Gene Expression
1/42
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
43 Terms
What is gene expression?
The process of transcription and translation where genes are expressed as proteins.
What role do transcription factors play in gene expression?
Transcription factors are DNA-binding proteins that can activate or repress transcription by influencing RNA polymerase's ability to bind to the promoter.
What is the promoter?
A DNA sequence that enables the transcription of a particular gene, serving as a binding site for RNA polymerase.
What is the difference between exons and introns?
Exons are coding regions of a gene that are expressed, while introns are non-coding regions that are removed during mRNA splicing.
What is mRNA splicing?
The process of removing introns and joining exons in a pre-mRNA transcript to produce mature mRNA.
What is alternative splicing?
A process that allows a single gene to code for multiple proteins by varying the combination of exons included in the final mRNA.
What is the difference between genomic DNA and cDNA?
Genomic DNA contains the complete set of genes, while cDNA is synthesized from mRNA and represents only the expressed genes.
What is transcriptional regulation?
The control of the amount and timing of mRNA production from a gene.
What is post-transcriptional regulation?
Regulation that occurs after transcription, affecting mRNA stability, splicing, and translation.
What are small non-coding RNAs?
RNA molecules that do not code for proteins but play roles in regulating gene expression at the transcriptional and post-transcriptional levels.
What is the proteasome?
A protein complex that degrades unneeded, damaged, or misfolded proteins by proteolysis.
Why do different cell types express different proteins?
Different cell types express different proteins due to variations in gene expression regulation, despite having the same DNA.
How does chromatin modification affect gene expression?
Tightly packaged chromatin limits RNA polymerase access to genes, reducing transcription; loosely packaged chromatin allows more access, increasing transcription.
What is epigenetics?
The study of changes in gene expression caused by mechanisms other than changes in the underlying DNA sequence, often involving chemical modifications to DNA and histones.
How does DNA methylation affect gene expression?
Methylation of DNA leads to tighter packing of chromatin, preventing transcription and gene expression.
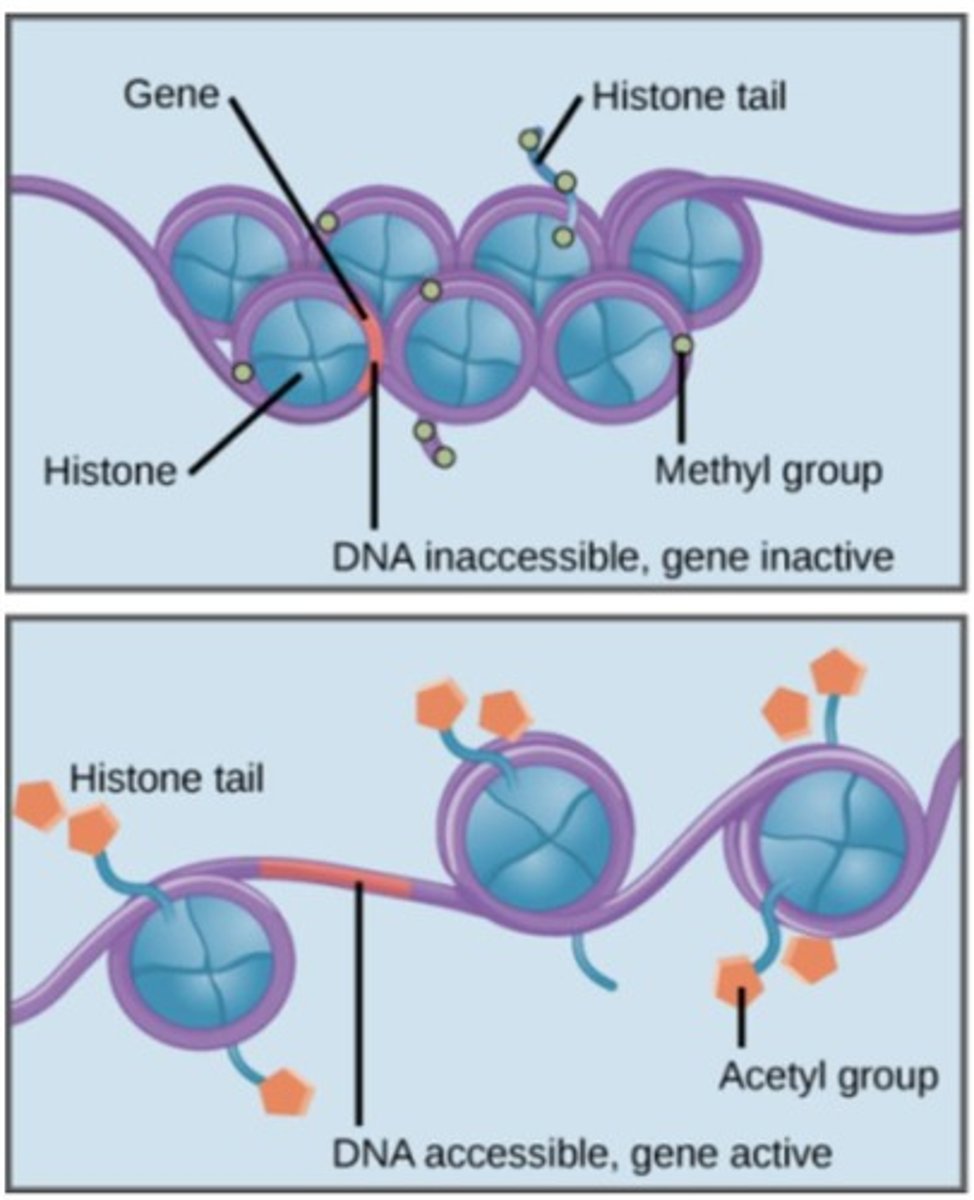
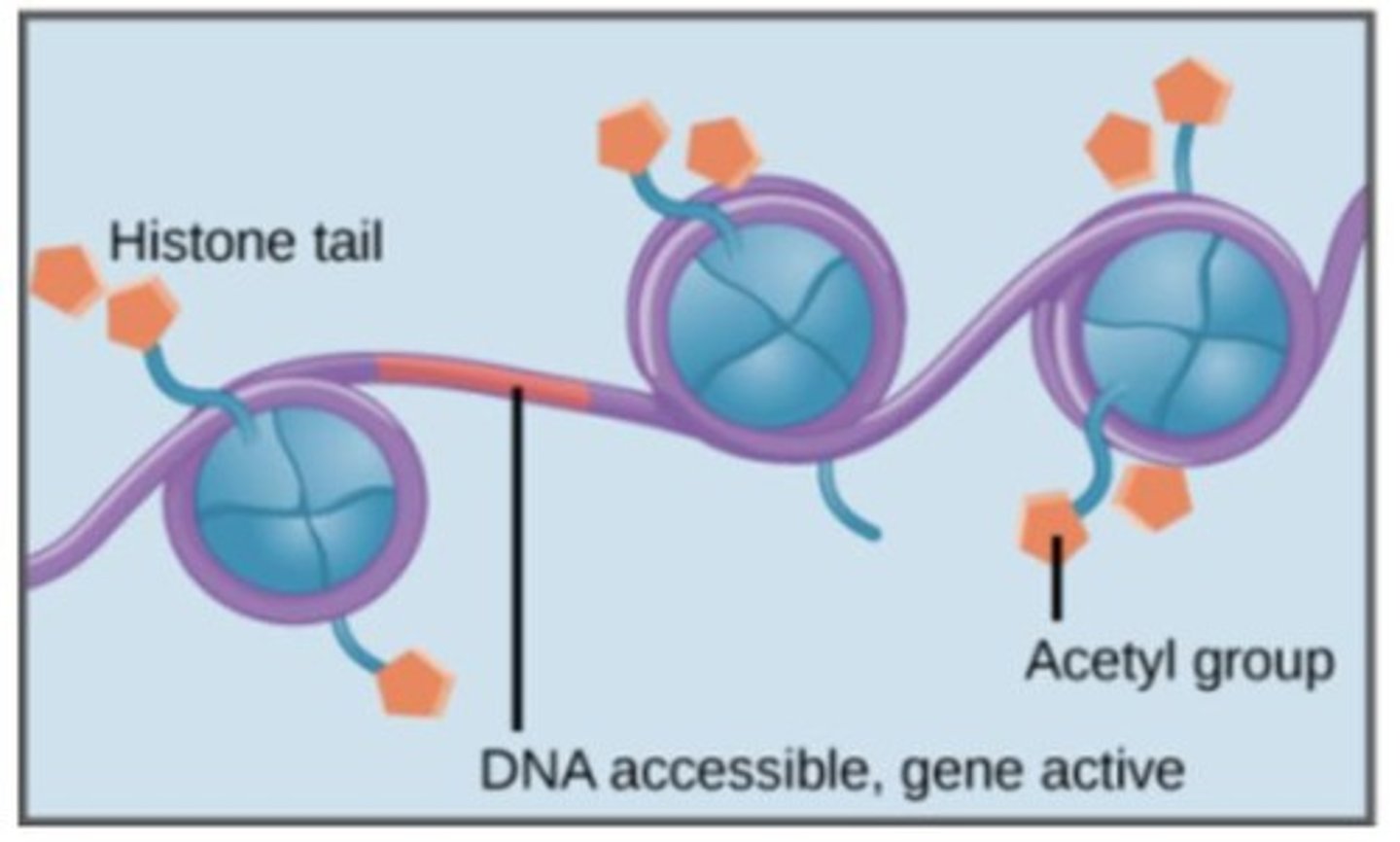
What is histone acetylation?
A chemical modification that adds acetyl groups to histones, leading to looser chromatin structure and increased gene expression.
What is the significance of the combination of transcription factors?
The combination of transcription factors determines the specific regulation of gene expression, integrating multiple signals for precise control.
What happens to gene expression in response to extracellular signals?
Gene expression can change quickly in response to extracellular signals, allowing cells to adapt to environmental changes.
What is the role of RNA polymerase in transcription?
RNA polymerase is the enzyme that synthesizes RNA from the DNA template during transcription.
How do activators and repressors affect transcription?
Activators enhance transcription by helping RNA polymerase bind to the promoter, while repressors inhibit transcription by making it harder for RNA polymerase to bind.
What is the relationship between DNA, RNA, and proteins?
DNA is transcribed into RNA, which is then translated into proteins; this is often summarized as DNA makes RNA makes protein.
What is methylation in gene expression?
The addition of methyl groups to DNA, which generally leads to less transcription.
What is acetylation in gene expression?
The addition of acetyl groups to DNA, which generally leads to more transcription.
How is gene expression regulated by epigenetic enzymes?
By activating or inhibiting the enzymes that add or remove methyl and acetyl groups.
Where does transcription occur in eukaryotes?
In the nucleus.
Where does translation occur in eukaryotes?
In the cytoplasm.
What is the main difference in transcription between prokaryotes and eukaryotes?
In prokaryotes, transcription and translation occur simultaneously in the cytosol, while in eukaryotes, they are separated by the nuclear membrane.
What percentage of eukaryotic DNA is coding?
Only about 2% of the DNA is coding.
What are exons?
The coding parts of genes that are expressed.
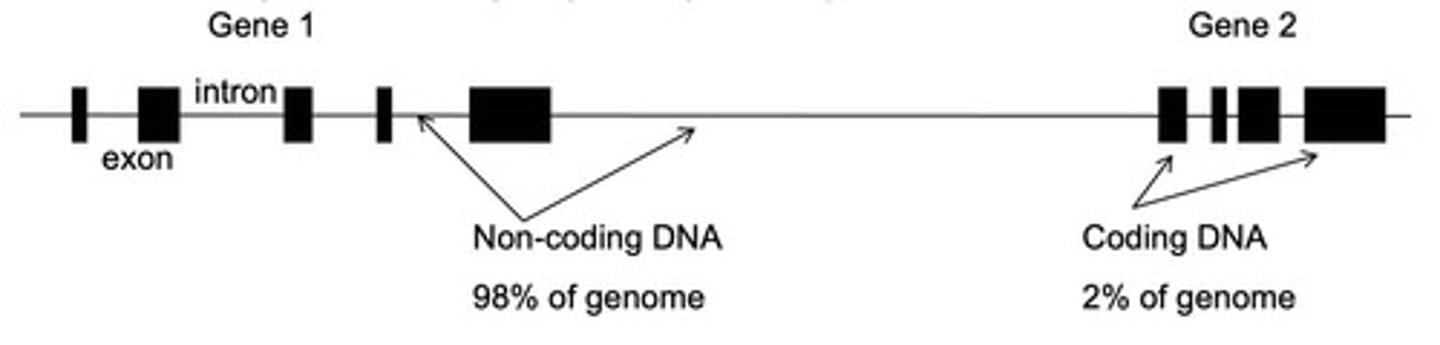
What are introns?
The non-coding parts of genes that are removed during RNA splicing.
What is splicing?
The process of removing introns from RNA transcripts and assembling exons in the correct order.
Why is cDNA useful in research?
It is smaller and more stable than genomic DNA, making it easier to work with.
What role do small non-coding RNAs play in gene regulation?
They regulate gene expression by degrading mRNA or blocking its translation.
What are miRNAs?
Micro RNAs that regulate gene expression by binding to target mRNAs.
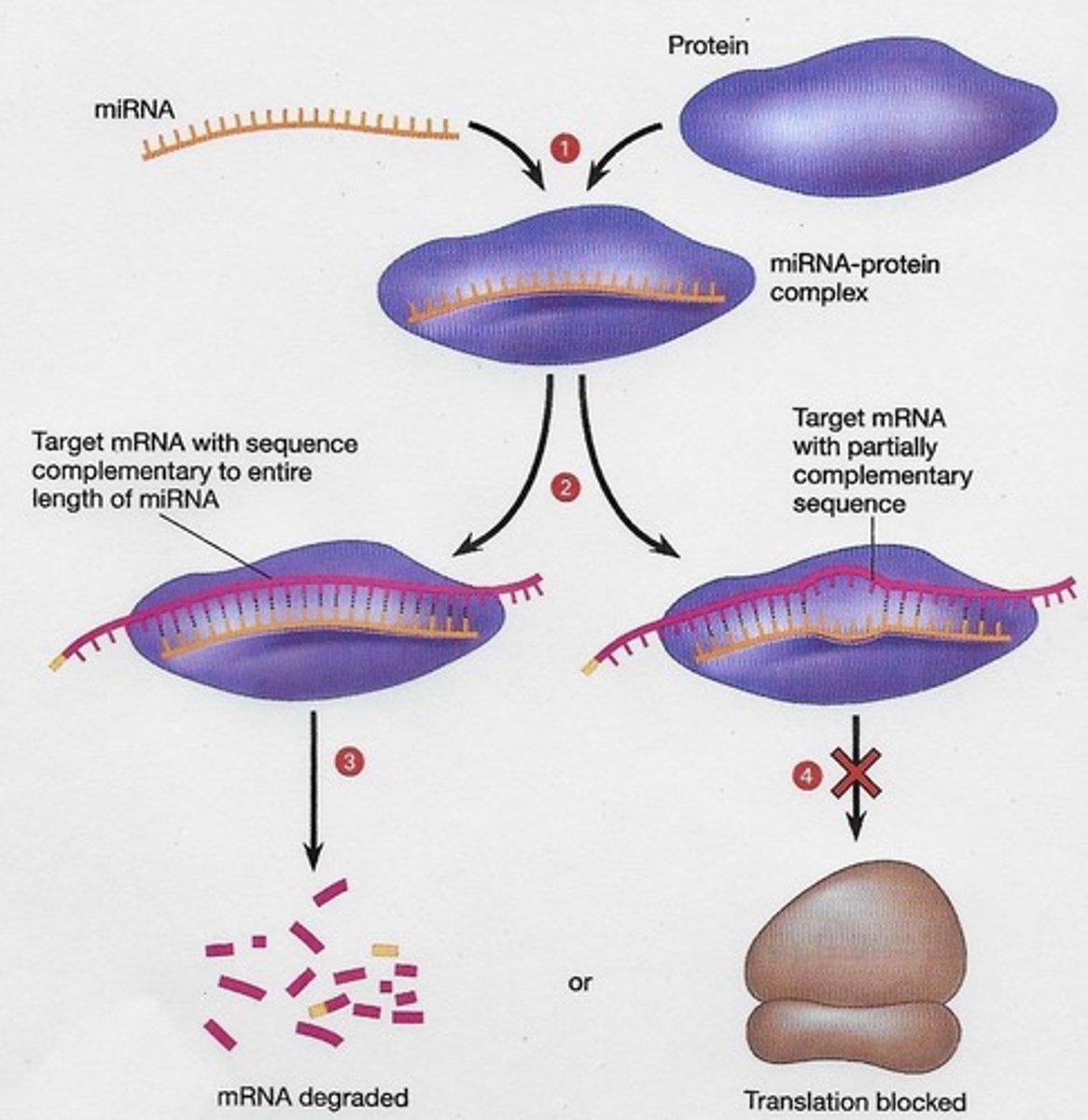
What is gene knockdown?
A method used to block the expression of a specific gene to study its function.
How does ubiquitin ligase function in protein degradation?
It adds ubiquitin to target proteins, marking them for destruction by the proteasome.
What is the significance of transcription factors?
They act on promoters to regulate transcription in eukaryotic cells.
What is chromatin remodeling?
Changes to DNA structure that make it more accessible for transcription.
What are the two main levels of gene expression regulation?
Transcriptional regulation and post-transcriptional regulation.
What is RNA processing?
The modification of RNA after transcription, including splicing and transport.
What happens during mRNA transport?
mRNA is exported from the nucleus to the cytoplasm for translation.
What is the role of small interfering RNAs (siRNAs)?
They are used to knockdown gene expression in laboratory experiments.
What is the relationship between protein activity and cellular signals?
Some proteins need to be activated by signals such as proteolysis or chemical modification.