APES UNIT 1
1/104
Earn XP
Description and Tags
AP Environmental Science
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
105 Terms
Ecosystem
A community of living (biotic) organisms interacting with non-living (abiotic) components through nutrient and energy cycles.
Organism
A living thing that can function on its own.
Species
Organisms that resemble each other, share genetic makeup, and can interbreed to produce fertile offspring.
Interspecific
Interaction between different species.
Population
Organisms of the same species that interact and occupy a specific area.
Community
Populations of different species interacting in an area.
Ecological Niche
The role and function of an organism within its ecosystem, including its habitat and interactions.
Physical Environment
Influences how organisms affect and are affected by resources and competitors.
Niche
Reflects the specific adaptations a species has acquired through evolution.
Characteristics of a Niche
Habitat
Interactions with biotic and abiotic factors
Role in the food web
Resources available
Symbiosis
A close and long-term biological interaction between two different species.
Amensalism
One species suffers, while the other is unaffected.
Example: Black walnut tree releases chemicals that kill nearby plants.
Commensalism
One organism benefits, while the other is unaffected.
Using another organism for transportation
Using another organism for housing
Using something another organism created
Competition
The struggle between organisms for resources like food, mates, or territory.
Intraspecific Competition
Competition between members of the same species.
Interspecific Competition
Competition between members of different species.
Predator-Prey Competition
Predators compete for food, while prey compete for survival.
Mutualism
Both species benefit from the interaction.
Parasitism
One species benefits while the other is harmed.
Predation
A predator hunts and kills prey for food.
Opportunistic Predators
Eat almost anything.
Specialist Predators
Target specific prey.
Saprotrophism
Organisms obtain nutrients by decomposing dead matter.
Law of Tolerance
The abundance and distribution of a species depend on its tolerance to physical and chemical factors.
Tolerance Limits
If a factor exceeds an organism’s limits, it can limit growth, abundance, or distribution.
Limiting Factor
Any abiotic factor that limits or prevents population growth.
Terrestrial Limiting Factors
Soil nutrients
Water and light availability
Temperature
Aquatic Limiting Factors
pH levels
Dissolved oxygen
Light availability
Salinity
Predator-Prey Relationships
Prey increase → Predators increase
Predators eat too many prey → Prey decrease
Fewer prey → Predator population declines
Resource Partitioning
Division of resources among species to reduce competition.
Morphological Partitioning
Species evolve different structures to use the same resource.
Spatial Partitioning
Species use the same resource but in different areas.
Temporal Partitioning
Species use the same resource but at different times.
Biome
A major regional or global biotic community characterized by dominant plant life and prevailing climate.
Deserts
Definition – Defined by low rainfall, not temperature.
Coverage – 20% of Earth's surface, receiving <20 inches (50 cm) of rain per year.
Temperature Extremes – Low humidity leads to extreme daily temperature changes.
Location – Found between 15° and 35° latitude.
Cold Deserts – Arctic tundra has low rainfall, making it a cold desert.
Desert Plants & Adaptations
Succulents – Store water in fleshy leaves or stems.
Deep roots tap groundwater.
Open stomata at night.
Shallow roots quickly absorb rainwater.
Small surface area minimizes sunlight exposure.
Waxy leaves reduce water loss.
Cactus Adaptations
Sharp spines provide shade, reduce airflow, and deter herbivores.
Secrete toxins into soil to limit competition.
Wildflowers
Depend on water for germination.
Short life spans.
Complete their lifecycle in one growing season.
Store biomass in seeds.
Desert Animals & Adaptations
Small body size.
Nocturnal behavior.
Small surface areas reduce water loss.
Burrow underground to stay cool.
Aestivation – Summer hibernation to conserve energy.
Forests
Coverage – One-third of Earth's land surface, mainly in North America, Russia, and South America.
Importance – 75% of global plant biomass and primary productivity.
Forest Ecozones –
Boreal forests near poles.
Tropical forests near the equator.
Tropical Rainforests
Found near the equator.
Annual rainfall >80 inches (200 cm).
Warm, stable temperatures year-round.
Multilayered canopy limits sunlight penetration.
Highly diverse plant and animal species.
Rapid decomposition, but nutrient-poor soil.
Trees have buttressed trunks, shallow roots, and large leaves.
Forest Layers
Closed Canopy – Tree crowns cover >20% of the ground. (80% of forests)
Open Canopy – Tree crowns cover <20% of the ground.
Temperate Deciduous Forests
Found in North America, Europe, and Asia.
Distinct seasons with a growing period of 140–200 days.
Temperature: –20°F to 85°F (–30°C to 30°C).
Annual rainfall: 30–60 inches (75–150 cm).
Fertile soil enriched by leaf litter.
Diverse understory vegetation.
Common trees: Oak, maple, hickory, beech, willow.
Animals: Squirrels, deer, foxes, black bears, bobcats.
Temperate Coniferous Forests
Found in coastal and mountainous regions with mild winters.
Common trees: Cedar, pine, spruce, fir, redwood.
Forest Layers:
Overstory – Tallest trees.
Understory – Young trees and shrubs.
Thick waxy needles reduce transpiration.
Animals hibernate, migrate, or have thick fur.
Taiga (Boreal Forest)
Largest terrestrial biome (North America, Eurasia, Siberia).
Cold-tolerant coniferous trees (pine, spruce, larch).
Harsh climate with low productivity.
Seasons:
Short, warm, moist summers.
Long, dry, freezing winters.
Thin, nutrient-poor, acidic soil.
Animals: Moose, bears, lynxes, wolves, bats.
Grasslands Overview
Characteristics – Dominated by grasses, few trees/shrubs.
Types:
Savannas (Tropical Grasslands)
Temperate Grasslands
Savannas (Tropical Grasslands)
Found in Africa, Australia, South America, India.
Warm climate with 20–50 inches (50–130 cm) of seasonal rainfall.
Fires occur during the dry season.
Animals: Elephants, lions, giraffes, hyenas, zebras.
Temperate Grasslands
Examples: Pampas (Argentina), Steppes (Russia), Prairies (North America).
Hot summers, cold winters, moderate rainfall.
Deep-rooted grasses enrich fertile soil.
Seasonal fires prevent tree growth.
Animals: Bison, coyotes, deer, prairie dogs, hawks.
Tundra Overview
Extremely cold, low precipitation, nutrient-poor soil.
Low biodiversity and short growing seasons.
Permafrost limits plant growth.
Arctic Tundra
Located near the North Pole, south of the taiga.
Growing season ~50 days.
Annual precipitation: 6–10 inches (15–25 cm).
Soil is nutrient-poor and slow to form.
Plant Adaptations:
Short, clumped plants survive strong winds.
Can photosynthesize in low light.
Reproduce by budding instead of flowers.
Animal Adaptations:
Insulated with fat and fur.
Many hibernate or migrate.
Herbivores: Caribou, hares, lemmings.
Carnivores: Arctic foxes, wolves, polar bears.
Alpine Tundra
Found in high-altitude mountains.
Growing season: 180 days.
Well-drained soil.
Similar plants to Arctic tundra.
Animals: Mountain goats, sheep, elk, beetles.
Aquatic Biomes Overview
Includes Antarctic, marine, lakes, wetlands, rivers, and streams.
Nutrients come from water.
Water disperses gametes and larvae.
High thermal capacity reduces the need for temperature regulation.
Buoyancy reduces the need for legs/trunks.
Water screens out UV radiation.
Antarctic Biome
Coldest climate on Earth.
Interior: −70°F (−57°C); Coast: 14°F (−10°C).
Low precipitation (~6.5 in/year); deserts get <10 in (~250 mm).
Rainfall rare, mostly coastal.
Dry air & low humidity.
Ice sheet from compressed snow.
Winters: Dark, cold, no phytoplankton.
Summers: High phytoplankton growth → krill thrive.
Marine Biome
Oceans = 75% of Earth's surface, 3% salt.
Evaporation = major rainfall source.
Affects climate (temp, wind, clouds).
Marine algae & bacteria absorb CO₂ & release O₂.
Highest net primary productivity per area.
Ocean Circulation
N. Hemisphere = more land; S. Hemisphere = more ocean.
Greater seasonal temp differences in N. Hemisphere.
Air & ocean currents move heat from equator → poles.
Convection: Warm air/water rises, cool sinks.
Wind drives surface currents.
Deep currents controlled by temp & density.
Thermohaline currents drive constant ocean water movement.
Ocean Zones
Littoral (Intertidal) Zone: Near shore.
Neretic Zone: Continental shelf.
Photic Zone: Sunlit upper layer, high photosynthesis.
Corals & Coral Reefs
Corals: Marine invertebrates in colonies.
Polyps: Tiny animals with tentacles & calcium exoskeleton.
Zooxanthellae: Photosynthetic algae inside corals.
Types of Coral Reefs:
Fringing (near coasts)
Barrier (parallel to coast, deeper lagoons)
Atolls (rings of coral around lagoons).
Lakes Biome
Formed by glaciers, craters, tectonic activity, oxbow rivers.
Inputs: Rain, runoff, groundwater.
Outputs: Evaporation, human use, outflow.
Lake Zones:
Littoral: Near shore, plants thrive.
Limnetic: Open water, sunlight penetration.
Profundal: Deep, dark, low oxygen.
Benthic: Bottom, decomposers.
Types of Lakes
Oligotrophic: Young, deep, nutrient-poor, clear water.
Mesotrophic: Moderate nutrients & productivity.
Eutrophic: Old, shallow, nutrient-rich, murky, oxygen-poor.
Lake Stratification & Turnover
Thermal Stratification:
Epilimnion (warm surface)
Thermocline (rapid temp change)
Hypolimnion (cold deep water).
Seasonal Turnover: Mixing of layers in spring & fall.
Wetlands Biome
Water-covered areas that support aquatic plants.
Types: Saltwater, freshwater, brackish.
Services:
Flood control, carbon sink, groundwater recharge.
Traps sediments, supports biodiversity.
Threats: Agriculture, dams, development, invasive species, pollution.
Rivers & Streams
Nutrient levels depend on terrain, vegetation, erosion.
Inputs: Groundwater, precipitation, runoff, springs.
Zones:
Source Zone: Cold, clear, oxygen-rich, rocky, trout habitat.
Transition Zone: Warmer, slower, more nutrients.
Floodplain Zone: Murky, warm, joins estuaries.
Riparian Areas
Lands next to rivers & lakes.
Support water-loving plants.
Prevent erosion, provide habitat, filter pollutants.
Carbon Cycle
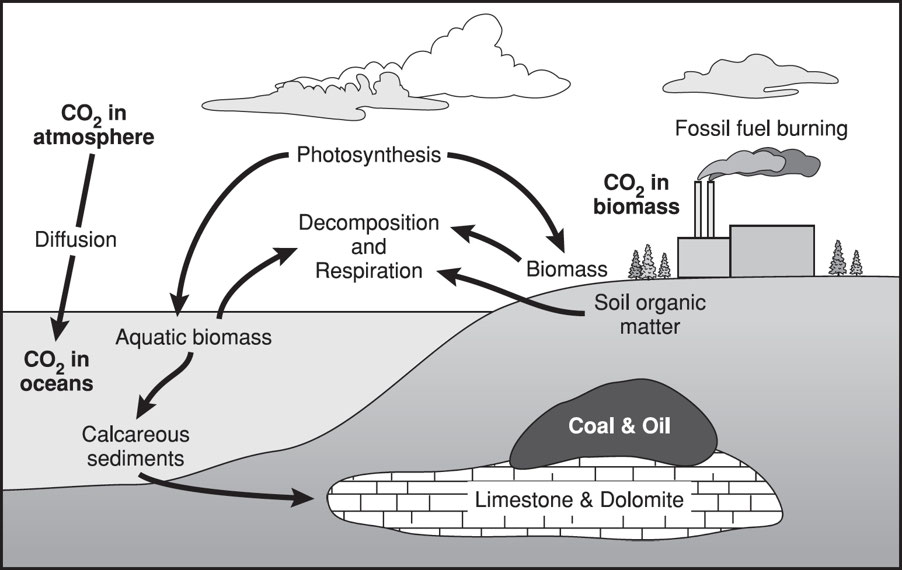
Carbon Cycle Overview
🔹 Definition: The exchange of carbon among the biosphere, geosphere, hydrosphere, and atmosphere.
🔹 Importance: Carbon is the building block of life, found in carbohydrates, fats, proteins, and nucleic acids.
🔹 Atmosphere: Carbon dioxide (CO₂) makes up less than 1% of the air.
🔹 Oceans: Carbon enters by dissolving atmospheric CO₂.
🔹 Soil: One-third of soil carbon is stored in organic form.
🌊 Carbon Precipitation
Dead soft tissue & calcium carbonate (CaCO₃) in shells sink into deeper ocean layers.
🌊 Ocean Acidification
CO₂ absorption increases acidity, harming coral reefs & externally fertilized eggs.
🌊 Calcium Carbonate Impact
Increased acidity slows CaCO₃ precipitation, reducing CO₂ absorption.
Major Carbon Reservoirs (Sinks)
🌿 Plant Matter: Photosynthesis removes ~15% of atmospheric carbon.
🌍 Terrestrial Biosphere: Forests store 90% of above-ground carbon & 75% of soil carbon.
⛰ Sedimentary Deposits: Limestone (CaCO₃) is the largest carbon reservoir.
🌊 Oceans: CO₂ dissolved in seawater is used by phytoplankton & marine organisms.
Human Impact on the Carbon Cycle
⚙ Before Industrial Revolution: CO₂ levels were balanced through photosynthesis, respiration, & natural CO₂ cycling.
⚠ After Industrial Revolution:
✔ Deforestation reduces carbon storage.
✔ Fossil fuel combustion releases long-term stored carbon.
✔ Climate change effects:
🌊 Increased ocean acidity
☁ Increased atmospheric particulate matter
❄ Faster melting of ice reserves
🌪 Stronger & more frequent storms
Nirtogen Cycle
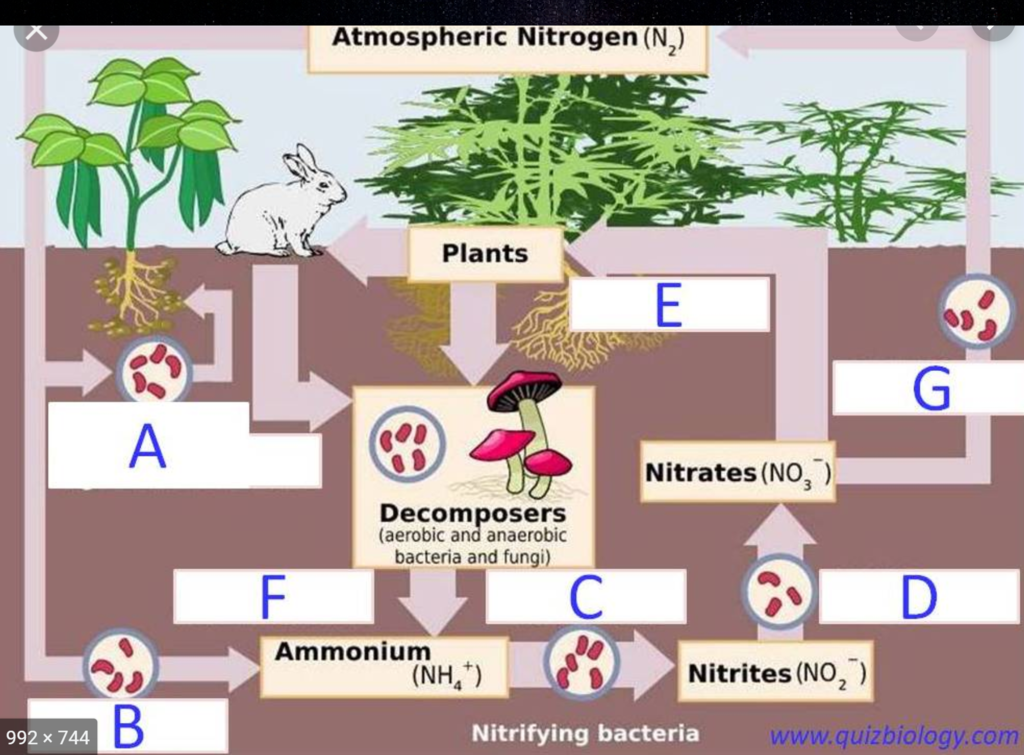
Nitrogen Cycle Overview
🔹 Nitrogen Composition: Makes up 78% of the atmosphere.
🔹 Importance: Needed for amino acids, proteins, DNA, and RNA.
🔹 Major Stores: Found in the atmosphere, soil, and oceans.
🔹 Biological Limitation: Atmospheric nitrogen (N₂) is abundant but not directly usable by most organisms.
🔹 Key Role: Essential for photosynthesis, plant growth, and decomposition.
Human Impact on the Nitrogen Cycle
⚠ Disruptions:
✔ Fossil fuel combustion
✔ Inorganic fertilizer use
✔ Wastewater & sewage production
⚠ Consequences:
✔ Water acidification
✔ Eutrophication (excess nutrients causing algal blooms)
✔ Increased toxicity in water ecosystems
Nitrogen Cycle Processes
🌱 1. Nitrogen Fixation:
🔸 Converts N₂ into ammonia (NH₃) or nitrate (NO₃⁻)—usable nitrogen forms.
🔸 Key Players:
Legumes (alfalfa, clover, soybeans)
Nitrogen-fixing bacteria (Rhizobium)
🌱 2. Nitrification:
🔸 NH₃ → NO₂⁻ → NO₃⁻ (ammonia to nitrite to nitrate)
🔸 Produces the most useful nitrogen forms for plants.
🌱 3. Assimilation:
🔸 Plants absorb NH₃, NH₄⁺, and NO₃⁻ through roots.
🌱 4. Ammonification:
🔸 Decomposers break down dead matter into NH₃ & NH₄⁺ (usable nitrogen).
🌱 5. Denitrification:
🔸 Anaerobic bacteria convert NH₃ into NO₂⁻, NO₃⁻, N₂, & N₂O, releasing nitrogen back into the atmosphere.
Phosphorus Cycle
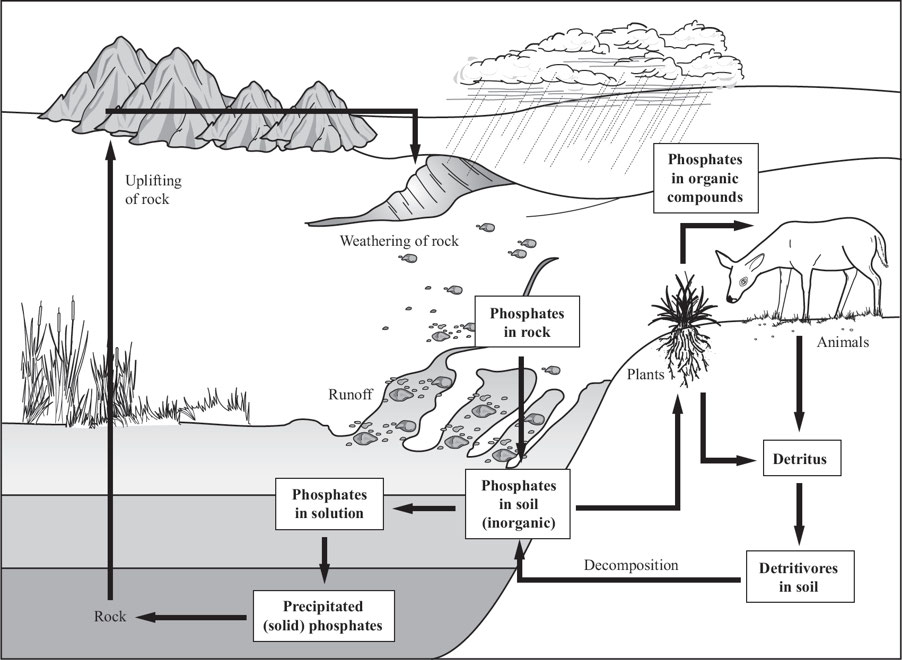
Phosphorus Cycle Overview
🔹 Importance: Essential for nucleotides, ATP, cell membranes, bones, teeth, and shells.
🔹 Main Reservoir: Sedimentary rocks (not found in the atmosphere).
🔹 Forms: Exists as phosphate ion (PO₄³⁻) or hydrogen phosphate ion (HPO₄²⁻).
Phosphorus Movement
🪨 Weathering:
✔ Released slowly from terrestrial rocks by acid rain & weathering.
✔ Dissolves into soil, where it is absorbed by plants.
🌱 Limiting Factor in Soils:
✔ Low concentration & solubility make phosphorus a key component in fertilizers.
Human Impact on the Phosphorus Cycle
⚠ Runoff from agriculture & sewage:
✔ Increases cyanobacteria, algae, and aquatic plants.
✔ Leads to oxygen depletion → kills aquatic organisms.
⚠ Fertilizer use & mining:
✔ Phosphate-rich fertilizers (e.g., guano, rock phosphate) alter the cycle.
✔ Large-scale mining of phosphorus for inorganic fertilizers & detergents.
⚠ Deforestation:
✔ Clearing tropical forests reduces available phosphorus stored in vegetation.
Hydrologic Cycle
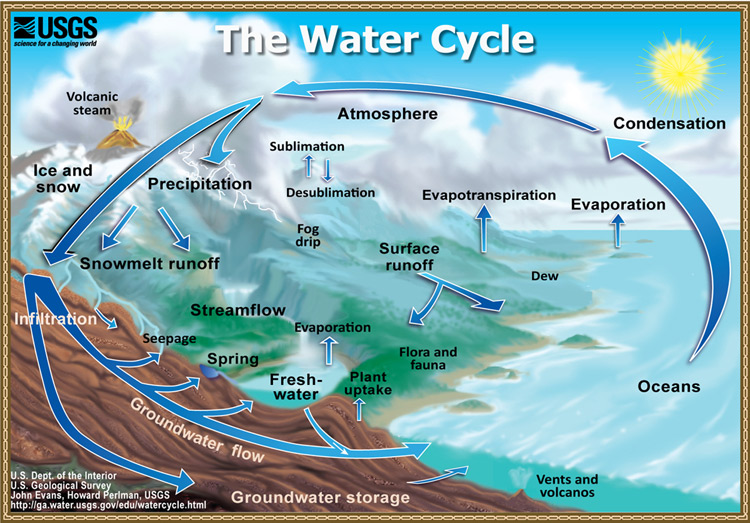
Water Cycle Overview
☀ Powered by the Sun:
✔ Evaporates water from oceans, lakes, rivers, soil, and vegetation.
✔ Keeps Earth from overheating.
🌊 Oceans & Water Storage:
✔ 97% of Earth's water is in oceans.
✔ Oceans contribute 78% of global precipitation.
✔ 86% of global evaporation comes from the sea.
⚖ Dynamic Equilibrium:
✔ Evaporation = Precipitation (balances the cycle).
✔ Warm air holds more water vapor than cold air.
Processes in the Water Cycle
☁ Condensation: Vapor → Liquid.
💨 Evaporation: Liquid → Vapor.
🌿 Evapotranspiration: Water transfer from land (soil, plants, surfaces) → atmosphere.
🌍 Infiltration: Water enters soil from the ground surface.
🌧 Precipitation: Rain, snow, sleet, hail falling to Earth.
🏞 Runoff: Water flows over land instead of absorbing.
Water Distribution
🌎 70% of Earth's surface is water.
✔ 97% in oceans.
✔ 3% freshwater (mostly in glaciers & ice caps).
✔ Remaining freshwater: groundwater, lakes, rivers, soil moisture, and atmospheric moisture.
Water Properties
🔥 High Energy for Evaporation.
🧊 Expands when frozen.
🌊 High specific heat capacity: Slow temperature changes.
☀ Filters UV radiation in aquatic ecosystems.
💧 High boiling point.
⚡ Strong hydrogen bonds hold water molecules together.
Water Polarity & Effects
🌳 Capillary Action: Helps tree roots absorb water for growth.
❄ Floating Ice: Essential for life near poles due to different molecular arrangements.
🌀 Dissolves many compounds due to polarity.
🚫 Interacts with non-polar molecules.
Freshwater Renewal
✔ Freshwater depends on regular movement of water through Earth’s surface & atmosphere.
Aquifers
💧 Aquifer: Underground water storage in geologic formations.
✔ Confined (Artesian) Aquifer:
Saturated with water under pressure due to impermeable layers.
✔ Recharge Zone: The surface area that supplies water to an aquifer.
✔ Unsaturated Zone: Soil contains both water & air but is not fully saturated.
✔ Water Table: The depth at which the ground is fully saturated with water.
Threats to Aquifers
⚠ Groundwater depletion from excessive pumping.
✔ When extraction > recharge, the water table drops.
✔ Major causes:
Agriculture (largest contributor).
Municipal & domestic use.
Climate change reducing inputs.
Effects of Groundwater Depletion
📉 Increased pumping costs due to deeper wells.
🌍 Land subsidence: Ground sinks due to water loss.
🚱 Water shortages affect domestic & agricultural needs.
🌊 Saltwater intrusion: Saltwater contaminates freshwater aquifers.
🏞 Reduction in surface water: Lakes, ponds, & streams shrink.
🐑 Overgrazing & erosion worsen due to water scarcity.
Fundamentals of Primary Productivity
☀ Ultimate Energy Source: The Sun powers life on Earth.
🌿 Photosynthesis: Plants convert light energy into food.
Photosynthesis Process
📉 Removes CO₂ from the atmosphere.
🌞 Uses light energy to create carbohydrates & organic compounds.
🌱 Chlorophyll in chloroplasts captures sunlight.
🔥 Cellular Respiration:
Breaks down glucose for energy.
Forms cellulose, lipids, amino acids, & proteins.
Gas Exchange in Photosynthesis
🌬 Oxygen Released into the atmosphere.
💨 CO₂ Emitted during respiration.
📌 Plants absorb more CO₂ than they release, making them carbon sinks.
Factors Affecting Photosynthesis
📈 Carbon Dioxide Concentration: More CO₂ → Faster photosynthesis.
💡 Light Amount & Wavelength: Different wavelengths impact efficiency.
💧 Water Availability: Essential for photosynthesis.
🌡 Temperature: Extreme temperatures slow down photosynthesis.
Trophic Levels & Food Webs
🔺 Trophic Level: The position an organism occupies in a food chain.
🌿 Producers → Primary Consumers → Secondary Consumers → Tertiary Consumers
🔗 Food Web: Interconnected food chains in an ecosystem.
Ecological Pyramids
📊 Ecological Pyramid: Shows energy flow with producers at the base.
💡 Energy decreases as it moves up the pyramid.
Inverted Biomass Pyramids (Aquatic Systems)
🌊 Seen in coral reefs & oceans.
🦠 Phytoplankton (producers) have short life spans.
🦐 Zooplankton (consumers) live longer & accumulate more biomass.
🐟 Fish & aquatic predators have lower death rates, further inverting the pyramid.
Energy Transfer in Trophic Levels
🔥 Only 10% of biomass is transferred between levels.
📈 Higher consumers live longer & grow slower than producers.
Laws of Energy Transfer
⚖ Second Law of Thermodynamics: Energy is lost as heat in each transfer.
♻ Entropy: Systems naturally become more disordered over time.
Cellular Respiration
⚡ Cellular Respiration: Process where glucose is oxidized to produce carbon dioxide, water, and ATP (chemical energy).
🔄 Opposite of Photosynthesis: Photosynthesis stores energy, while respiration releases it.
Heterotrophs
🌱 Heterotrophs: Organisms that rely on photosynthetic organisms for energy.
🦁 Examples: Animals, fungi, and some bacteria.
Energy Flow in Ecosystems
🔺 10% Rule: Only 10% of energy is passed on to the next trophic level, the rest is lost as heat.
🌍 Energy Flow: Energy moves from producers → consumers in ecological pyramids.
Sunlight as the Ultimate Energy Source
☀ Solar Energy: 35% heats water, land, and evaporates water.
🌿 Plant Use: 8% is available to plants, but only 1% is used for photosynthesis.
Productivity
🌱 Primary Productivity: Rate at which autotrophs (plants) generate biomass.
🐾 Secondary Productivity: Rate at which heterotrophs (consumers) generate biomass.
Biomass Pyramids
📊 Biomass Pyramid: Shows the amount of organic mass at each trophic level.
🐟 Marine Inversion: In oceans, zooplankton have more biomass than phytoplankton due to size differences.