M4L2: Community Diagnosis
1/54
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
55 Terms
Diagnosis
process of identification of the client’s needs and problems based on the analysis of data and or information gathered
Community Diagnosis
the process of determining the health status of the community and the factors responsible for it
Community Diagnosis
a quantitative and qualitative description of the health of the citizens and factors affecting their health
Community Diagnosis
allows the identification of problems and areas of improvement, thereby stimulating action
NANDA (North American Nursing Diagnosis Association)
(Schemes in stating the diagnosis)
nursing diagnostic labels
NANDA (North American Nursing Diagnosis Association)
(Schemes in stating the diagnosis)
more focused on the individual
Shuster and Goeppinger
(Schemes in stating the diagnosis)
a format of nursing diagnosis for population groups which utilizes a 3-part statement:
a. The health risk or specific problem to which the community is exposed (Risk)
b. The specific aggregate or community with whom the nurse will be working to deal with the risk or problem (Among)
c. Related factors (strength and weaknesses) that influence how the community will respond to the health risk or problem (Related)
a. The health risk or specific problem to which the community is exposed (Risk)
b. The specific aggregate or community with whom the nurse will be working to deal with the risk or problem (Among)
c. Related factors (strength and weaknesses) that influence how the community will respond to the health risk or problem (Related)
(Schemes in stating the diagnosis: Shuster and Goeppinger)
3-part statement
Risk
(Schemes in stating the diagnosis: Shuster and Goeppinger - 3-part statement)
The health risk or specific problem to which the community is exposed
Among
(Schemes in stating the diagnosis: Shuster and Goeppinger - 3-part statement)
The specific aggregate or community with whom the nurse will be working to deal with the risk or problem
Related
(Schemes in stating the diagnosis: Shuster and Goeppinger - 3-part statement)
Related factors (strength and weaknesses) that influence how the community will respond to the health risk or problem
Omaha System
(Schemes in stating the diagnosis)
a framework for care of individuals, families and communities by nurses, nursing educators and physicians and other health care providers
Omaha System
(Schemes in stating the diagnosis)
a comprehensive and research based classification system for client problems that exists in the public domain.
A problem classification scheme
An intervention scheme
A problem rating scale for outcomes
(Schemes in stating the diagnosis: Omaha System)
(3) Components
A problem classification scheme (client assessment)
(Schemes in stating the diagnosis: Omaha System - Components)
serves as a guide in collecting, classifying, analyzing, documenting and communicating health and health related needs and strengths
First level
(Schemes in stating the diagnosis: Omaha System - Components)
A problem classification scheme (areas of concern)
- general level: 4 domains
Second level
(Schemes in stating the diagnosis: Omaha System - Components)
A problem classification scheme (areas of concern)
- problems or areas of concern under the 4 domains
Third level
(Schemes in stating the diagnosis: Omaha System - Components)
A problem classification scheme (areas of concern)
- the problems or areas of concern is categorized
Qualifier 1
(Schemes in stating the diagnosis: Omaha System - Components)
A problem classification scheme (areas of concern)
- Third level
: health promotion, potential problem, or actual problem
Qualifier 2
(Schemes in stating the diagnosis: Omaha System - Components)
A problem classification scheme (areas of concern)
- Third level
: Levels of clientele
Fourth level
(Schemes in stating the diagnosis: Omaha System - Components)
A problem classification scheme (areas of concern)
- specific level where signs and symptoms of actual problems are clustered
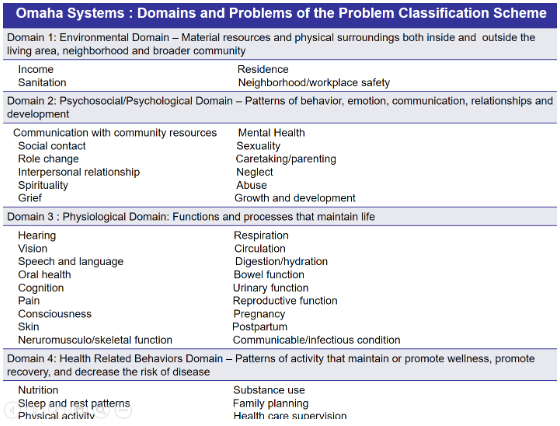
(Schemes in stating the diagnosis: Omaha System)
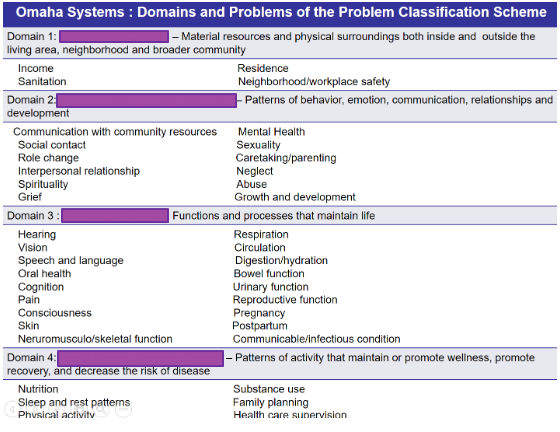
1. The health status of the community including the population’s level of vulnerability
2. Community health capability or the ability of the community to deal with its health problems.
3. Community action potential or the patterns in which the community is likely to work on its health problems.
(3) Conditions in Formulating A Nursing Diagnosis
Comprehensive Community Diagnosis
Problem- Oriented Community Diagnosis
(2) Types of Community Diagnosis
Comprehensive Community Diagnosis
(Types of Community Diagnosis)
aims to obtain a general information about the community
Demographic Variables
Socio-economic & Cultural Variables
Health & Illness Patterns
Health Resources
Political/ Leadership Patterns
(Types of Community Diagnosis: Comprehensive Community Diagnosis)
(5) Elements
Demographic Variables
(Types of Community Diagnosis: Comprehensive Community Diagnosis - Elements)
should show the size, composition & geographical distribution of the population.
Demographic Variables
(Types of Community Diagnosis: Comprehensive Community Diagnosis - Elements)
Total population
Demographic Variables
(Types of Community Diagnosis: Comprehensive Community Diagnosis - Elements)
Age & sex distribution
Demographic Variables
(Types of Community Diagnosis: Comprehensive Community Diagnosis - Elements)
Vital indicators e.g. growth rate, CBR, CDR, life expectancy
Demographic Variables
(Types of Community Diagnosis: Comprehensive Community Diagnosis - Elements)
Patterns of migration
Demographic Variables
(Types of Community Diagnosis: Comprehensive Community Diagnosis - Elements)
Population projection
Socio-economic & Cultural Variables
(Types of Community Diagnosis: Comprehensive Community Diagnosis - Elements)
Social indicators
Economic indicators
Environmental indicators
Cultural factors
Social indicators
(Types of Community Diagnosis: Comprehensive Community Diagnosis - Elements)
Socio-economic & cultural variables (indicators)
- communication
- transportation
- educational level
- housing conditions
Economic indicators
(Types of Community Diagnosis: Comprehensive Community Diagnosis - Elements)
Socio-economic & cultural variables (indicators)
- poverty level
- unemployment & underemployment rates
- types of industry present
- common occupation
Environmental indicators
(Types of Community Diagnosis: Comprehensive Community Diagnosis - Elements)
Socio-economic & cultural variables (indicators)
- land areas that contribute to vector problems
- terrain characteristics, land usage
- climate/season
- water supply, waste disposal
- air, water land pollution
Cultural factors
(Types of Community Diagnosis: Comprehensive Community Diagnosis - Elements)
Socio-economic & cultural variables (indicators)
- Ethnicity, religion
- social class, race
- political orientation
- language
Health & Illness Patterns
(Types of Community Diagnosis: Comprehensive Community Diagnosis - Elements)
Leading causes
Health Resources
(Types of Community Diagnosis: Comprehensive Community Diagnosis - Elements)
manpower resources and material resources
Political/ Leadership Patterns
(Types of Community Diagnosis: Comprehensive Community Diagnosis - Elements)
vital element in achieving the goal of high level of wellness among the people. It mirrors the sensitivity of the government to the people’s struggle for better lives.
Problem- Oriented Community Diagnosis
(Types of Community Diagnosis)
type of assessment that responds to a particular need of a target group
Examples
- Air pollution
- Improper Disposal of Garbage
- Flooding
- Unsafe water supply
Determining the objectives
Defining the Study Population
Determining the Data to be collected
Collecting the data
Developing the instrument
Actual data gathering
Data Collection
Data Presentation
Data Analysis
Identifying the community health nursing problems
Priority Setting
(11) Steps in conducting community diagnosis
Data presentation
(Steps in conducting community diagnosis)
Will depend largely on the type of data obtained
Descriptive data
(Steps in conducting community diagnosis: Data presentation)
narrative report
Numerical data
(Steps in conducting community diagnosis: Data presentation)
may be presented into tables or graphs making it easier to show comparisons including patterns and trends
Nature of condition/problem presented
Magnitude of the problem
Modifiability of the problem
Preventive potential
Social concern
(Steps in conducting community diagnosis: Priority setting)
(5) Criteria
Nature of condition/problem presented
(Steps in conducting community diagnosis: Priority setting - Criteria)
Categories of Community Health Nursing Problems
- Health status problems
- Health resource problems
- Health-related problems
Health status problems
(Steps in conducting community diagnosis: Priority setting - Criteria)
Categories of Community Health Nursing Problems
- increased or decreased morbidity, mortality, fertility
Health status problems
(Steps in conducting community diagnosis: Priority setting - Criteria)
Categories of Community Health Nursing Problems
- reduced capability for wellness
Health resource problems
(Steps in conducting community diagnosis: Priority setting - Criteria)
Categories of Community Health Nursing Problems
- Lack of or absence of manpower, money, materials or institutions necessary to solve health problems
Health-related problems
(Steps in conducting community diagnosis: Priority setting - Criteria)
Categories of Community Health Nursing Problems
- social, economic, environmental and political factors that aggravate the illness producing situations in the community
Magnitude of the problem
(Steps in conducting community diagnosis: Priority setting - Criteria)
severity of the problem that can be measured in terms of the proportion of the population affected by the problem
Modifiability of the Problem
(Steps in conducting community diagnosis: Priority setting - Criteria)
refers to the probability of reducing, controlling or eradicating the problem
Preventive Potential
(Steps in conducting community diagnosis: Priority setting - Criteria)
probability of controlling, reducing the effects posed by the problem
Social Concern
(Steps in conducting community diagnosis: Priority setting - Criteria)
perception of the population/community as they are affected by the problem and their readiness to act on the problem