enzyme kinetics
1/24
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
25 Terms
catalysts
speed up attainment of reaction equilib rium
kinetics change
thermodynamics do not
how much faster are catalysed reactions compared to non catalysed
10^3 - 10^ 17 faster
which form is in vivo glucose incorportated
beta form
how do enzymes lower the activation energy
enzymes reduce the energy barrier by providing alternate reaction pathway with lower activation energy
when is active site most complementary
transition state
the stabilisation lowers the energy barrier
examples of cofatcors
essential ions
coenzymes
cosubstrates
prosthetic groups
essential ions
loosely bound or tightly bound in metalloenzymes
eg magnesium with ATP
prosthetic groups def and examples
conzyme of cofactor bound tightly to enzyme
eg haem, vitamins
cosubstrate
coenzyme
lossely bound and needs to be recycled
eg ATP
rate equation
v = k[s]
velocity is proportional to concentration of substrate
initial velocity is directly proportional so 1st order for linear processes
which step is rate limiting
catalytic
curve and rate equation for catalysed reactions
curve is hyperbolic
linear at low conc of substrate
at high conc, 0 order kinetics, full saturation, changing conc has no effect
due to active site of enzyme
michaelis menten equation
Vmax is max velocity
Km is the michaelis constant
Vo is the initial velocity
Vo = Vmax * [S] / Km + [S]
![<ul><li><p>Vmax is max velocity</p></li><li><p>Km is the michaelis constant</p></li><li><p>Vo is the initial velocity</p><p><mark data-color="#778b38" style="background-color: #778b38; color: inherit">Vo = Vmax * [S] / Km + [S]</mark></p></li></ul><p></p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/837c1d92-dde5-4dc8-9337-0a95db23dae0.png)
Km
measure of affinity of the enzyme for the substrate
enzyme-substrate disassociation constant
the concentration of substrate needed for half of the maximum velocity
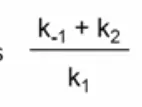
k2
in the michaelis constant
the rate of catalysis
negligible more or less k-1/k+!
maximum velocity
the velocity when the enzyme is saturated with substrate
proportional to enzyme concentration
Kcat
measure of the number of molecules of substrate converted to product per second per active site
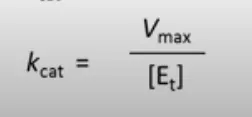
equation for the maximum rate at saturating [S]
Vmax = kcat[Et]
[Et] is the total enzyme concentration - number of active sites
when does kcat = k2
in simple reactions
the higher the kcat / km
the more efficient the reaction
which step is slow in michaelis menten equation
formation of product is the slowest step k2
so k2 is negligible
what is a rate constant at low [S] and use
kcat/km
compares catalytic efficiency of different enzymes
relative abilities of different compounds to serve as a substrate for an enzyme
lineweaver burk plot
linear transformation of the michaelis menten equation
plot reciprocal 1/vo versus 1/[S]
what is the x axis intercept on a lineweaver burk plot
-1/Km
what is the y axis intercept on a lineweaver burk plot
1/Vmax