2 cell to cell adhesions
1/30
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
31 Terms
Cell–cell junctions use
cadherins, desmosomal cadherins, claudins, occludin, JAM, and connexins depending on the junction type.
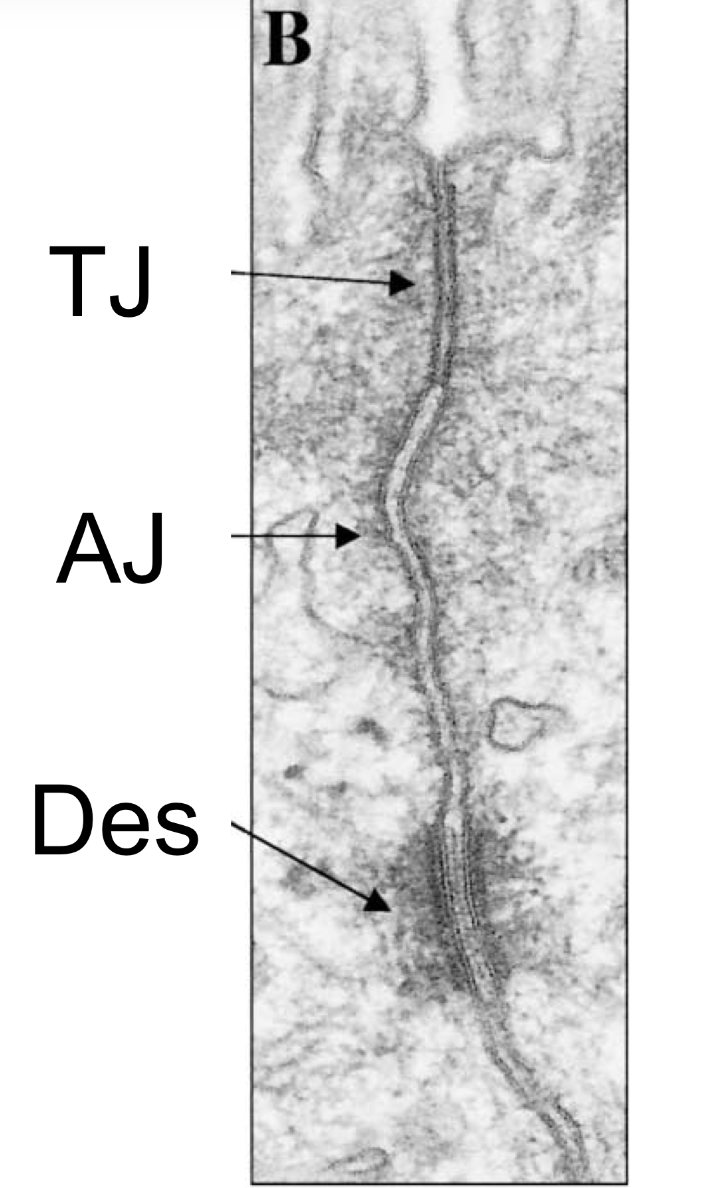
How tight junctions adherence junctions and desmosomes look on em
What adhesion molecules form adherens junctions (AJs)?
Classical cadherins:
E-cadherin
N-cadherin
M-cadherin
P-cadherin
What’s the cytoskeleton linkage in classical Catherine’s ?
Actin
What are linker proteins in adheren junctions
α-catenin, β-catenin, p120-catenin.
What adhesion molecules do desmosomes use?
Desmoglein, Desmocollin (desmosomal cadherins).
What cytoskeleton component does desmosomes have ?
intermediate filaments (keratin IFs).
What linker proteins are part of desmosomes
plakoglobin (γ-catenin), plakophilin, desmoplakin.
What adhesion molecules do tight junctions (occluding junctions) use?
Claudins, Occludin, JAM.
What are tight junctions linked to ? And by what?
Linked to actin, spectrin, microtubules via ZO-1, ZO-2, ZO-3.
What adhesion molecule does gap junctions or communication junctions use ?
Connexins → 6 connexins = connexon, two connexons align to form the channel.
Adheren junctions form what and to do what?
actin adhesion belt → controls shape changes, coordinated movement, and tissue integrity.
Adheren junctions allow for what signaling ?
Allow mechanochemical signaling through β-catenin and Rho GTPases.
desmosomes do what in function ?
Provide mechanical strength, especially in epidermis and myocardium.
Resist shear forces.
Tight junctions do what in function ?
Create diffusion barrier between apical & basolateral domains → essential for polarity and controlled paracellular transport.
Gap junctions do what in functions ?
Allow passage of ions, sugars, amino acids → electrical & metabolic coupling
AJs + actin belt =
coordinated epithelial sheet-like behavior.
Desmosomes anchor
IF networks → create tissue-wide mechanical continuity.
TJs separate
apical from basolateral membrane → maintain epithelial polarity.
GJs synchronize
contraction (heart) and allow tissue-wide homeostasis.
Mutations in desmosomal proteins
→ skin & heart disease:
Epidermolysis bullosa simplex (KRT 5/14).
Palmoplantar keratoderma (KRT, PKG).
Arrhythmogenic Right Ventricular Cardiomyopathy (DSP, DSG2, DSC2, PKP mutations).
Tight junction dysfunction
Allows pathogens/viruses to invade through TJ complexes.
Cadherins in development
Differential expression (E-cadherin → N-cadherin switching) drives cell sorting during embryogenesis.
Controlled by Snail, Twist, Slug.
What is the transmembrane component of signal relay junctions ?
cadherijs neurexin, neuroligan , ig superfamily
What’s the transmembrane components of leukocyte adhesion to endothelia
selectins (initial) → integrins (stable )
What’s the cytoskeleton components of leukocyte adhesion to endothelia
Actin
What is the cytoskeleton component of signal relay junctions ?
Actin
What is the function component of signal relay junctions ?
heterotypic cell-cell adhesions (e g. pre-synaptic and post-synaptic cells, neuromuscular junction),
creates a confined environment for passage of molecules between cells
What’s the function of leukocyte adhesion to endothelia
low affinity adhesion, allows leukocytes to roll over other cell layers
Firm arrest and extravasation
Selection dependent adhesion
Mediates rolling of leukocytes on endothelium
Low-affinity, transient, Ca²⁺-dependent
Binds carbohydrate ligands
Allows leukocytes to “slow down” and sample endothelium
Occurs first
Integrin dependent adhesion
Mediates firm arrest + crawling + diapedesis
High-affinity, requires Mg²⁺
Integrins on leukocytes bind ICAM (Ig-superfamily) on endothelium
Activated by chemokines → conformational change → extravasation