AP PSYCH
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/386
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 9:11 PM on 4/17/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
387 Terms
1
New cards
socrates and plato
the mind and body are separate, the mind continues after death, knowledge is innate
2
New cards
Aristotle
need data, knowledge comes from observation and is not innate
3
New cards
rene descartes
agreed with the greeks, dissected animals, fluid in brain flows through nerves to muscles causing movement
4
New cards
francis bacon
founder of modern science, empiricism
5
New cards
john locke
tabula rasa; the mind is a blank slate at birth on which experience writes
6
New cards
empiricism
knowledge is the result of experience and that scientific knowledge is developed through observation and experimentation
7
New cards
wilhelm wundt
established the first psychology lab, wanted to measure the “atoms of the mind”, the fastest mental processes
8
New cards
edward bradford titchener
introduced structuralism to study the elements of the mind, used introspection
9
New cards
structuralism
early school focused on identifying the elements of the mind the way early chemists developed the periodic table to classify elements
10
New cards
introspection
the process of looking inward to directly observe one’s own psychological processes
11
New cards
charles darwin
natural selection of mental and physical traits, adaptive evolution influenced william james
12
New cards
william james
introduced functionalism, principles of psychology
13
New cards
functionalism
assumes a purpose, smelling and thinking must have helped us evolve
14
New cards
mary whitin calkins
student of william james, denied a phd because she was female, memory researcher, first female president of the apa
15
New cards
Margaret floy washburn
student of edward titchener, first female to earn psych phd, the animal mind
16
New cards
behaviorism
approach that focused on observable behaviors, ignoring any underlying cognitive factors. Created by John B. Watson
17
New cards
freud
developed psychoanalysis and personality theory
18
New cards
abraham maslow and carl rogers
humans strive to reach their full potential, unconditional love, personal growth
19
New cards
humanism
“third force” in psychology, the study of potential and personal growth
20
New cards
cognitive psychology
the study of mental processes; thinking perceiving, learning, remembering, communicating, and solving problems
21
New cards
cognitive neuroscience
the study of the brain activity linked with cognition
22
New cards
psychology
the scientific study of the behavior and mental processes of humans and other animals, uses empiricism and the scientific method to critically evaluate evidence
23
New cards
behavior
any observable and measurable action taken by a person or animal
24
New cards
nature
behaviors and mental processes occur because they are innate
25
New cards
nurture
behaviors and mental processes occur as a result of experience or the environment
26
New cards
positive psychology
the scientific study of human flourishing, the goal of discovering and promoting human strengths and virtues, strengthens individuals and communities
27
New cards
case study
a descriptive technique in which one individual or group is studies in depth in the hope of revealing universal principles
28
New cards
strengths in a case study
allow for examination of rare or unusual behavior, provide a large amount of qualitative data, suggests directions for further study
29
New cards
strengths in a naturalistic observation
subjects behave normally outside of a lab setting, data collection is unobtrusive
30
New cards
limitations in a naturalistic observation
independent variable cannot be isolated, cannot determine cause and effect, observations by researchers may be subjective
31
New cards
strengths of the survey method
able to take a “quick pulse” of people beliefs, behaviors or opinions, able to include many cases
32
New cards
limitations of the survey method
response bias, wording effects can skew the outcome, acquiring a random sample is difficult, can not determine cause and effect
33
New cards
correlation
a measure of the extent to which two factors vary together and how well either factor predicts the other
34
New cards
positive correlation
two sets of data tend to rise or fall together, measured from r=0.1 to +1.0
35
New cards
negative correlation
one set rises while the other falls measured from r=-0.1 to -1.0
36
New cards
random sampling
choosing a representative sample of the population being studied
37
New cards
random assignment
assigning the participants to the experimental or control group by chance
38
New cards
independent variable (IV)
the factor in an experiment that is manipulated; the variable whose effect is being studied, given only to the experimental group
39
New cards
dependent variable (DV)
the outcome that is measured in an experiment; the variable that may change when the independent variable is manipulated, measured in both groups
40
New cards
confounding variable
a factor other than the factor that is being studied that might influence a study’s results; age, IQ, ethnicity, sex, political beliefs
41
New cards
experimental validity
the extent to which a test or experiment measures or predicts what it is supposed to
42
New cards
ethical guidelines safeguard human research participants
informed consent, protection from harm, debriefing, right to withdraw, confidentiality
43
New cards
descriptive statistics
numerical data used to measure and describe characteristics of groups, includes measures of central tendency (mean, median, and mode) and measures of variation (range and standard deviation)
44
New cards
mean
mathematical average of a set of numbers, add the scores and divide by the number of scores
45
New cards
median
the middle score in a distribution, arrange scores from highest to lowest with half of the data above and half below the number
46
New cards
mode
the most frequently occurring data point in a distribution
47
New cards
the influence of outliers on data and which measure of central tendency is best used to describe the data
the median will be a better descriptor of data when the mean is impacted by outliers
48
New cards
range
the difference between the highest and lowest scores in a distribution
49
New cards
standard deviation
a computed measure of how much scores vary around the mean score
50
New cards
1 standard deviation from the mean
68%
51
New cards
2 standard deviations from the mean
95%
52
New cards
3 standard deviations from the mean
99%
53
New cards
inferential statistics
examine relationships between variables in sample, allows us to infer/predict trends based on data taken from a sample of a population
54
New cards
descriptive statistics
describe a population or data set, uses measures of central tendency, uses measures of variation
55
New cards
statistical significance
statistical statement of how likely it is that a result occurred by chance
56
New cards
neuron
a nerve cell that is the basic building block of the nervous system
57
New cards

axon
attached to the soma, the neuron that passes messages away from the cell body to other neurons, muscles, or glands
58
New cards
neural impulse
action potential; electrical signal traveling down the axon
59
New cards

myelin sheath
the fatty tissue layer segmentally encasing the axons; covers the axon of some neurons and hooks speed neural impulses
60
New cards

terminal branches of axon
the ends of the axon containing terminal button which hold synaptic vesicles that store neurotransmitters
61
New cards

dendrites
bushy, branching extensions that receive messages from other cells, conducting impulses toward the cell body
62
New cards

cell body/soma
the part of the neuron that contains the nucleus, the cell’s life support center
63
New cards
deterioration of the myelin sheath can lead to:
motor impairments such as multiple sclerosis
64
New cards
glial cells
cells that support, nourish, and protect neurons; they also play a role in thinking, learning, and memory
65
New cards
how is a neural impulse generated
if the combined received chemical signals exceed a minimum threshold, the neuron fires, transmitting an electrical impulse (action potential) down its axon by means of a chemistry-to-electrical process
66
New cards
threshold
the level of stimulation required to trigger a neural impulse
67
New cards
what is the outside of an axon’s membrane charged with before the beginning of the action potential?
positivly charged sodium (Na+) ions
68
New cards
what is the inside of an axon’s membrane charged with before the beginning of the action potential?
negatively charged proteins and a small amount of positively charged potassium (K+) ions
69
New cards

first step in an action potential
the first section of the semipermeable axon opens its gates once the threshold is met, Na+ ions flood through the channels
70
New cards

why do Na+ ions rush in the channels
the ions try to balance the charge of the slightly negative membrane, this causes a slight depolarization
71
New cards

what is the second step in an action potential
the depolarization changes the electrical charge of the next part of the axon, gates in this second area now open, which allows even more Na+ ions to flow into the channel
72
New cards

how do K+ ions move out
at the same time, gates open in the first part of the axon allowing K+ ions to flow out, this depolarizes that section of the axon
73
New cards

what happens after K+ ions move out
the sodium/potassium pumps continues to depolarize new sections of the axon and depolarize previous sections
74
New cards

how does the impulse move
polarthe influx of the positive ions is the neural impulse, the impulse moves down the axon like dominos, one falling after the other
75
New cards
polarization
the resting rate of the neuron, charge is more positive outside the membrane, and more negative on the inside
76
New cards
depolarization
the action potential; the rushing in and out of positively charged ions
77
New cards
repolarization
the refractory period; the closing of the membrane and reestablishing a more negative charge inside
78
New cards
how do neurons communicate with each other
the sending neuron releases neurotransmitters across a synapse to the receiving neuron
79
New cards
neurotransmitter
chemical messengers that travel across the synapse and bind to receptor sites on the receiving neuron
80
New cards
synapse
the junction between the axon tip of the sending neuron and the dendrite or cell body of the receiving neuron
81
New cards
what happens when an action potential reaches an axon’s terminal branch
it stimulates the release of neurotransmitter molecules
82
New cards
acetylcholine (ACh)
enables muscle action, learning, and memory, produces neurons that deteriorate with Alzheimer’s
83
New cards
dopamine
influences movement, learning, attention, and emotion, oversupply linked to schizophrenia, undersupply linked to tremors and decreased mobility in parkinson’s disease
84
New cards
serotonin
affects mood, hunger, hunger, sleep, and arousal, undersupply linked to depression
85
New cards
norepinephrine
helps control alertness and arousal, undersupply can depress mood
86
New cards
GABA (gamma-aminobutyric acid)
a major excitatory neurotransmitter, undersupply linked to seizures, tremors, and insomnia
87
New cards
glutamate
a major excitatory neurotransmitter; involved in memory, oversupply can overstimulate the brain, producing migraines or seizures
88
New cards
endorphins
neurotransmitters that influence the perception of pain or pleasure, oversupply with opiate can suppress the body’s natural endorphin supply
89
New cards
how does an agonist work
it mimics a neurotransmitter, opening receptor sites
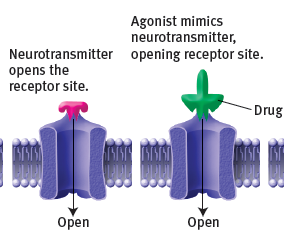
90
New cards
how does an antagonist work
blocks a neurotransmitter’s actions, can also work by blocking reuptake
91
New cards
nerves
bundled axons of many neurons that form neural cables connecting the cns with muscles, glands, and sense organs
92
New cards
three types of neurons
sensory, motor, and interneurons
93
New cards
sensory neurons
contain afferent nerve fibers, carry information from the sense organs to the CNS
94
New cards
motor neurons
contain efferent neurons, carry messages from the CNS to the muscles and glands
95
New cards
what is the CNS
made up of the brain and spinal cord, decision maker, responsible for coordinating incoming sensory messages and outgoing motor messages
96
New cards
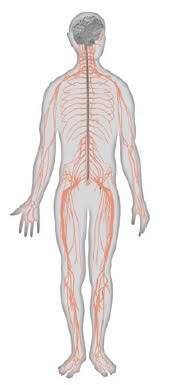
what is the peripheral nervous system
made up of sensory and motor neurons, connects the body to the CNS by gathering information from the senses and transmitting messages from the CNS
97
New cards
two parts of the pns
somatic and autonomic
98
New cards
somatic nervous system
controls the body’s skeletal muscles
99
New cards
autonomic nervous system
controls the glands and the muscles of the internal organs, operates automatically
100
New cards
sympathetic nervous system
arouses the body, mobilizing its energy, *fight, flight, or freeze*