Carbohydrates and Lipids
5.0(1)
5.0(1)
New
Card Sorting
1/80
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
81 Terms
1
New cards
carbohydrates are made out of carbon hydrogen and oxygen, lipids are made out of carbon hydrogen oxygen and some times phosphate (only in phospholipids)
How are carbohydrates and lipids chemically different?
2
New cards
Carbs are used for short term energy storage and fast energy, lipids are used for long term energy storage and insulation
How do carbs and lipids differ in function?
3
New cards
carbohydrates in general
CH2O is the general formula for…
4
New cards
C6H12O6
chemical formula for glucose
5
New cards
glucose, fructose, galactose
3 monosaccharides
6
New cards
lactose, maltose, sucrose
3 disaccharides
7
New cards
maltose
glucose - glucose
8
New cards
sucrose
glucose + fructose
9
New cards
lactose
glucose + galactose
10
New cards
isomer
molecules with the same chemical formula but different structure (ex. glucose, fructose, and galactose)
11
New cards
plants
Where is glucose found?
12
New cards
fruit, corn
where is fructose found?
13
New cards
parts of milk sugar
where is galactose found?
14
New cards
C12H22O11
chemical formula for disaccharides
15
New cards
an anabolic process used to build a macromolecule
dehydration synthesis
16
New cards
when 2 monomers combine, an OH (hydroxyl) group and H (hydrogen molecule) are removed and form its own molecule (H2O)
explain dehydration synthesis
17
New cards
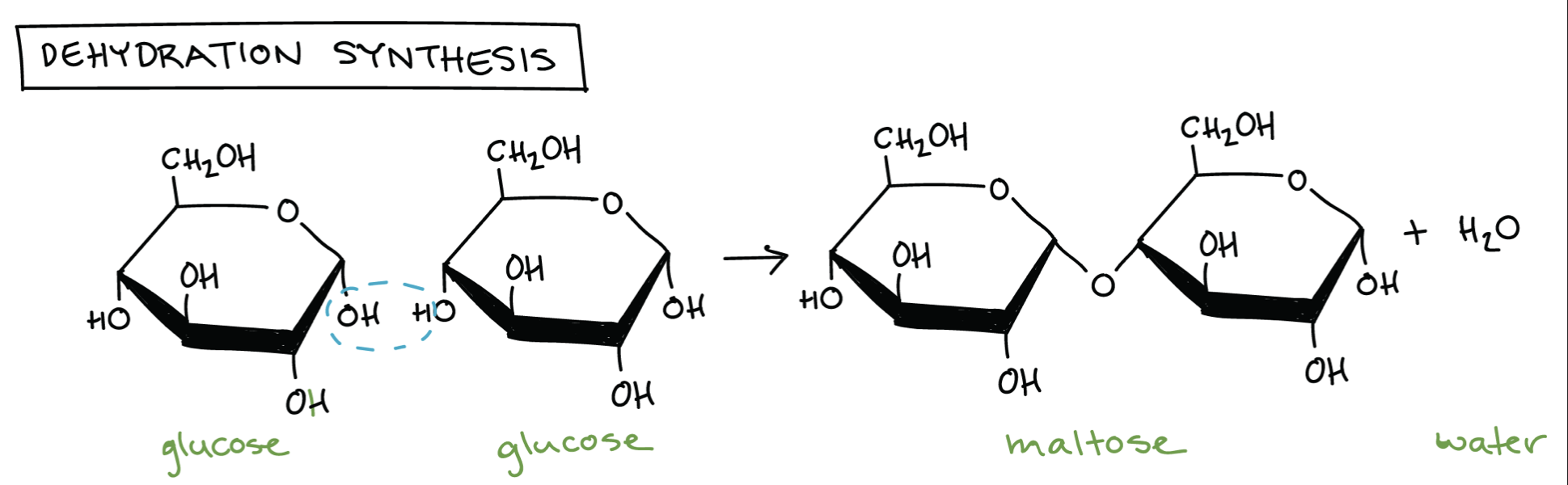
dehydration synthesis
18
New cards
a long chain of glucose
what is a polysaccharide
19
New cards
starch, glycogen, cellulose, chitin
four polysaccharides
20
New cards
potatoes, rice, grains
where is starch found
21
New cards
cell walls of fungi, exoskeletons of artheropods
where is chitin found
22
New cards
cell walls of plants
where is cellulose found
23
New cards
liver
where is glycogen found
24
New cards
beta bonds hold glucose molesules
info on cellulose
25
New cards
alpha bonds hold glucose molecules
info on starch
26
New cards
beta bonds hold glucose molecules
info on chitin
27
New cards
alpha bonds hold glucose molecules
info on glycogen
28
New cards
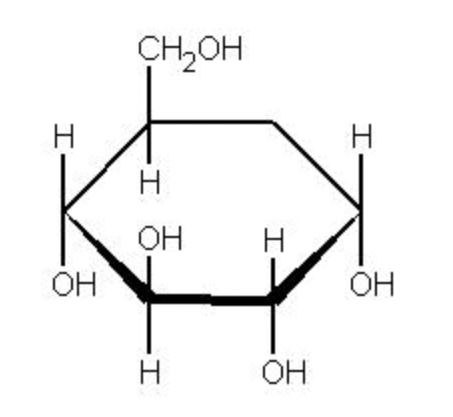
alpha glucose
29
New cards
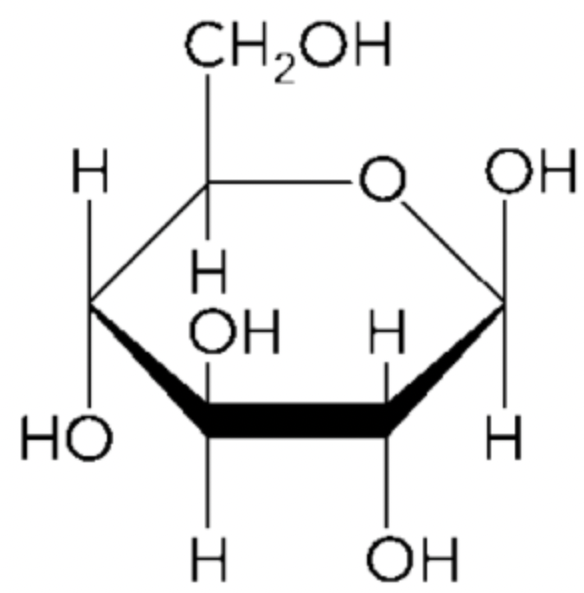
beta glucose
30
New cards
glycosidic
What is the name of the bond that links two alpha glucose molecules?
31
New cards
glycosidic
What is the name of the bond that links two alpha glucose molecules?
32
New cards
we don’t have the enzymes for it
why can’t we digest (break down) the bond that holds two beta glucose molecules together?
33
New cards
glycogen is a polymer, glucose is a monomer. glucose is found anywhere and glycogen is found in the liver
What are some differences between glycogen and glucose?
34
New cards
alpha glycosidic
what bond holds starch
35
New cards
alpha glycosidic
what bond holds glycogen
36
New cards
beta glycosidic
what bond holds cellulose
37
New cards
beta glycosidic
what bond holds chitin
38
New cards
ester
what bond holds triglycerides
39
New cards
Oils, Animal products, Milk products
Where are fats found in your diet (in what foods)?
40
New cards
grains, Starches, Fruit, corn
Where are carbs found in your diet (in what foods)?
41
New cards
3 fatty acids and glycerol
What are the building blocks of fats?
42
New cards
no kink, no double bond, solid at room temp
info on saturated fats
43
New cards
kink and double bond, liquid at room temp, if there’s just a double bond it doesn’t mean its unsaturated
info on unsaturated fats
44
New cards
red meat, animal fats
saturated fatty acids examples
45
New cards
oils
unsaturated fatty acids examples
46
New cards
heart disease when someone has too much fat in their diet
how is atherosclerosis caused
47
New cards
deposit of fatty plaque blocks blood flow in the coronary artery (lumen) which brings blood and nutrients to the heart
what happens when you have atherosclerosis
48
New cards
heart attack from blocked blood flow
what can atherosclerosis result in
49
New cards
when you digest food, you produce CO2 and it travels through your lungs to get breathed out OR We produce carbon dioxide and out body produces water and with oxygen you have CO2
how is CO2 in your blood?
50
New cards
3 fatty acids and a glycerol
what are triglycerides produced from
51
New cards
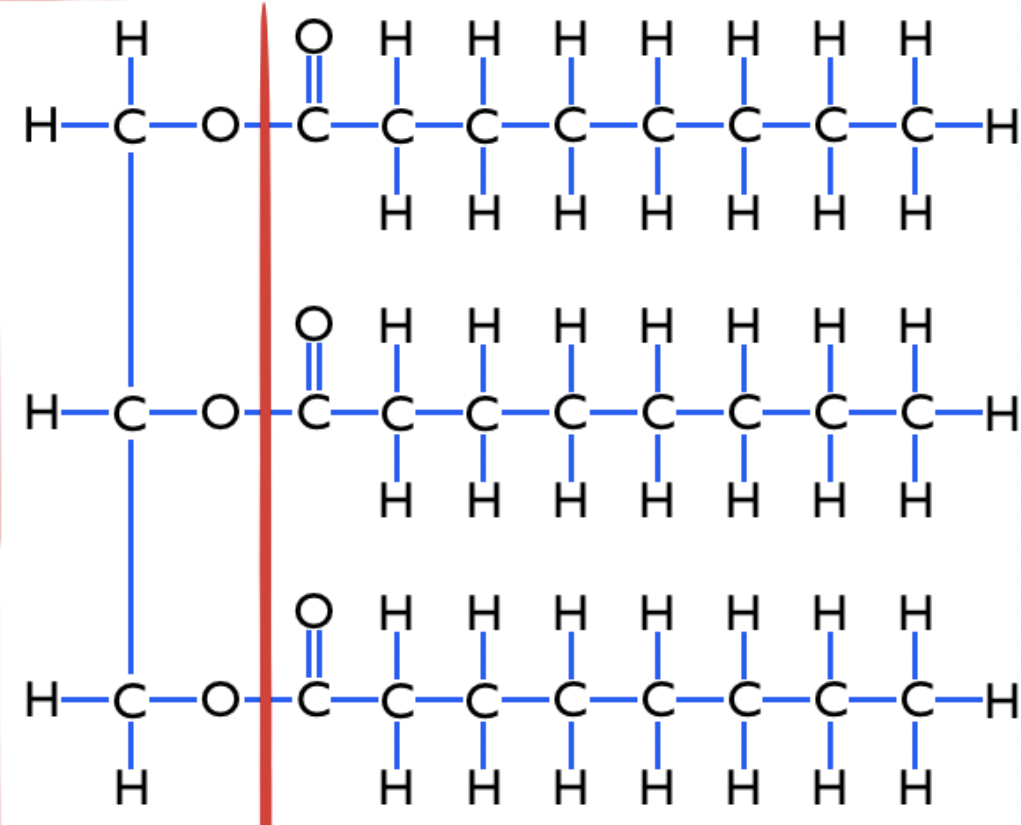
triglyceride (photo)
52
New cards
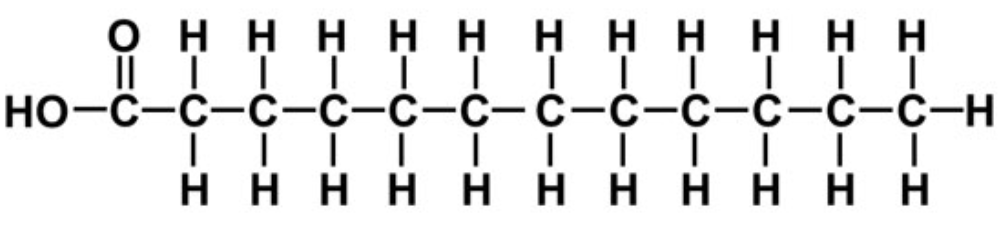
saturated fatty acid
53
New cards
saturated fatty acid
54
New cards
fatty acid
long carbon chain and with a carboxyl group at one end
55
New cards
cell membrane
where are phospholipids found in
56
New cards
2 fatty acids attached to one glycerol and a phosphate
what are phospholipids made out of
57
New cards
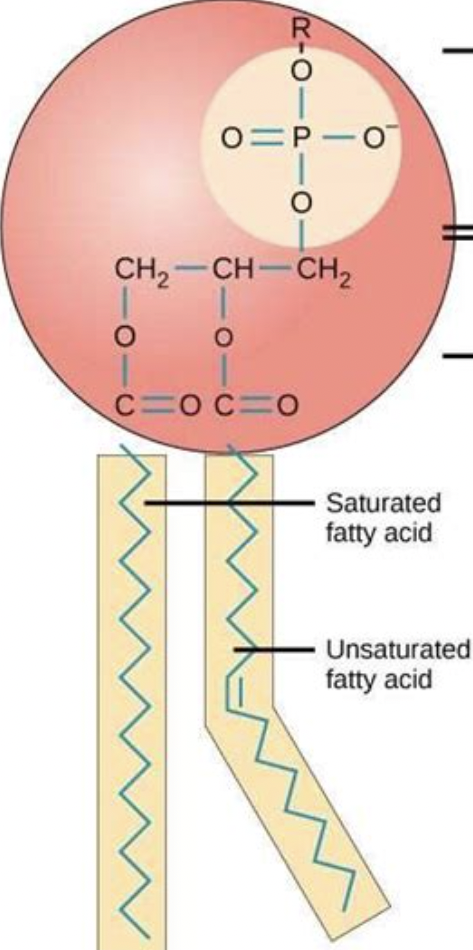
phospholipid pic
58
New cards
polar, hydrophilic
describe the head
59
New cards
non-polar, hydrophobic
describe the tail
60
New cards
they line up
what happens when you put phospholipids in water?
61
New cards
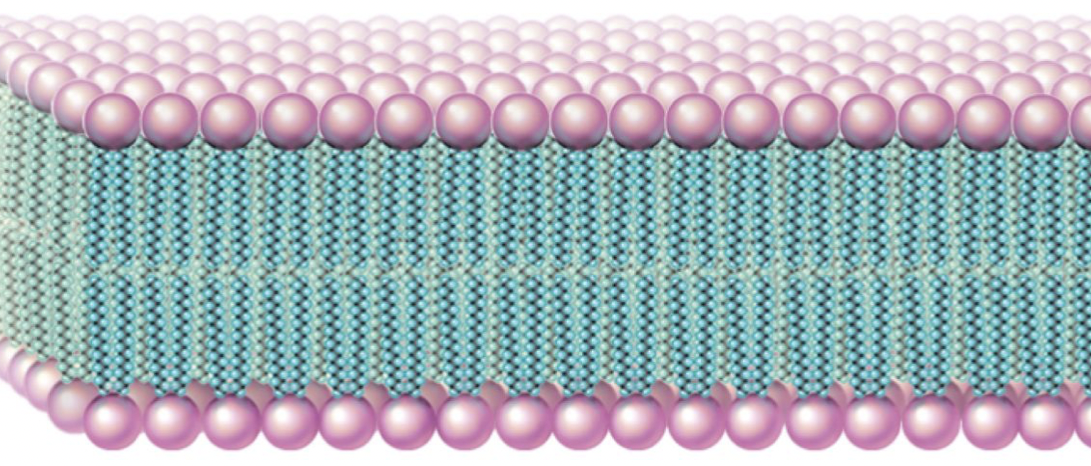
phospholipids bilayer
62
New cards
reproductive hormones, bile, cortisone, vitamin D, and colesterol
where are steroids found
63
New cards
bile
anything that breaks up larger molecules (fat in this case) into smaller molecules
64
New cards
4 fused carbon rings
what is the structure of cholesterol?
65
New cards
a male hormone
what is Testosterone
66
New cards
a female hormone
what is Progesterone
67
New cards
a female hormone
what is estrogen
68
New cards
cortisone
anti inflammation hormone
69
New cards
Testosterone, Estrogen, Progesterone, Cortisone, bile, BUT cholesterol is the base of all steroids
which steroids need cholesterol to be built?
70
New cards
Working out more + reduce intake of animal products
how to help people with high cholesterol
71
New cards
Methyl group
CH3
72
New cards
glycosidic
What is the bond between any 2 monosaccharides?
73
New cards
Hydroxyl group
OH
74
New cards
carboxyl group
COOH
75
New cards
CHO
what elements are triglycerides made from
76
New cards
CHOP
what elements are phospholipids made from
77
New cards
insulation, long term energy storage, energy, padding/cushioning
functions of lipids
78
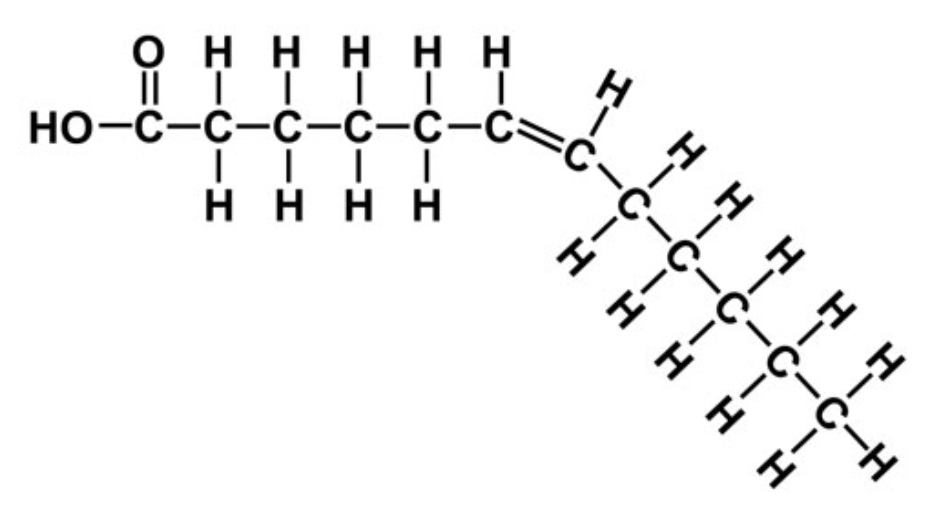
New cards
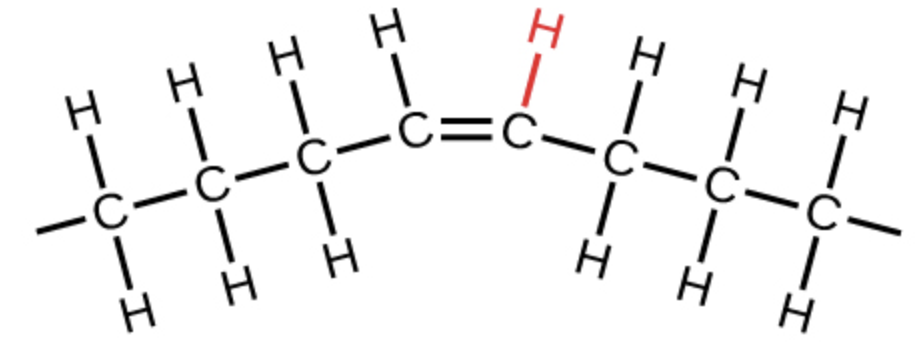
cis fats pic
79
New cards
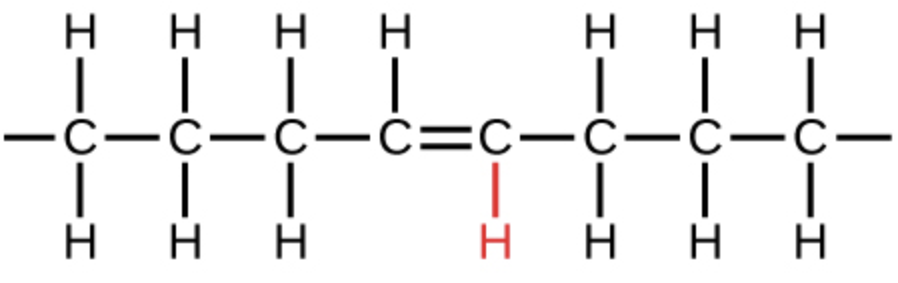
trans fats pic
80
New cards
H is at the top
cis fats
81
New cards
H is at the bottom
trans fats