NCEA Biology Scholarship: patterns of macro-evolution speciation
1/7
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
8 Terms
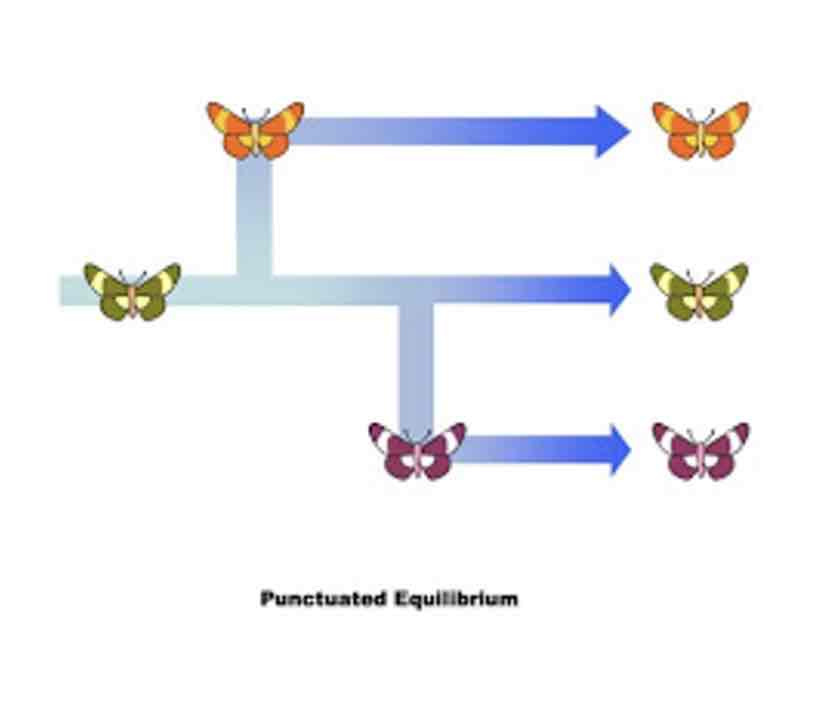
Punctuated equilibrium
Where one species gradually evolves into a new species overtime
Very long and slow process
Very slow changes to the environment
Slow, steady rate of change
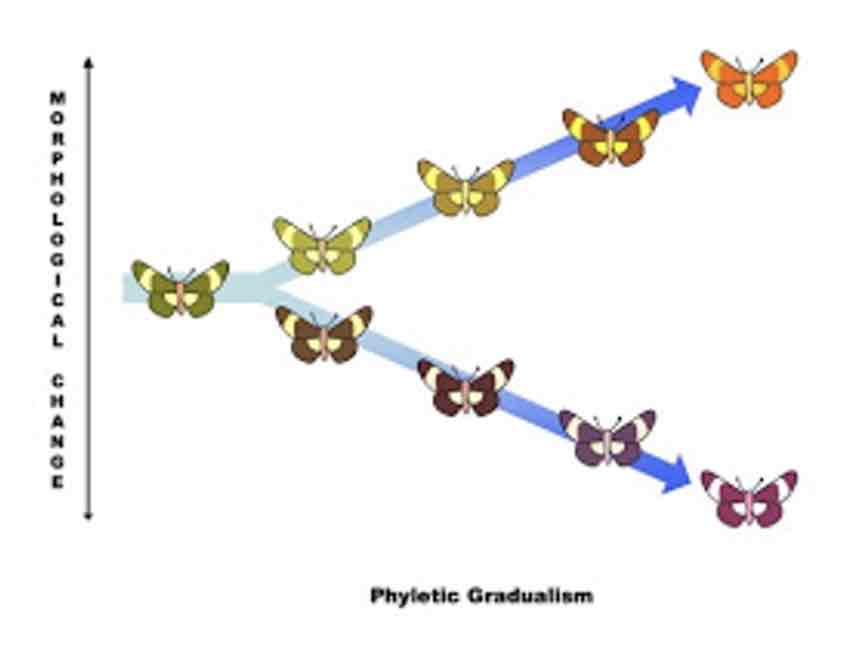
Phyletic Gradualism
Long periods of stasis punctuated by rapid speciation events
Change in selective pressures, forces species to adapt
Long period of stasis—nothing changes until all of a sudden drastic event occurs causing species to adapt to differing selective pressures
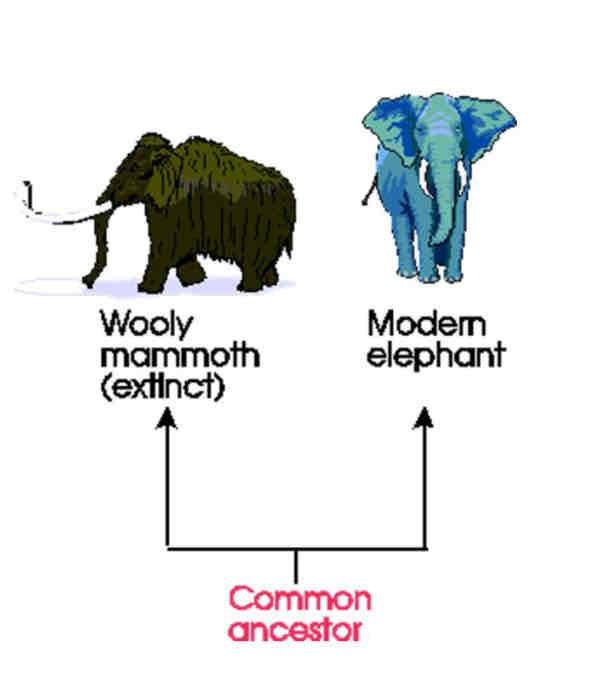
Parallel evolution
Where two related species arise from a common ancestor. The two species then evolve in the same way over time, likely in response to similar environmental selection pressures.
Often comes from divergent evolution
Both species evolve at the same time and rate
Gradualism—occurs over a long period of time
Shared homologous structures proof that two species share common ancestors
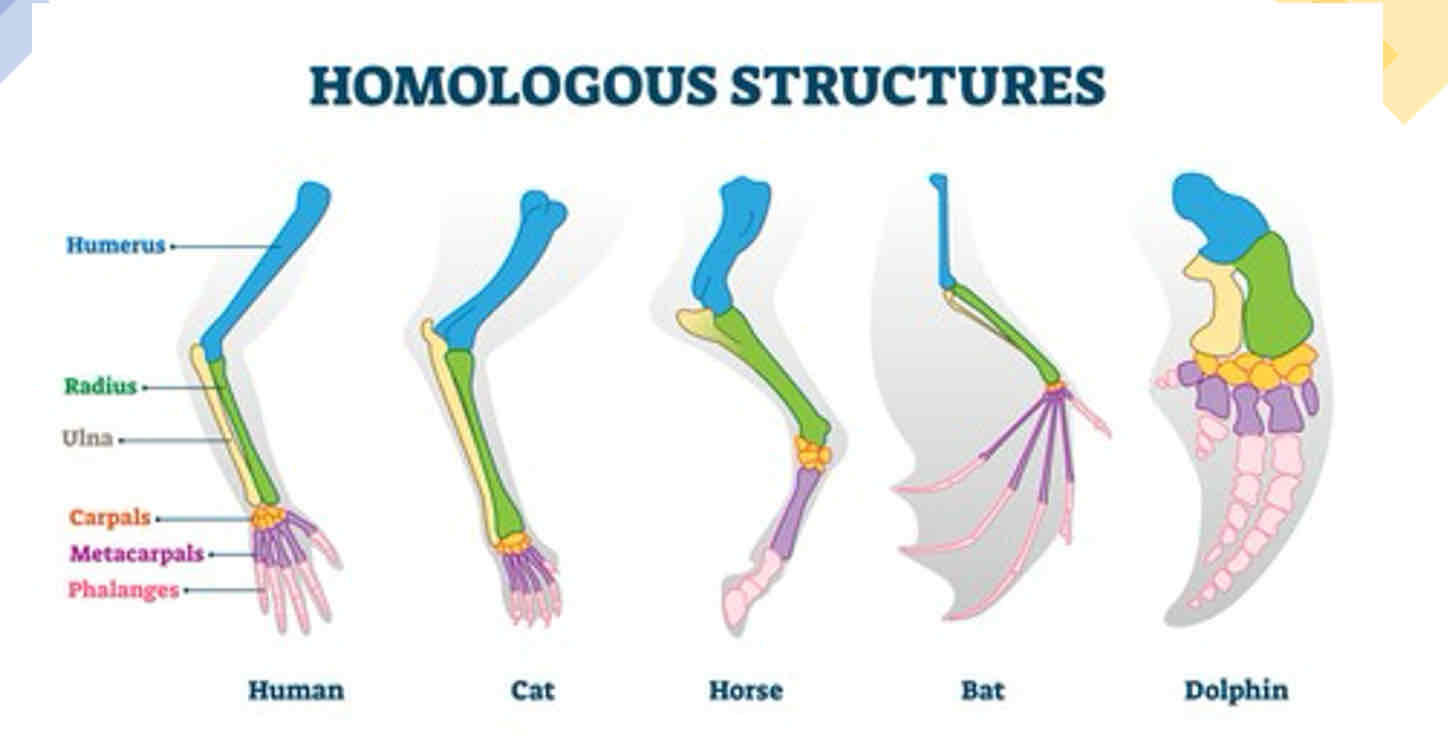
Homologous structures
Evidence two species have a common ancestor is that they share similar features, such as an organ, system, or body part—these features are called homologous structures
E.g. all mammals share a common ancestor as they all share homologous structures
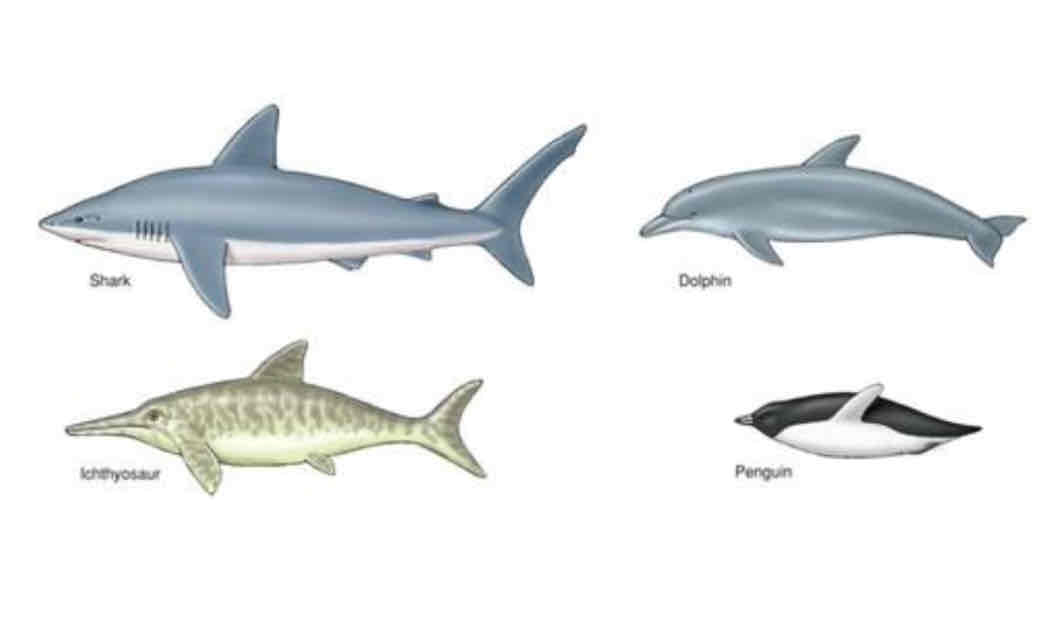
Convergent evolution
Where two unrelated species evolve similar features due to similar selection pressures
Analogous features evident
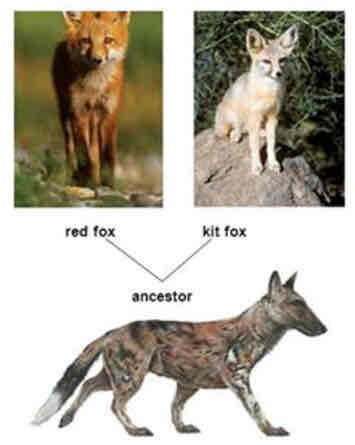
Divergent evolution
Where two seperate species evolve from one common ancestor.
Homologous structures are evidence of this type of evolution
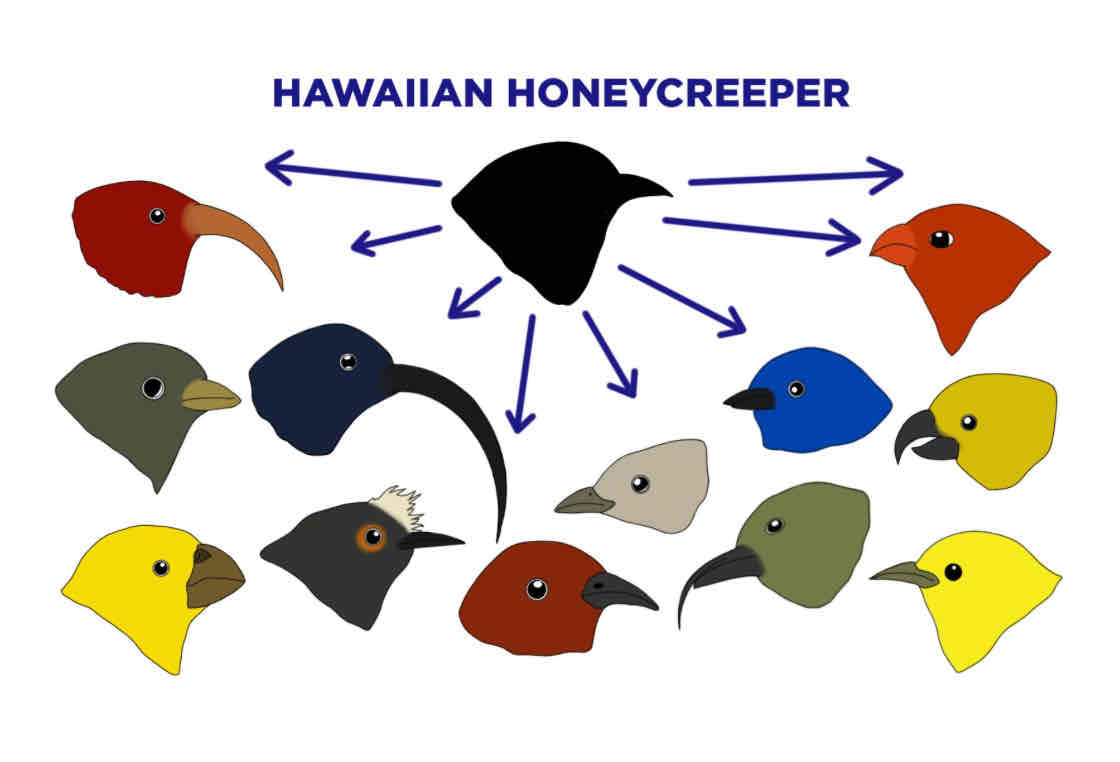
Adaptive radiation
Where more than one species evolve from one common ancestor
Occurs due to the opening up of new niches and rapid bursts of evolution (punctuated)
Occurs as punctuated event opened up lots of new niches, empty habitats + food sources, adapted to fill these spaces
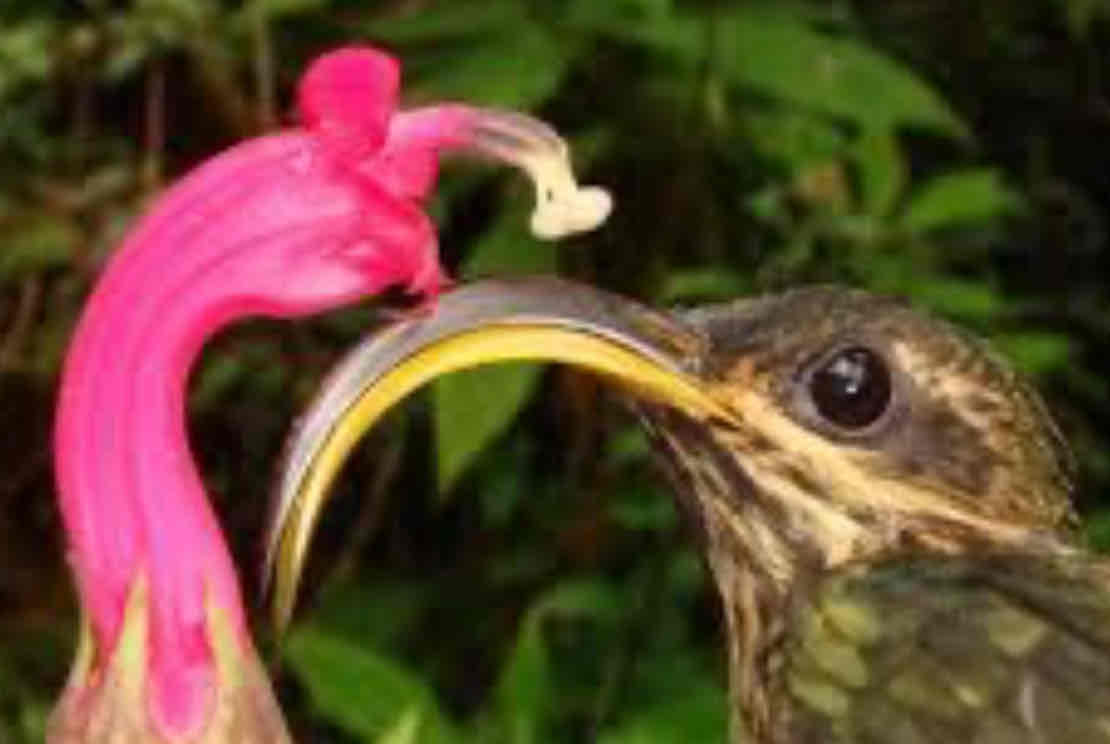

Co-evolution
Where two unrelated species that have a close relationship become selection pressures for each other—when one evolves, the other does too
If one becomes extinct, the other will become extinct
Mutualism—both individuals in species gain a survival advantage
Survival advantage—e.g. no other bird species to compete with in taking nectar from flower