IB HL Biology Enzymes: Structure, Function, and Factors Affecting Activity
1/26
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
27 Terms
What is the role of enzymes in biological reactions?
Enzymes act as biological catalysts that speed up chemical reactions without being consumed.
What suffix do most enzymes end with?
-ase
What is activation energy (EA)?
The amount of energy required to initiate a chemical reaction.
How do enzymes affect activation energy?
Enzymes lower the activation energy, allowing reactions to proceed faster.
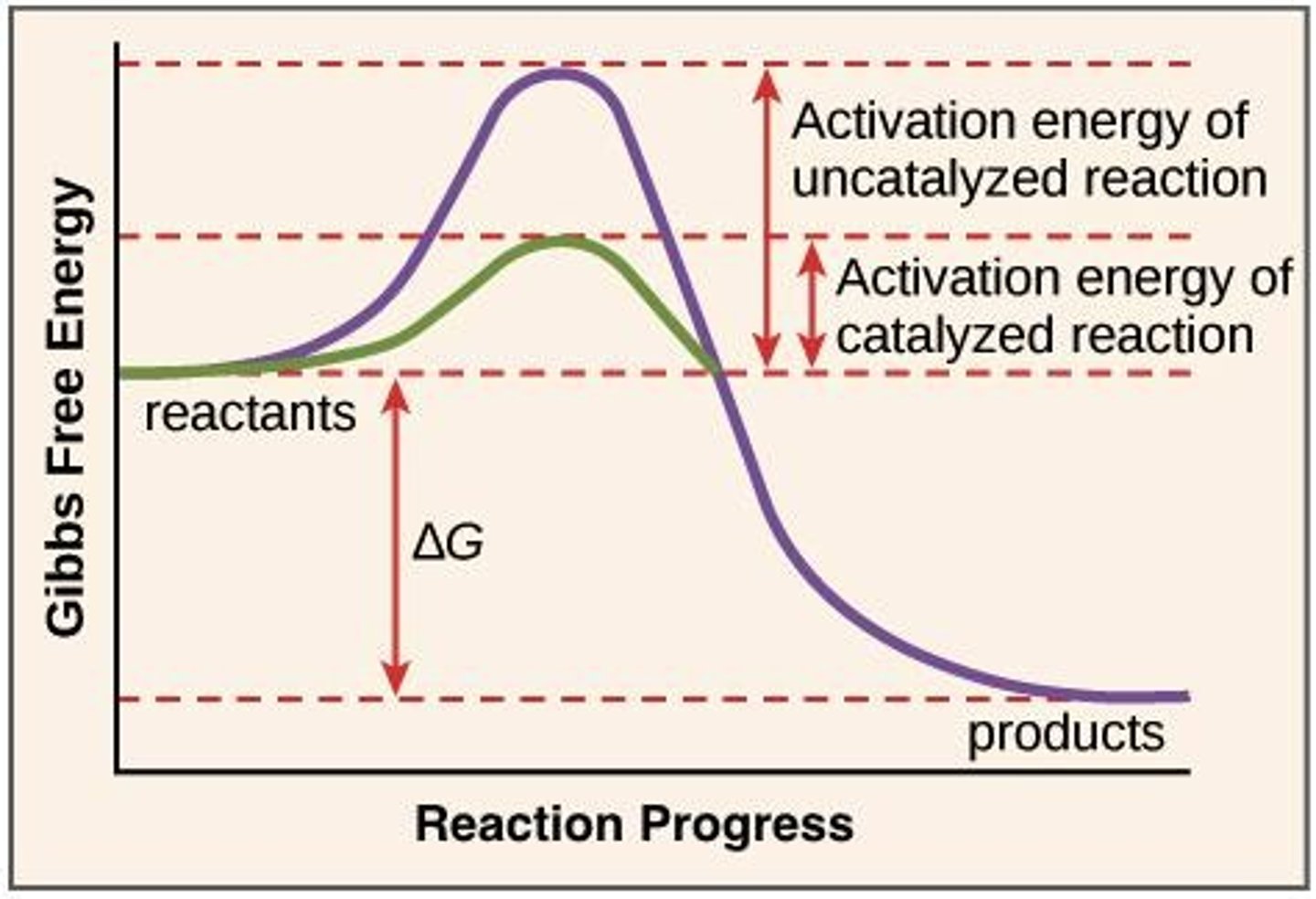
What is the transition state in a reaction coordinate diagram?
The transition state is the point with the highest energy during a reaction, indicating instability.
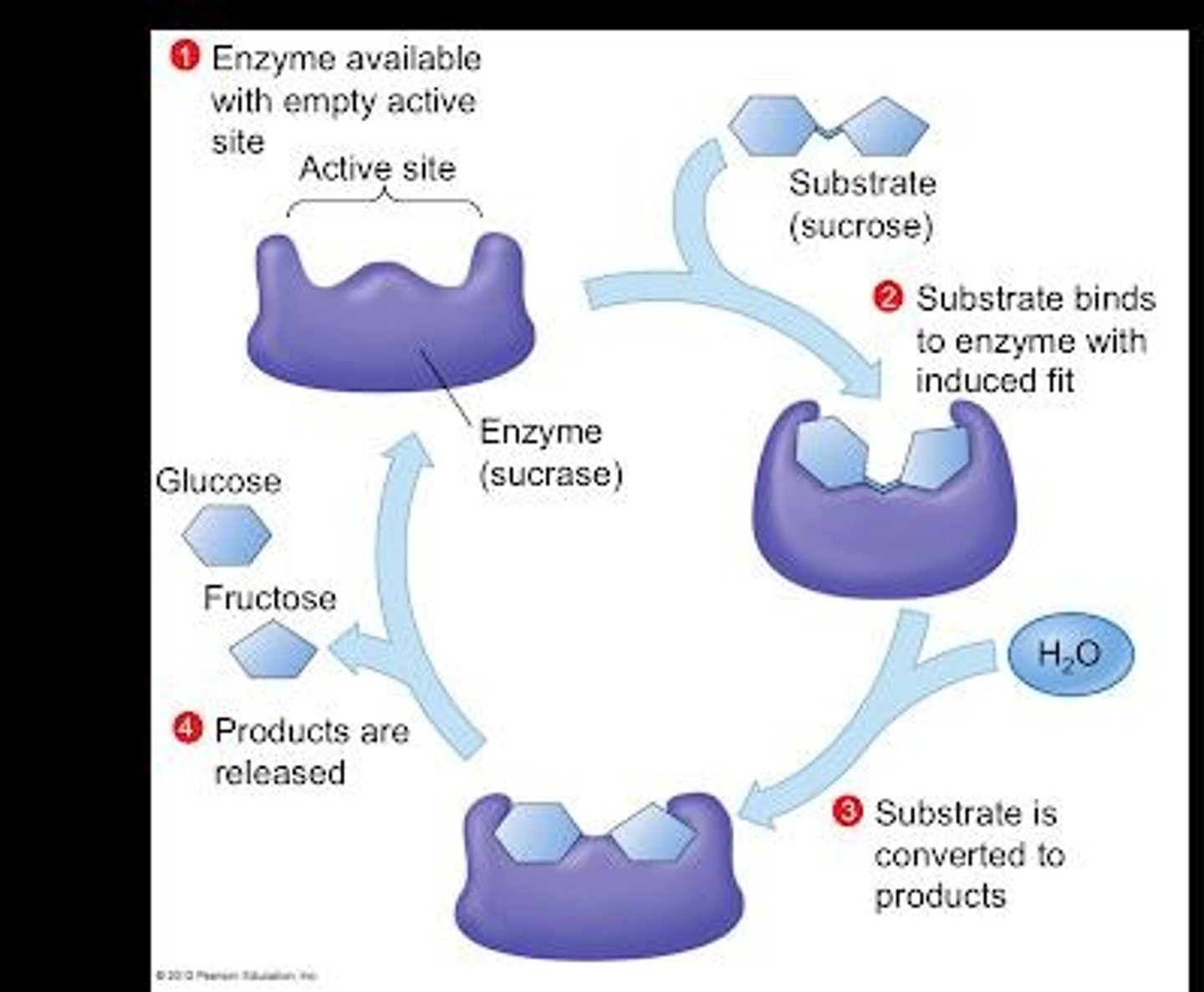
What is the active site of an enzyme?
The active site is the region where the substrate binds to the enzyme.
What determines the specificity of an enzyme?
The 3D structure of the enzyme and the chemical properties of the active site.
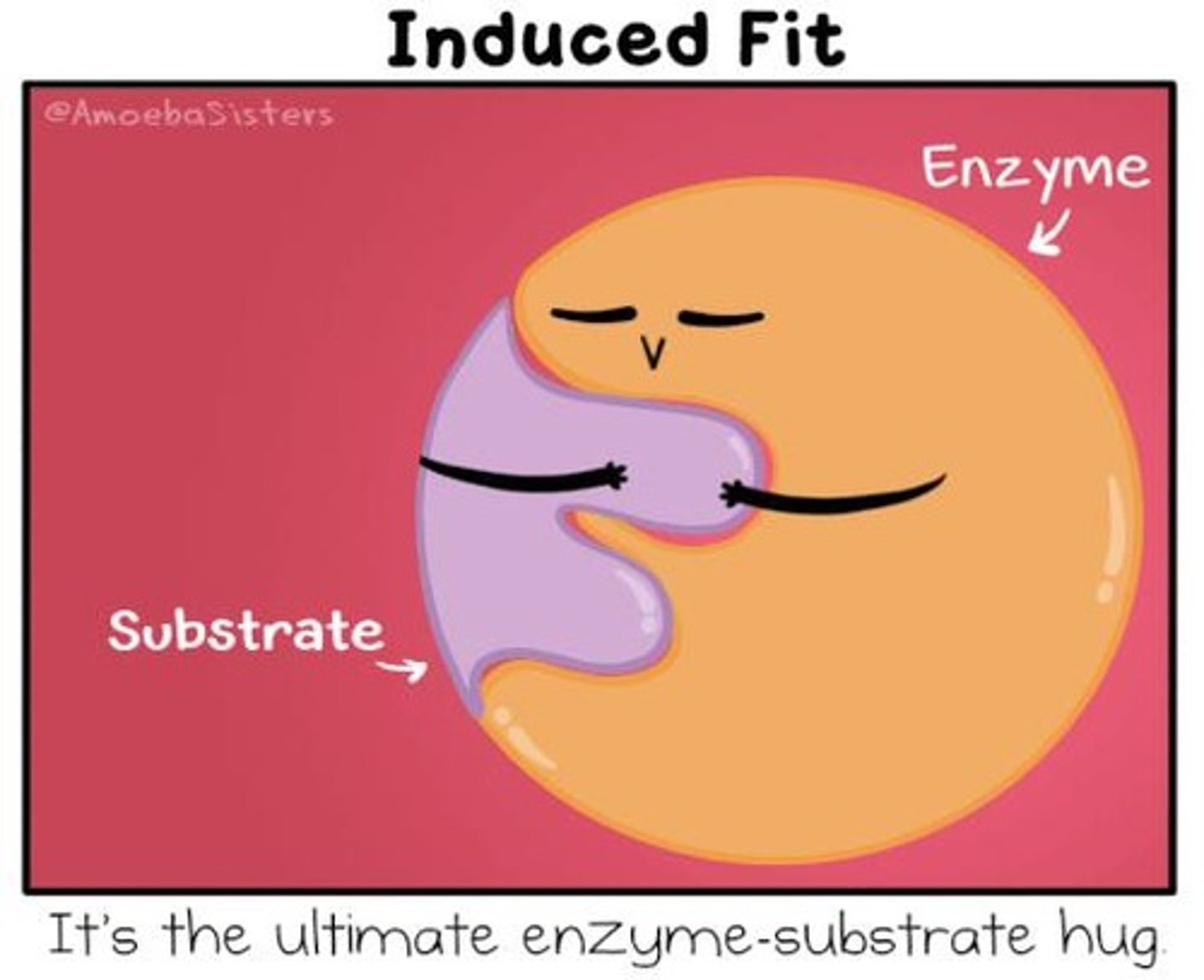
What is meant by 'induced fit' in enzyme activity?
Induced fit refers to the slight change in shape of the enzyme and substrate upon binding, enhancing the fit.
What are anabolic reactions?
Reactions that build larger molecules, typically requiring energy input.
What are catabolic reactions?
Reactions that break down large molecules into smaller ones, often releasing energy.
Give an example of an anabolic pathway.
Synthesizing polypeptides or building glycogen.
Give an example of a catabolic pathway.
Digestion of starches or cellular respiration.
What happens to enzymes at high temperatures?
Enzymes can denature, losing their structure and function.
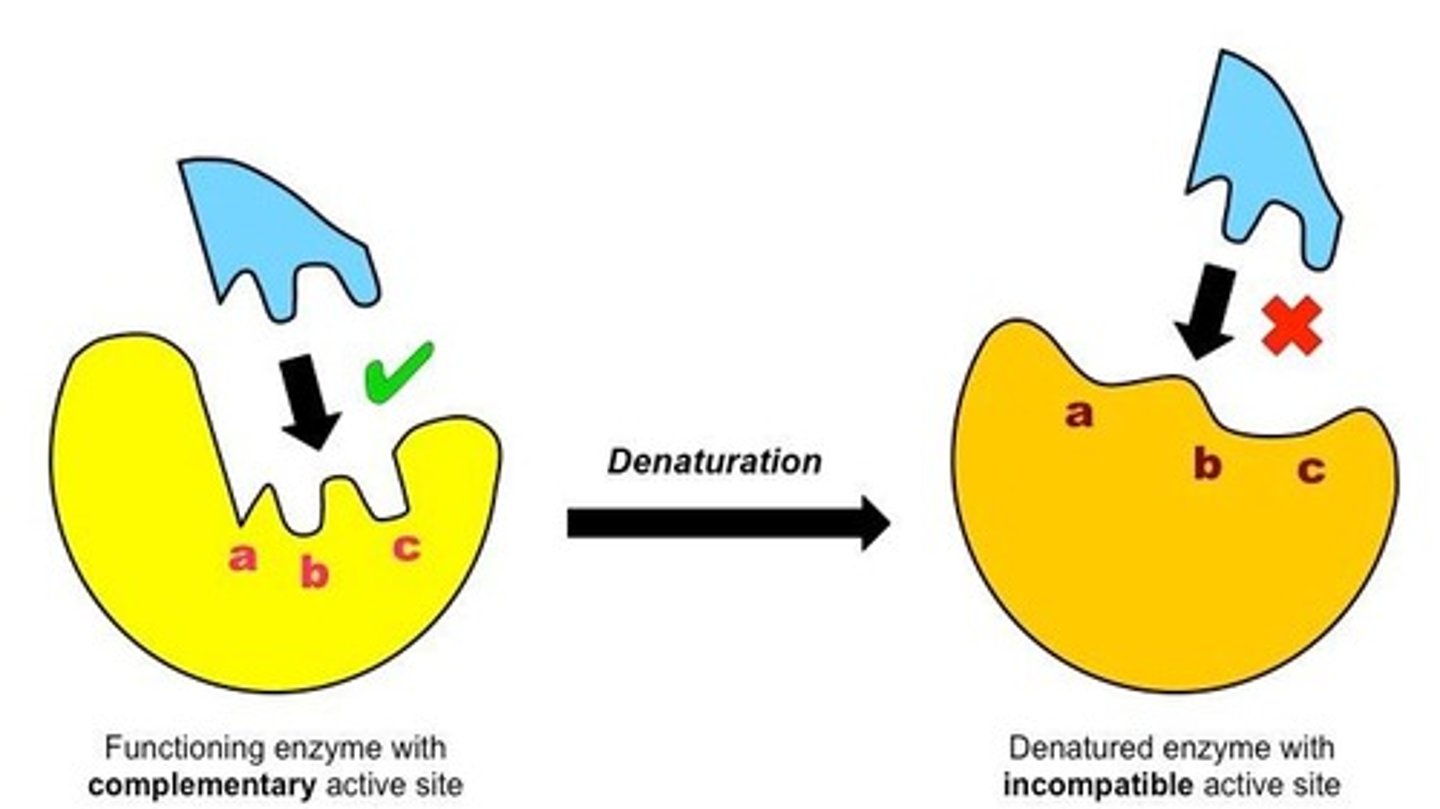
What is denaturation in the context of enzymes?
Denaturation is the process where enzymes lose their 3D structure due to extreme conditions, affecting their function.
How does pH affect enzyme activity?
Extreme pH levels can lead to denaturation, altering the enzyme's structure and function.
What is the significance of molecular motion in enzyme activity?
Molecular motion allows substrates to collide with enzymes, facilitating the formation of the enzyme-substrate complex.
What can increase the rate of enzyme-substrate collisions?
Increasing the temperature can enhance molecular motion, leading to more collisions.
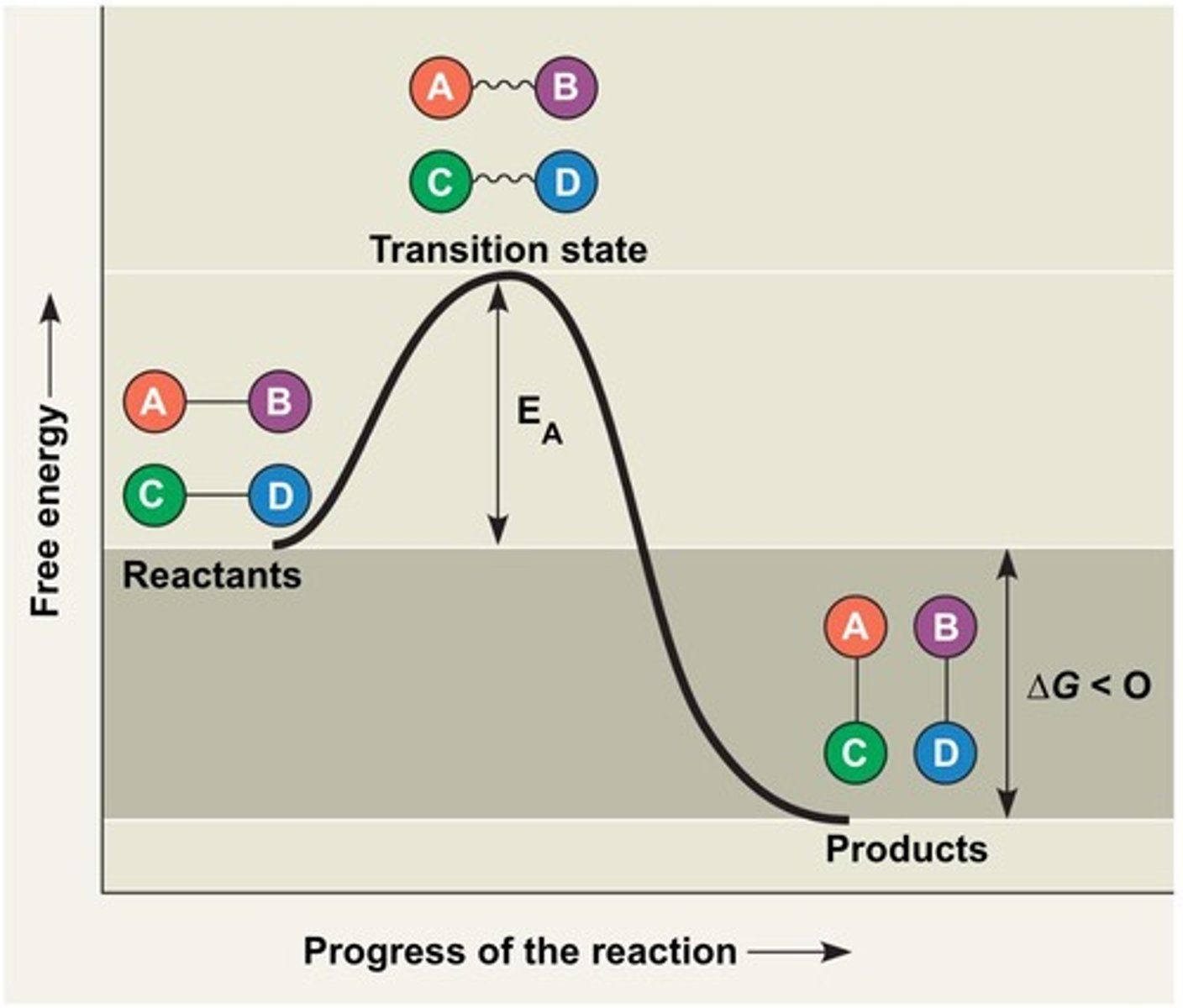
What is a reaction coordinate diagram?
A graph that illustrates the energy changes during a chemical reaction, showing reactants, products, and activation energy.
What is the difference between condensation and hydrolysis reactions?
Condensation reactions build larger molecules and release water, while hydrolysis reactions break down molecules using water.
What is the role of ribosomes in enzyme activity?
Ribosomes synthesize polypeptides, which are catalyzed by enzymes.
What is the relationship between enzyme structure and function?
The 3D structure of an enzyme is critical for its function, as it determines the shape and properties of the active site.
What is the enzyme-substrate complex?
The complex formed when a substrate binds to an enzyme's active site.
What is the importance of the correct orientation in enzyme-substrate binding?
Correct orientation ensures effective binding and catalysis of the reaction.
What happens to enzyme activity when the temperature is too low?
Enzyme activity decreases as molecular motion slows down, reducing collisions.
What is the effect of enzyme inhibitors?
Enzyme inhibitors decrease enzyme activity by blocking the active site or altering its shape.

What are the two main types of metabolic pathways?
Anabolic pathways (building) and catabolic pathways (breaking down).
What is the significance of enzymes in living organisms?
Most biological reactions would not occur at a significant rate without enzymes.