Topic A - Mechanics
1/43
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
44 Terms
Define a scalar quantity & give examples
Quantity that has only magnitude(size)
Examples: Distance, Energy, Speed, Mass, Power, Temperature
Define a vector quantity & give examples
Quantity with a magnitude (size) and a spatial direction.
Examples: Displacement, Acceleration, Velocity, Momentum, Force
How do you add vectors algebraically
Resolve all vectors in horizontal and vertical components.
Sum the vertical components and horizontal components individually.
Use Pythagoras theorem to solve for the resultant vector.
Use TOA to find the angle.
List SUVAT
S - displacement/distance - m
U - initial speed/velocity - ms-1
V - final speed/velocity - ms-1
A - acceleration - ms-2
T - time - s
Distance
How far in total an object has travelled
Displacement
How far an object has travelled from the start to finish in a straight line (with direction).
Speed
Total distance travelled per unit second
Velocity
Rate of change of displacement
Acceleration
Rate of change of velocity
What is the gradient on a displacement time graph?
The velocity
How do you measure the instantaneous velocity on a displacement time graph?
Take the gradient of the tangent line of the point you are measuring.
What is the gradient on a velocity time graph?
The acceleration
What is the area under on a velocity time graph?
The displacement
What is the area under on a acceleration time graph?
The change in velocity
List the 5 SUVAT equations.
s = (u + v / 2)*t
v = u + at
s = ut + ½ at2
v2 = u2 + 2as
s = vt - 1/2at2
Define Projectile Motion
The motion of an object thrown into the air.
What is the only force that will be acting on a object after the initial force and if air resistance is negligible ?
Weight Force - 9.8ms-2
What is the principle when air resistance isn’t negligible?
It is proportional to the square of the velocity.
F = ½ ρAv2
State the air resistance formula
F = ½ ρ A v2
How does the path a projectile takes change when Air resistance is increased? (List 3 things)
It reaches a lower vertical height
It travels less far horizontally
The path become asymmetrical with the section before the peak as it is longer than the section afterwards
What are the 4 main ways energy can be transferred?
Mechanically - an object moving due to a force acting on it
Electrically - a charge moving through a p.d
Heating - energy transferred from a hotter object to a colder object
Radiation - energy transferred by e.g. light/sound
Work
Amount of energy transferred from one stores to another.
State the mechanical work formula
W = Fscosθ
What is the difference if work done is negative or positive?
If the work done is positive then work has been done on the object, if it is negative then work has been done by the object.
What is the formula for GPE?
ΔEp = mgΔh
What is the formula for EPE?
ΔEH = ½ k (Δx)2
Any object being deformed.
What is the formula for KE?
½ mv2
(½ mv2 - ½ mu2)
Any object in motion.
What does the area under a Force Displacement graph represent?
The work done.
State the law of conservation of energy
In any closed system energy cannot be created or destroyed it can only be transferred from one store to another.
ΔEt = 0
It is a law of physics and empirical.
Empirical
Based on observations or experiments.
Theoretical
Based on theories or hypotheses.
Power
The rate of work done.
Define efficiency
The ratio of how much useful energy was put in, to how much useful energy was put out.
What are the 2 formulas for efficiency?
η = useful work out / total work in
η = useful power out / total power in
What is a Sankey diagram and what do they show?
A Sankey diagram is a visual representation of energy transferred in applications/scenarios.
What can a resultant force on an object change?
The objects shape (compresses, extend, deform) and the objects velocity (speed and or direction).
Tension
The force exerted by a string, rope, cable, spring etc.
It is the same along all points
What law must all elastic objects obey?
They must all obey Hooke’s Law, where force is proportional to extension.
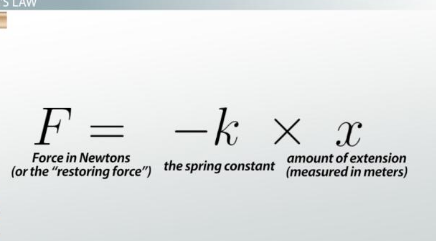
What is weight force?
Mass x gravitational field strength.