BIOL101: Ch. 10 - The Structure and Function of DNA
1/97
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
98 Terms
Nucleus
Where inside a cell is DNA stored?
Nucleotides
Nucleic acids are made of monomers called
DNA
Which is double stranded?
RNA
Which is single stranded?
RNA
Which has the sugar ribose?
C5H10O5
What is the chemical formula of ribose?
DNA
Which has the sugar deoxyribose?
C5H10O4
What is the chemical formula of deoxyribose?
Cytosine
In both DNA and RNA, G pairs with
Thymine
In DNA, A pairs with:
Uracil
In RNA, A pairs with:
Sugar and phosphate
The backbone of DNA is made up of ____ and _____.
Phosphodiester
The nucleotides are held together by _______ in the backbone
hydrogen
The two DNA molecules are held together by ______ bonds between the bases
Antiparallel
Are the strands of DNA parallel or anti-parallel?
Semi-Conservative Replication
Each ‘old’ strand acts as a template against which a new strand is synthesized
Opens up the two strands of DNA, so it breaks the hydrogen bonds between the strands so it separates
What is the function of helicase?
Can extend and continue to synthesize our DNA in a 5’ to 3’ direction
What is the function of DNA polymerase?
DNA Ligase
Which enzyme helps create the covalent bonds between deoxyribose and phosphate in the DNA backbone?
Lagging strand
Would you find Okazaki fragments in the leading or lagging strand?
DNA Ligase
What enzyme glues Okazaki fragments together?
3’ to 5’
In what direction does DNA polymerase read the DNA? 3’ to 5’ or 5’ to 3’?
5’ to 3’
In what direction are the new strands synthesized? 3’ to 5’ or 5’ to 3’?
Origins of replication
The areas where DNA replication begins are called:
Gene
Is a sequence of DNA that codes for one functional product, like a polypeptide
One polypeptide
How many products (polypeptides) does 1 gene code for?
Synthesized
If a gene is being expressed then the protein is being: synthesized or suppressed
DNA
The blueprint or recipe for the protein is coded in the:
Nucleus
DNA is located in the
Ribosomes
Proteins are made by structures called ________ in the cytoplasm
No
Is DNA ever allowed to leave the nucleus?
RNA
The information in the DNA is transcribed into a molecule called ______, which goes out to the cytoplasm.
Nucleus
Where does transcription take place?
CTTATGT
Transcribe this piece of DNA:
GATTACA
RNA Polymerase
What enzyme creates mRNA from DNA?
Promoter
How does the RNA polymerase know where the gene starts? What region does it bind to?
Terminator
How does the RNA polymerase know where the gene ends? What region tells it to fall off?
Cap on 5’ end
What is added to the start of the mRNA?
Tail on 3’ end
What is added to the end of the mRNA?
Cap on 5’ end helps ribosomes attach and protects mRNA
What is the function of the cap on mRNA?
Tail on 3’ end protects against degradation and helps in interactions with the ribosome
What is the function of the tail on mRNA?
adenine
The tail is made of nucleotides with the base _________
Exons
The parts of the mRNA needed to make (express) the protein are called:
Introns
The junk DNA which is not needed to make the protein is called:
Introns
Which is spliced out (removed) from the mRNA: introns or exons?
Nucleotides
What is the language of DNA? Nucleotides or amino acids?
Amino acids
What is the language of proteins? Nucleotides or amino acids?
Cytoplasm
Where does translation take place?
mRNA
A codon is 3 nucleotides on the mRNA or tRNA?
tRNA
An anti-codon is 3 nucleotides on the mRNA or tRNA?
3 nucleotides
How many nucleotides code for 1 amino acid?
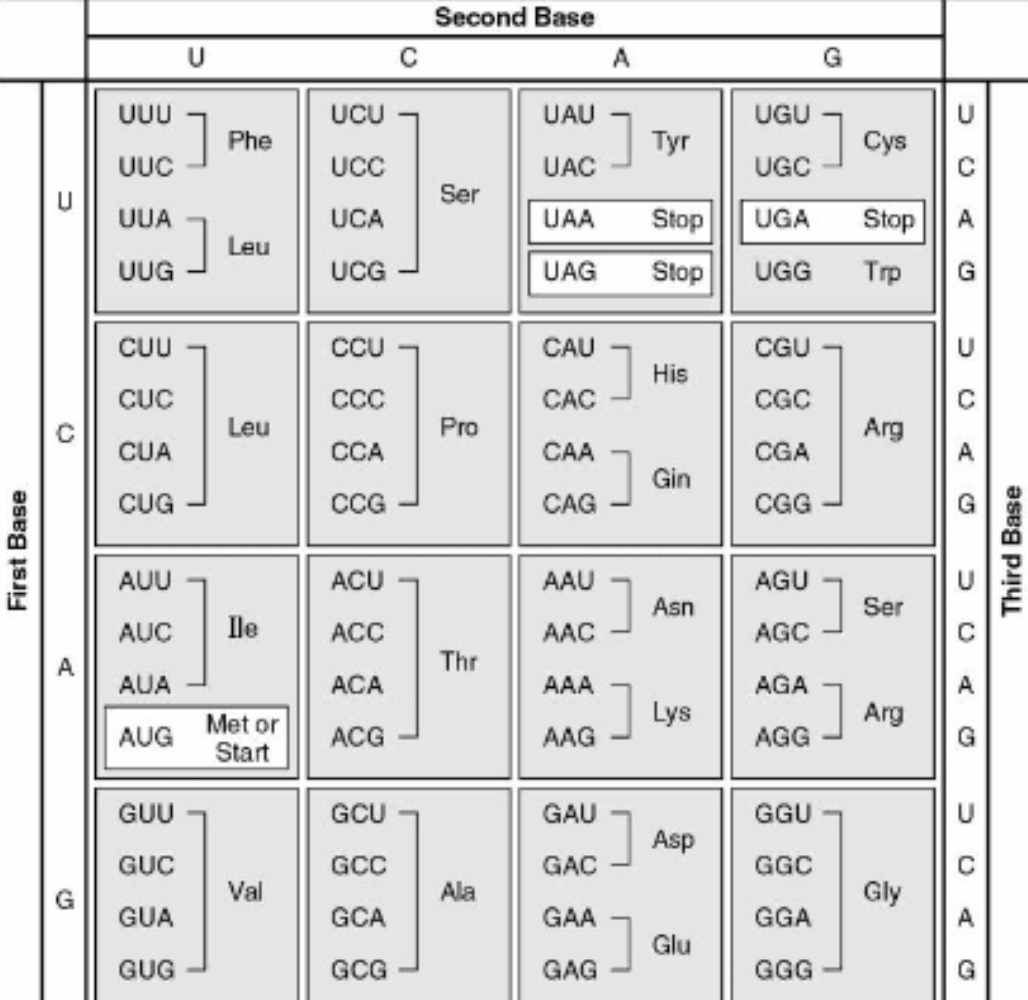
AUG
What is the start codon?
UAA, UGA, UAG
What are the 3 stop codons?
None
What amino acids do the stop codons code for?
Proline
What amino acid does the codon CCU code for?
Transfer
What does the t in tRNA stand for?
Amino acids
What does the tRNA transport?
tRNA
To make sure that we have the right amino acid, the mRNA codon is matched to the _____ anti-codon
Two
How many subunits make up a ribosome?
r
Ribosomes are made of _RNA and protein.
Nucleolus
Where is rRNA made?
Amino acid
What does the A stand for in A site?
Peptide
What does the P stand for in P site?
Exit
What does the E stand for in E site?
small
During initiation, the ______ subunit joins with the mRNA first.
anti
How does the small subunit know where to stick on? It looks for the ____ codon.
Methionine (AUG)
What is the first amino acid in every protein?
Peptide bonds
The bonds that form between amino acids are called:
Primary, Secondary, Tertiary, Quaternary
What are the 4 levels of protein folding?
Rough ER
In which cell organelle are proteins often modified?
Is the process of breaking the polypeptide bonds between amino acids in proteins
What is meant by cleavage?
Adding a phosphate group from ATP to specific amino acids on a protein
What is meant by phosphorylation?
Is the enzymatic attachment of sugar chains to proteins, significantly altering their structure, stability, folding, function and interactions
What is meant by glycosylation?
DNA sequence
What is changed if there is a mutation?
Random
Are mutations programmed or random?
The protein won’t work correctly, The protein works better, The protein is not affected
What are the 3 possible results of mutation on the protein?
DNA polymerase
What enzyme usually works to prevent mutations during DNA replication?
Rare
Are mutations during DNA replication rare or common?
UV light, ionizing radiation, air pollution
List some known mutagens. I’ll start you off with cigarette smoke.
One base
In a point mutation, how many bases are changed?
deleted
In a frame-shift mutation bases are either inserted or ________
Point mutation
Is this a frame shift or point mutation in my name: HUPHES
Frame shift
Is this a frame shift or point mutation in this sentence: HEF ATC ATS AT
Frame shift
Is this a frame shift or point mutation in this sentence: HEF ATC ATS AT
Silent
If there is a mutation in DNA but the amino acid code remains the same, the mutation is:
Missense
If there is a mutation in DNA and the amino acid code is different, the mutation is:
Nonsense
If there is a mutation in DNA and the polypeptide is much too short, the mutation is:
One
In sickle cell anemia, how many bases are changed/mutated?
Beta chain
Where is the mutation on the alpha or beta chain?
Missense
Is the mutation of SSA silent, missense or nonsense?
No
Does the hemoglobin protein function correctly in SSA?
Severe malaria/Plasmodium Falciparum
SSA protects you from which other disease?
Primary Structure
Which level has a straight chain of AA?
Secondary Structure
Which level do alpha helix and beta sheet form?
Tertiary
Which level does the 3D structure emerge?
Quaternary
Which level do several polypeptides come together to make a protein?