1.4.1 government intervention
1/9
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
10 Terms
what is a “tradable pollution permit”
is a form of pollution control that uses the market mechanism to insentivise producers and consumers to reduce their total carbon emissions
why does a pollution permit incentivise firms to cut carbon emmision
the price of the pollution permit increases, meaning the cost of production increases = firms incenticised to use cleaner technology
draw a pollution permit
increasing the scarcity of a pollution permit only increases prices
this makes it more expensive for a business to emit carbon
perfectly inelastic supply = fixed amount of permits
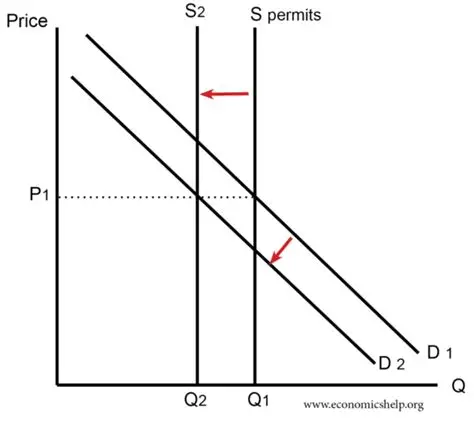
how does a pollution permit effect the negative externality of pollution
pollution permits internalises the cost to third parties. Producers are paying more for the pollution permit due to the damages done to the environment. COP increases. Price increases to the socially optimum level at P* and quantity decreases to the socially optimum output of Q*.
EV - Without the pollution permit, firm operate at P1 Q1 which is not socially optimal, this causes DWL
EVALUTAION ON POLLUTION PERMIT
it is difficult to measure the pollution levels. Multinationals shift production around due to globalisation
Difficult to know how many pollution permits that is given out by the government
what is state provision of public goods + examples
information gaps can cause market failure, governments may directly provide and fund information campings to help inform decision making
lifestyle campaign
advantages + disadvantages of information provision
ADV - doesn’t interfere with the market mechanism allowing market forces to determine market price and quantity
DIS - consumer behaviour doesn’t change - consumers may choose to ignore information or may not understand
EVALUTAION of information provision
EV
if consumers act rationally or irrationally
the size of the information gap - consumers may already know information without it being provides = ignore
what is regulation
government creating rules to limit the harm of negative externalities of consumtion or production,
Advantages and disadvantages of regulations
ADV - overcome information failure by making an activity compulsory
fail to meet regulation = fine = compensation = internalise the externality
DIS - may have knock on effects on industries = job losses
potential3 for informal economy or shadow market to aviod the law