L2 - Neurons and Glia
1/30
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
31 Terms
Reticular Theory
Argues that neurons are a fused, continuous “web” of interconnected fibers.
Neuron Doctrine
Argues that neurons are individual cells that communicate with each other by contact at synapses.
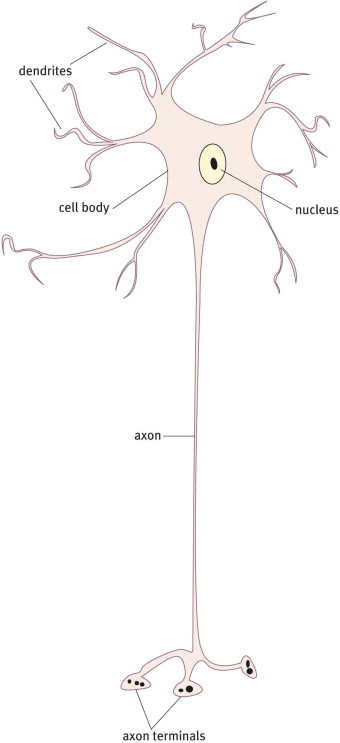
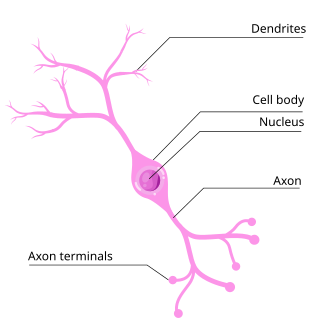
Soma
Region of the neuron that contains the nucleus and other organelles; processes information and signals to the next neuron.
Dendrite
Neurite that receives inputs from other neurons
Axon
Neurite specialized to conduct action potentials across the nervous system.
Axon hillock
The beginning of the axon that extends from the soma.
Axon proper
The middle part of the axon, covered in myelin sheath.
Axon terminal
The site where the axon comes in contact with other neurons and passes information on to them.
Axon collaterals
Branches of the axon
Recurrent collaterals
Axon collaterals that return to the original cell, or communicate with the dendrites of neighboring cells
Synapse
The point of contact between two neurons
Synaptic Cleft
The space between the presynaptic and postsynaptic membranes
Unipolar neuron
Neuron with one neurite extending from the soma
Bipolar neuron
Neuron with two neurites extending from the soma
Multipolar neuron
Neuron with multiple neurites extending from the soma
Spiny neurons
Neuron whose dendrites have spines
Aspiny neurons
Neuron whose dendrites do not have spines
Sensory neurons
Neurons that register a change in the environment (sensory information) from the environment and sends a signal to the brain.
Motor neuron
Neurons that communicate information from the brain to tissues and organs throughout the body, allowing for movement.
Interneuron
Neurons that serve as a relay between sensory and motor neurons in the nervous system. Form connections only with other neurons
Glia
Cells in the brain that insulate, nourish, support, and clean the brain
Myelinating glia
Provide layers of membrane that insulate and speed up axons called myelin.
Node of Ranvier
Periodical gaps in the myelin sheath where the axonal membrane is exposed.
Schwann cells
Myelinating glial cells found in the peripheral nervous system (PNS)
Oligodendroglial cells
Myelinating glial cells found in the central nervous system (CNS)
Microglia
Known as the brain’s “resident immune cells,” functioning as phagocytes to remove debris left by dead or degenerating neurons and glia.
Synaptic pruning
Microglia help remove unnecessary synapses during brain development and learning -> important for refining brain circuits.
Ependymal Cell
Lines the ventricles of the brain and central canal of the spinal cord and is essential for developing cerebral-spinal fluid.
Astrocytes
Star shaped glial cells that fill the space between neurons, support and nourish the brain, help form the blood-brain barrier, and regulate neural activity.
Immunohistochemistry
Use of antibody that binds to a protein target to detect and visualize target proteins within tissue sections
In Situ Hybridization
Uses labeled RNA probes to bind to complementary mRNA sequences, revealing gene expression patterns within individual cells.