Physiology Lecture 25: Vasculature
1/68
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
69 Terms
Pulmonary circulation
this is the blood circulation from the right side of the heart to the lungs
Systemic circulation
blood circulation from the left heart to every part of the body except the lungs
systemic
systemic has 90% of the blood while pulmonary has 10%
Does the pulomnary or systemic circulation carry the most blood
high, low
The operating pressures of the systemic circulation are ___________(high/low) while in pulmonary circulation they are ___________(high/low)
Dilation, constriction
The response to CO2 in system circulation is vaso______________(dilation/contstriction) while in pulmonary is vaso____________(dilation/constriction)
variable, low
The resistance to blood flow in systemic circulation is ______________ while in the pulmonary circulation it is always _____
Long, short
The length of the vessels in the systemic criculation are ____________(short/long) while in pulmonary circulation they are __________(short/long)
Compliance
the ability a blood vessel to stretch and take on a larger volume of blood at a given change in pressure (change in volume divided by change in pressure)
Variable, high
In systemic circulation, the compliance of the vessels are ______________, but in pulmonary circulation the vessel compliance is always very ________
False
True or false: exchange fo gases, nutrients, or wastes take place at major vessels
Capillaries
this is where all exchange of gases, nutrients and wastes happens, they are not smooth muscles
One
capillaries are ________ cell(s) thick
capillaries
All blood vessels except for what contain a smooth muscle layer
Endothelium
this is the one cell thick inner lining of all blood vessels which also form the capillaries
More, lower
Veins are _________(more/less) compliant that arteries, and operate at ______________(higher/lower) pressures
Valves
Veins have these, which help ensure unidirectional flow at low pressures
muscle contractions
Along with valves, what helps blood flow through veins
artery →arteriole → capillary bed → venule → vein
In what order does blood flow through the capillary system
Ohm's law
this is the equation that we use to talk about blood flow. Blood flow (Q)= Pressure difference/resistance
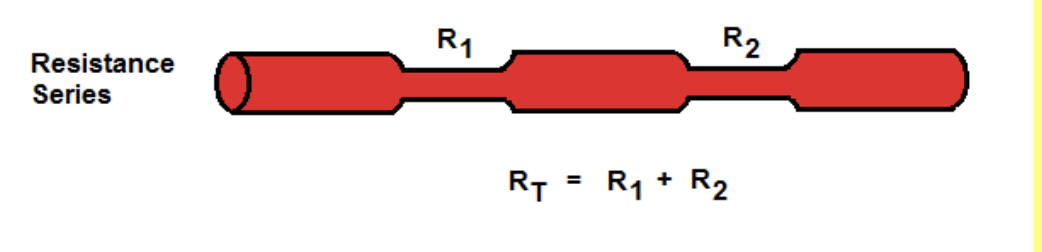
Series
Resistance in ___________ causes each resistor to be added together
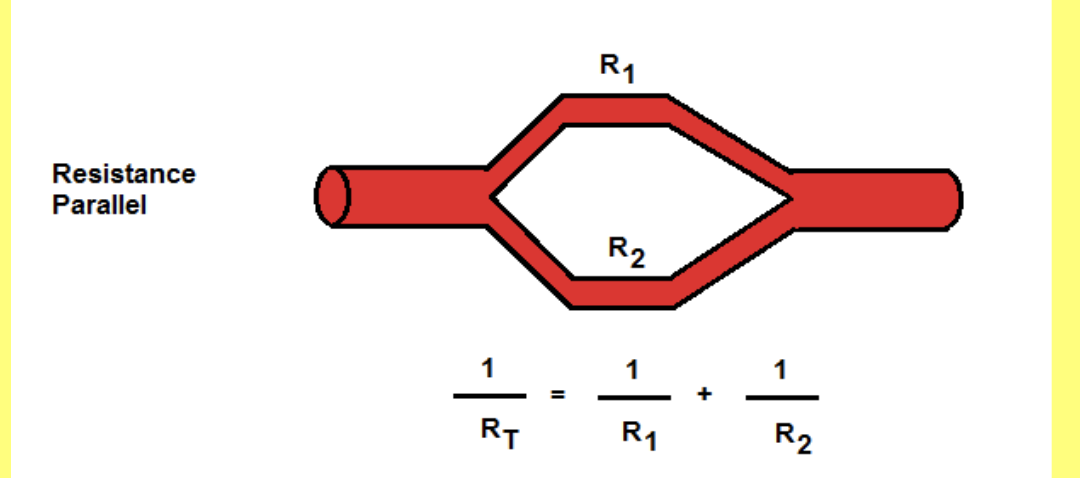
Parallel
Resistance in __________ is the inverse of the resistances added, so that the resistance in parallel is always less than the resistance of one of the individual resistores
1/R = (1/R1) + (1/R2)
How do you find resistance in parallel
Kidneys
which vasculature operates at the highest pressures? (like which area)
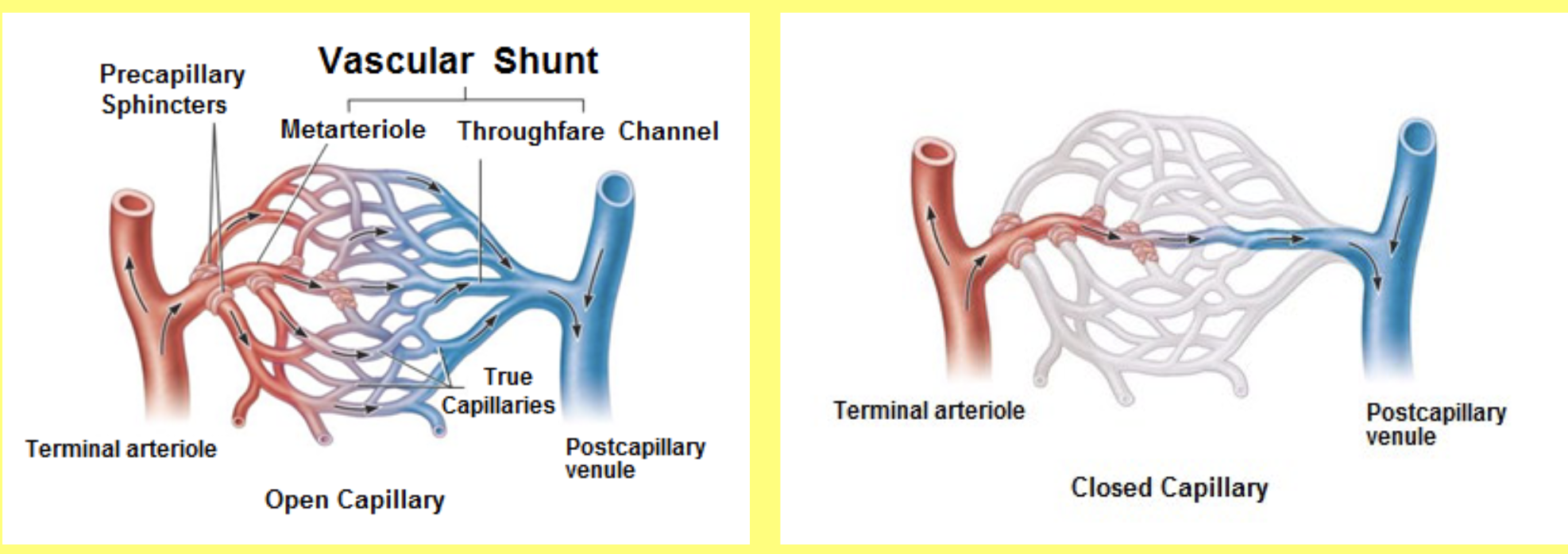
Vascular shunt
this is the the vessel through a capillary bed that allows some blood to flow through the bed even when the capillary bed is closed
Precapillary sphincters
these are the annular smooth musce cells that surround the precapillary arterioles and regulate blood flow into the capillary
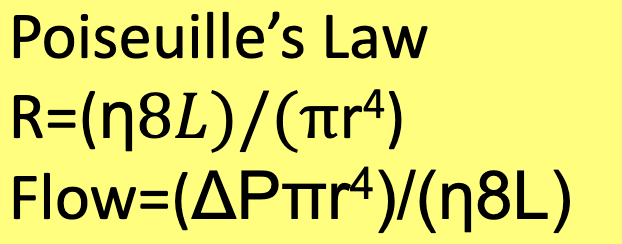
Poiseuille's law
this is the law that states the reltationship between Resistance, viscosity, length of the vessel, radius of the blood vessel. It is R=n8L/pi*r^4
Radius
the thing that has the biggest difference on resistance of the vasculature is _____________
Arterioles, highest
The largest fall in blood pressure occurs at the ____________ because they have the ______________(highest/lowest) resistance. This is where the major resistance vessels are located to maintain systemic blood pressure
Pulse pressure
the difference in pressure between systolic and diastolic pressure
Mean arterial pressure
this is the measure of systemic pressure, which is equal to the diastolic pressure plus 1/3 of the pulse pressure. This is also proportional to afterload
MAP= CO * TPR
this is the equation to calculate MAP with cardiac output and total peripheral resistance
LaPlace's Law
this is the way that we get tension using pressure and radius. Tension = Pressure * radius
More
The larger the blood vessel is, the ________(more/less) tension will be experienced on the vessel for the same pressure
True
True or False: aneurisms occur in larger vessels, and never at capillary beds
large, slow
Even though the capillaries are smal, the cross sectional area is very ____________, so the blood flow through the capillary bed is ___________(faster/slower) than the arteriole or venule associated with it
Starling landis equilibrium
this is the matehmatical description of how hydrostatic pressures, oncotic pressures, and vessel leakiness affect the net filtraiton rate
water
Hydrostatic pressures always push _____ away
pull
oncotic pressures always _____ water towards them
NFR = Kf (Pc + oi) - (Pi + oc)
What is the equation for net filtration rate
Kf
This is the variable that is "how leaky" a vessel is
Pc
This is the hydrostatic pressure of the capillary (pressure of water pushing OUT on the capillary)
Pi
This the hydrostatic pressure of the interstitial fluid (pressure of the water pushing ON the capillary wall inward)
Oc
This is the oncotic pressure of the capillary (the force of the proteins pulling water INTO the capillary)
Oi
This is the oncotic pressure of the interstitial fluid (force of proteins pulling water OUT of the capillar)
1-2 mmHG
overall, at most capillaries the net pressure is this pressure driving OUT of the capillary
Lymphatic vessels
these are vessels containing slits and valves that remove excess fluid from the tissues and return it to the circulation
button, valves
Lymphatic vessels have ___________ like junctions that act as pores, and ___________ that allow lymph flow to go in one direction, and these pump fluid back to the heart
immune
the lymphatic vessels connect to nodes that are aoart of the _____ system
Subclavian trunk, venous
The lymph vessels drain their fluid into the ____________ ___________ of the ___________ system so that the fluid returns to the heart
Side veins
the lymphatic vessels run along ______ ________ to help move fluid towards the heart
subclavian veins
The fluid of the lymphatic system reenters the circulation at the _______ _______
PP = P(systolic)- P(diastolic)
how do you measure pulse pressure
MAP = P(diastolic) +1/3PP
what is the equation for MAP relating to pulse pressure
MAP = CO x TPR
What is the equation for MAP relating to TPR
pressure = flow x resistance
what is ohms law?
Tension - pressure x radius
what is LaPlaces Law
larger blood vessels will experience more tension on the wall of the vessel at the same pressure
what does Laplaces law describe
Net Filtration pressure (MFP) = pressure (out) - pressure (in)
how do you measure net filtration pressure
at the arteriole and the venule to get an overall view of the capillary. Most capillaries have a new rate of 1-2 mmHg
what 2 places do we want to measure NFR and why?
greater
for serial resistors, the total resistance (Rt) is lesser/greater than the largest single resistor
less
for parallel resistors, the total resistance (Rt) is lesser/greater than the smallest single resistor
capillary
hydrostatic pressure is the pressure of fluid in the ________
higher solute
oncotic pressure is the pressure of fluid moving toward _____ _____
proportional
flow of blood follows ohms law such that flow is (proportional/inversely proportional) to pressure differences along the blood vessel
inversely proportional
flow of blood follows ohms law such that flow is (proportional/inversely proportional) to the resistance of the blood vessel
1/r^4, radius
the resistance of a blood vessel is proportional to _____. Because of this, small changes in the _____ of a blood vessel leads to large changes in resistances and the flow of blood
proportional
the pressures exerted by the walls of the blood vessel are ______ to the radius.
interstital space
at the arterial end, the dominant pressure pushes fluid into the _______ space
Oc
due to the drop of pressure in the venous end, it allows ___ to dominate resulting in the reabsorption of fluid at the venous end