Computer networks, connections and protocols
1/58
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
59 Terms
What are standalone computers?
Not connected to any network
What are networks?
A system connecting two or more computers
What are the advantages to networking?
can share files
can share hardware eg printers
The internet connection can be shared between the devices
Updates on software can be installed into all computers at once
Can communicate with users cheaply and easily
User accounts can be stored centrally, so users can log in from any device on the network
What are the disadvantages to networking?
increased security risks to data
malware and viruses spread very easily between computers
if a servers fails, the computer connected to it may not work
computers may run more slowly if there is a lot of data travelling on the network
What are local area networks (LAN)?
covers a small geographical area located on a site
all the hardware for LAN is owned by the organisation using it
LANS are wired with UTP cable, fibre optic or wireless using Wi-Fi
often found in businesses, schools or universities
What are wide area networks (WAN)?
covers a large geographical area, connecting LANS together
infrastructure is hired (the underlying facilities that support this) from telecommunication companies who own and manage it
WANS are connected with telephone lines, optic cables or satellite links
What is the function of a switch?
connects devices on a LAN
recieves data from one device and transmits it to the device on the network with the correct mac adress
What is the function of a router?
connects the LAN to the internet
responsible for transmitting data between networks
crucial role for directing data packets to their destination
assigns a unique IP address to each device
How do wireless networks work? What are there advantages?
Uses radio waves to transmit data
A wireless access point (WAP) is needed to connected devices wirelessly
Advantages:
Convenient as you can move around while still being connected
Cheaper as you need fewer wires
Describe the features of Bluetooth
A direct connection between two devices so data can be shared
Connection range is low
Low bandwidth
Often used in mobiles/wearing devices
Describe the features of Wi-fi
Can be used by multiple devices to connect to a LAN at the same time
Has a high connection range
High bandwidth compared to Bluetooth
Often used in homes
What is wireless access point (WAP)?
A WAP is a switch that allows devices to connect wirelessly
What do wireless network interface controllers (NIC) do?
An internal piece of hardware that allows a device to connect to a network
What are dongles?
USB dongles can be plugged into computers to allow them to connect wirelessly to the internet
HDMI dongles can use wireless networks to stream high-quality video to TV
What are ethernet networks?
Uses different types of ethernet cables to connect devices to a LAN
Transmission data - copper cables (UTP)
wired connections assure maximum, bandwidth, security and reliability
with twisted pair cables the wires are twisted around each other to reduce interference
Transmission data - coaxial cables
Made of single copper wire surrounded by a plastic layer for insulation and a metallic mesh which provides shielding from outside interface
Transmission data - fibre optic cables
Uses light to transmit data
Covers much longer distances and don’t suffer interference
Are expensive
What is bandwidth?
The amount of data that can be sent and receive successfully in a given time
This is not a measure of how fast data travels, but how much data can be sent in transmission media(the physical or wireless transfers of data)
Measured in bits per second
What is the impact of the numbers of users have on a network?
Too many users or devices on the same network can cause the network to slow down if there is a insufficient bandwidth for the data
Do wireless or wired connections have more bandwidth?
Wired connections have a higher bandwidth than wireless as it is less susceptible to interference
Do fibre optic cables or copper cables have more bandwidth?
Fibre optic cables have a higher bandwidth than copper cables
What is the error rate?
Less reliable connections = increased number of errors during data transfer
This means data will be resent until it arrives correctly
The quality of the wireless connections is dependant on the range of devices from the wireless access point and other environmental factors
What is latency?
The delay from transmitting data to receiving it
Caused by bottlenecks (when main components cant keep up with demands)
What is the client-server model?
A network that uses a server
A client makes a request to the server and the server processes the request and responds
The server stores:
Passwords
User profiles
Access information
This so it does not accept the wrong request
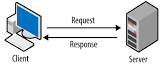
What are advantages of a client-server model?
Easier to keep track of files
Easier to perform backups
Easier to install software updates on all computers
Reliable and always on
Easier to manage network security
What are disadvantages of a client-server model?
Can be expensive to set up and maintain
Requires IT specialist to maintain
The server is a single point of failure
Users will loose access if the server fails
Server may become overloaded if too many clients access it at once
What is a peer to peer model?
Does not use a server
A peer is a computer on a network connected to all other peers and is equal to all other peers
Peers:
-Serve their own files to each other
-Responsible for its own security
-Responsible for its own backup
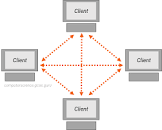
What are the advantages of a peer to peer model?
Easy to maintain
Specialist isn’t required
No dependency on a single server
No expensive hardware
What are the disadvantages of a peer to peer model?
Network is less secure
Users will need to manage their own backups
Can be difficult to maintain a well ordered file store as duplicates are made when copying files between devices

Describe star topology
All the devices are connected to a central switch or server that control the network
What are the advantages of star topology’s?
If a device fails or a cable is disconnected it does not affect the rest of the network
It is simple to add more devices to the network
Better performance - data goes straight to the central device so all devices can transmit data at one and there are fewer collisions
What are the disadvantages of star topology’s?
In a wired network every device needs a cable to connect to the central switch or server which can be expensive
If there is a problem with the switch the whole network will be affected
Describe the bus topology
What are the disadvantages?
All devices are connected to a single backbone cable
Devices sent data in both directions
Disadvantages:
Data collisions which slows the network
Describe the ring topology
What are the disadvantages?
Data moves in one direction around the ring, preventing collisions
Disadvantages
Only one computer can send of data at a time
Data passes through many computers before reaching its destination
Describe mesh topology
It is decentralised
Networking devices are either directly or indirectly connected to every other one so do not need a switch
Work by sending data along the faster route from one device to another
Describe a full mesh topology
Every device is connected to every other device
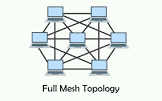
Describe a partial mesh topology
Not all devices are fully connected
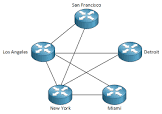
What are advantages of full mesh topology?
No single point of failure
When one device fails then data is sent along a different route to get to its target
What are the disadvantages of mesh topology’s?
Expensive
What is a network standard?
A set of agreed requirements for hardware and software
Important as it allows manufactures to create products and programs that will be compatible with products and programs from other manufactures
What are network protocols?
A set of rules for how devices communicate an how data is transmitted
What are communication protocols?
Specify how communication between two devices must start and end, how data must be organised and what devices must do if data goes missing
Describe MAC addresses
Every device needs a unique identifier so it can be found on a network
Mac addresses are assigned to all network-enabled devices by the manufacturer
Unique to each device and cannot be changed
Mac addresses are 48-64-bit binary numbers and are converted to hexadecimal
Mainly used in LANS
Describe IP addresses
IP addresses are used when sending data between networks
Assigned automatically or manually before devices enter a network
IPv4 - 32 bits 162.0.88.7
IPv6 - 128 bits 65F8:49A4:… 8 times
32 bit binary IP address is translated into four denary numbers
What does the protocol TCP/IP do?
Dictates how data is sent between networks
What does the TCP (transmission control protocol) do?
Sets the rules for how devices connect on the network and is in charge of splitting data packets and ressembling the packets back into its original data once they reach the recieving device
What does the IP (internet protocol) do?
Responsible for directing packets to their destination across the network
What are the other key protocols and what do they do?

What are layers? What are the features?
A group of protocols which have similar functions
Self contained - dont need to know whats happening in each layers
Serves the layer above
What are the advantages of layers?
Breaks down network communication in manageable pieces
Layers can be chnages without other layers being affected
Standards for each layers forces companies to make compatible hardware and software to different brands
Data can only be passed between adjacent layers
What do layers do?
Does hidden work for an action on the layer above
Describe the internet
A network of networks - a WAN which connects devices
Based around the protocol TCP/IP
What are URLs?
Adresses used to access web servers and resources on them
What is domain name service (DNS)?
Used to translate website domain names into IP addresses so you dont have to remember a IP address to access websites
What is hosting?
When a business uses its servers to store files of another organisation ..
What is the cloud?
Data and programs stored over the internet
What are the advantages of the cloud?
Users can access files and applications from any connected device
Easy to increase storage
No need to buy expensive hardware
No need for IT staff
Cloud hosts provide security and back-ups
Software is updated automatically
What are the disadvantages of the cloud?
Need connection to the internet
Dependent on host
Data can be vulnerable to hackers
Unclear who has ownership over data
Subscription fees may be expensive