Cell bio & Chem Exam 3
1/36
Earn XP
Description and Tags
ChatGPT is my savior
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
37 Terms
What does the plasma membrane denote?
It denotes the boundary of a cell.
Define the extracellular matrix (ECM).
The ECM is a network of secreted molecules outside the cell’s plasma membrane that provides structural support, biochemical signals, and a scaffold for tissue organization.
Fill in the blank: The molecules residing outside the cell membrane, including those in the ECM, play an important role in cell–cell interactions, signaling, and ____
adhesion
What is the glycocalyx and what is its function?
The glycocalyx is a cell coat formed by glycoproteins and glycolipids on the outer surface of the plasma membrane. It mediates cell–cell interactions and provides mechanical protection.
What is the basement membrane, and where is it typically located?
The basement membrane is a specialized, continuous sheet of ECM (50–200 nm thick) found on the basal side of epithelial cells, surrounding nerve fibers, muscle cells, and lining blood vessels.
How does the basement membrane function in preventing cancer cell invasion?
It acts as a physical barrier that helps prevent the invasion of tissues by cancer cells.
What is collagen, and why is it important in the ECM?
Collagen is a fibrous glycoprotein that is the most abundant protein in the body. It provides high tensile strength and forms the insoluble framework of tissues.
Describe the structural features of collagen molecules.
Collagen molecules are trimers composed of three polypeptide (α) chains that wind around each other to form a triple helix, stabilized by hydrogen bonds between hydroxylated proline and lysine residues.
Fill in the blank: Vitamin C is required for the _____ of proline and lysine residues in collagen, which is critical for forming the triple helix structure.
hydroxylation
What are proteoglycans and what role do they play in the ECM?
Proteoglycans are complexes made of a core protein attached to glycosaminoglycans (GAGs). They are highly acidic, bind large amounts of water, and help form a gel-like network that gives tissues strength and flexibility.
What is fibronectin and how does it aid in cell migration?
Fibronectin is an ECM glycoprotein with a modular structure that provides binding sites for cells and other ECM molecules, forming "highways" that guide cell migration.
What role do laminins play in the basement membrane?
Laminins are glycoproteins that help form interconnected networks in the basement membrane, providing strength, flexibility, and anchoring cells during migration and adhesion.
Define integrins and explain their role in cell–ECM interactions.
Integrins are transmembrane receptor proteins composed of alpha and beta subunits. They link the ECM to the cell’s cytoskeleton, mediate cell adhesion, and participate in signal transduction.
What are hemidesmosomes and what is their function?
Hemidesmosomes are specialized adhesive structures that anchor epithelial cells to the basement membrane, ensuring tissue stability.
What are selectins, and which cell types express them?
Selectins are membrane glycoproteins that bind specific oligosaccharides. E-selectin is found on endothelial cells, P-selectin on platelets and endothelial cells, and L-selectin on leukocytes.
What are cadherins, and what ion is essential for their function?
Cadherins are Ca²⁺-dependent glycoproteins that mediate cell–cell adhesion. Calcium ions are essential for maintaining their rigid conformation required for proper adhesion.
Name the three major types of gated ion channels.
Voltage-gated, ligand-gated, and mechano-gated channels.
How does facilitated diffusion differ from simple diffusion?
Facilitated diffusion uses specific transporter proteins and exhibits saturation kinetics, while simple diffusion is a passive, linear process without protein assistance.
What is active transport, and why is it necessary for cells?
Active transport is the movement of molecules against their concentration gradient using energy (e.g., ATP), which is necessary to maintain ion gradients critical for cellular functions.
Describe the function of the sodium–potassium pump.
The sodium–potassium pump uses ATP to actively transport 3 Na⁺ ions out of the cell and 2 K⁺ ions into the cell, thereby maintaining essential ion gradients and contributing to the resting membrane potential.
What is the purpose of the Nernst equation in neuronal signaling?
The Nernst equation calculates the equilibrium potential for a specific ion based on its concentration gradient and charge.
What does the Goldman equation calculate?
The Goldman equation calculates the overall resting membrane potential by considering the contributions and permeabilities of multiple ions.
Define depolarization in the context of neuronal signaling.
Depolarization is the process in which the inside of a neuron becomes more positive, primarily due to the influx of sodium ions.
What is repolarization, and which ion movement primarily causes it?
Repolarization is the return of the neuron's membrane potential to its resting state, primarily due to the efflux of potassium ions.
What is saltatory conduction and why is it advantageous?
Saltatory conduction is the process by which action potentials jump between nodes of Ranvier in myelinated axons, greatly increasing the speed of signal transmission.
List the major structural components of a neuron.
Dendrites, cell body (soma), axon, myelin sheath, nodes of Ranvier, and terminal knobs (axon terminals).
What is the function of the myelin sheath in neurons?
The myelin sheath insulates the axon, reducing ion leakage and increasing the speed of electrical signal conduction.
Outline the main steps in neurotransmission at the neuromuscular junction.
An electrical signal travels down the axon, triggering voltage-gated calcium channels to open at the terminal; calcium influx causes vesicles to release neurotransmitters, which bind to ligand-gated ion channels on the target cell, initiating a new signal
Explain mechanotransduction in cell signaling.
Mechanotransduction is the conversion of mechanical forces applied to a cell’s surface into biochemical signals inside the cell, often through focal adhesions.
Fill in the blanks: During active transport, molecules are moved against their ______ gradient using energy from ______.
concentration; ATP
Goldman’s equation
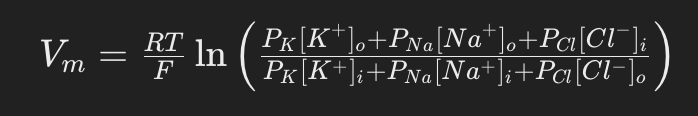
Membrane potential (Vₘ) (Goldberg equation)
The voltage difference across the cell’s membrane.
Gas constant (R) (Goldberg equation)
The constant representing the gas constant used in the equation.
Absolute temperature (T) (Goldberg equation)
The temperature measured in Kelvin.
Faraday’s constant (F) (Goldberg equation)
The constant representing the charge per mole of electrons.
Permeability (P) (Goldberg equation)
The coefficient indicating how readily ions cross the membrane.
Ion concentrations ([ion]ₒ and [ion]ᵢ) (Goldberg equation)
Represent the extracellular and intracellular concentrations of ions, respectively.