Reproduction #12 (pt 3: Sexual reproduction (crossing over / recombination, independent assortment, & Gametes))
1/8
Earn XP
Description and Tags
lecture #12
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
9 Terms
meiosis I - Prophase I
in what stages do crossing over (recombination) occur in?
crossing over (recombination)
definition: gene swapping between homologous non-sister chromatids
steps:
1) proteins attach homologous chromosomes in a synapsis
2) attached homologous chromosomes form a tetrad
3) Non-sister chromatids overlap, forming an x-shapes chiasma
chiasma occurs at a locus
____ can swap alleles between homologous non-sister chromatids
creates a new assortment of alleles along a chromosome
produces recombinant chromosomes that combine alleles inherited from each parent
end result: chromosomes have the same number of genes but the sister chromatids are no longer identical (daughter cell are completely unique from mother cell)
locus
definition: location of a gene on the chromosome
alleles of a gene are always found in the same location on homologous chromosomes
Remember: alleles of a gene are always found in the same location on homologous chromosomes
No, XY are non-homologous chromosomes
can crossing over (recombination) occur between XY sex chromosomes?
Yes, XX are homologous chromosomes
can crossing over (recombination) occur between XX sex chromosomes?
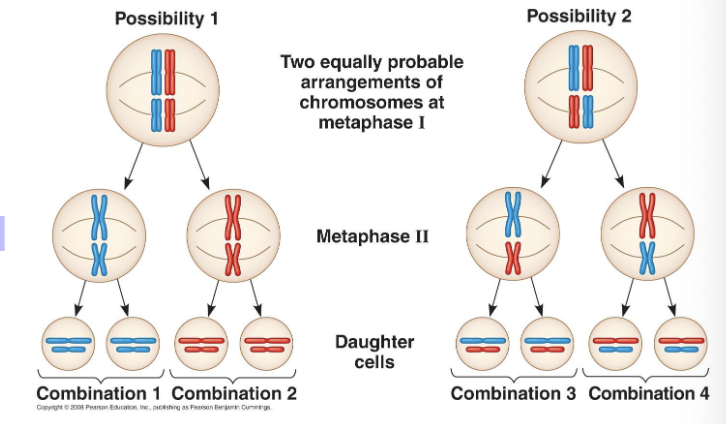
meiosis I - metaphase I
in what stages do independent assortment occur in?
independent assortment
Definition: homologous pairs of chromosomes orient randomly
each pair of chromosomes sorts maternal and paternal homologues into daughter cells independently of the other pairs
possible # of combinations is 2^n (where n is the # of chromosomes in a single set)
for humans: n = 23
there are more than 8.4 million (2^23) possible combinations
Gametes
the resulting cells formed from the completion of meiosis II
they continue to mature and develop to reach their final functional potential (but they NEVER undergo further mitosis)