NS 3310 Lecture 1
1/44
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
45 Terms
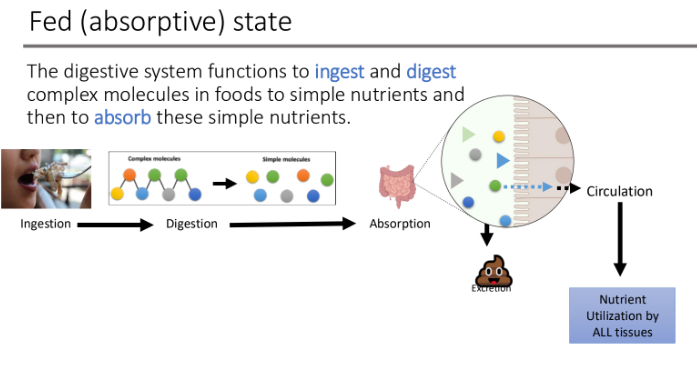
Fed (absorptive) state: The digestive system functions to ingest and digest complex molecules in foods to _____ and then to ____ them
simple nutrients; absorb
Digestion: What is ingestion?
entry of food into the GI tract by eating/drinking foods (oral cavity). This is an active process it involves choices and decision making.
Digestion: Mechanical digestion and propulsion involves the ____ and ___ of food (oral cavity) and propelling the food along the _____ tract
crushing; shearing; digestive
Digestion: Chemical digestion involves the chemical breakdown of food into small ____ and ____ molecules; this makes it suitable for absorption by the _______
organic; inorganic; intestinal epithelium
Digestion: Secretion is the release of what 5 things by the epithelium and accessory organs
water
acids
enzymes
buffers
salts
Digestion: Absorption: Digestive products (simple molecules) and water pass from the _____ into _____ of the GI tract (SI, LI) for distribution to body cells
alimentary canal; interstitial fluid
Digestion: What is elimination/defecation?
Excretion of wastes from the body and foods that cannot be digested/absorbed
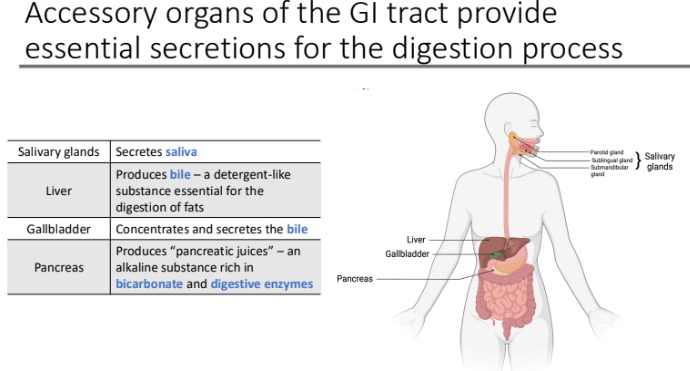
What are the 4 accessory organs of the GI tract?
Salivary glands
Liver
Gallbladder
Pancreas
Accessory organs of the GI tract provide essential secretions for the digestion process. Describe them
Salivary glands → secretes saliva
Liver → Produces bile – a detergent-like substance essential for the digestion of fats
Gallbladder→ concentrates and secretes the bile
Pancreas → Produces “pancreatic juices” – an alkaline substance rich in bicarbonate and digestive enzymes
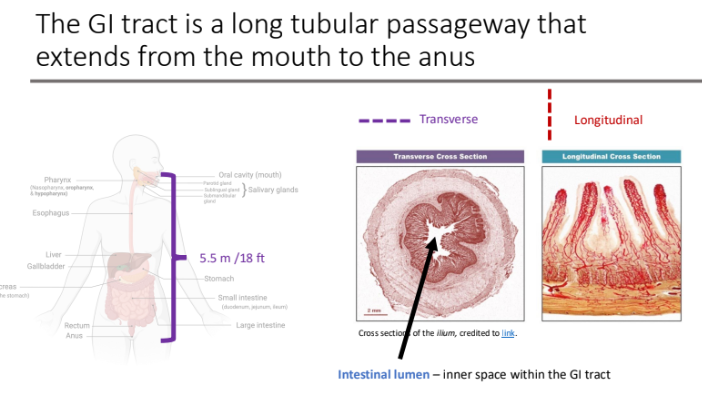
The GI tract is a long tubular passageway that extends from the mouth to the anus
The intestinal wall is made up of 4 layers, each with distinct compositions and functions. What are the 4 layers?
Mucosa
Submucosa
Muscularis externa
Serosa or Adventitia
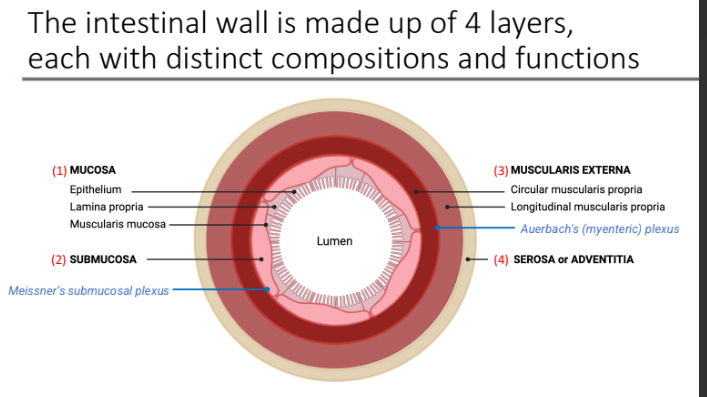
Mucosa (1st layer, inner lining) is composed of three things. Name them
Epithelium
Lamina propria
Muscularis mucosa
Mucosa (1st layer, inner lining): What is the epithelium?
a layer of epithelial cells (enterocytes)
Mucosa (1st layer, inner lining): The lamina propria is connective tissue that contains what 5 things?
Small blood and lymphatic vessels
Nerve fibers
Lymphoid tissue (provides immune defenses)
Exocrine (ductal system)
Endocrine glands (in some parts)
Mucosa (1st layer, inner lining): Muscularis mucosa - contains ____ and separates what from what?
smooth muscle; the mucosa from the submucosa
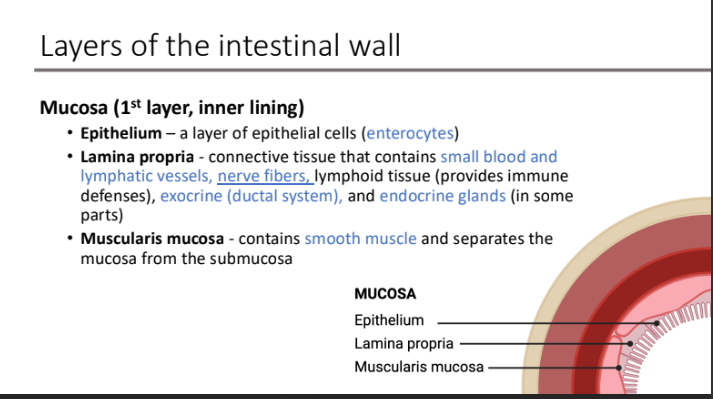
Submucosa (2nd layer) - houses a portion of what nervous system also known as?
enteric nervous system known as Meissner’s submucosal plexus (neuronal network).
Meissner’s submucosal plexus (neuronal network) functions to ____ cells in the mucosa to induce ____ in response to local stimuli (ingestion of food or drink) and _____ signaling from the CNS
innervate cells; secretions; parasympathetic
The submucosa Contains large____ and ____ that receive digestive products from the smaller vessels of the lamina propria.
blood vessels; lacteals

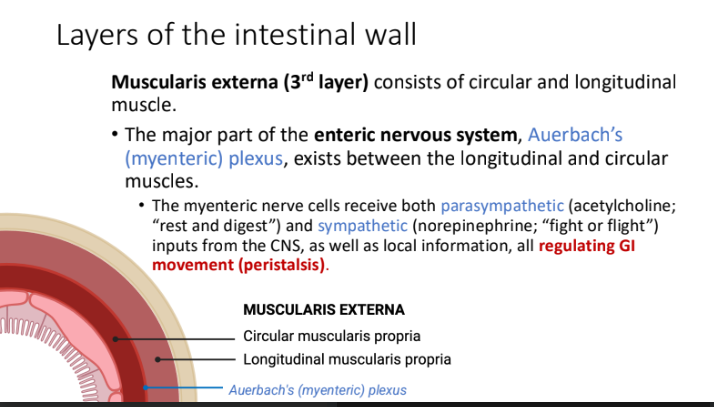
Muscularis externa (3rd layer) consists of ____ and ____ muscle.
circular; longitudinal
Muscularis externa (3rd layer): What exists between the longitudinal and circular muscles?
The major part of the enteric nervous system, Auerbach’s
(myenteric) plexus
The myenteric nerve cells receive both ____ and ____ inputs from the CNS, as well as local information, all regulating ____
parasympathetic (acetylcholine; “rest and digest”)
sympathetic (norepinephrine; “fight or flight”)
GI movement (peristalsis).
Serosa or Adventitia (4th layer, most outer layer) form by a single layer of ____ supported by a thin layer of connective tissue. Comprised of two parts:
mesothelium
Parietal layer: lines the body cavity
Visceral layer: covers organs
The main function of the serosa or adventitia is to produce a serous fluid that lubricates organ surfaces, reducing ___ during movement, and provides a ____ barrier.
friction; protective
What are examples of intraperitoneal organs (has serosa)
stomach,
spleen,
first part of the duodenum,
jejunum,
ileum
transverse colon,
sigmoid colon.

In areas where there is NO serosa covering the muscular layer, a dense network of____ (adventitia layer) firmly attaches the digestive tract to ____
collagen fibers; adjacent structures.
Adventitia wraps and bind organs that sit ___ the _____ cavity
outside; peritoneal
What are internal structures and organs that have adventitia?
esophagus,
pancreas,
most of the duodenum,
ascending colon
descending colon.

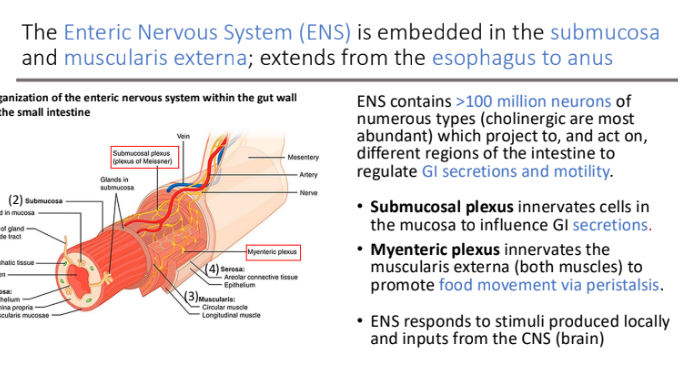
The Enteric Nervous System (ENS) is embedded in the ____ and ____; extends from the ____ to ___
submucosa; muscularis externa
esophagus; anus
ENS contains >100 million neurons of numerous types (____ are most abundant) which project to, and act on, different regions of the intestine to regulate?
cholinergic; GI secretions and motility.
Submucosal plexus ____ cells in the mucosa to influence ___
innervates; GI secretions.
Myenteric plexus innervates the ____ to promote?
muscularis externa (both muscles); food movement via peristalsis.
What does the ENS respond to?
stimuli produced locally and inputs from the CNS (brain)
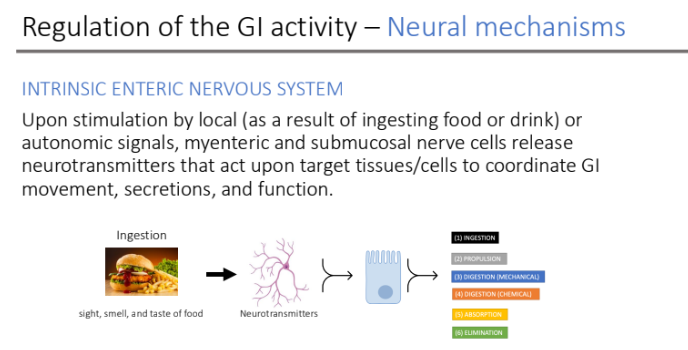
Regulation of the GI activity – Neural mechanisms: Intrinsic enteric nervous system: Upon stimulation by local (as a result of ingesting food or drink) or autonomic signals, ____ and ___ nerve cells release
_____ that act upon target tissues/cells to coordinate GI
___, ____, and ____
myenteric; submucosal; neurotransmitters
movement, secretions, and function.
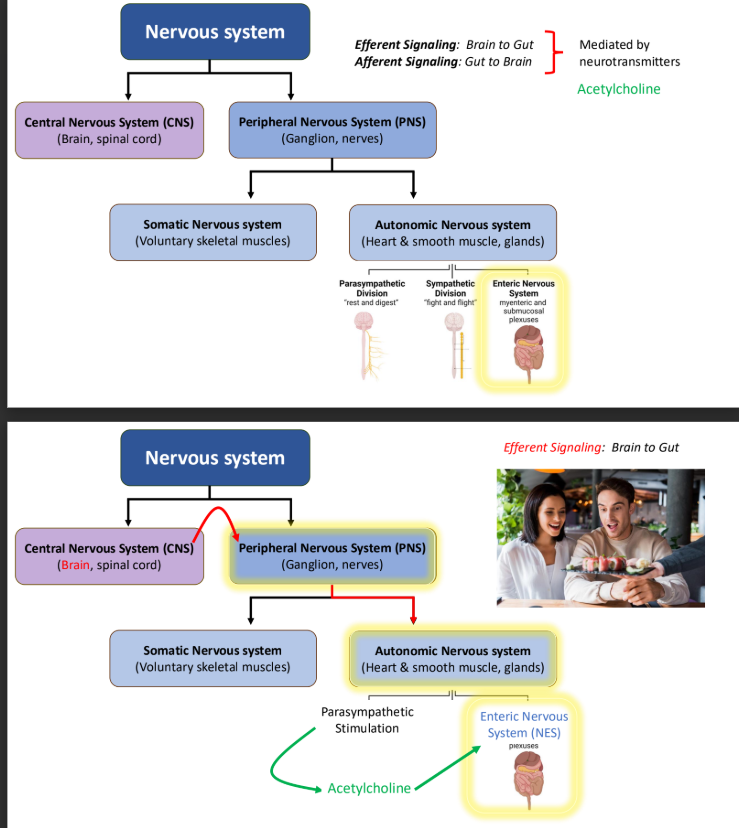
Regulation of the GI activity – Neural mechanisms: What is the extrinsic enteric nervous system?
The parasympathetic and sympathetic arms of the peripheral NS function along with the ENS to regulate gut function.
Extrinsic ENS: Parasympathetic stimulation via the ___ nerve, and the release of ____ , promote digestion and absorption by doing what three things?
vagal; acetylcholine
increasing GI secretions
increasing muscle tone and peristalsis
relaxing GI sphincters
Extrinsic ENS: Sympathetic stimulation via the release of _____, inhibits digestion leading to what three things?
norepinephrine (NE)
decreased secretion,
decreased movement
constriction of sphincters.

Nervous System chart: What is efferent and afferent signaling?
Efferent: brain to gut
Afferent: gut to brain
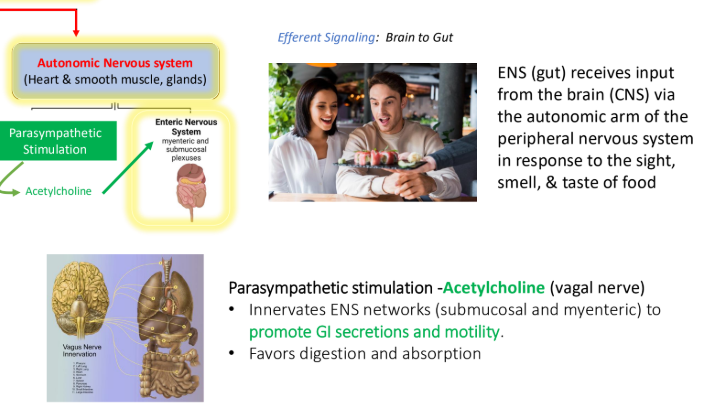
Autonomic Nervous System: Parasympathetic stimulation is done through?
Acetylcholine (vagal nerve)
Parasympathetic stimulation: Acetylcholine (vagal nerve) innervates ENS networks (___ and ___) to promote what two things?
submucosal; myenteric
GI secretions
Motility

Parasympathetic stimulation favors what two things?
Digestion
Absorption
Autonomic Nervous System: Sympathetic stimulation is done through?
-Norepinephrine
Sympathetic stimulation Inhibits GI motility in the ____ and inhibits ____ release by cholinergic neurons in the GI
myenteric plexus; acetylcholine
Sympathetic stimulation slows what process?
digestive and absorptive process
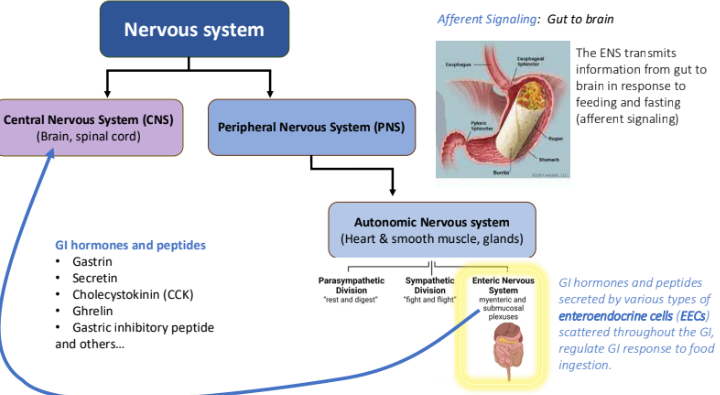
Afferent Signaling in Nervous System: GI hormones and peptides secreted by various types of _____ scattered throughout the GI, regulate?
enteroendocrine cells (EECs); GI response to food ingestion.
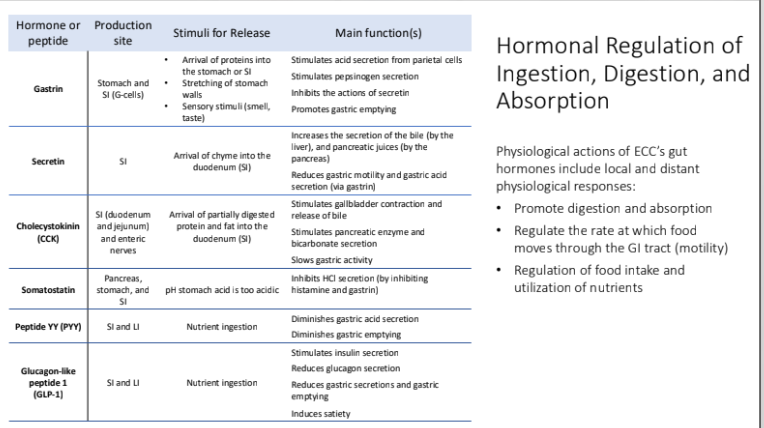
Hormonal Regulation of Ingestion, Digestion, and Absorption: Physiological actions of ECC’s gut hormones include local and distant physiological responses: What are three examples?
Promote digestion and absorption
Regulate the rate at which food moves through the GI tract (motility)
Regulation of food intake and utilization of nutrients