Cardiac Radiology
1/86
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Lectures 23, 24
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
87 Terms
What is a normal vertebral heart sum for canine?
9.7 ± 0.5 vertebrae
normal range 8.5-10.5
What is a nomal vertebral heart sum for feline?
7.5 ± 0.3 vertebrae
Explain how to perform a vertebral heart sum.
draw your lines in short and long axis (carina to apex then approximately 90 degree)
take each line and measure parallel to thoracic spine beginning at T4 vertebral body
count the number of vertebrae caudally
sum your two line measurements
When you make your line from the carina to apex of the heart, what is the normal proportions for right and left sides?
3/5 on the right
2/5 on the left
How many intercostal spaces is the cat heart normally on a lateral radiograph?
less than or equal to 2.5 ICS
How big is a feline heart normally on a VD or DV radiograph?
approximately half to two-thirds width of thorax
What part of the heart sits at 11 to 1 o’clock?
aorta
What part of the heart sits at 1 to 2 o’clock?
pulmonary artery
What part of the heart sits at 2 to 3 o’clock?
left atrium
What part of the heart sits at 3 to 5 o’clock?
left ventricle
What part of the heart sits at 5 to 9 o’clock?
right ventricle
What part of the heart sits at 9 to 11 o’clock?
right atrium
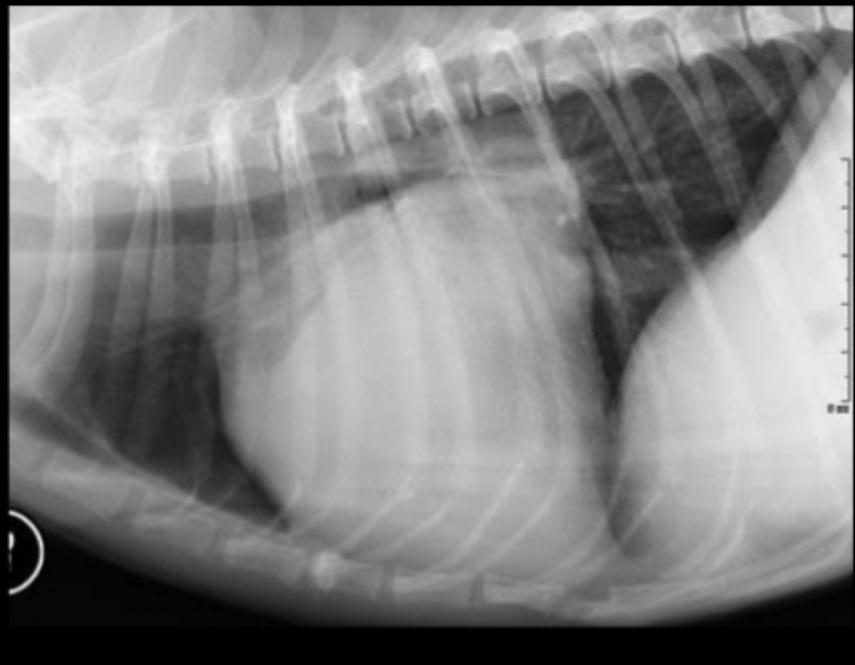
What part of the heart is enlarged in this lateral radiograph?
left atrium
What radiographic changes can we see on a lateral view if there is left atrial enlargement?
straightening of caudo-dorsal heart margin
What radiographic changes can we see on a VD view if there is left atrial enlargement?
splitting of mainstem bronchi
round opacity superimposed over caudal aspect of heart
with severe changes you can see left auricular appendage bulge at 2-3 o’clock on VD
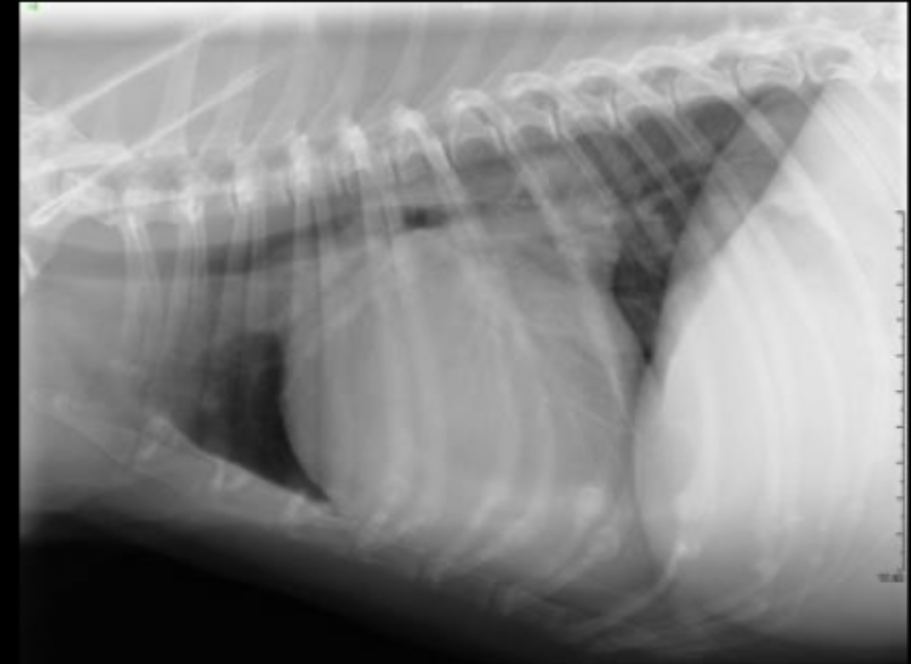
What part of the heart is enlarged on this lateral radiograph?
left ventricle
What radiographic changes can we see on a lateral or VD/DV view if there is left ventricular enlargement?
may appear radiographically normal
in severe enlargement, heart may elongate
dorsal displacement of the entire thoracic trachea (thoracic inlet to carina)
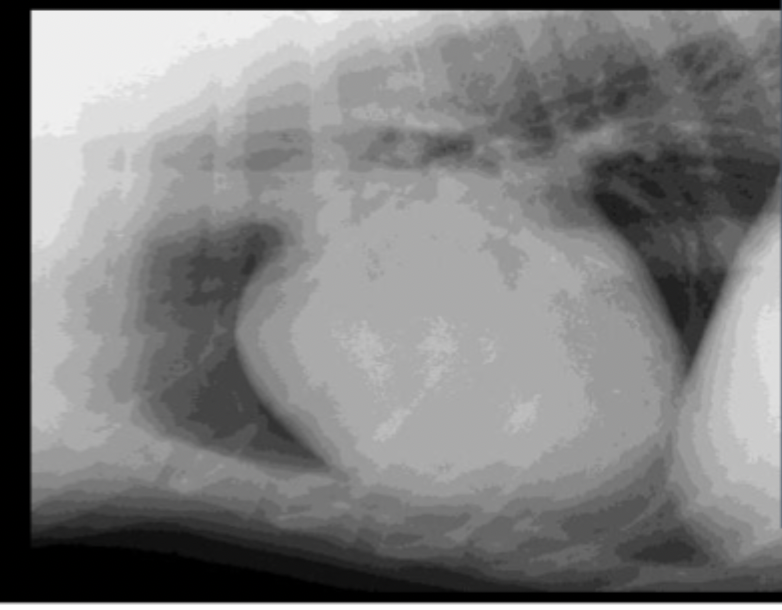
What part of the heart is enlarged on this lateral radiograph?
right atrium
Right atrial enlargement is more obvious on which view?
VD
What radiographic change can we see due to right atrial enlargement?
shift apex of heart
What radiographic changes can we see as a result of right ventricular enlargement?
bulging on VD/DV (reverse D pattern)
elevation of apex from sternum on left lateral
What are common causes of right ventricular enlargement?
hypertrophy most common
heartworm disease
pulmonic stenosis
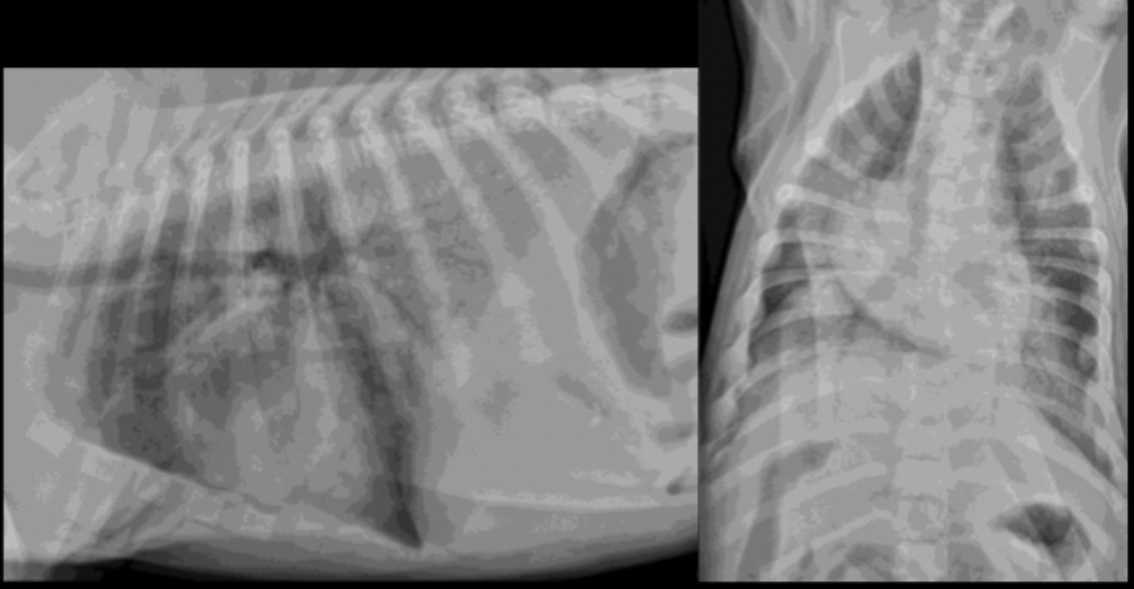
A 4 month old puppy fell in the pool yesterday and presents today struggling to breathe. What is the predominant pulmonary pattern?
alveolar
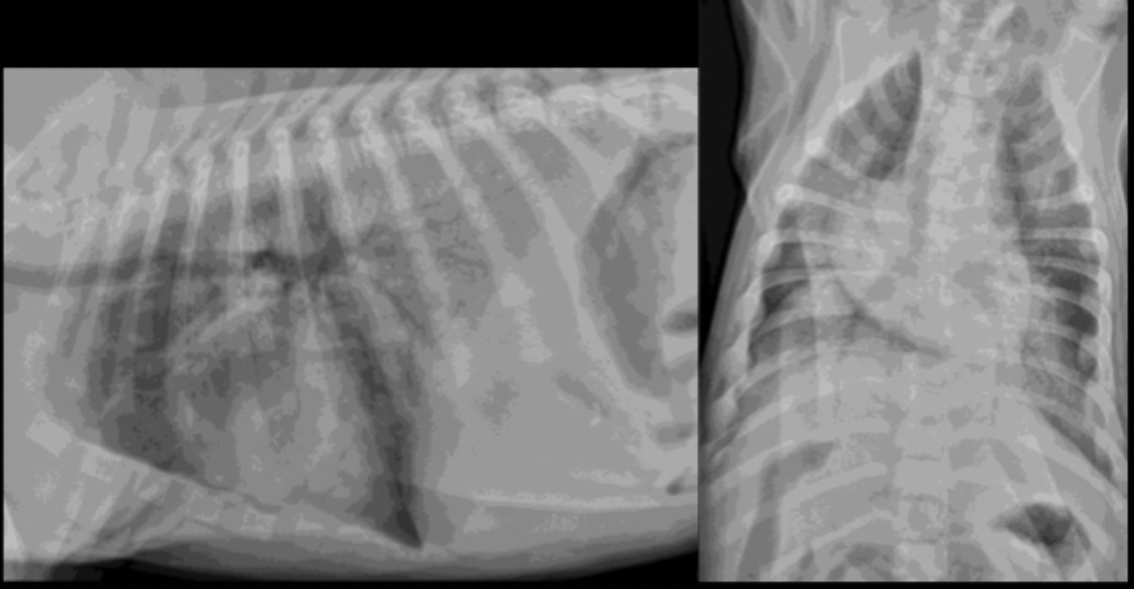
A 4 month old puppy fell in the pool yesterday and presents today struggling to breathe. What is your primary differential?
non-cardiogenic pulmonary edema
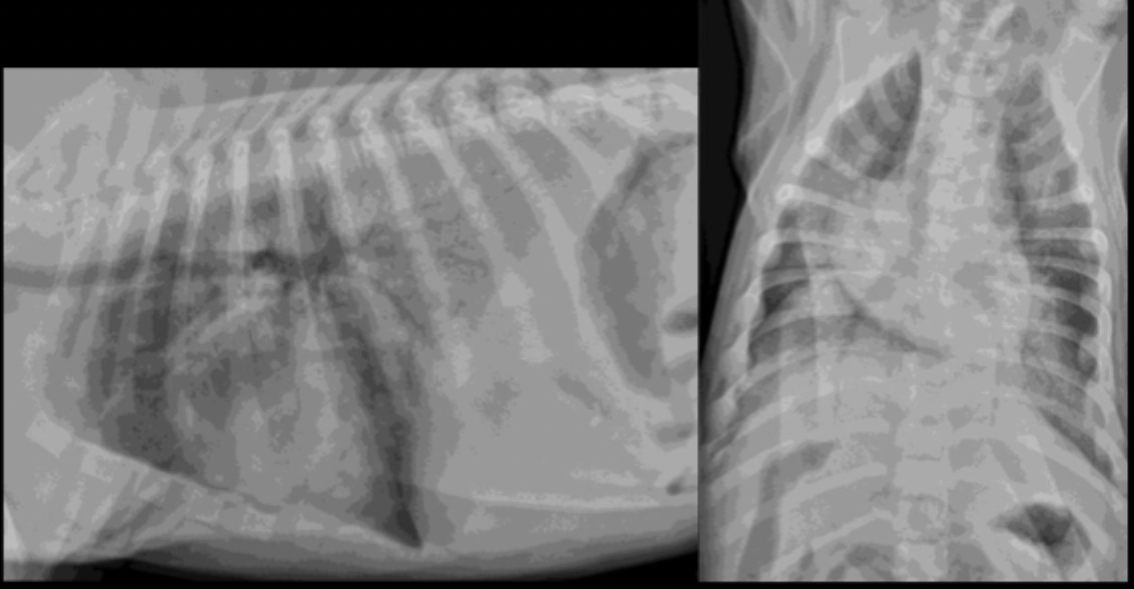
A 4 month old puppy fell in the pool yesterday and presents today struggling to breathe. Why si your primary differential not aspiration pneumonia?
because this is a caudo-dorsal alveolar pattern, not ventral
What are causes for non-cardiogenic pulmonary edema?
neurologic (seizures)
severe allergic reaction
advanced uremia
pancreatitis
irritating inhalants
drowing (or near drowning)
List some common acquired cardiac diseases/abnormalities.
mitral valve insufficiency
tricuspid valve insufficiency
heartworm disease
cardiomyopathy
pericardial effusion
Define heart failure.
Failure of left or right ventricle of heart affects portion of circulation “upstream” from affected chambers.
Unilateral is most common but can be combined in late disease.
What are radiographic indications of left sided carciac failure/
pulmonary venous congestion (vein dilated, larger than corresponding artery)
pulmonary edema
If you suspect pulmonary edema is due to left sided heart failure, what can you do to confirm?
give a diuretic (lasix)
if edema due to left sided heart failure, there will be a rapid response within 12-24 hours
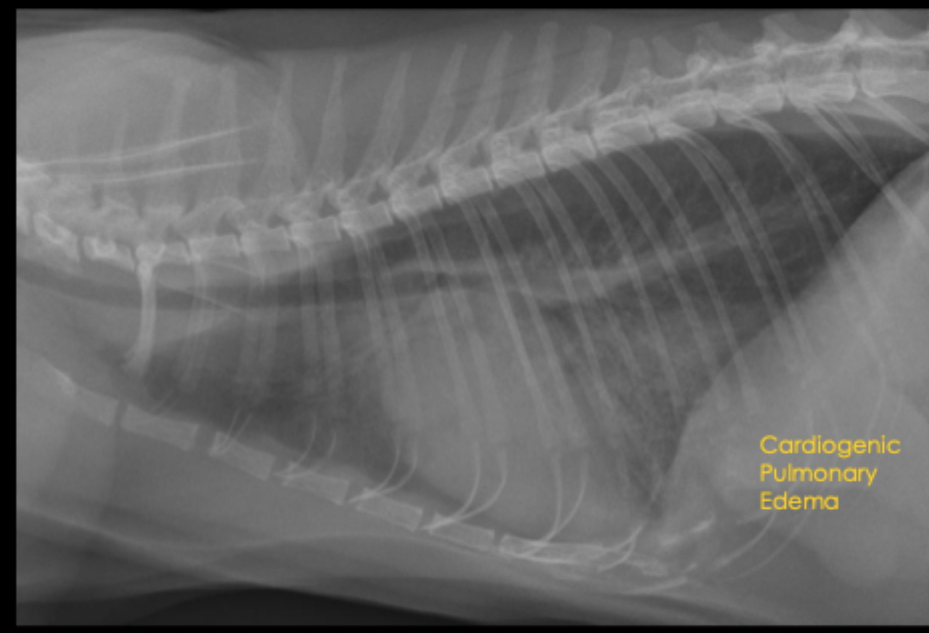
What is the radiographic appearance of cardiogenic pulmonary edema in dogs?
interstitial to alveolar pulmonary pattern in caudal lung lobes and perihilar region
pattern is patchy to diffuse
left atrial dilation, pulmonary vein dilation, cardiomegaly
What is the radiographic appearance of cardiogenic pulmonary edema in cats?
there is no typical pattern of cardiogenic edema in cats
often a more patchy pulmonary pattern
can also have pleural effusion with left-sided heart failure
What are radiographic indications of right sided heart failure?
hepato-splenomegaly
ascites
pleural effusion
enlarged CVC
What are the four general categories of common acquired cardiac diseases?
valvular
myocardial
heartworm disease
pericardial effusion
Common presentation: cough
middle aged to old small breed dogs
degenerative disease of atrioventricular valves (nodular, myxomatous changes, usually mitral)
valves fail to close properly
chronic degenerative valvular disease
Mitral valve insufficiency can create what on radiograph?
left atrial enlargement with progression to include left ventricular enlargement
Cough associated with mitral valve insufficiency can be caused by what?
left atrial compression of left caudal lobar bronchus
left sided congestive heart failure results
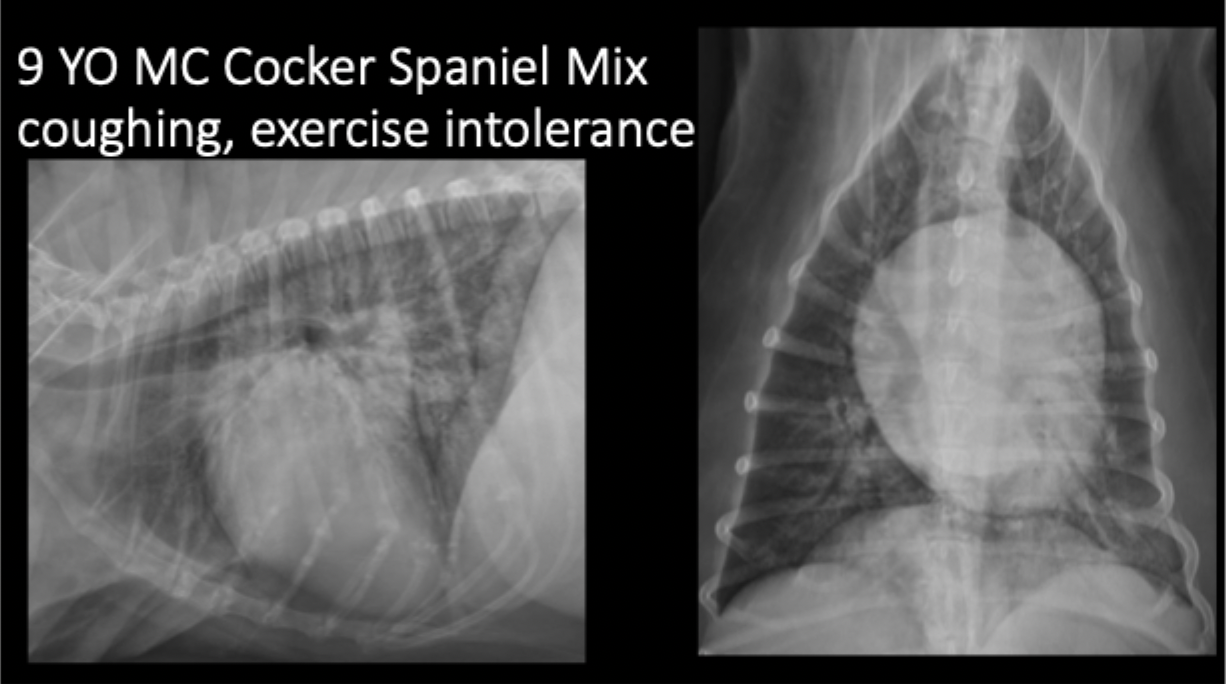
A 9yo MC Cocker Spaniel mix presents for coughing and exercise intolerance. What is the primary pulmonary pattern?
primarily unstructured interstitial pattern
predominantly in the caudodorsal lungs and perihilar region
left worse than right
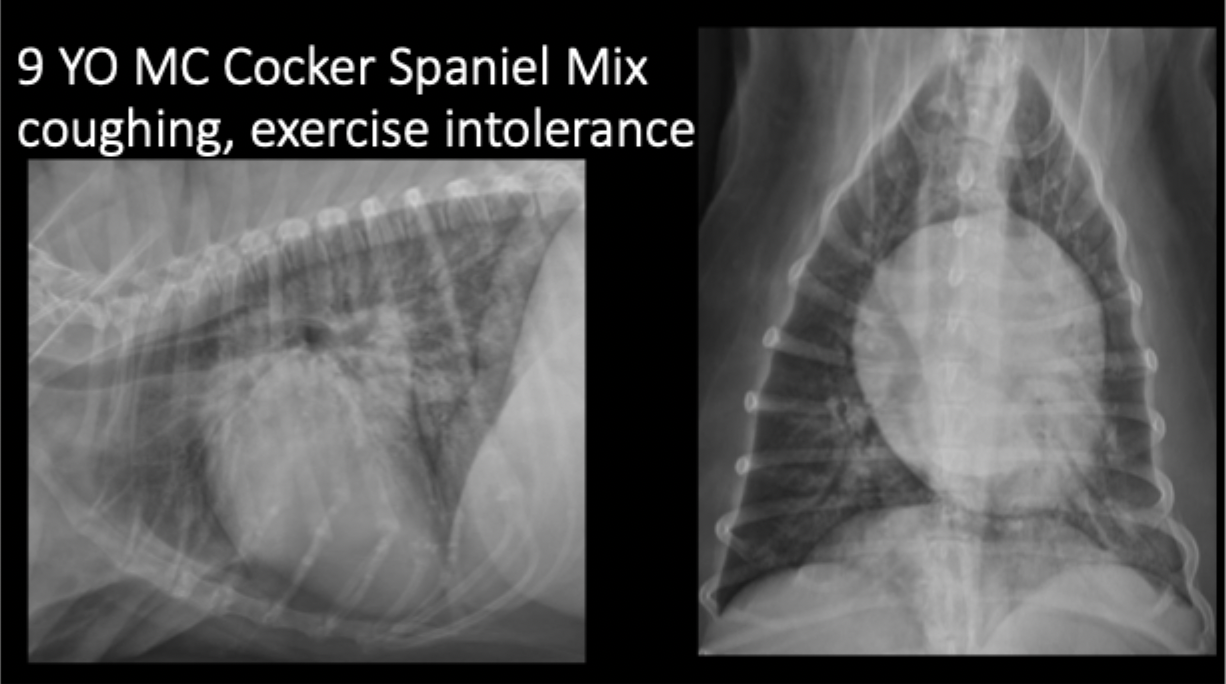
A 9yo MC Cocker Spaniel mix presents for coughing and exercise intolerance. Your primary pulmonary pattern is unstructured interstital but what other pattern is present?
focally more severe alveolar pattern
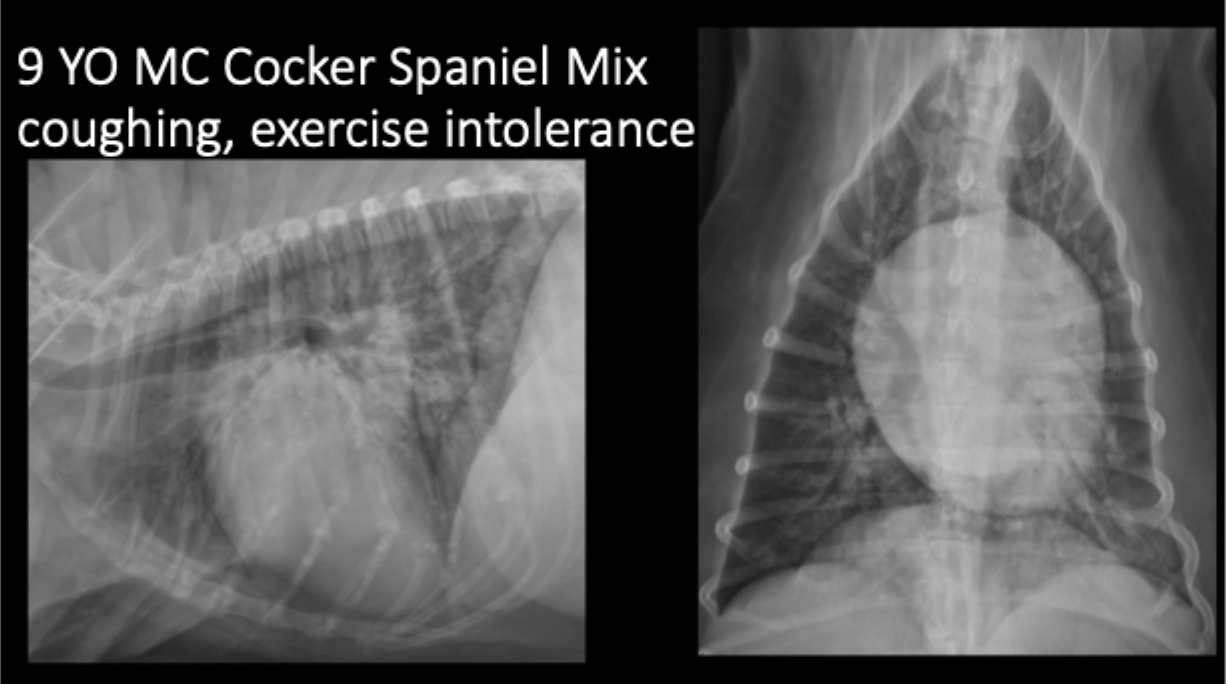
A 9yo MC Cocker Spaniel mix presents for coughing and exercise intolerance. What can be seen in this radiograph as far as heart features?
left sided cardiomegaly and left atrial enlargement
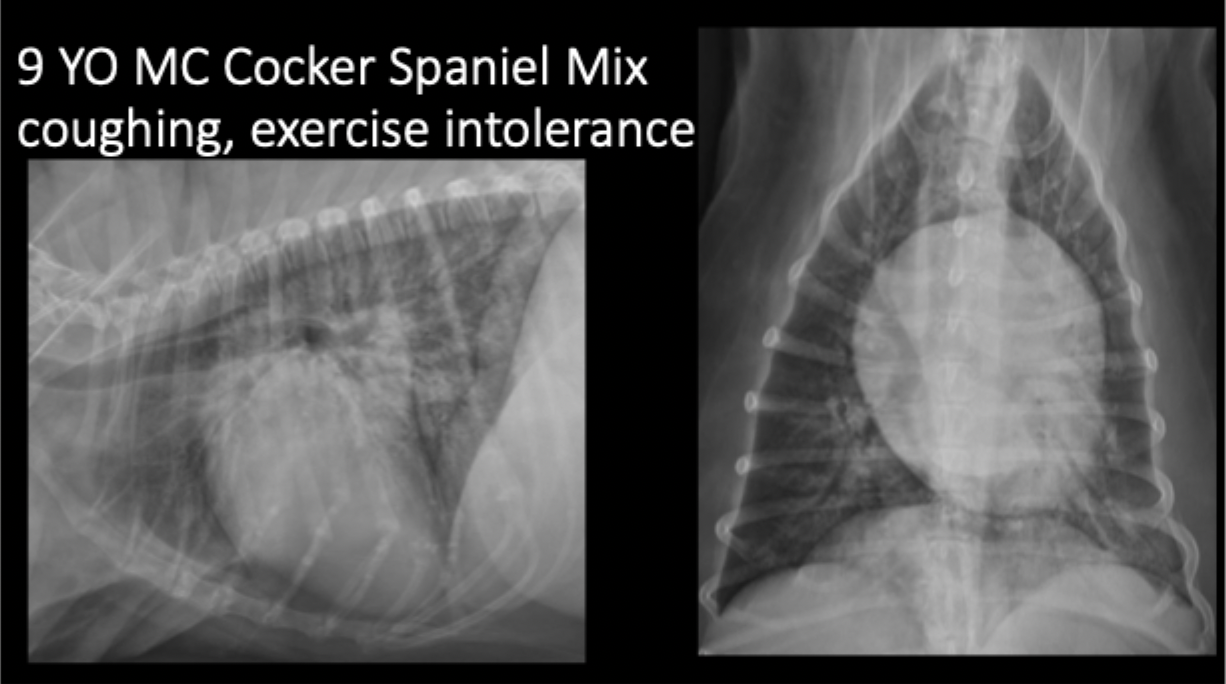
A 9yo MC Cocker Spaniel mix presents for coughing and exercise intolerance. What is your primary differential?
cardiogenic edema secondary to left sided congestive heart failure
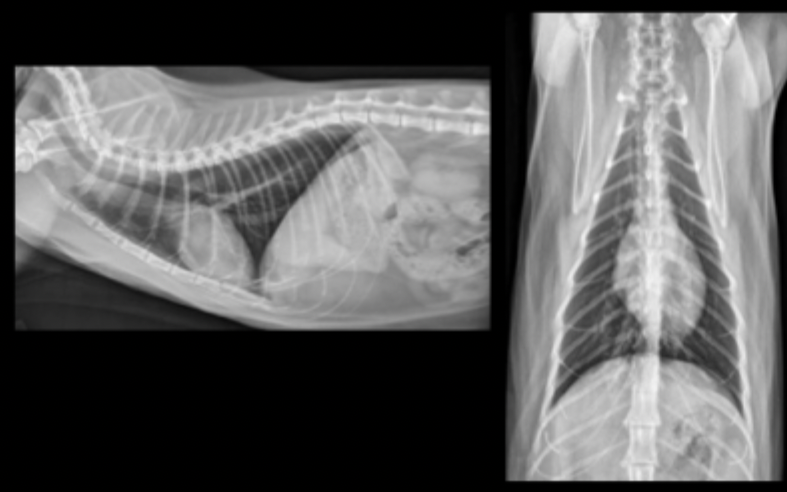
What can be seen in these cat radiographs?
Nothing, these radiographs are normal
What presenting signs can be associated with feline hypertrophic cardiomyopathy?
murmur, gallop rhythm, severe dyspnea, hind or fore limb paralysis (“saddle thrombus”)
What breed has a hgiher incidence of feline hypertrophic cardiomyopathy?
Maine coon
What radiographic changes can be seen with feline hypertrophic cardiomyopathy?
heart may be normal
mild to severe left atrial enlargement
apex often displaced rightward
classic “valentine shaped” heart
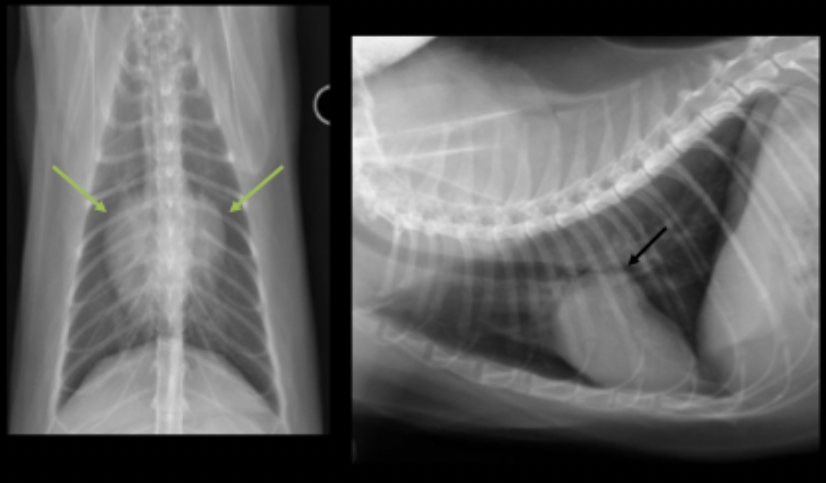
What can be seen on these feline radiographs?
left atrial enlargement
What pulmonary pattern can be seen in this radiograph?
diffuse interstitial pattern
What pattern does feline cardiogenic edema generally present as?
random
patchy
peri-vascular in distribution
True or false: Feline cardiogenic edema will show a dramatic (rapid) response to treatment.
True
What breeds do we most commonly see canine dilated cardiomyopathy?
large and giant breed dogs (great dane, boxer, doberman)
cocker spaniel
What clinical signs can be associated with canine dilated cardiomyopathy?
dyspnea, tachypnea, pulmonary edema
What radiographic changes can be seen with canine dilated cardiomyopathy?
heart may be normal to severe cardiomegaly
mild to severe left atrial enlargement (may be only change visible)
radiographic presentation varies between breeds
Canine dilated cardiomyopathy is caused by what?
myocardial dysfunction (decreased contractility of ventricle leads to atrial dilation)
Mature heart worms live where? What does this cause?
the right outflow tract
causes pulmonary arterial intimal thickening —> inflammation and mechanical obstruction
Heart worm disease can present with what clinical signs?
cough, exercise intolerance
Radiographic changes with heartworm disease are related to what?
worm burden
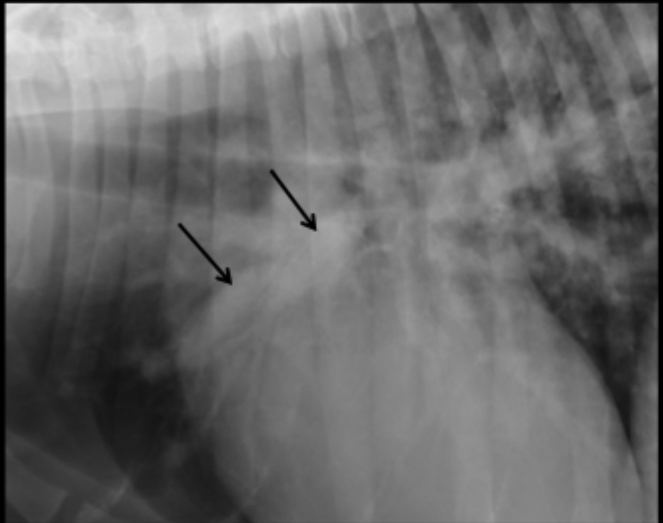
What can be seen in this magnified canine radiograph?
dilated cranial lobar artery due to heartworm disease
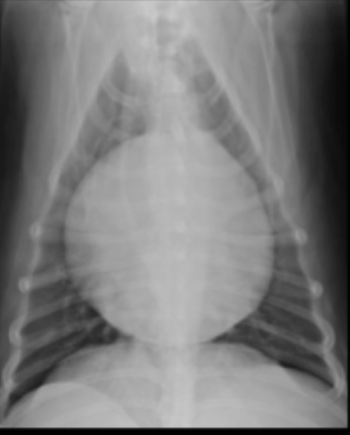
What part of the heart is enlarged in this radiograph?
Main pulmonary artery (bulge at 1:00)
What lung changes can be associated with heartworm disease?
eosinoohilic bronchopneumopathy
pulmonary thromboemboli
unstructured interstitial pattern throughout the lungs
What is the most common cause of pericardial disease?
effusion
What presenting signs can be associated with pericardial disease?
weakness
collapse
pale
What can be seen in this canine radiograph?
pericardial effusion
What are abdominal manifestations of pericardial effusion?
dilated CVC
hepato-splenomegaly
ascites
What border description of the heart can be associated with pericardial effusion?
curved caudal dorsal border
What are causes of pericardial effusion?
idiopathic (golden retrievers)
neoplastic (right atrial tumors or chemodectomas)
hemorrhage
infectious
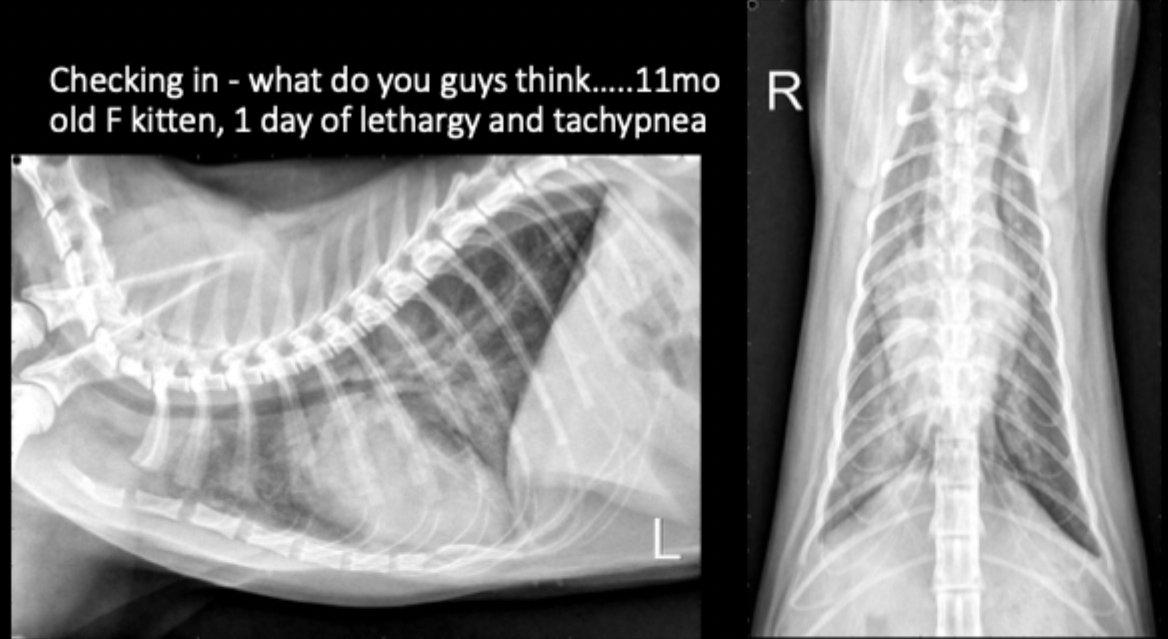
11 month old female kitten presents with 1 day history of lethargy and tachypnea. What is your primary differential?
cardiogenic pulmonary edema, likely due to congenital malformation
What are the four categories of congenital cardiac disease?
valvular stenotic lesions
valvular incompetence lesions
shunting lesions
vascular ring anomalies
How does subaortic stenosis/stenotic aortic valve appear on radiograph?
enlargement of the aortic arch due to turbulent blood flow (11-1 o’clock(
elongation of the left ventricle due to hypertrophy
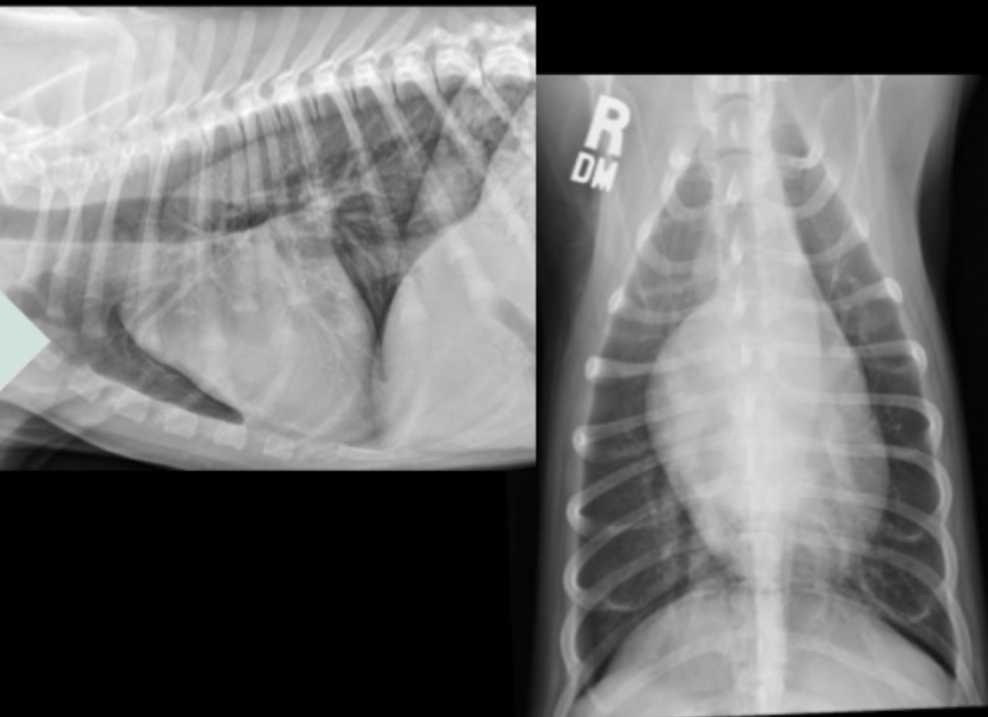
What can be seen in these radiographs?
subaortic stenosis/stenotic aortic valve
How does pulmonic stenosis present on radiograph?
dilated main pulmonary artery (1-2 o’clock)
enlargement of right ventricle secondary to hypertrophy
± pulmonary under circulation (small arteries and veins)
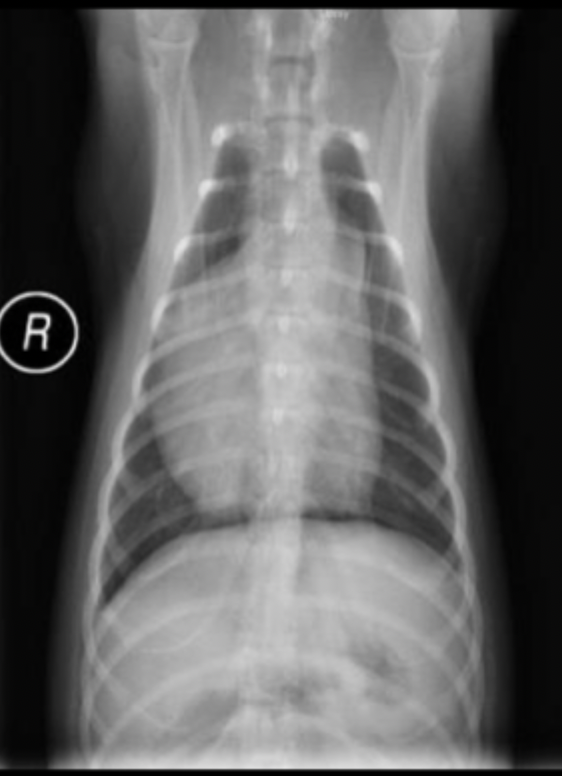
What can be seen on this radiograph?
pulmonic stenosis
What radiographic changes can be associated with pulmonic stenosis?
enlargement of right ventricle secondary to hypertrophy
dilated main pulmonary artery
bulge at 1-2 o’clock
Sometimes on lateral view: apex elevated from sternum, bulge in cranio-dorsal margin of heart
What breed is predisposed to mitral valve dysplasia?
cavlier king charles spaniel
What radiographic changes can be associated with mitral valve dysplasia?
left heart enlargement (left atrium ± left ventricle)
± pulmonary venous congestion
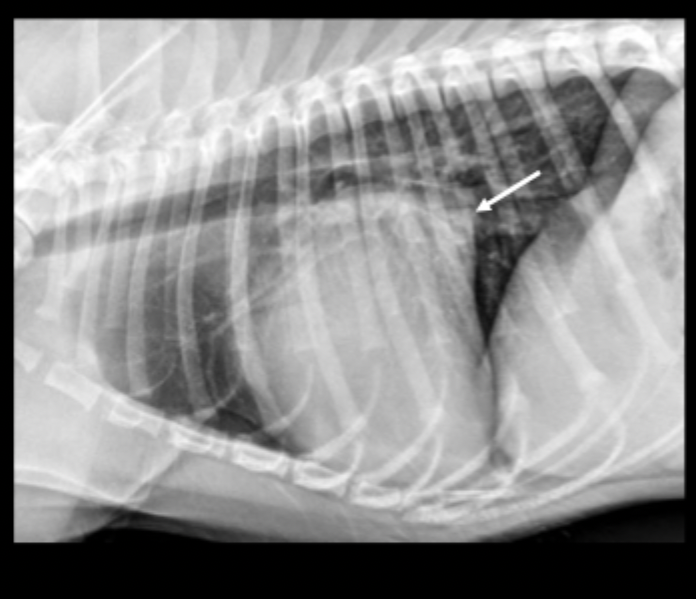
What can be seen in this radiograph?
left atrial enlargement due to mitral valve dysplasia
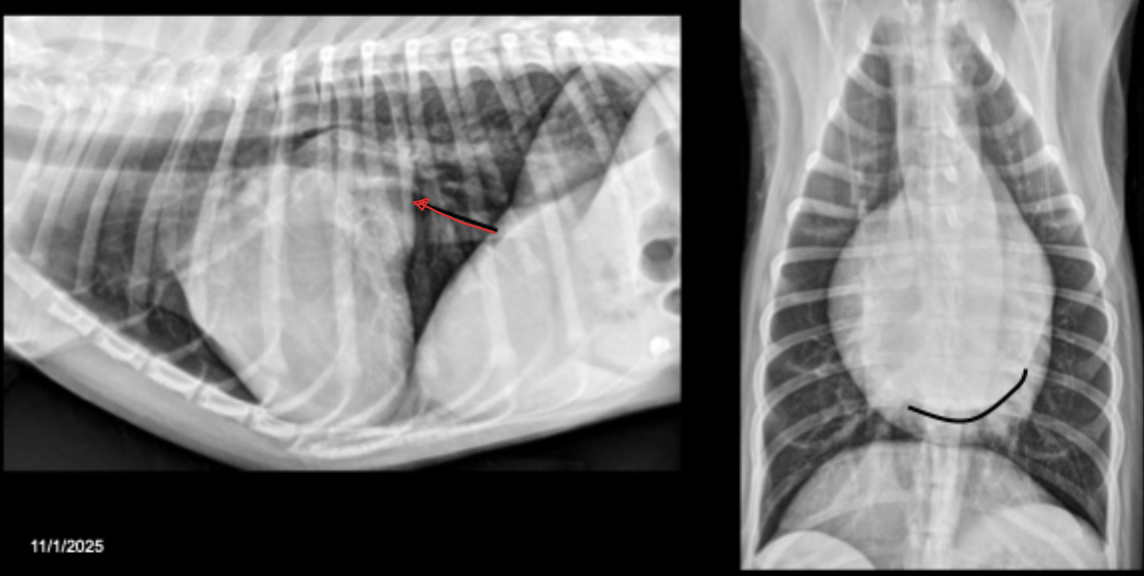
What can be seen in these radiographs?
mitral valve dysplasia
Shunting lesions almost always shunt in which direction?
left to right (high pressure to low pressure)
What radiographic changes can we see with shunt lesions?
heart may be radiographically normal
look for overperfused lung (congestion/distention of main vessels, increased size and number of peripheral vessels)
progresses to left sided heart failure
A ventricular septal defect is a ___ to ___ shunt.
left to right
Ventricular septal defect is usually located where?
in the membranous septum
What breeds do we commonly see affected with a ventricular septal defect?
english bulldog, springer spaniel, cats
What are radiographic changes assoicated with ventricular septal defect?
often difficult to identify radiorgaphically (use echocardiography)
can see variable heart enlargement, mild pulmonary over circulation
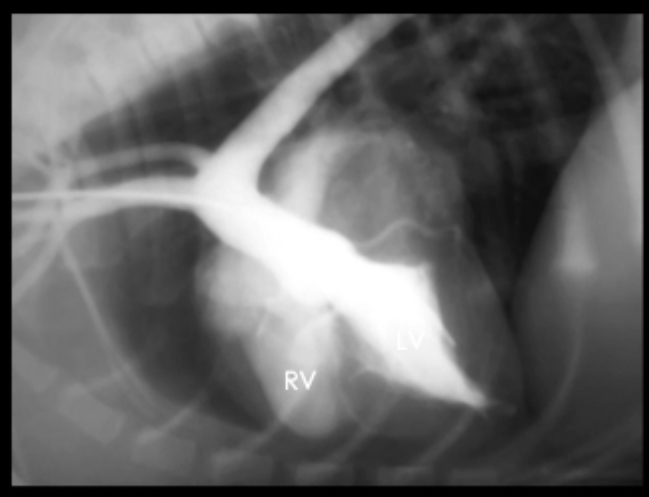
What can be seen in this angiogram?
ventricular septal defect
What connects aorta with pulmonary artery?
ductus ateriosus
What is the “three knuckles” sign?
associated with patent ductus arteriosus but rare
dilation of aortic root, main pulmonary artery (1-2 o’clock), and left auricle (3 o’clock)
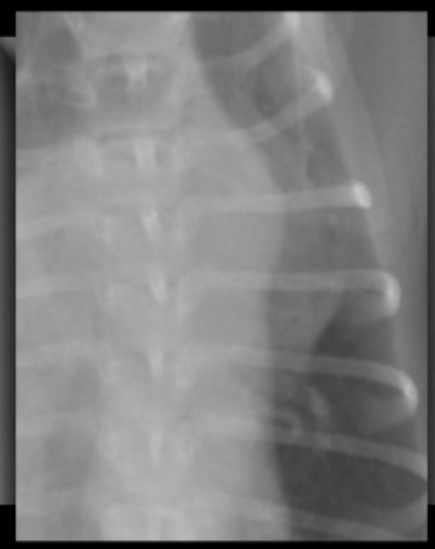
What is seen in this magnified radiograph?
three knuckles sign associated with patent ductus arteriosus
What radiogrpahic changes can we see with aptent ductus arteriosus?
generalized cardiomegaly
“three knuckles sign” rare, usually onlt 1-2 bulges
pulmonary over circulation