GastroIntestinal Track (GI Track)
1/16
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
17 Terms
Gastrointestinal Track (GI Track)
Also called “Alimentary Canal”
One way tube from the mouth to the anus
Order: Mouth, pharynx, oesophagus, stomach, small and large intestines
~7m long
Nutrient absorption (NOT digestion, absorption) is maintained through positive feedback sans some exceptions
Calcium & Iron absorption is regulated based on body’s needs
GI Track: Accessory Organs/structures
Step 0: Mouth, teeth, salivary glands
Begins digestive process.
Teeth aid in mechanical digestion
GI Track
Step 1: Mouth (Oral Cavity)
Chews and mixes food with saliva
Amylase enzyme breaks down polysaccharides in sugar/carbohydrates into glucose/simpler sugar molecules
GI Track
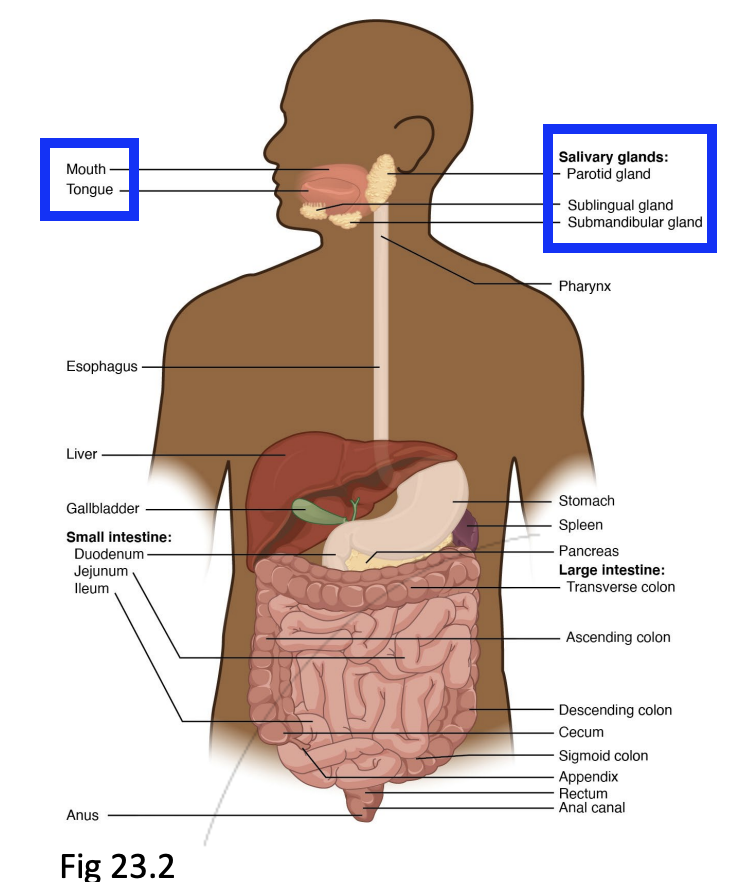
Step 2: Pharynx (Back of the mouth, past the Uvula)
Epiglottis shuts the trachea, allowing food to pass down the oesophagus
Food passes from the mouth into the oesophagus through swallowing (deglutition)
Skeletal muscles and mucus-producing glands are present in the pharynx
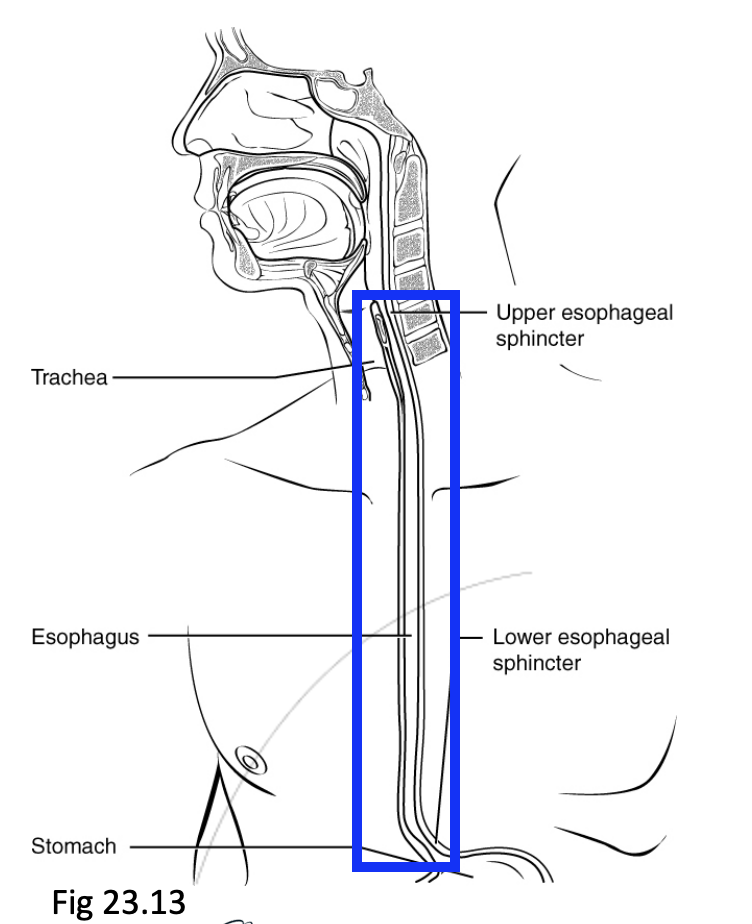
Upper oesophageal sphincter is at the lower end of the pharynx
GI Track
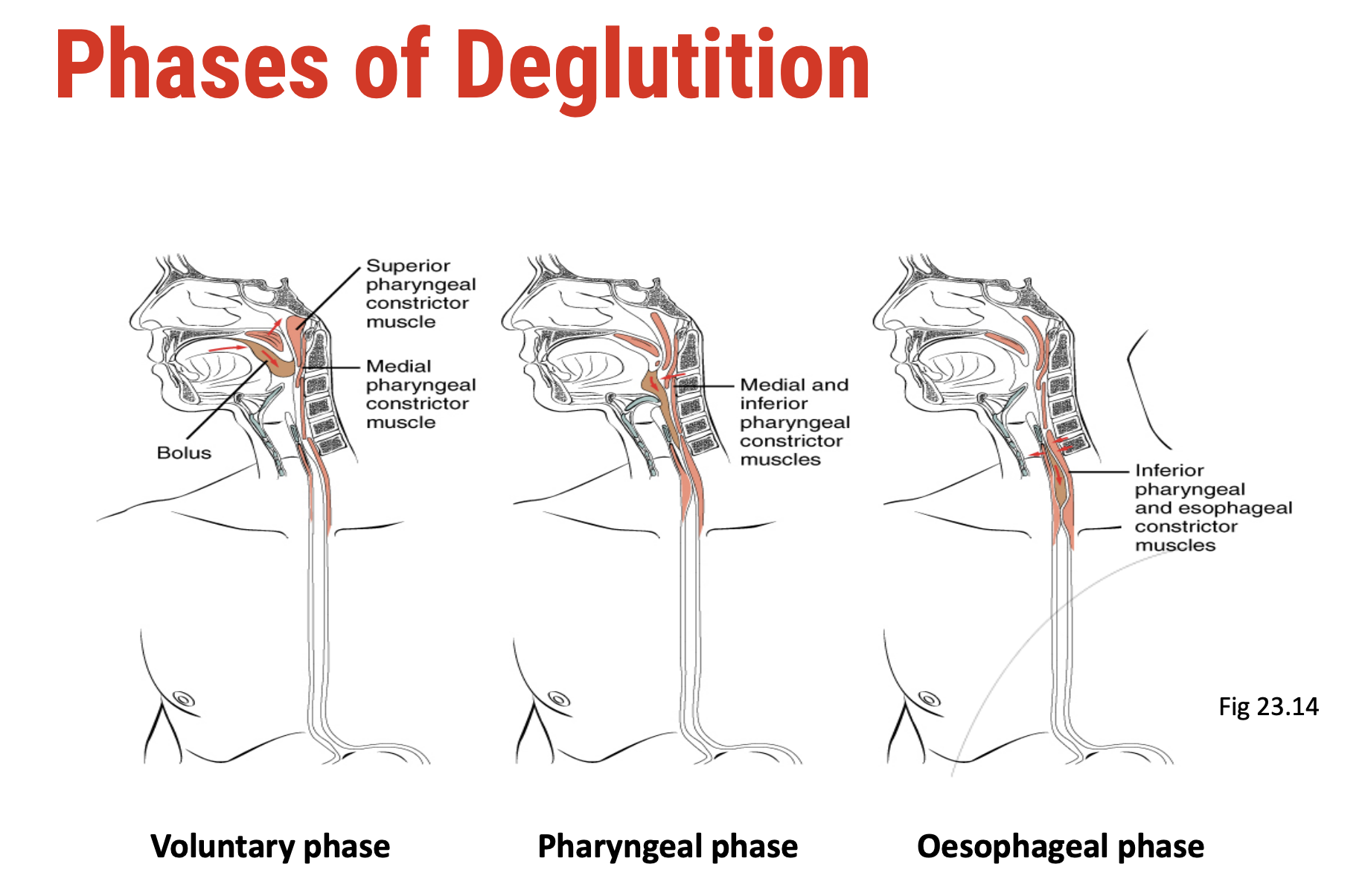
Step 2.5: Deglutition in Pharynx (Swallowing)
Voluntary phase
Body controls how long the food remains in mouth
Pharyngeal phase
Food becomes ‘bolus’. Presence of a bolus in the pharynx stimulates pharyngeal receptors, triggering a contraction from the pharynx to the oesophagus. Mucus is secreted, coating the bolus enabling smooth movement.
Oesophageal phase
Presence of a bolus in the oesophagus stimulates receptors in oesophageal lining, triggering peristalsis. Mucus is secreted, coating the bolus enabling smooth movement.
GI Track
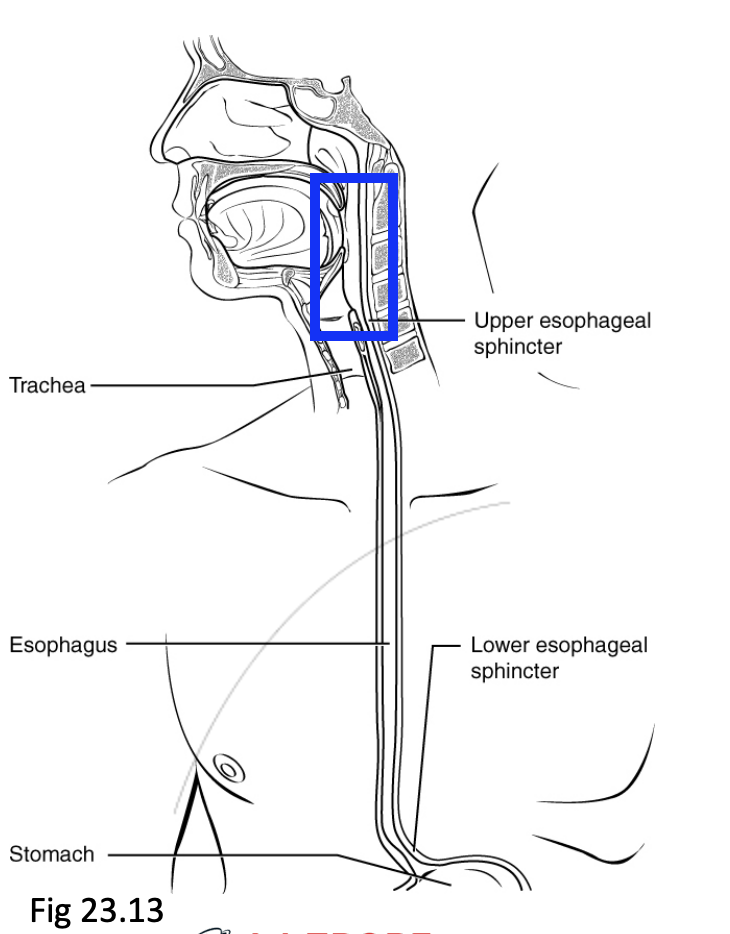
Step 3: Oesophagus
Peristalsis propels food towards the stomach
Each end of the oesophagus has an upper and lower oesophageal sphincter.
Both sphincters prevent reflux from occuring
GI Track
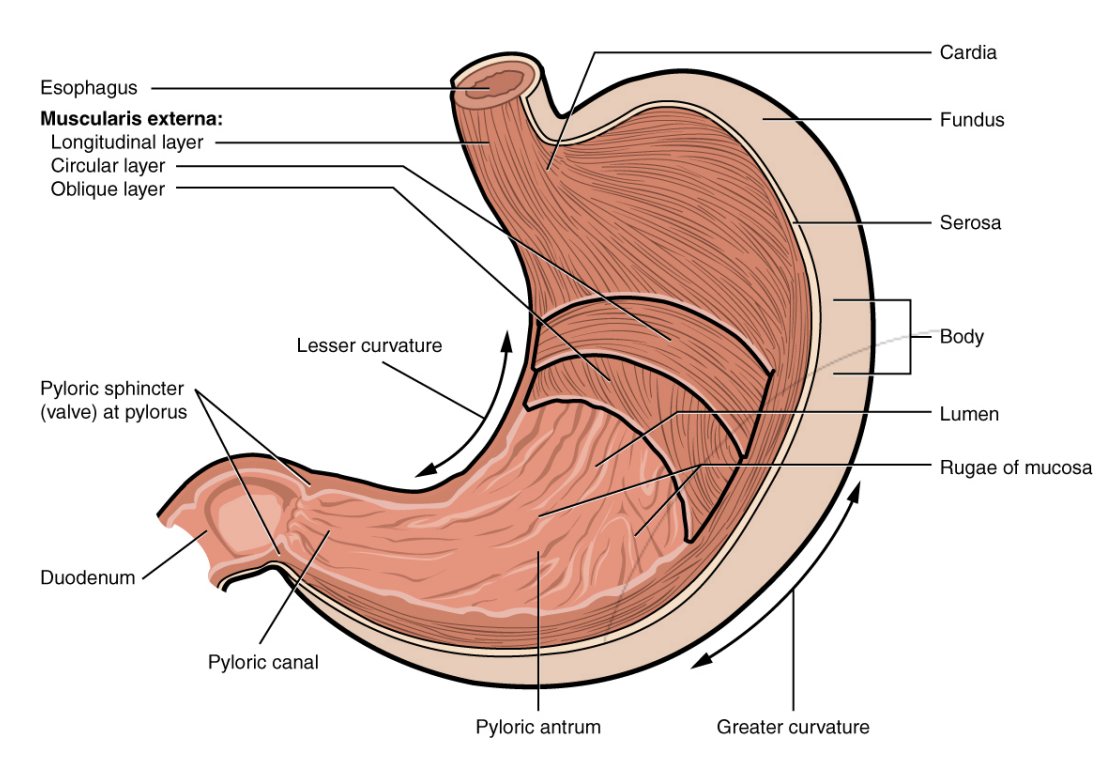
Step 4.1: Stomach
Structure
3 Layers of muscle
Longitudinal layer
Circular layer
Oblique layer
Oblique layer is unique to stomach, allowing mechanical digestion
Stomach-to-small intestine passage called pyloric sphincter. Located at the distal end of the stomach
GI Track
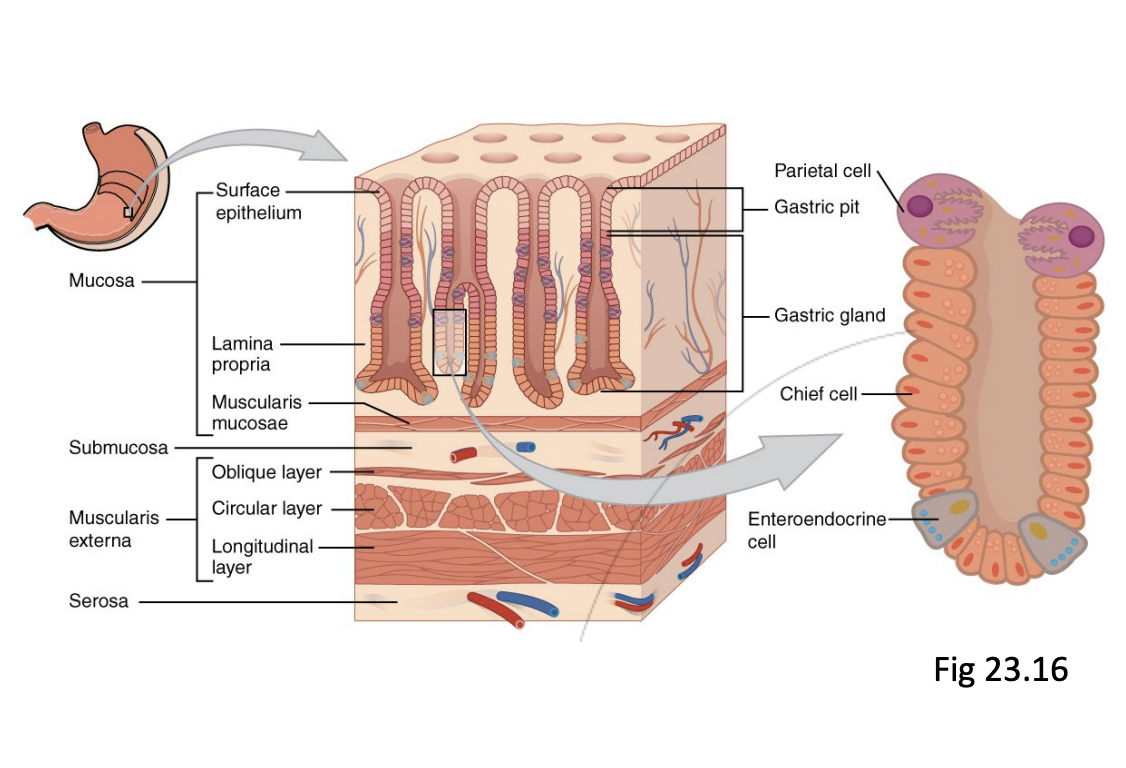
Step 4.2: Stomach
Function
2 functions:
Mechanical digestion:
Unique form of peristalsis occurs due to contraction of oblique muscle layer in stomach
Chemical Digestion:
Release of gastric juices that aid the digestion of protein (e.g hydrochloric acid released by chief cells & parietal cells) ~pH = 1
‘Bolus’ enters the stomach, but leaves as ‘chyme’
GI Track
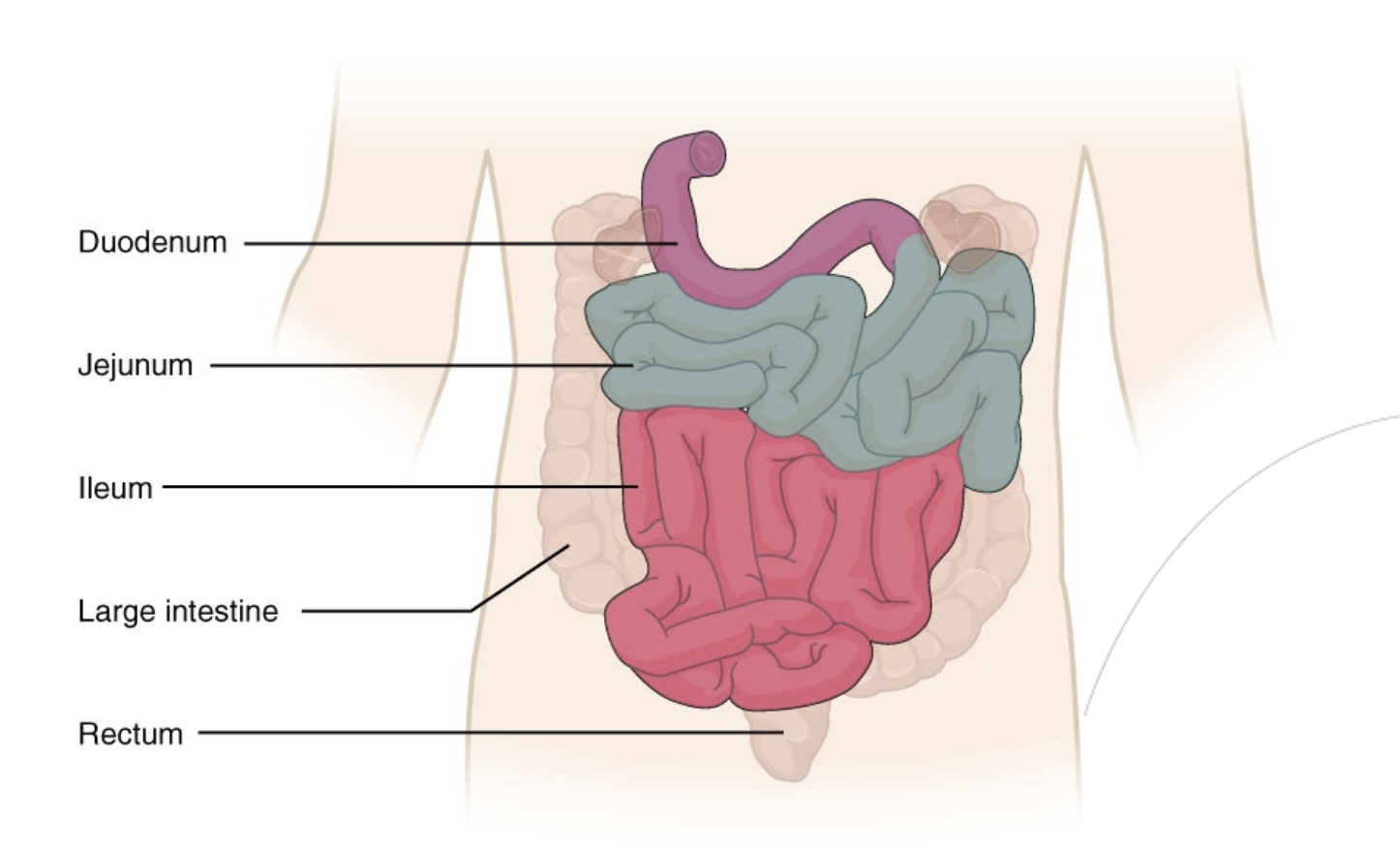
Step 5.1: Small Intestine
Overall Structure
3 Sections:
Duodenum - shortest region
Jejunum
Ileum
GI Track
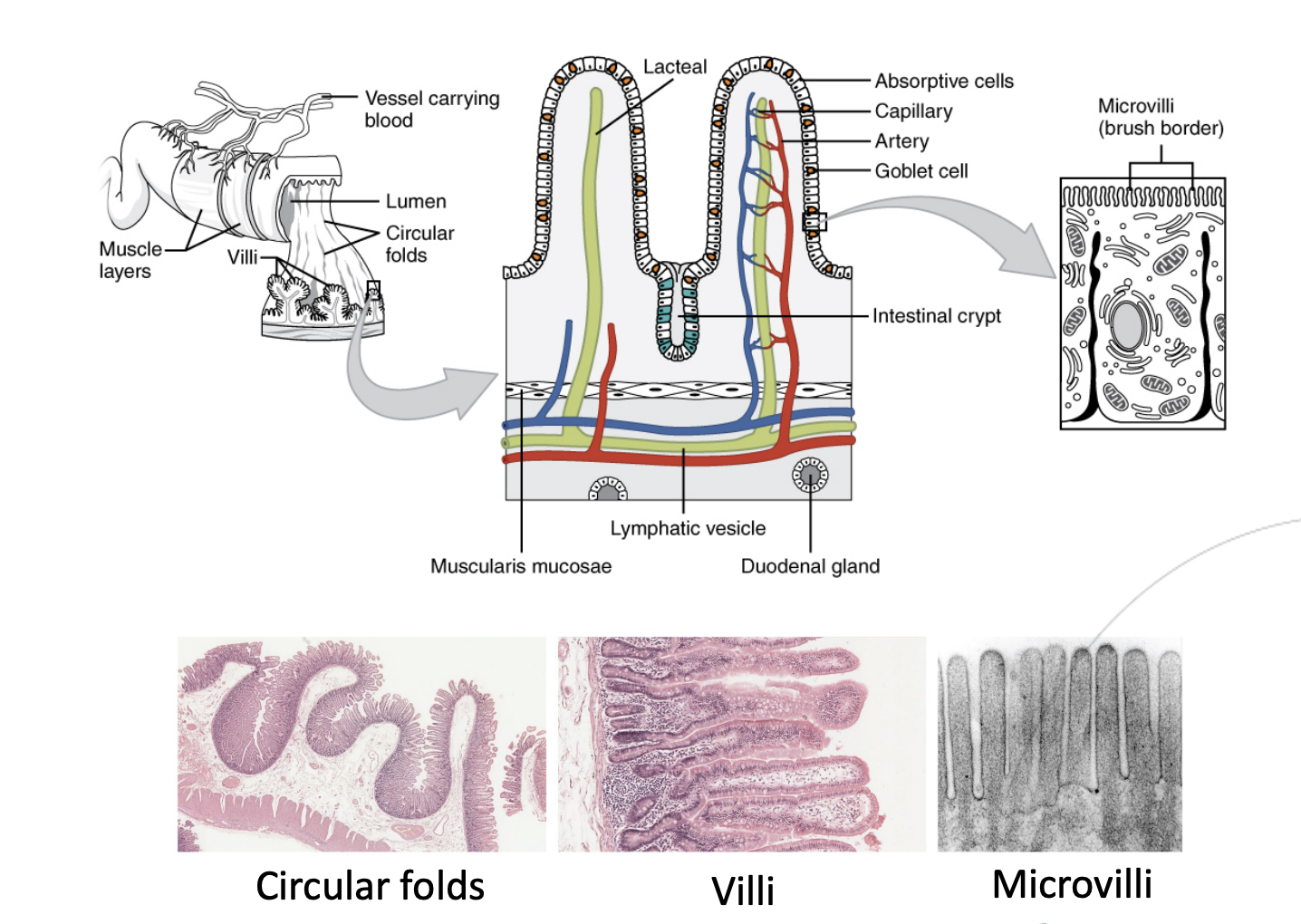
Step 5.2: Small Intestine
Cell Structure
Inner lining of small intestine (also called musosa) is - Circular folds
Found primarily in duodenum and jujenum
Cellular projections - Intestinal villi
Projections on each intestinal wall cell (also called enterocyte) into the inside of the intestine (also called lumen)
Intestinal glands - Crypt cells
Secrete digestive enzymes
Finer projections on intestinal villi - Microvilli
Crucially increase the surface area of every enterocyte. Where brush border enzymes are produced - enzymes that help digest carbohydrates & proteins.
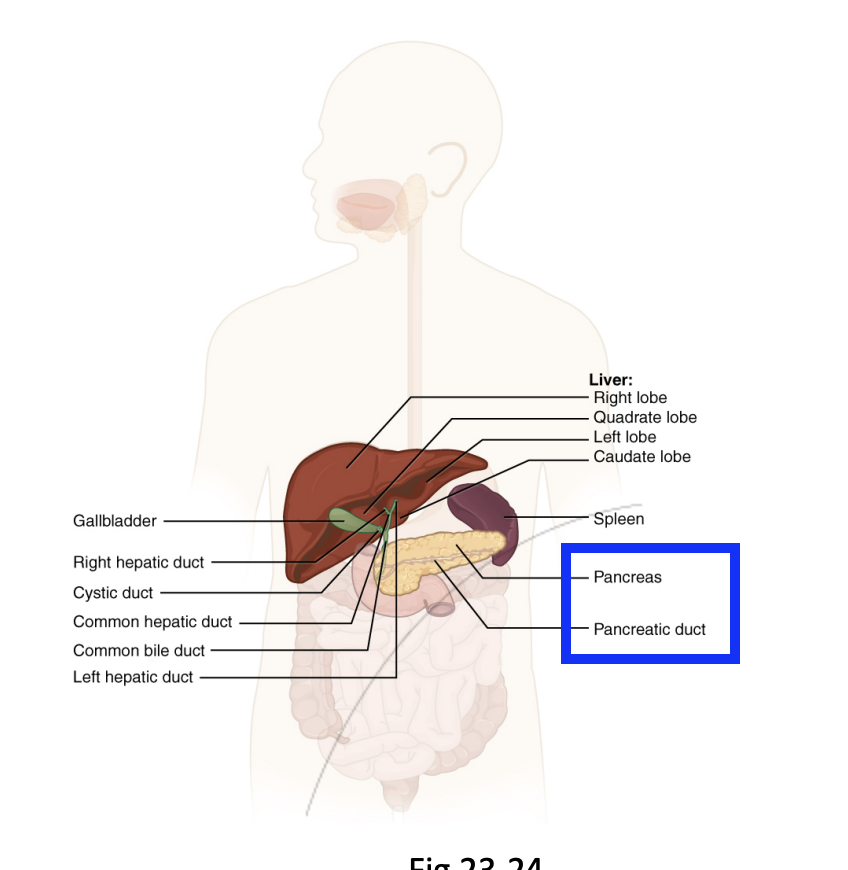
GI Track: Accessory Organs/vestigial structures
Step 5.5.1: Pancreas
Releases pancreatic juices into the small intestine (duodenum), helping break down chyme.
Aids Nutrient processing
Helps neutralise stomach acid
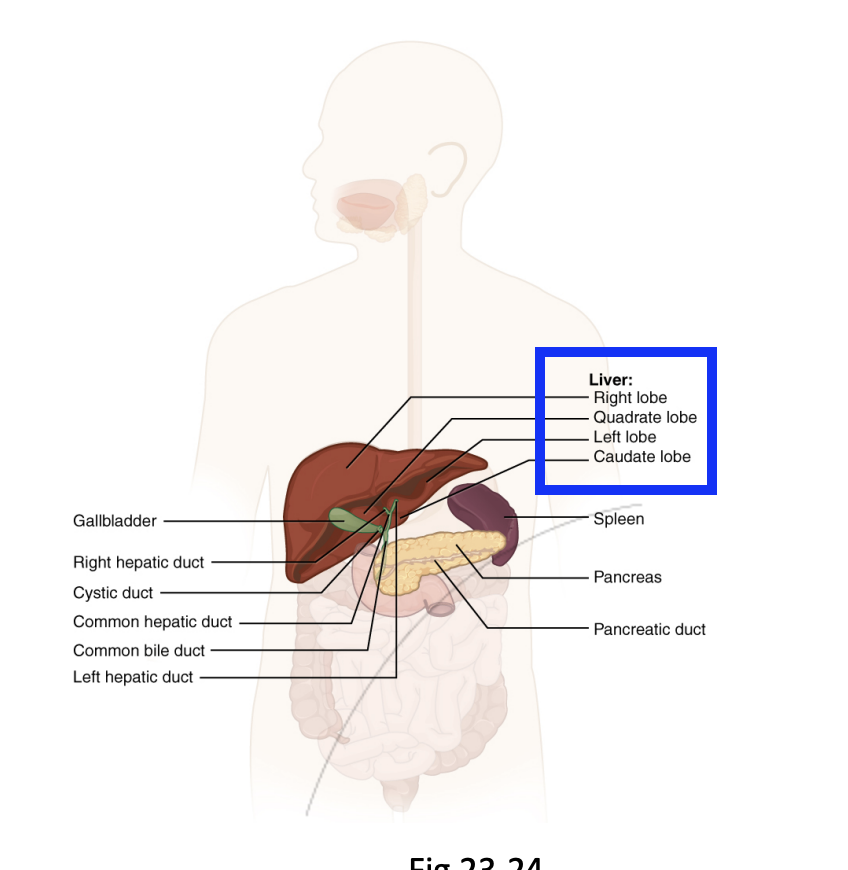
GI Track: Accessory Organs/vestigial structures
Step 5.5.2: Liver
Releases bile into the small intestine (duodenum), helping break down fats and eliminate waste products.
Aids Nutrient processing
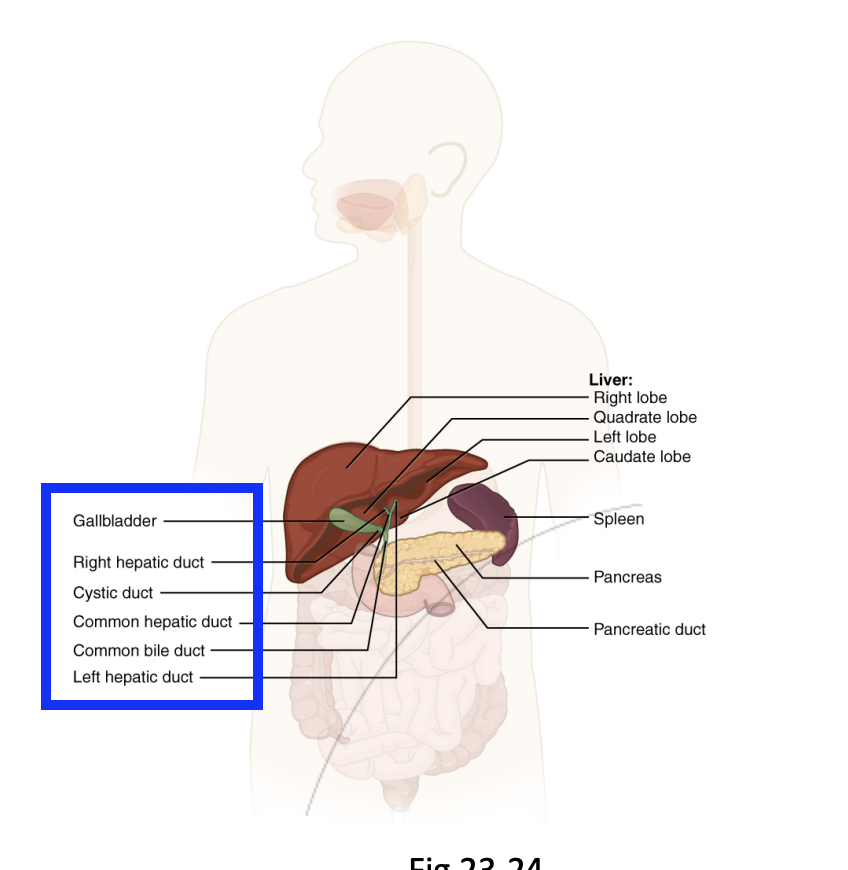
GI Track: Accessory Organs/vestigial structures
Step 5.5.3: Gallbladder
Stores excess bile from the liver as a concentrate.
Bile can be stored or released
GI Track
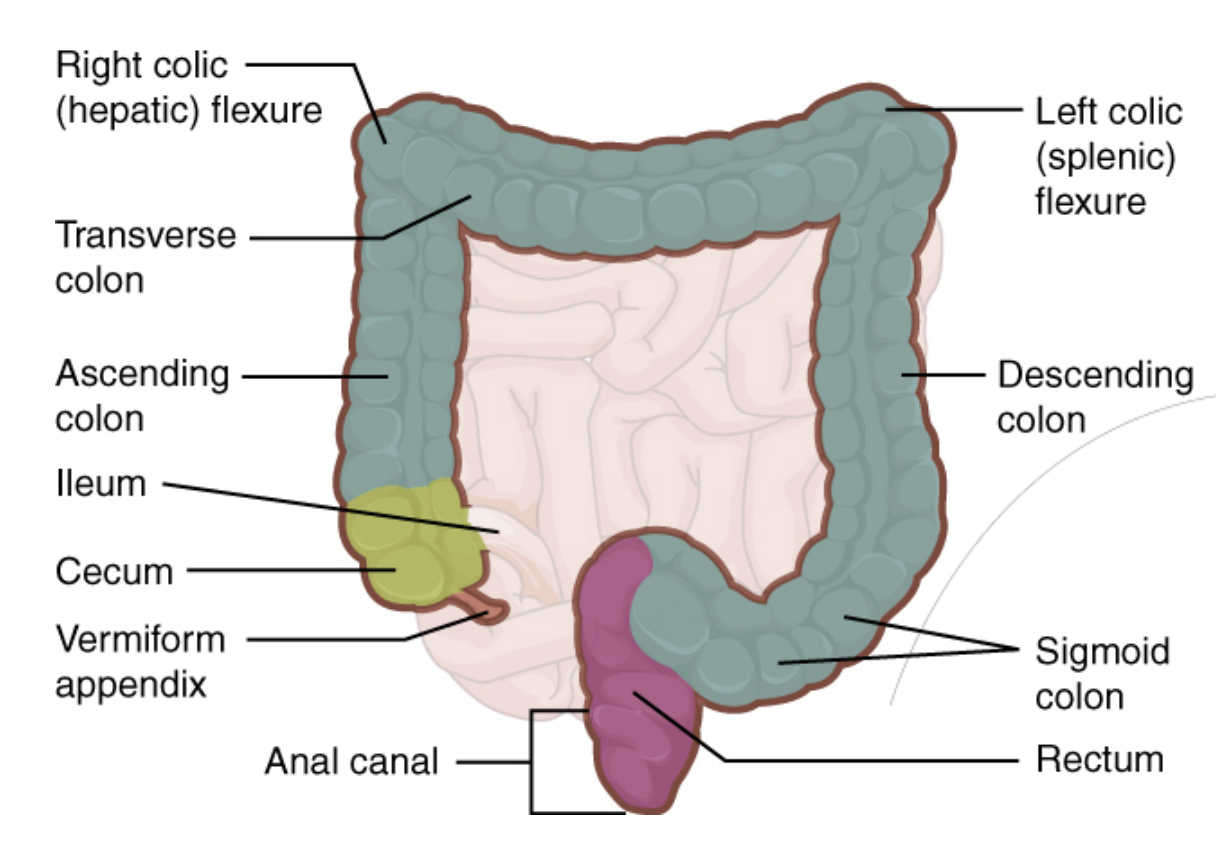
Step 6.1: Large Intestine
Overall Structure
Sections:
Cecum
Colon
a. Ascending colon
b. Transverse colon
c. Descending colon
d. Sigmoid colon
Rectum
Anus
GI Track
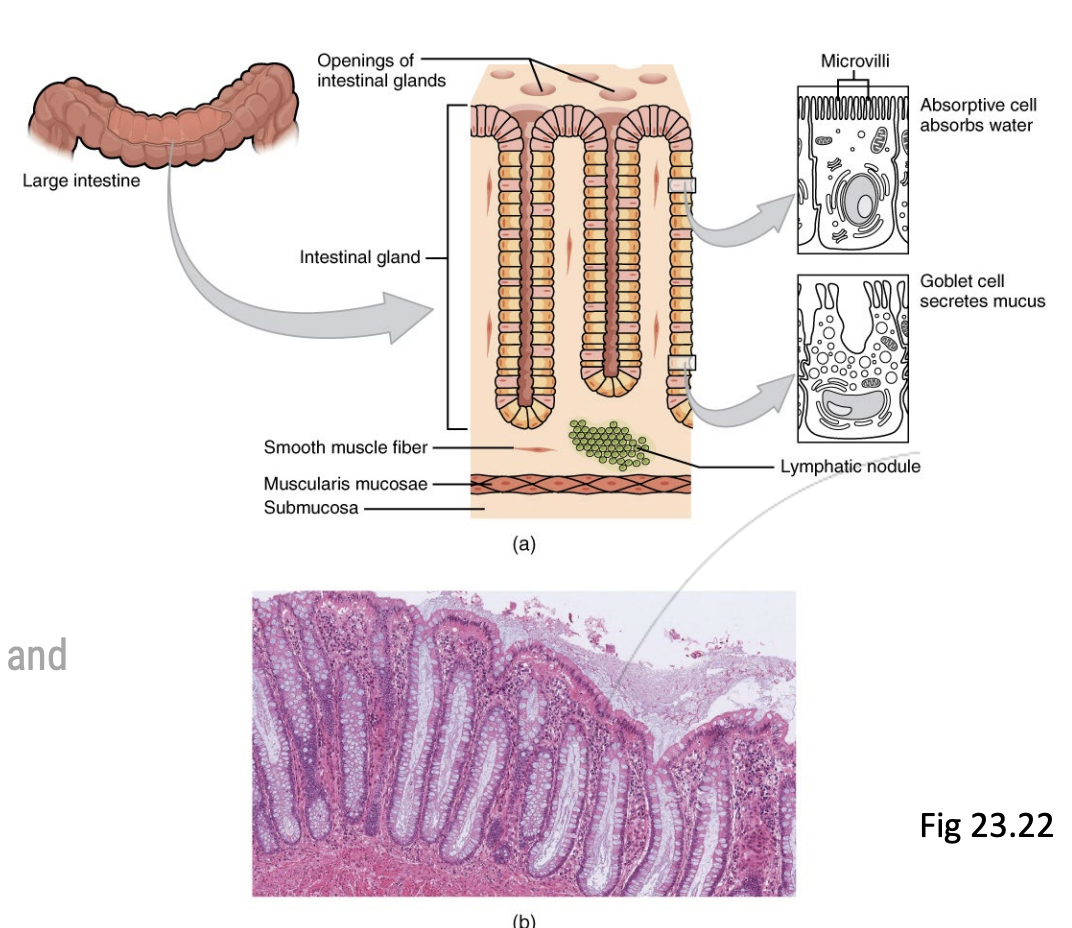
Step 6.2: Large Intestine
Cellular Structure
Much simpler than small intestine
Less enzyme-secreting cells
Many more Enterocytes line the walls of the small and large intestine
Have microvilli that absorb water and salt, and remaining nutrients missed
Goblet cells
Secrete mucus to make movement of stool easier to move and protects cells
GI Track
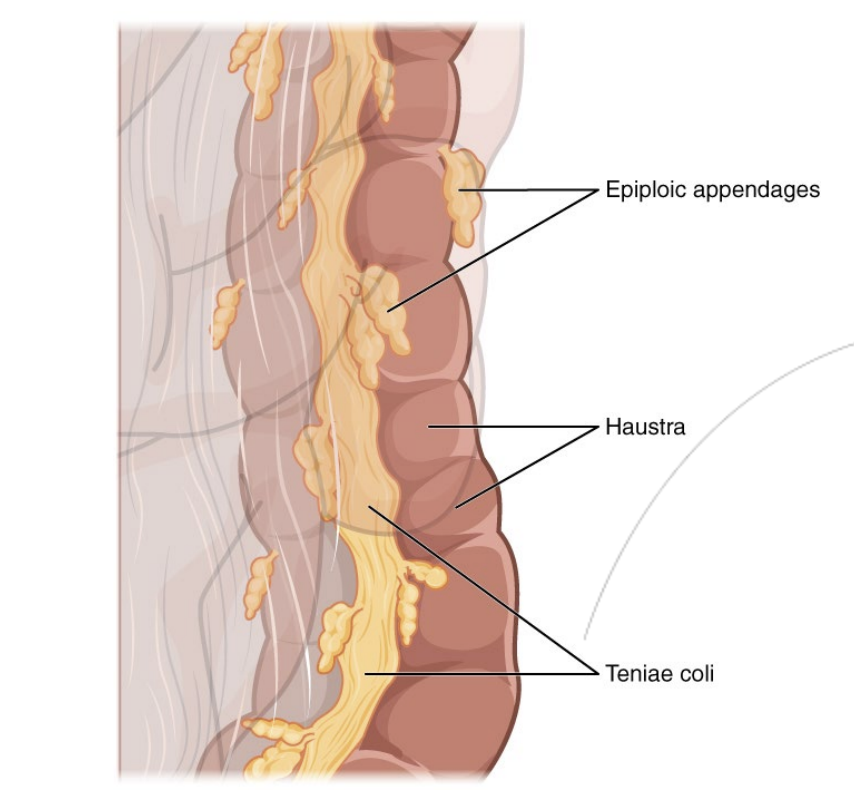
Step 6.3: Large Intestine
Unique Structure
Teniae coli
Bands of smooth muscle that line the large intestine. Contractions aid the movement haustrum that move the stool.
Haustra (singular: haustrum)
Give wrinkled appearance of large intestine
Epiploic appendages
Functon unknown
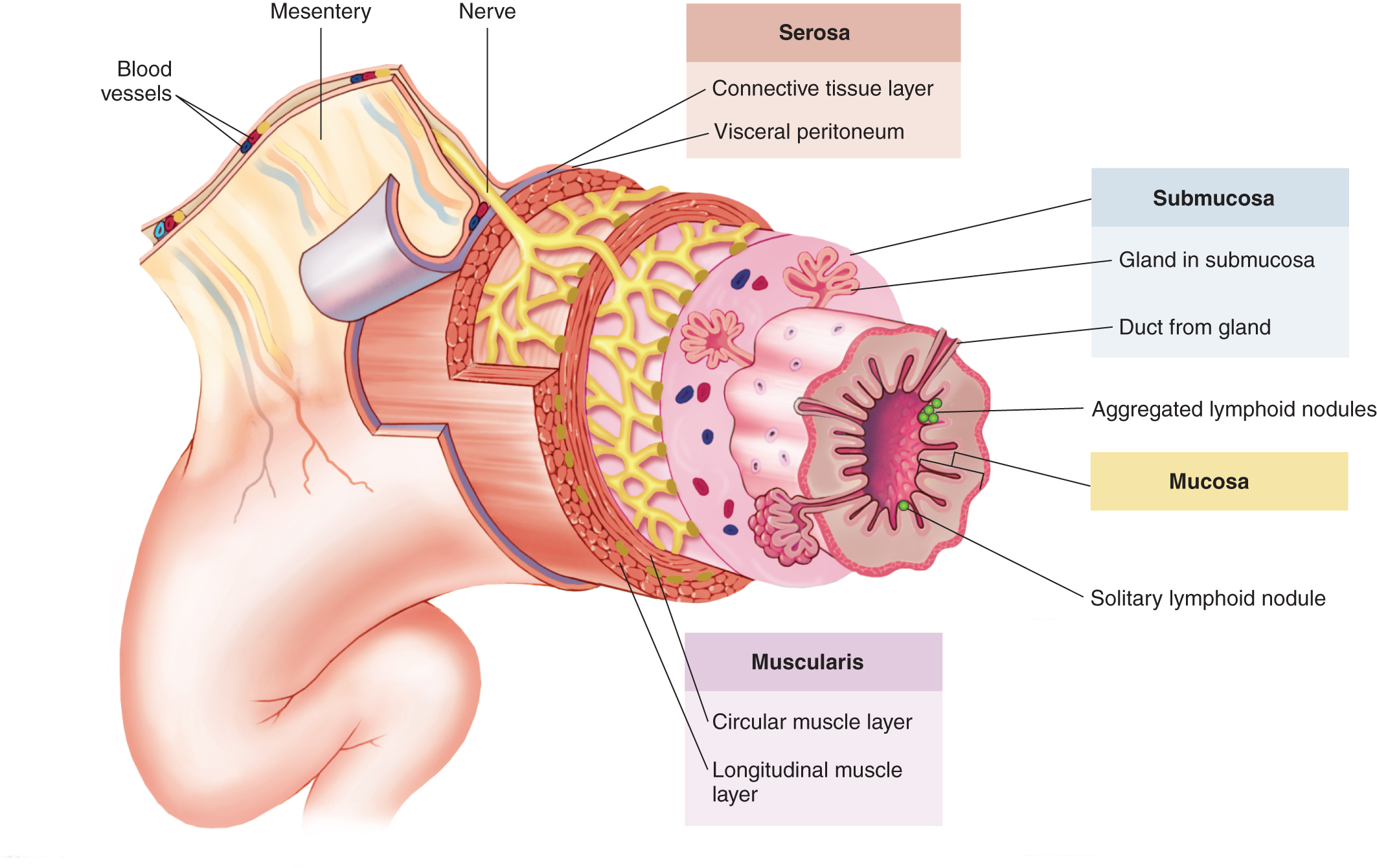
GI Track Layers