scrotum and prostate
1/56
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
57 Terms
a hydrocele is defined as an abnormal fluid collection between the:
two layers of tunica vaginalis
“bell clapper” is another term used to describe which abnormality
testicular torsion
normal testes will descend into scrotal sac by
6 months of age
carcinoma of prostate gland most commonly develops in the:
peripheral zone
what artery gives rise to the testicular arteries
anterior aspect of abdominal aorta
a fibrous sheath enclosing the testes describes which structure
tunica albuginea
which function is considered a responsibility of the prostate gland
produce ejaculation fluid
thickened portion of the tunica albuginea is termed the
mediastinum testis
what structure supports the posterior border of the testes
spermatic cord
what structure divides the male urethra into proximal and distal segments
verumontanum
an anechoic structure arising from the rete testes describes which structure
spermatocele
what structure transports sperm fro the testes to the prostatic urethra
vas deferens
a spermatic vein is considered dilated after diameter exceeds
4mm
scrotum is divided into two separate compartments by the
median raphe
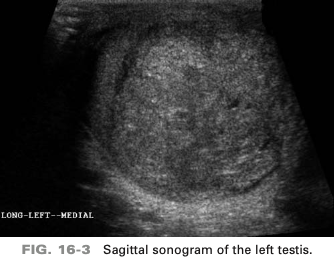
a 35-year-old patient presents with palpable scrotal mass. He is afebrile and denies any scrotal pain. On the basis of this clinical history the sono finding is most suspicious for…
testicular carcinoma
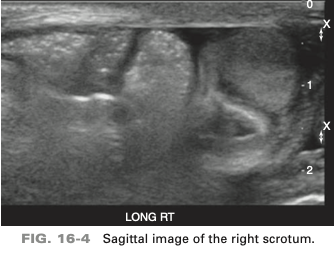
an 85-year-old patient presents with intermittent scrotal swelling. He states the swelling “comes and goes”. On the basis of the clinical history, the sono finding is most suspicious for
scrotal hernia
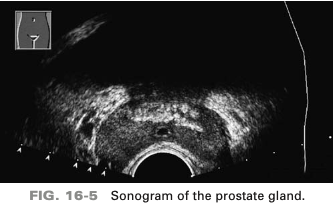
hyperechoic foci are identified in which of the following regions of the prostate gland
central zone
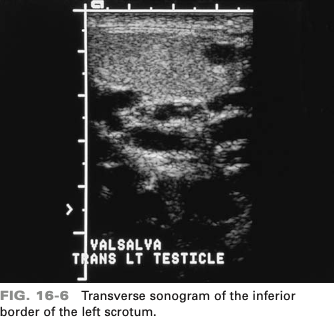
a 30-year-old patient presents with a tender scrotal mass. The sonographic finding is most suspicious for which abnormality
a varicocele
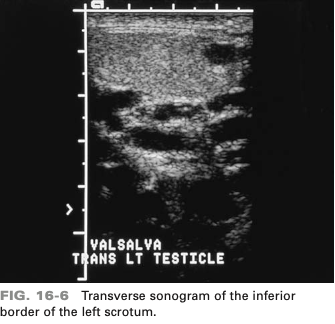
which complications is associated with this abnormality (varicocele)
infertility
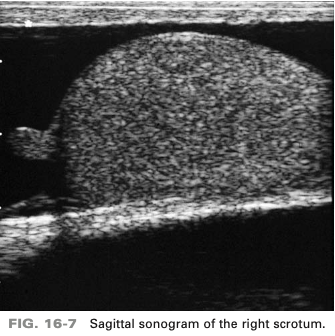
a patient presents with a history of scrotal swelling and tenderness. He denies any scrotal trauma. On basis of clinical history, the sono finding are most consistent with
hydrocele
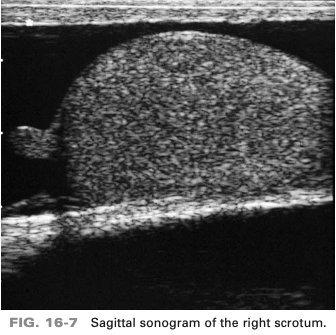
echogenic structure superior to the testes most likely respresents
epididymal head
which condition most commonly causes epididymitis
bladder infection
what region in the prostate most commonly develops benign prostatic hypertrophy (BPH)
transitional zone
twisting of spermatic cord on itself is a predisposing factor of which abnormality
testicular torsion
a 30-year-old patient presents with a low-grade fever and acute testicular pain. An enlarged hypoechoic right testis is demonstrated on ultrasound. Hypervascular flow is the basis of this clinical history, the sono findings are suspicious for
orchitis
sudden onset severe scrotal pain in an adolescent patient is most suspicious for
testicular torsion
the epididymis connects the testes by
rete testes
function of seminal vesicles
stores sperm
majority of blood supplied to prostate gland is through the
capsular artery
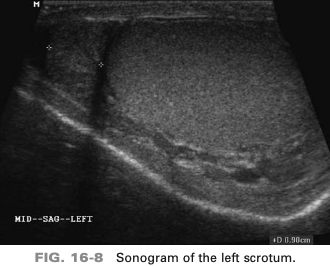
a 45-year-old patient presents with acute scrotal pain after. mountain-biking trip. On the basis of this clinical history, the sono findings are suspicious for
epididymitis
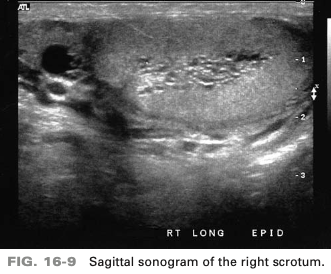
A 76-year-old patient presents with a history of palpable mass in superior portion of the right scrotal sac. A nonvascular cystic mass is identified in the medial portion of the testis. This is suspicious for
tubular ectasia of the rete testis
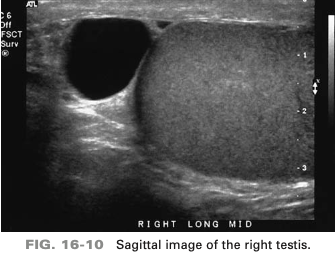
an asymptomatic patient presents with a palpable right scrotal mass discovered during a recent physical exam. The ono finding is most consistent with
spermatocele
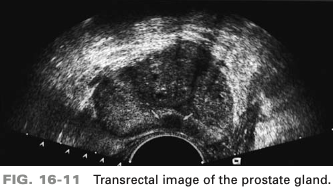
patient presents with history of hematuria and elevated PSA. Neoplasm identified by arrows is in which region of prostate
peripheral zone
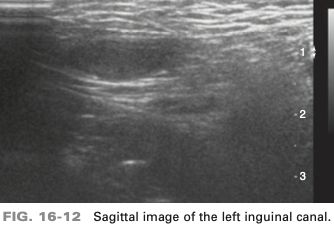
sag image of left inguinal canal in an 8-month-old male infant is most likely
undescended testicle
normal monoclonal level of PSA should not exceed
4 ng/mL
decreased urine output is most commonly linked with abnormality in which structure
prostate gland
location of epididymis is
posterior and lateral to the testis
blood is supplied directly to the epididymis through what artery
cremasteric
what vein receives the left testicular vein
left renal vein
what pathology is the most common cause of acute scrotal pain
epididymitis
what describes the echogenicity and location of seminal vesicles
hypoechoic structure superior to the prostate gland
what artery contains the spermatic cord
cremasteric
A 60-year-old patient presents with a history of urinary frequency and a decrease in urinary out- put. These clinical symptoms are most commonly associated with:
benign prostatic hypertrophy (BPH)
cryptorchidism is associated with an increased risk in developing
testicular torsion
what region of prostate gland compromises only 5% of glandular tissue
transitional zone
what structure lines the prostatic urethra
periurethral gland
sono of mediastinum testis is described as
hyperechoic linear structure loacted in posterior medial aspect of testis
testes are formed by what
mesencymal duct
prostate is formed by what
urogenital sinus
clinical sign of torsion of appendages
blue dot sign
m.c tumour in prepubertal children, causes high AFP
yolk sac tumour
leydig tumours secrete
testosterone
sertoli tumours are hormone inactive but some secrete
estrogen
peripheral zone is ___ % of gland
70
BPH usually occurs in _______ zone
transitional
m/c cause for elevated PSA
BPH
benign enlargement of prostate occurs in
transition zone