Skeletal system
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/171
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Last updated 1:54 PM on 7/17/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
172 Terms
1
New cards
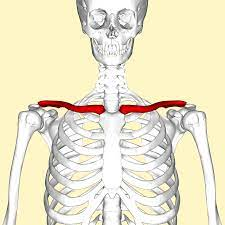
Clavicles
The two flat bones attaches to the sternum on their anterior side and to the shoulder blades
Xương đòn
Xương đòn
2
New cards
Scapulae
A pair of large, triangular bones located at the back of the thorax
Xương vai
Xương vai
3
New cards
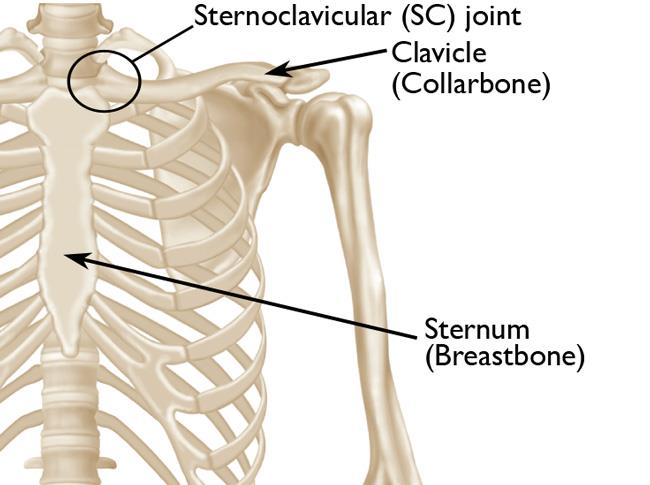
Sternoclavicular joint
Xương ức - đòn
4
New cards
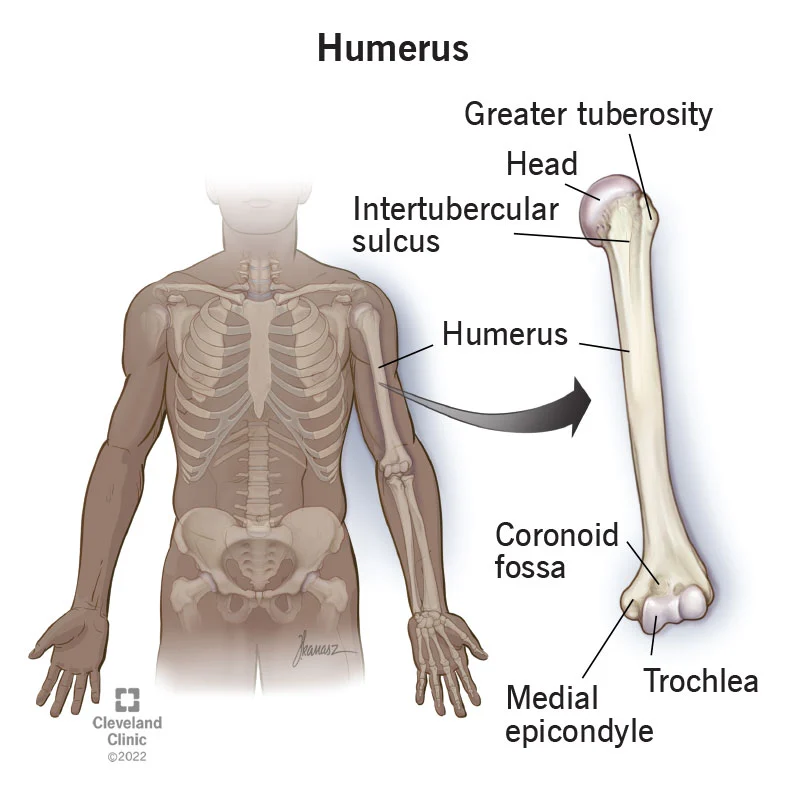
Humerus
Upper arm bone
5
New cards
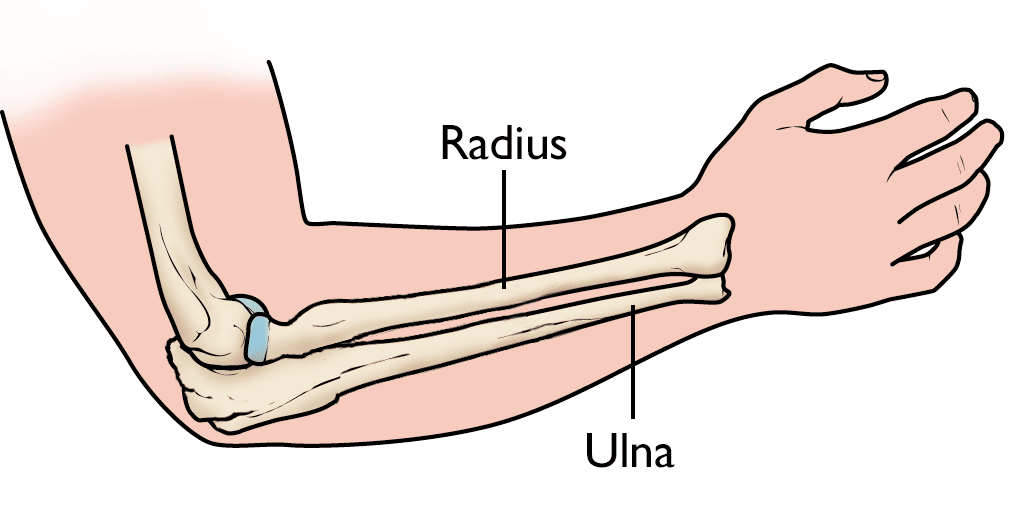
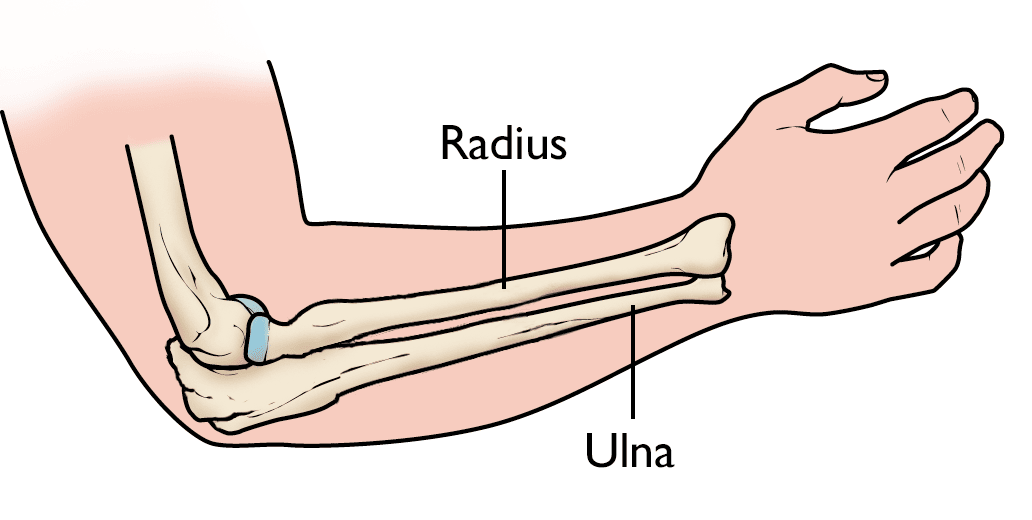
Ulna
The lower arm bone located on the little finger side of the humerus
6
New cards
Radius
The lower arm bone located on the thumb side
7
New cards
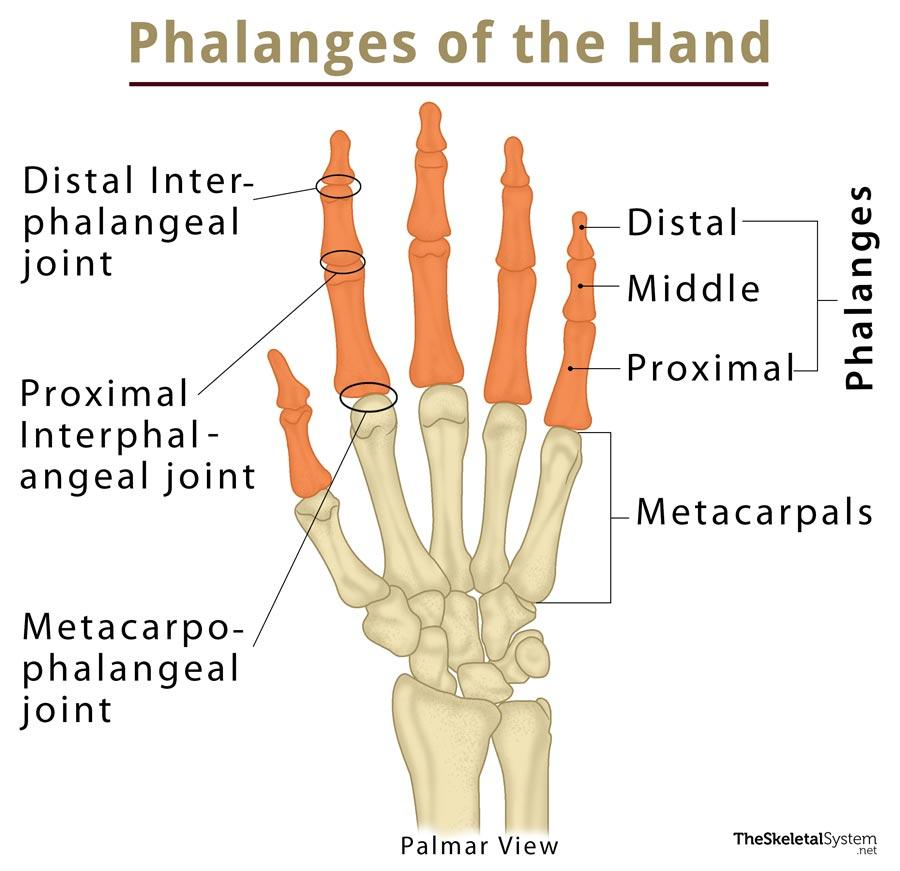
Phalanges
Bone of the fingers
8
New cards
Metacarpals
Bones of the palm
9
New cards
Carpals
Bones of the wrist
10
New cards
Two
How many phalanges are there in the thumb?
11
New cards
Three
How many phalanges are there in other fingers?
12
New cards
* Distal
* Middle
* Proximal
* Middle
* Proximal
What are the 3 types of phalanges?
13
New cards
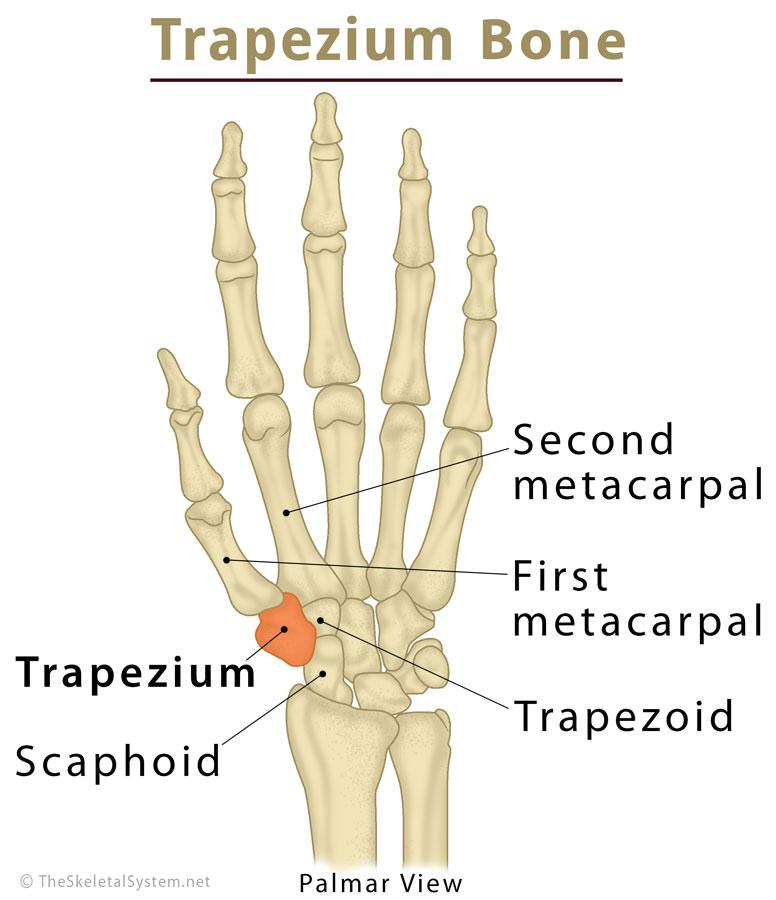
Trapezium
The carpal at the base of the thumb
Xương thang
Xương thang
14
New cards
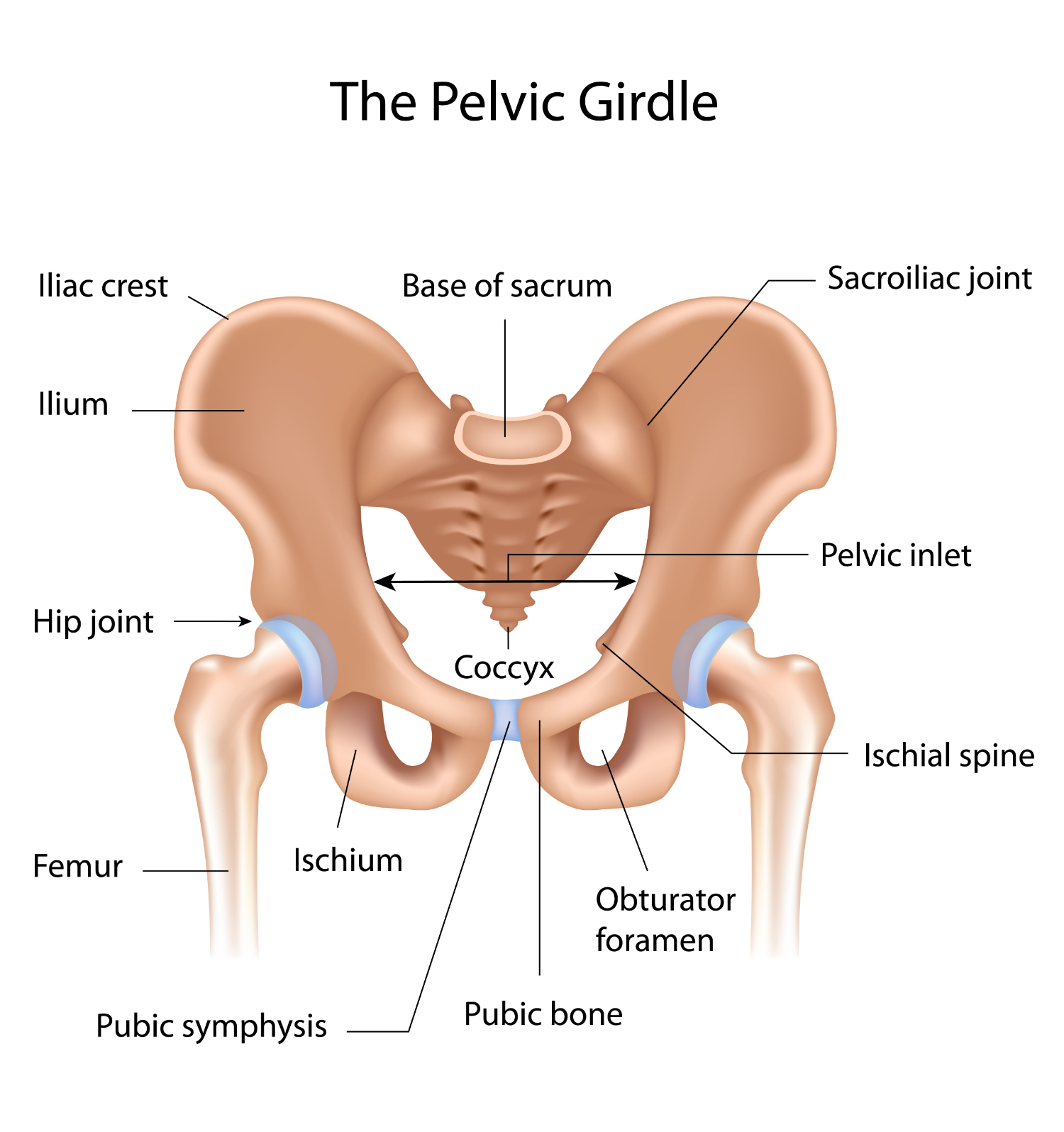
* Ilium (xương chậu)
* Ischium (xương ụ)
* Pubis (xương mu)
* Ischium (xương ụ)
* Pubis (xương mu)
Which three pairs of bones fuse to form the **pelvic girdle (đai chậu)**?
15
New cards
* The axial skeleton (head, torso)
* The appendicular skeleton (upper and lower extremities)
* The appendicular skeleton (upper and lower extremities)
What parts is the skeleton divided into?
16
New cards
Cranium
The brain case
17
New cards
8 bones
How many bones form the cranium?
18
New cards
14 bones
How many bones make up the face?
19
New cards
Ossicles
Tiny bones in the inner ears
20
New cards
Mandible
Jaw bone (only movable bone in the skull)
21
New cards
Suture
Immobile joints that hold the skull bones together
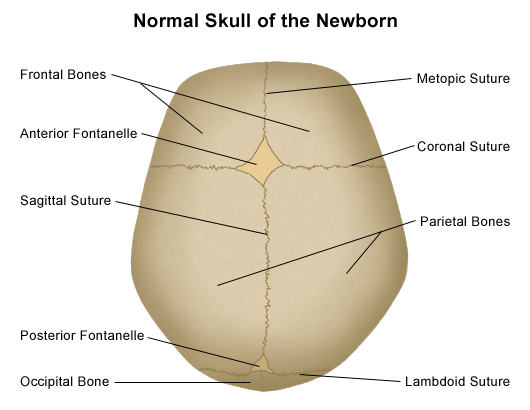
22
New cards
Coronal suture
Which suture unites the frontal bone and the two parietal bones?
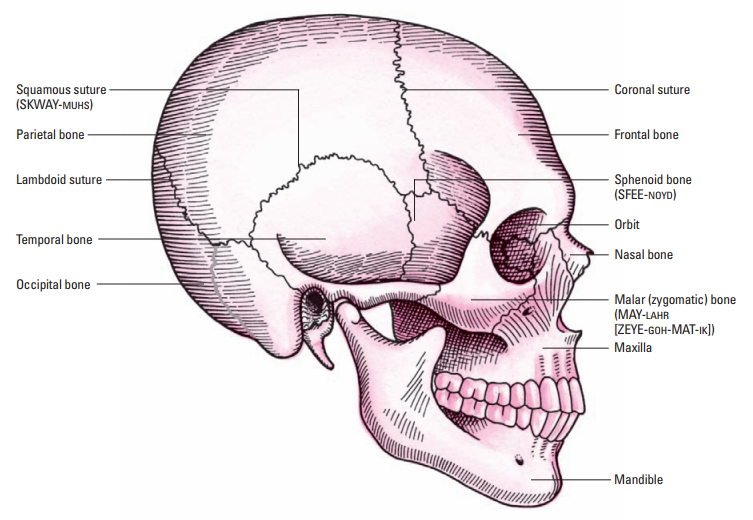
23
New cards
Squamous suture
Which suture connects the parietal bones with the temporal bones?
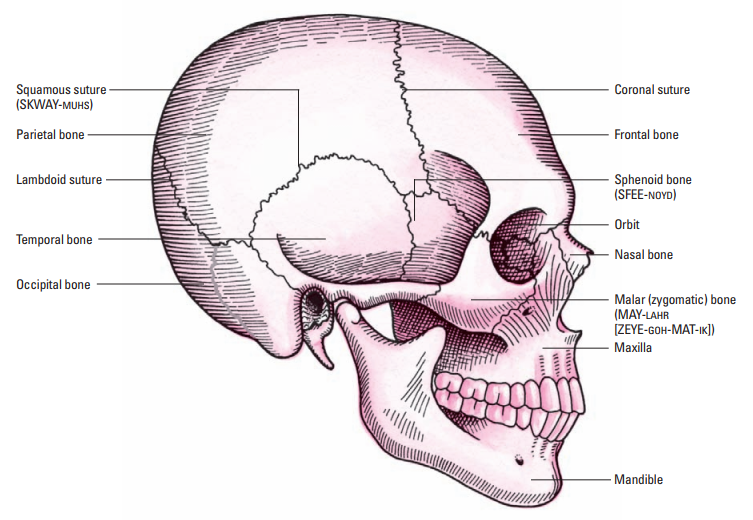
24
New cards
Lambdoid suture
Which suture connects the parietal bones to the occipital bone?
25
New cards
Anterior/posterior fontanel
A diamond-shaped area when the suture isn’t closed in infants
26
New cards
Sinuses
Air-filled spaces within the skull that lessen the bone weight, moisten incoming air and act as a resonating chambers for the voice
27
New cards
Foramen magnum
A large opening at the base of the occipital bone allows the spinal cord to pass from the encephalon into the spine
28
New cards
Orbit
Eye sockets
29
New cards
Sphenoid bone
A bone located in the cranial floor looks like a bat
An anchor for the frontal, parietal, occipital and ethmoid bones
An anchor for the frontal, parietal, occipital and ethmoid bones
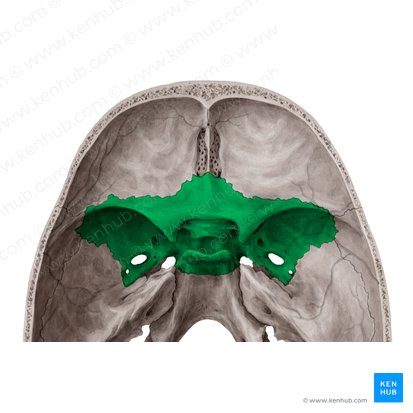
30
New cards
Maxillary bones
Facial bones that form the **upper jaw, nose, orbits and roof of the mouth**
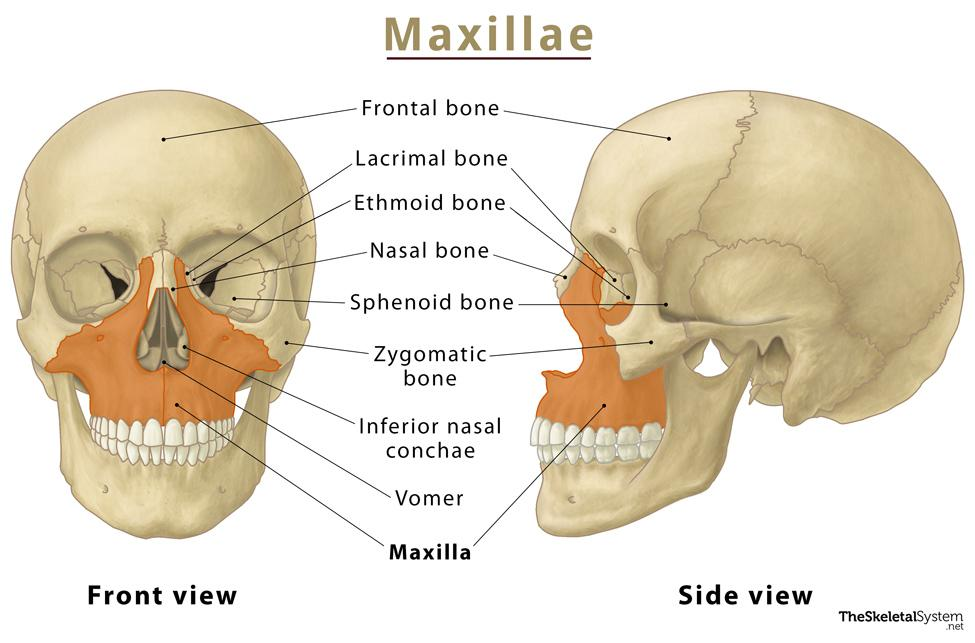
31
New cards
Zygomatic (Malar bones)
Cheekbones that attach to chewing muscles
32
New cards
Nasal bones
Bones that form the **upper part of the bridge of the nose**
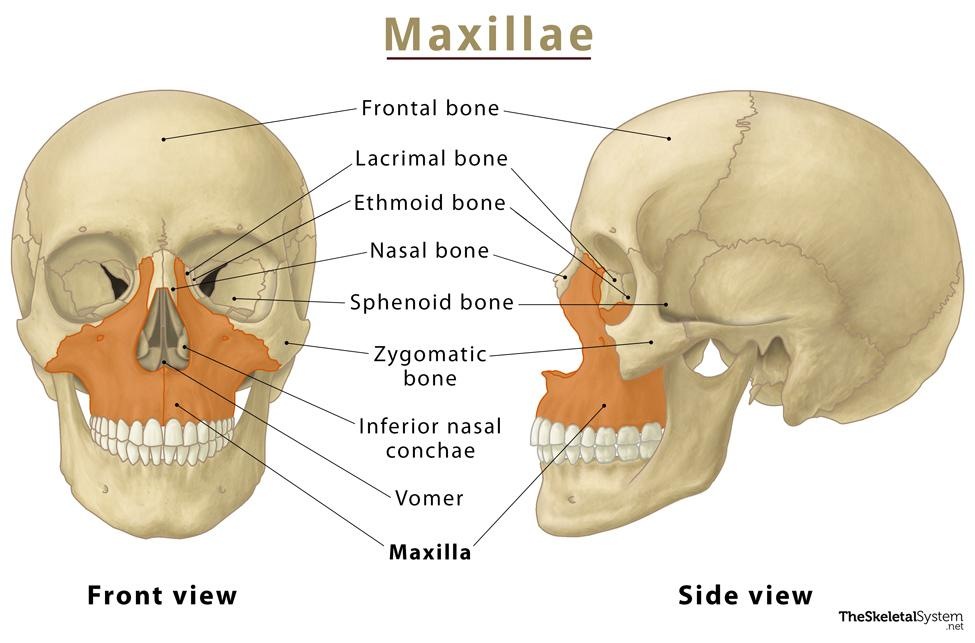
33
New cards
Lacrymal bones
Bones that contain the lacrymal bag
Xương lệ
Xương lệ
34
New cards
Vomer
Bone that is part of the nasal septum
Xương lá mía
Xương lá mía
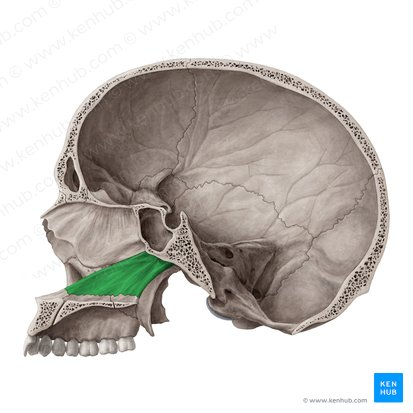
35
New cards
Palatine bones
Bones that form the posterior portion of the hard palate, the lateral side of the nasal cavity, and small part of the orbit
Xương vòm miệng
Xương vòm miệng
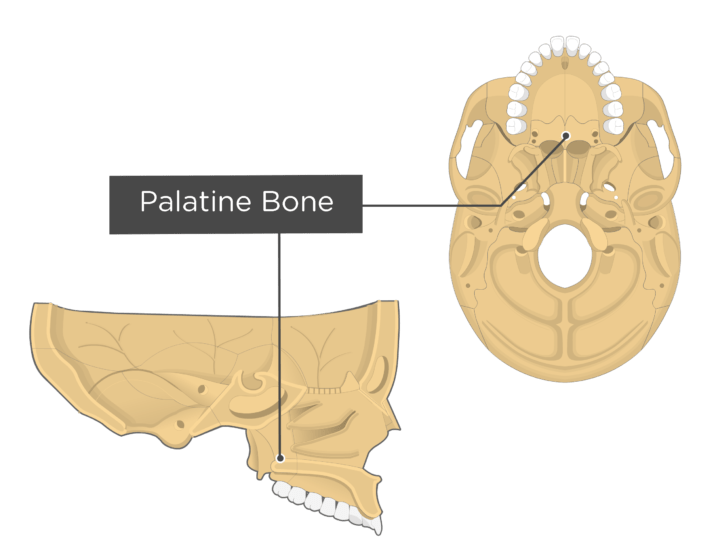
36
New cards
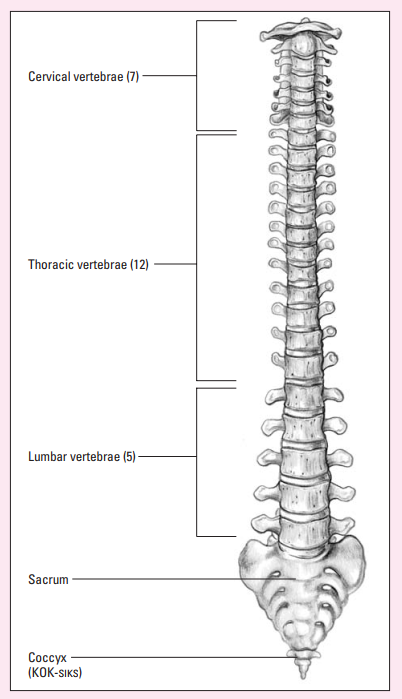
Vertebrae
The spinal column contains 24 _________.
Đốt sống
Đốt sống
37
New cards
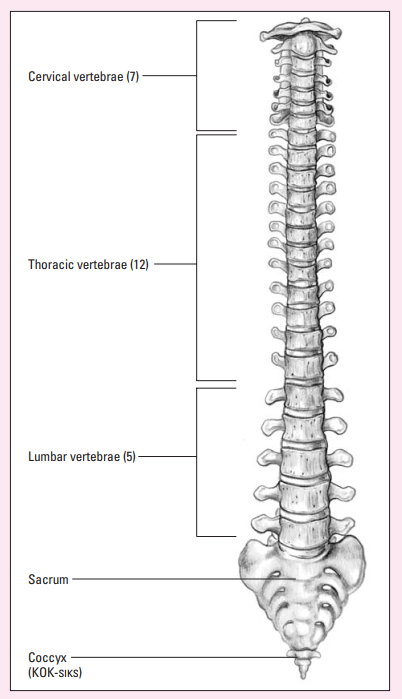
Sacrum
A single bone that results from the fusion of 5 vertebrae and attaches to the pelvic girdle
Xương cùng
Xương cùng
38
New cards
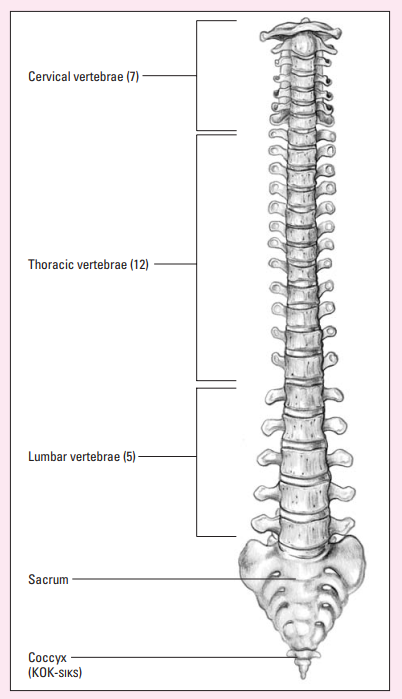
Coccyx
The tailbone
Xương cụt
Xương cụt
39
New cards
7 cervical vertebrae
Which vertebrae support skull and rotate?
40
New cards
12 thoracic vertebrae
Which vertebrae attach to the ribs?
41
New cards
5 lumbar vertebrae
Which vertebrae support the small of the back?
42
New cards
Sternum
A flat, sword-shaped bone that is attached to the clavicles
Xương ức
Xương ức
43
New cards
True ribs
Ribs that are directly attached to the sternum by costal cartilage
44
New cards
False ribs
Five pairs of ribs that aren’t attached directly to the sternum
45
New cards
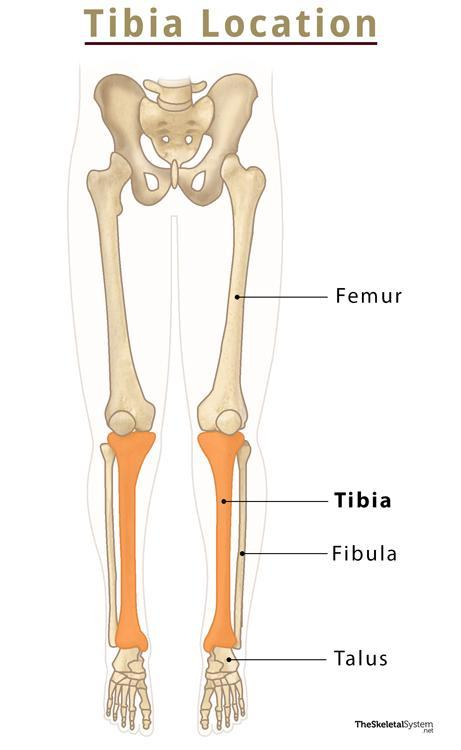
Femur
Upper leg bones
46
New cards
Acetabulum
Hip socket
47
New cards
Tibia (shinbone)
Largest and strongest of the lower leg bones
Articulate with the femur at the proximal end
Articulate with the femur at the proximal end
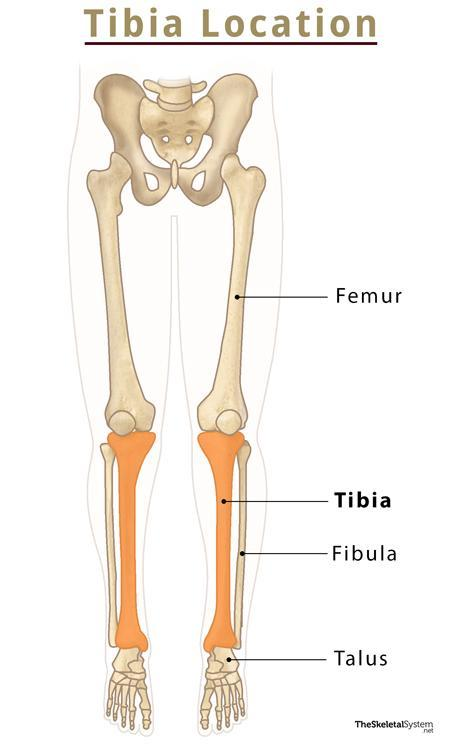
48
New cards
Fibula
The bone that connects with the tibia its proximal and distal ends
Also articulates with the talus that the distal end
Also articulates with the talus that the distal end
49
New cards
Patella
The kneecap that protects the knee joint and overlaps the distal end of the femur and the proximal end of the tibia
50
New cards
Lateral malleolus
The bony prominence on the outside of the ankle
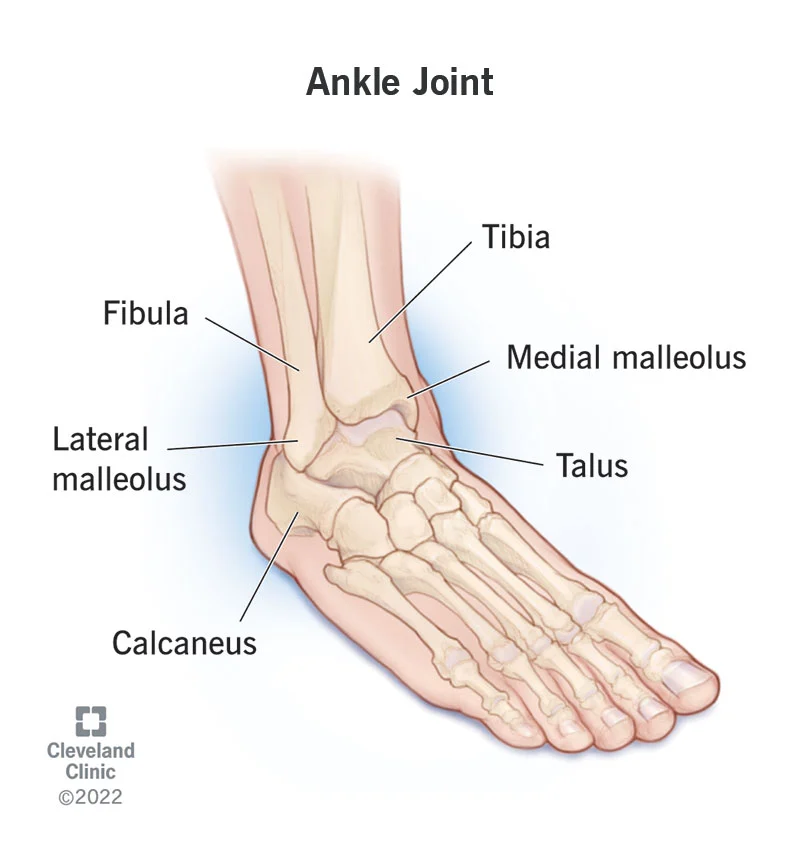
51
New cards
Astragalus
The talus bone forms part of the ankle joint
52
New cards
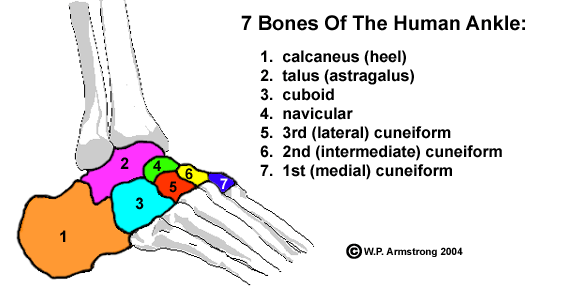
Calcaneus
The heel (the largest tarsal bone)
53
New cards
Scaphoid bone (Navicular)
Boat-shape bone
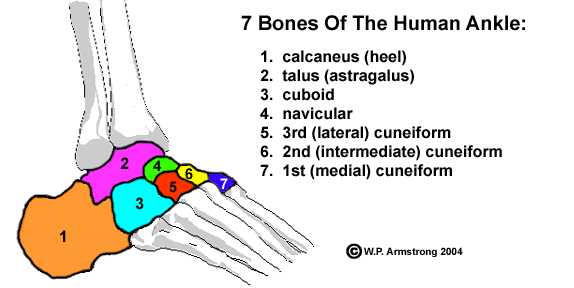
54
New cards
Cuneiforms
Three wedge-shaped bones that form the arch of the foot
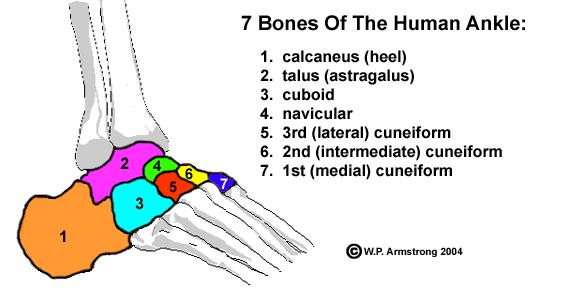
55
New cards
Metatarsal bones
Five bones that form the foot
Articulate with the tarsal bones and the phalanges
Articulate with the tarsal bones and the phalanges
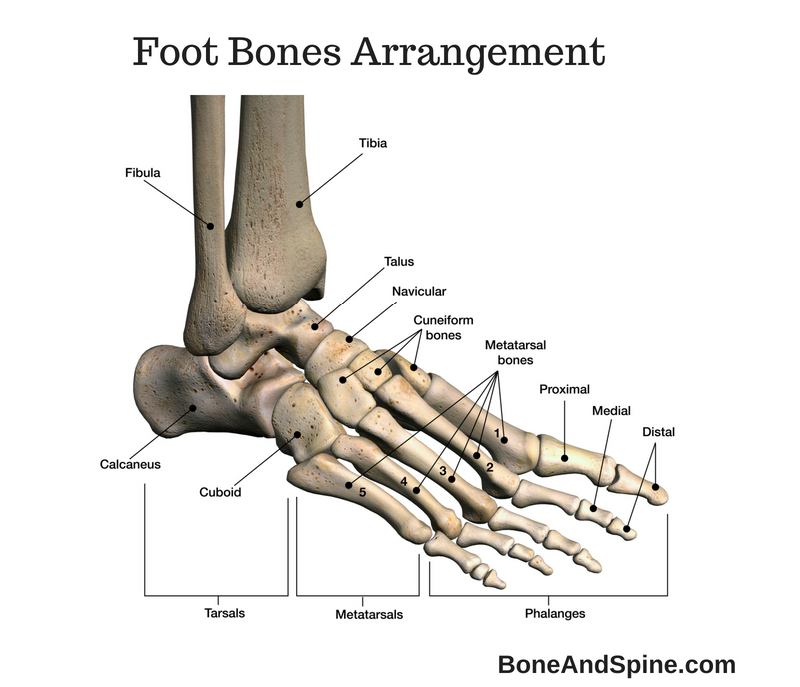
56
New cards
Phalanges
Fourteen toe bones (3 for each toe, 2 for the great toe)
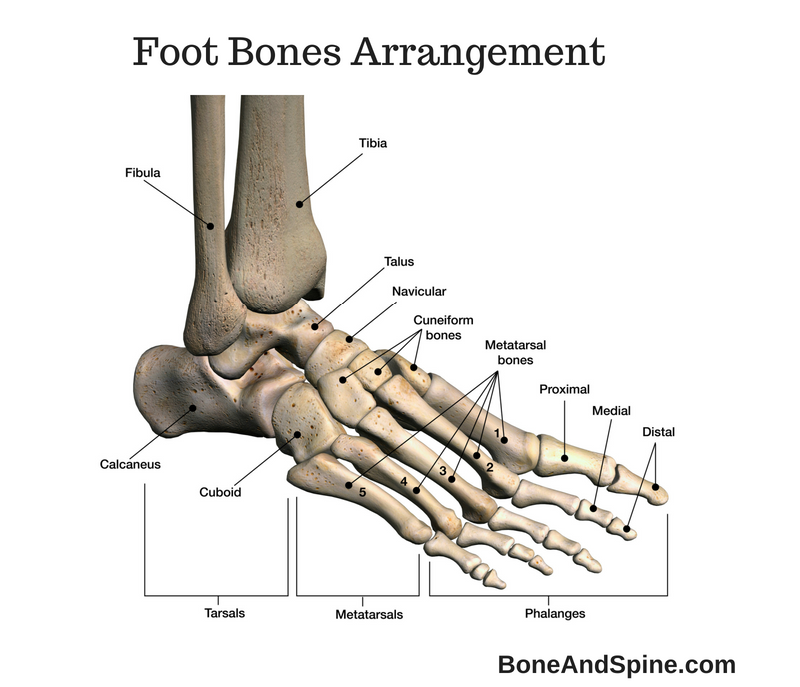
57
New cards
Main bones of the limbs (except the patella, wrists, ankles)
What do the **long bones** include?
58
New cards
Wrists, ankles
What do the **short bones** include?
59
New cards
Sternum, scapulae, cranium
What do the **flat bones** include?
60
New cards
Vertebrae, hip bones
What do the **irregular bone** include?
61
New cards
Outer layer (dense, smooth compact bone)
Inner layer (Spongy, porous bone)
Inner layer (Spongy, porous bone)
What are the 2 types of bone material?
62
New cards
**In the shaf**t of long bones
**The outer layer** of short, flat and irregular bones
**The outer layer** of short, flat and irregular bones
Where is the compact bone found?
63
New cards
**In the central regions of the epiphysis** of the long bones
**Inner portion** of short, flat, and irregular bones
**Inner portion** of short, flat, and irregular bones
Where is the cancellous bone found?
64
New cards
Diaphysis (diaphyses)
The long, narrow shaft of the bone
Contain bone marrow
Has 2 irregular ends
Contain bone marrow
Has 2 irregular ends
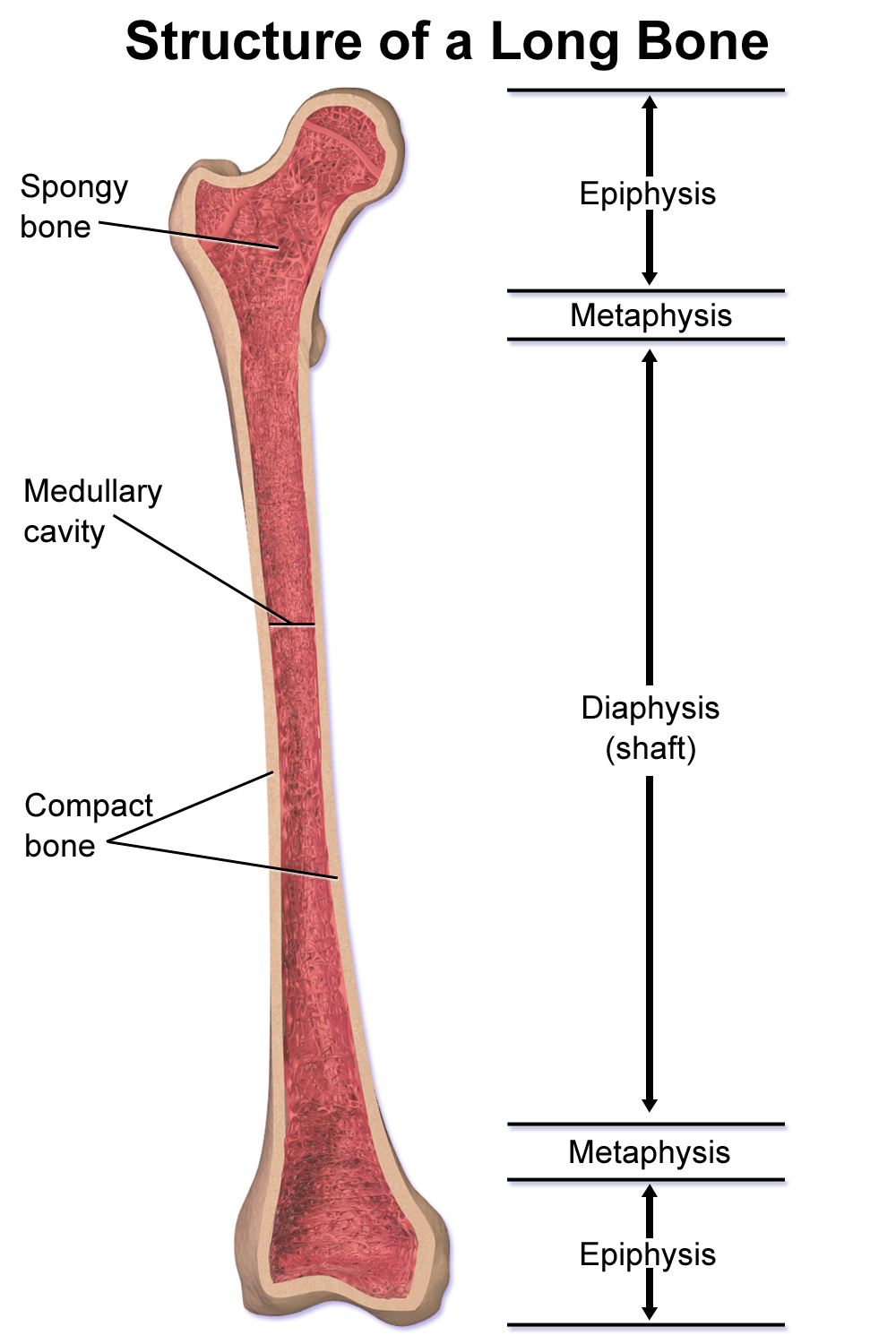
65
New cards
Epiphysis (epiphyses)
The bulbous ends of the long bones
Provide a large surface for muscle attachment and give stability to joints
Provide a large surface for muscle attachment and give stability to joints
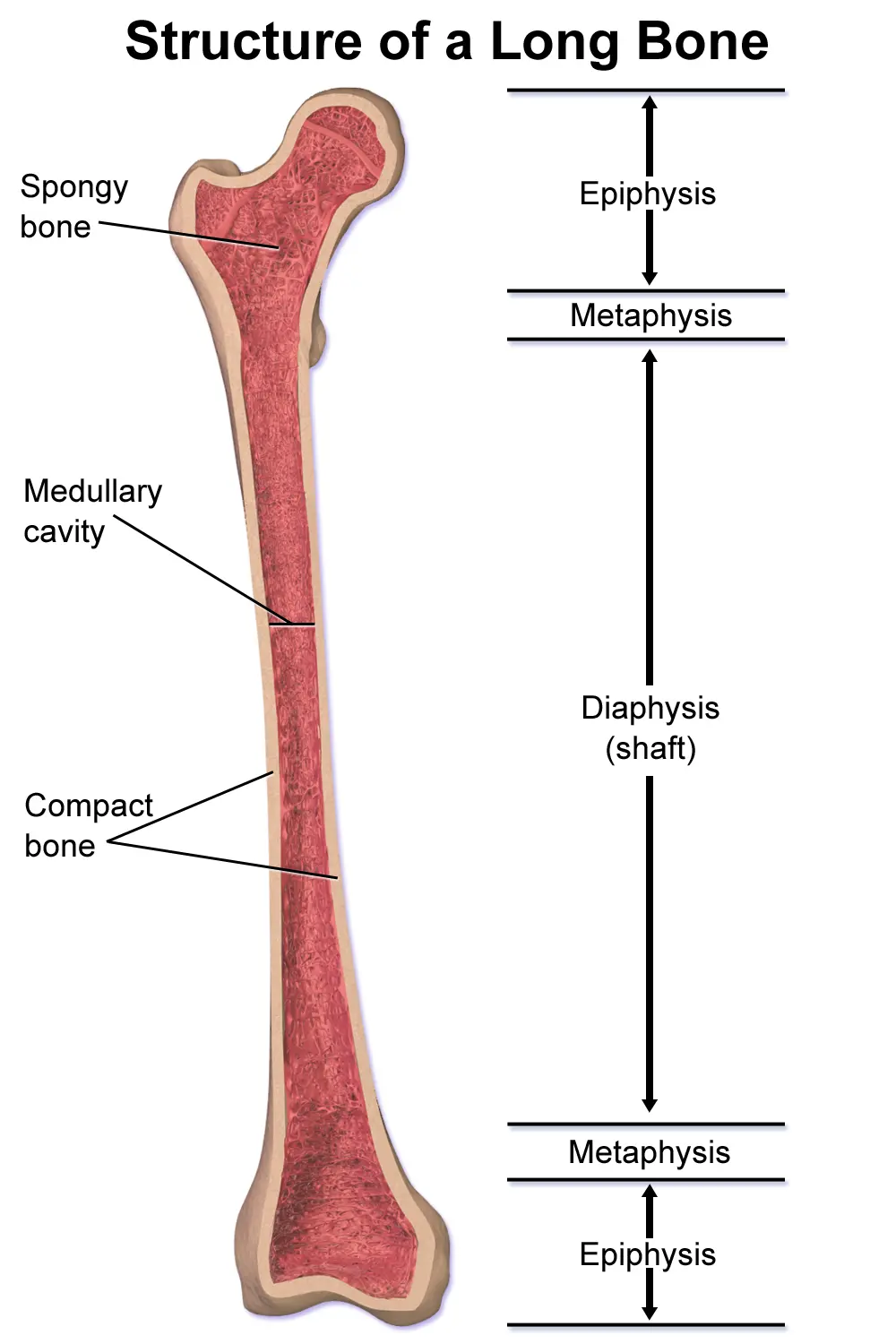
66
New cards
Articular cartilage
A thin layer of hyaline cartilage that covers and cushions the joint surface of the epiphyses
67
New cards
Periosteum
A dense membrane that covers the shafts of the long bones
Contain 2 layers: a fibrous outer layer + a bone-forming inner layer
Contain 2 layers: a fibrous outer layer + a bone-forming inner layer
68
New cards
Osteoblasts
Bone-producing cells
69
New cards
Osteoclasts
Bone-destroying cells
70
New cards
Medullary cavity
A cavity filled with bone marrow
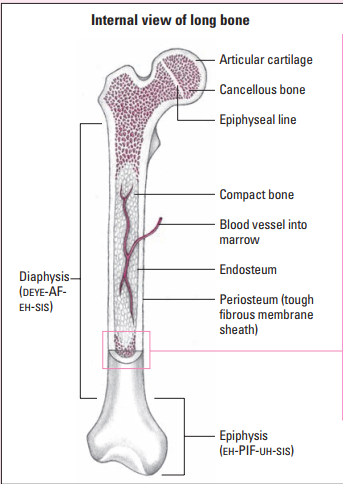
71
New cards
Endosteum
A thin membrane that lines the medullary cavity
Contain osteoblasts and osteoclasts
Contain osteoblasts and osteoclasts
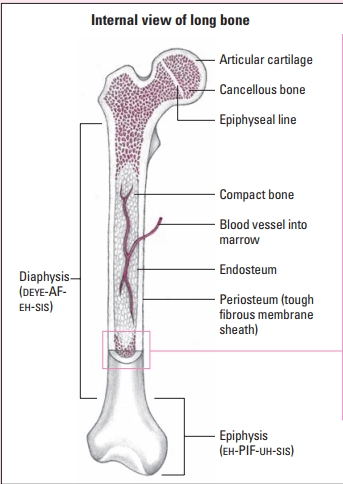
72
New cards
Lamellae
The thin layers of ground substance
A part of the haversian system
A part of the haversian system
73
New cards
Lacunae
Small hollow spaces that contain osteocytes
Part of the haversian system
Part of the haversian system
74
New cards
Canaliculi
Small canals
Part of the haversian system
Part of the haversian system
75
New cards
Haversian canals
Central canals that contain blood, lymph vessels, nerves and sometimes marrow
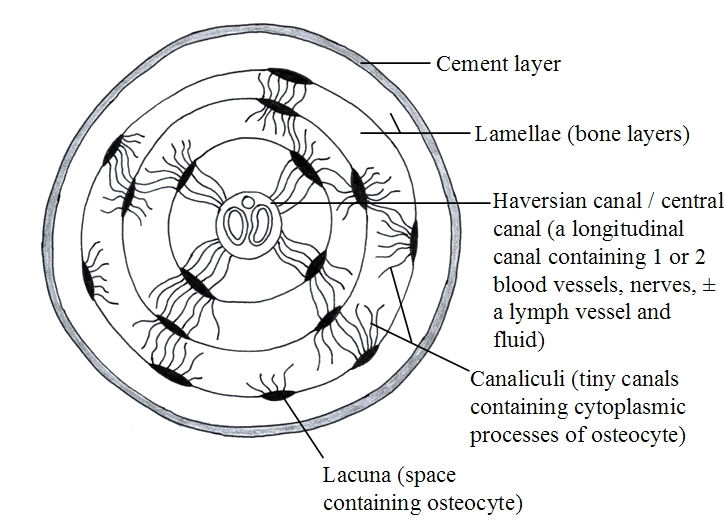
76
New cards
Volkmann’s canals
Canals that connect haversian canal to another and to the outer bone
77
New cards
Perform hematopoiesis
What is the role of red bone marrow?
78
New cards
Cartilage
A dense connective tissue that supports and absorbs shock bones and joints
Supports and shapes the auditory canal and intervertebral disks
Have no blood or nerve supply
Supports and shapes the auditory canal and intervertebral disks
Have no blood or nerve supply
79
New cards
Fibrous cartilage
Which type of cartilage forms **at the meniscus and the intervertebral disks**?
80
New cards
Hyaline cartilage
Which type of cartilage covers **articular bone surfaces, connects ribs and sternum, appears in the trachea, bronchi and nasal septum**?
81
New cards
Elastic cartilage
Which type of cartilage is located in the auditory canal, external ear and epiglottis?
82
New cards
Synarthrosis joints
Which type of joints is immovable?
83
New cards
Amphiathrosis
Which type of joints is slightly movable?
84
New cards
Diarthrosis
Which type of joint is freely movable?
85
New cards
Fibrous joints
* The articular surfaces of the 2 bones are bound closely by fibrous tissue
* Little movement is possible
* Example: cranial sutures
What type of joint is this?
* Little movement is possible
* Example: cranial sutures
What type of joint is this?
86
New cards
Cartilaginous joints
* Cartilage connects one bone to another
* Slight movement is possible
* Example: symphysis pubis
What type of joint is this?
* Slight movement is possible
* Example: symphysis pubis
What type of joint is this?
87
New cards
Synovial joints
* Body surfaces are covered by articular cartilage and joined by ligaments lined with synovial membrane
* Freely movable
* Example: joints of the arms and legs
* Freely movable
* Example: joints of the arms and legs
88
New cards
Articular capsule
A saclike envelope, whose outer layer is lined with a vascular synovial membrane
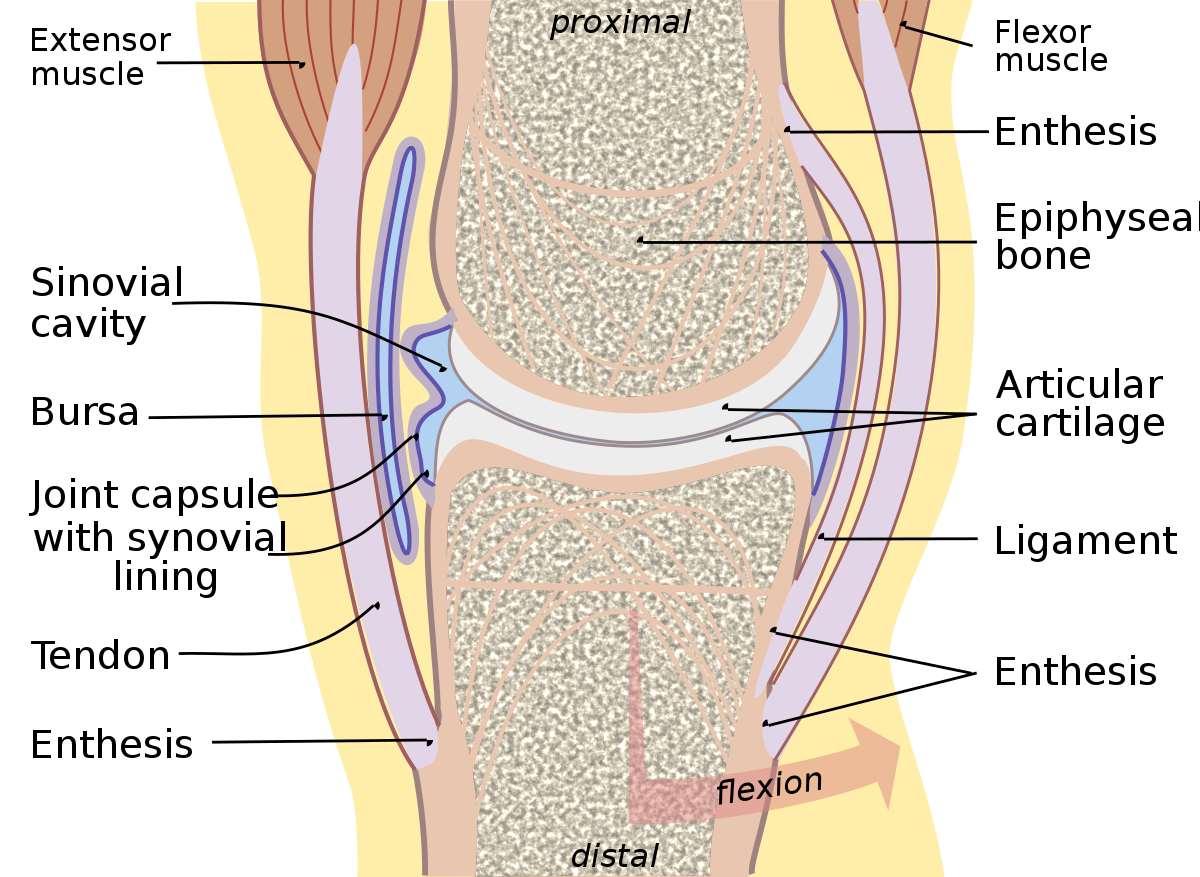
89
New cards
Bursa (bursae)
* Synovial fluid sacs located at friction points of all types of joints, tendons, ligaments and bones
* Function: cushion these structures, decrease stress on adjecent one
* Function: cushion these structures, decrease stress on adjecent one
90
New cards
Gliding joints
Which type of joints **allow** **adjacent bone surfaces to move against one another?**
Ex: wrists and ankles
Ex: wrists and ankles
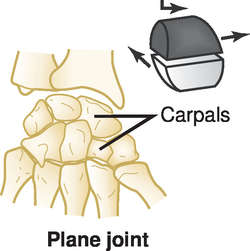
91
New cards
Hinge joints
Which type of joints **permits movement in only one direction?**
Ex: elbows and knees
Ex: elbows and knees
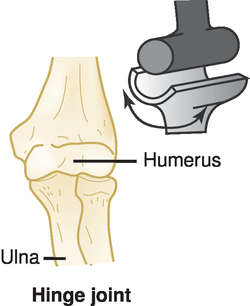
92
New cards
Pivot joints (rotary joints, trochoid joints)
Which type of joint **allows a movable bone to pivot around a stationary bone?**
Ex: neck and elbow
Ex: neck and elbow
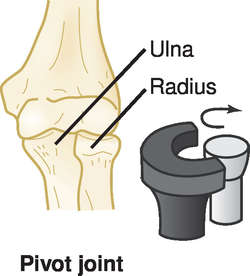
93
New cards
Condylar
* Knuckle joints
* Contain an oval head of one bone that fits into a shallow depression in a second bone
* Example: union between the radius and the carpal bones
* Contain an oval head of one bone that fits into a shallow depression in a second bone
* Example: union between the radius and the carpal bones
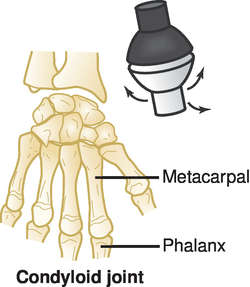
94
New cards
Saddle joints
* Resemble condylar joints but **allow greater freedom of movement**
* Example: carpometacarpal joints of the thumb
* Example: carpometacarpal joints of the thumb
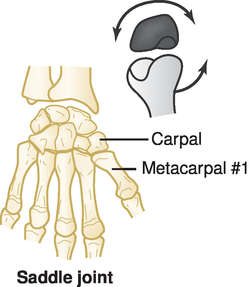
95
New cards
Ball-and-socket joints (spheroid joints)
Which type of joints have the spherical head of one bone fit into a socket of another bone?
Example: hip and shoulder joints
Example: hip and shoulder joints
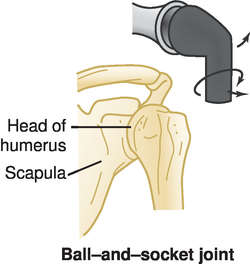
96
New cards
Crepitus
A cracking noise or the sensation that’s commonly felt when the hand is placed over a fracture site and broken bone ends are moved
97
New cards
Abduction
Moving away from the midline
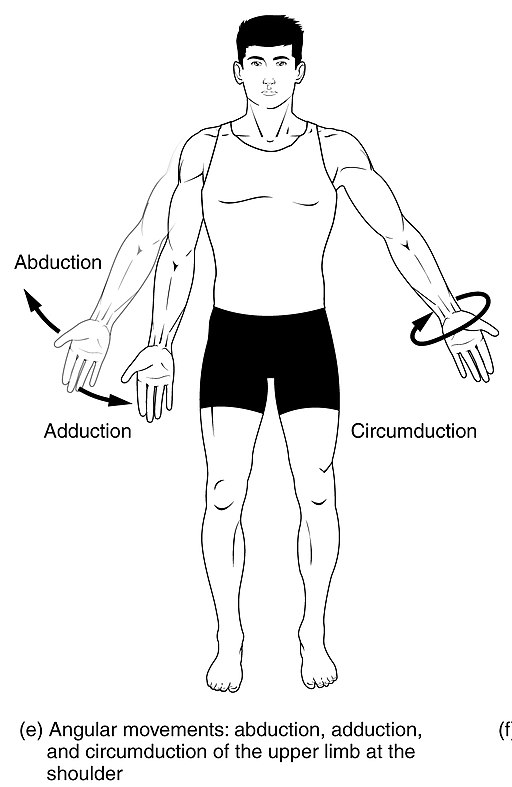
98
New cards
Adduction
Moving toward the midline
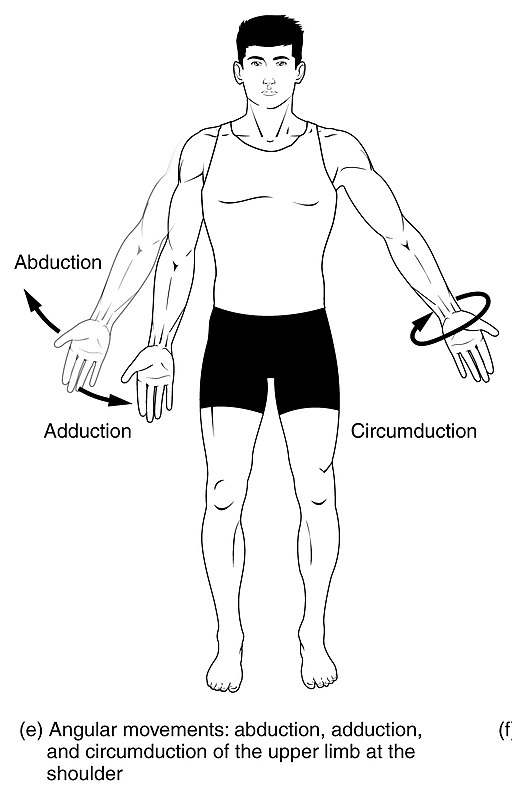
99
New cards
Circumduction
Moving in a circular manner
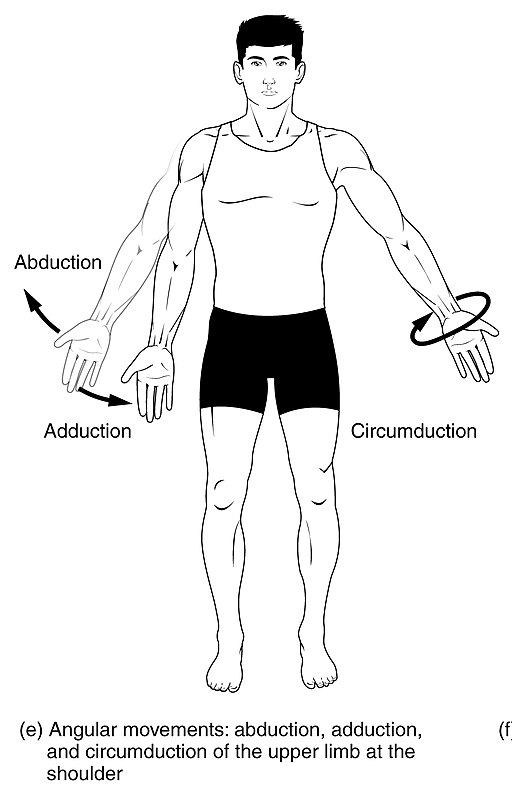
100
New cards
Flexion
Bending or decreasing the joint angle