Biology Unit 5 Cell Energetics IHS Skavaril
1/44
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
45 Terms
Photosynthesis equation
6𝐶𝑂2 + 6𝐻2𝑂 → 𝐶6𝐻12𝑂6 + 6𝑂2
Cellular respiration equation
𝐶6𝐻12𝑂6 + 6𝑂2 → 6𝐶𝑂2 + 6𝐻2𝑂
Cellular respiration
Process where cells turn glucose into ATP
Where does cellular respiration happen
Mitochondria
Matter
Something that you can hold — made of atoms
Energy
Something you cannot hold
What is stored in bonds between atoms
Energy
High energy bonds
Occurs between C-C and C-H bonds
How many phosphate groups does ADP have
Two
How many phosphate groups does ATP have
3
Does ATP or ADP have more energy
ATP
Reactants of photosynthesis
CO2 & H2O
What molecules gives plants material to make glucose
CO2 & H2O
Where does the energy for photosynthesis comes from
Sun
Products of photosynthesis
C6H12O6 (glucose) & O2
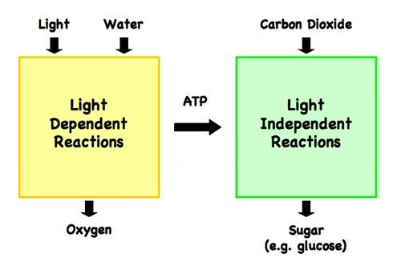
Where is photosynthesis performed
The chloroplasts; light dependent reactions in thylakoids, light independent reactions in stroma
What two parts does chloroplasts contain
The thylakoid and stroma
Inputs of light dependent reactions
Energy (red and blue light) & H2O (provides the matter)
Outputs of light dependent reactions
O2
Inputs of light independent reactions
ATP, NADPH, & CO2 (provides the matter)
ATP & NADPH are created from light dependent reactions
Outputs of light independent reactions
G3P & C6H12O6
What provides the energy for light independent reactions to occur
ATP & NADPH
How does NADP+ turn into NADPH
The process of reducing H2O into O2 releases/loses electrons, which is captured by NADP+, turning to NADPH
How does ADP turn into ATP
Some of the energy transferred from the light is used to make ATP
How does NADPH turn back into NADP+
Oxidizing CO2 into C6H12O6 requires electrons, and NADPH gives up its electrons to CO2 for the oxidization process to happen, turning back into NADP+
How does ATP turn back into ADP
As it is being converted back to ADP, it energizes the Calvin cycle, giving it the energy it needs to convert CO2 → C6H12O6
Calvin cycle
The part of photosynthesis where energy (ATP/NADPH) is used to convert CO2 into C6H12O6
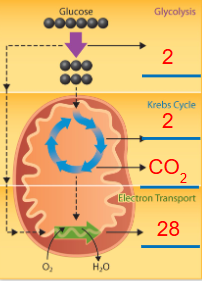
Glycolysis
First step of aerobic respiration
Does not require oxygen
Process where one glucose molecule is broken into two pyruvates (3-carbon molecules), releasing some energy
Occurs in cytoplasm
Yields NADH (electron carriers) — NAD+ becomes charged takes the energy released from the breaking of the glucose molecule
Generates 4 ATP but needs 2 ATP = net yield of 2 ATP
Krebs Cycle
Second step of aerobic respiration
Requires oxygen
Process where nutrients (the pyruvates) is taken and broken down to release stored energy
Occurs in mitochondria
Yields NADH & FADH2 (electron carriers) — NAD+ & FAD become charged after takes the stored energy released from breaking down nutrients
Generates 2 ATP
Waste product/output: CO2
Electron Transport Chain
Third step of aerobic respiration
Requires oxygen - final electron acceptor, forming H2O
Process where activated carriers (NADH & FADH2) donate electrons, creating a proton gradient essential for ATP synthesis, which drives the production of ATP—tldr; stage where energy from food/nutrients is converted into useable ATP
Occurs in mitochondria
Generates 28 ATP
Waste product/output: H2O
How many ATP does one glucose molecule typically yield in aerobic respiration
32 ATP
Alcoholic fermentation
Done by fungi, bacteria, etc.
Glycolysis occurs (NAD+ → NADH, ADP → ATP, two pyruvates)
The two pyruvates will produce CO2 and two ethanol molecules
NADH is oxidized (lose electrons/releases energy), converting back to NAD+ so glycolysis can occur again
Occurs in cytoplasm
Waste product/output: ethanol
Lactic acid fermentation
Done by cells (e.g. muscle cells)
Glycolysis occurs (NAD+ → NADH, ADP → ATP, two pyruvates)
The two pyruvates will produce two lactic acid
NADH is oxidized (lose electrons/releases energy), converting back to NAD+ so glycolysis can occur again
Occurs in cytoplasm
Waste product/output: lactic acid
How many ATP does one glucose molecule typically yield in anaerobic respiration
2 ATP
What are the charged versions of:
NADP+*
NAD+
FAD
ADP*
BOLD = Electron carriers
* = For photosynthesis (has P in formula)
H in formula = charged carrier
NADPH*
NADH
FADH2
ATP*
BOLD = Electron carriers
* = For photosynthesis (has P in formula)
H in formula = charged carrier
What is the end goal of cellular respiration
ATP
What can G3P used to make
All carbon-based molecules
Why is glucose specifically important
It has high energy bonds; the energy in that bond comes from the sun
What form does carbon go into as in the light independent reaction
CO2
What form does carbon go out as in the light independent reaction
G3P
When it’s hot, plants close their leaf hole, which allow gases to enter the leaf–would more photosynthesis occur or less?
Less photosynthesis because no CO2 can enter the leaf, so there is no building of G3P
Where does energy start in cellular respiration
Glucose
Where does energy end up in cellular respiration
32 ATP
How fast is the breakdown of glucose
Happens slowly over multiple steps
Why does glycolysis and Krebs cycle matter if ETC makes the most ATP
They charge the electron carriers to be able to produce the ATP in ETC