fine grained material. EX: like a chocolate chip cookie
This indicates two different phases of crystalization.
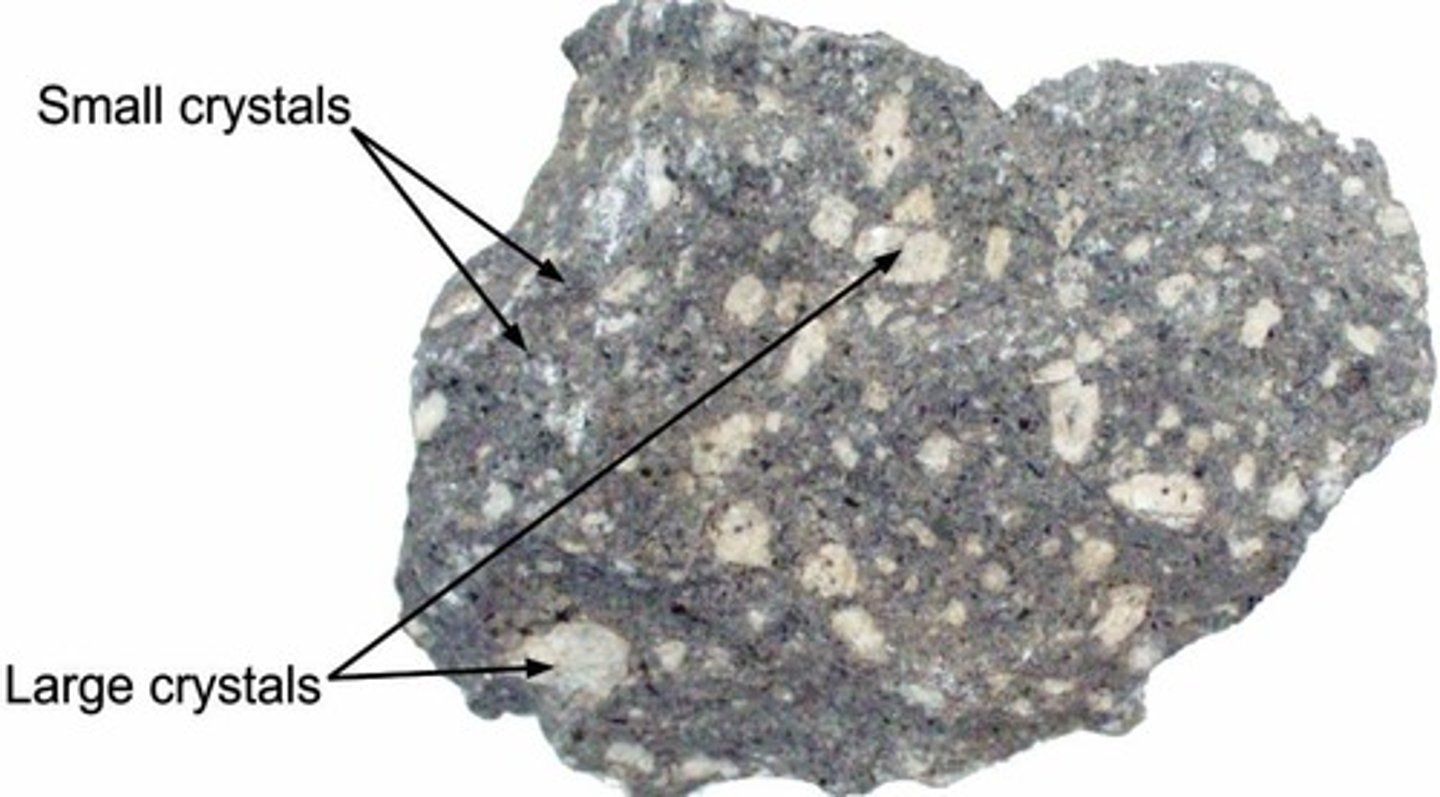

Within the porphyritic texture, large crystals are called _________ and small crystals are called ___________.
phenocrysts / matrix or groundmass
how does pegmatitic texture form?
Occurs if the magma cools REALLY slow
How does a glassy texture form?
Occurs if the magma cools REALLY fast.
Rocks can be divided into two large groups based on where they were formed, which are...
plutonic (intrusive)
Volcanic (extrusive)
Plutonic means the rock was formed...
below the surface
Volcanic means the rock was formed...
At the surface
What is a pluton?
a large body of intrusive igneous rock that forms when magma cools and crystallizes beneath the Earth's surface
What is a batholith?
One or more continuous plutons covering more than 100 km.
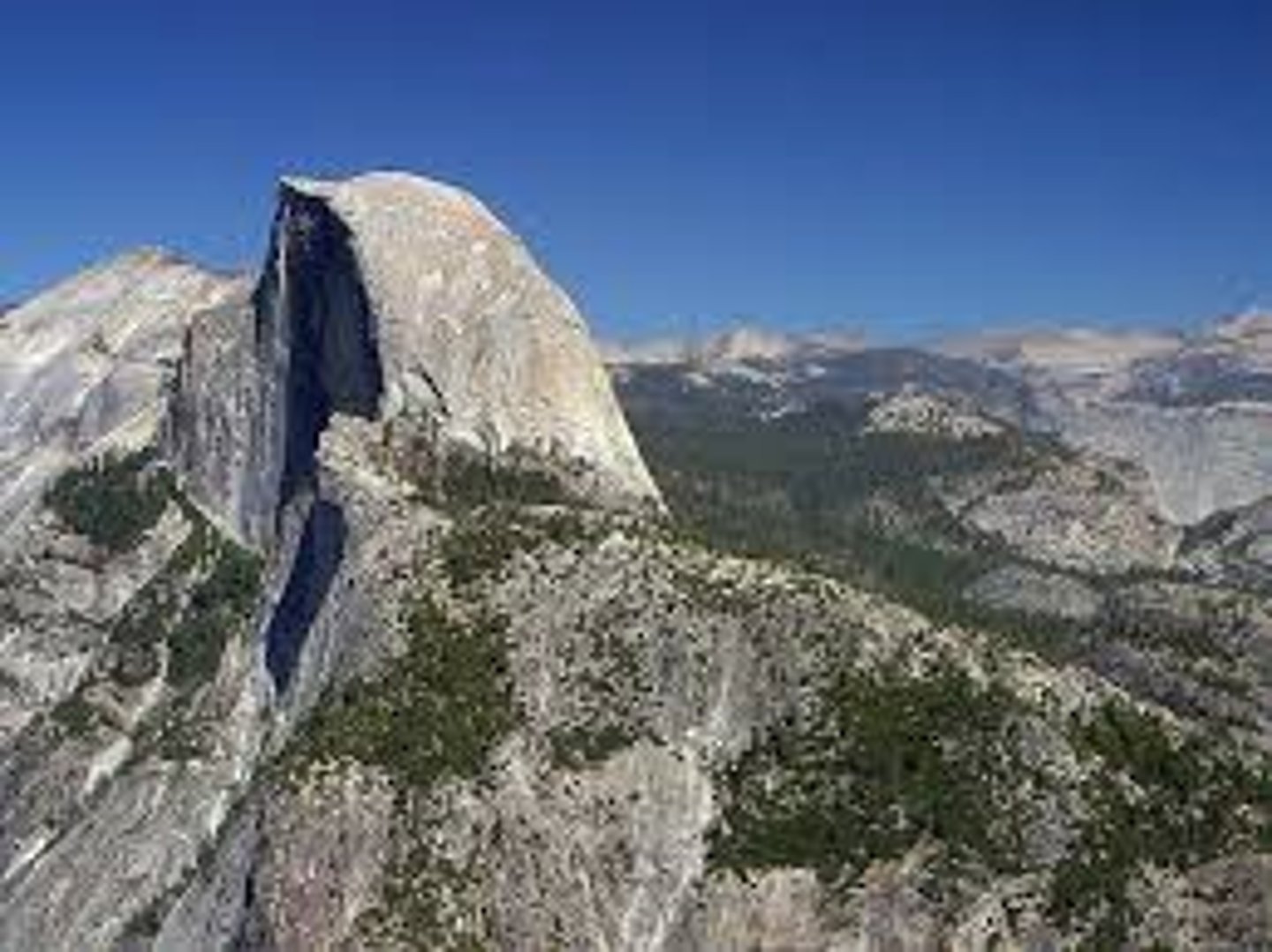

What is one example of a batholith
The sierra nevada batholith in california.
What are sheetlike plutons?
Pretty self explanatory, shaped like a thick sheet. Can be horizontal, vertical, inclined.
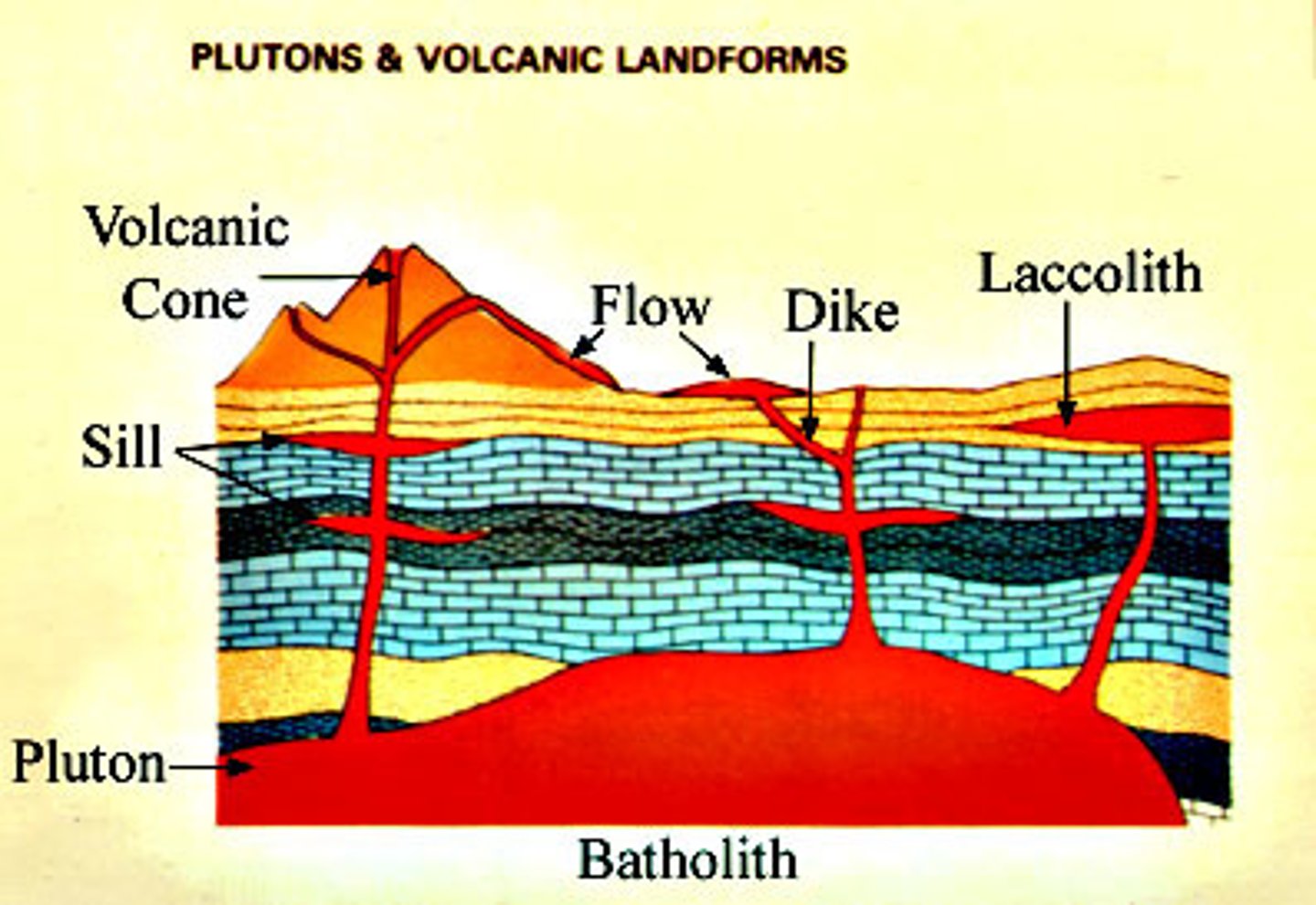
With sheetlike plutons, if they're horizontal, they're called _____. If they're not horizontal, they're called _______.
Sills, dikes.
What are the four "flavors" of rock
Ultramafic (we're ignoring this one tho)
Mafic
Intermediate
Felsic