ID E2: study guide
1/201
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
202 Terms
What are the ssx of dehydration?
dry/sticky mouth, lethargy, sunken eyes, wt loss, low urine output, dark urine, poor skin turgor, delayed cap refill, dizziness, confusion, lack of tears, falls, low BP, dec JVP
What are lab findings of dehydration?
Inc BUN/Cr (w/ ratio inc), low urine Na+
What are ssx of viral gastroenteritis?
SI, watery, vomiting, +/- abd pain, anorexia, systemic sx; NO tenesmus
What are ssx of bacterial gastroenteritis?
Colon, bloody, mucoid, abd pain, tenesmus, anorexia, systemic sx +/- V
When is testing warranted for diarrhea?
Severe illness: profuse water w/ hypovolemia, > 6 stools/day, severe pain, need for hospitalization
Bloody diarrhea
Immunocompromised, age > 70, IBD, pregnancy
Sx > 1 week
What is the primary goal of tx for diarrhea?
fluid/electrolyte replacement
*abx if bloody/mucoid, immunocompromised, age >70, comorbidities
*Antimotility, use w/ caution -effective but can prolong course (Lopermaide if no fever, no bloody stools)
Why should prescribing antimotility agents be limited or avoided in tx of gastroenteritis?
can prolong the course of illness
What are non-specific tx for acute viral diarrhea?
starchy diet, Pepto (avoid in kids d/t Reyes), probiotics, antimotility
What is the tx for viral gastroenteritis?
prevention is key, avoid food/water that may be contaminated; frequent hand-washing
Which gastroenteritis virus is the MC in the US?
Norovirus
Which gastroenteritis virus causes the highest mortality in children and has a vaccine available to limit disease?
Rotavirus
What are the MC viral organisms that cause gastroenteritis?
Adenovirus, Calicivirus, Norovirus, Rotavirus, CMV
How does non-inflammatory diarrhea present?
non-invasive toxin mediated diarrhea, afebrile, non-bloody, mild abd pain, no WBC’s in stool
How does inflammatory diarrhea present?
bacteria invade mucosa, bloody diarrhea, febrile, RBC & WBCs in stool, systemic sx, severe abd pain
*do NOT give anti-diarrheal agents
How does food poisoning d/t preformed toxins present?
short incubation period
*S. aureus, B. cereus
What foods are they typically associated with S. aureus food poisoning?
*preformed toxins
prepared food, eggs, salads, dairy, meat (ham, poultry), cream filled pastries
What foods are they typically associated with B. cereus food poisoning?
*preformed toxins
rice, meat (warm fried rice, mac n cheese)
How does food poisoning caused by food contaminated with an organism that produces a toxin after consumption present?
long incubation period
*C. perfringes, B. cereus
What foods are they typically associated with B. cereus food poisoning?
*post-consumption toxin
meat, vegetables, sauces, raw meat, milk products
What foods are they typically associated with C. perfringes food poisoning?
*post-consumption toxin
meat, poultry, gravy, inadequately reaheated foo
What is the MC community acquired inflammatory enteritis?
Camp jejuni
What are the sources of a Camp jejuni infection?
chicken, travel to underdeveloped countries, well or surface water, exposure to an animal w/ diarrhea
How long is the camp jejuni incubation period?
3 days
What are the sx of Camp jejuni?
inc pain -”pseduoappendicitis” prior to start of diarrhea
prodromal fever, dizziness, delirium; 10+ watery bloody BM/day, bloody stool on 2nd/3rd day, N/V
When should abx be prescribed for Camp jejuni?
usually self-limiting; abx if severe or risk of severe sx
(bloody stool, high fever, worsening, relapsing, sx > 1 week)
What is the gold standard test for dx Camp jejuni?
culture
What is the 1st line abx for Camp jejuni (if needed)?
Azithromycin 500 mg x 3 days
What are possible complications of Camp jejuni?
reactive arthritis, GBS
What are the sources of infxn for Salmonellosis?
Food: eggs, poultry, raw tuna, fresh produce, meat, fish, milk, butter, spices
Pets: reptiles, amphibians (turtles), birds, pet foods
What type of diarrhea is associated w/ Salmonellosis?
non-bloody loose stool or watery diarrhea x 4-10 days
Which abx is used for adults w/ severe diarrhea d/t Salmonellosis?
Cipro or Levo
How do the endotoxins and exotoxins of Shigellosis affect the body?
invade villi of LI, toxins damage the mucosa & villi, leading to mucus secretion and bleeding
What type of diarrhea is associated w/ Shigellosis?
bloody mucoid diarrhea, initially may be water; 8-10 BM/day in small volume
What are the possible complications of severe Shigellosis infxn?
proctitis or rectal prolapse, toxic megacolon, intestinal obstruction, colonic perforation, systemic sx; HUS
What organism causes Typhoid fever?
Salmonella eneteria typhi (S. typhi)
What sx are associated w/ weeks 1-3 of Typhoid fever?
1st: nonspecific → rapid step-wise fever w/ chills & bacteremia, brady, pulse-temp dissociation
2nd: abd pain, faint salmon-colored macules on trunk/abd (‘rose spots), fade w/ pressure
3rd: hepatosplenomegaly, intestinal bleeding, perforation d/t ileocecal lymphatic hyperplasia, septic shock, altered LOC
What is the tx for Typhoid fever?
FQs (cipro and ofloxacin), 3rd gen cephs, Azithro
*vaccine available
Which variety of E. coli:
travelers -mild/severe watery diarrhea, onset of sx is rapid; 1-5 days
Enterotoxigenic E. coli (ETEC)
Which variety of E. coli:
childhood diarrhea -linked to failure to thrive & wasting from infantile diarrhea; malnutrition if persistent
Enteropathogenic E. coli (EPEC)
Which variety of E. coli:
similar to shigellosis -inflammatory disease, LI ulceration, may proceed to bloody diarrhea
Enteroinvasive E. coli (EIEC)
Which variety of E. coli:
can cause shiga toxin (STEC); causes HUS, bloody diarrhea; TRIAD -hemolytic anemia, thromobocytopenia, AKI
*do NOT give abx
Enterohemorrhagic E. coli (EHEC) 0157:H7
How does cholera present?
massive dehydration (death w/in hours; high mortality)
painless watery diarrhea; “rice-water” stool, watery stool w/ fleck of mucous & fishy odor; high volume, NO fever, hypovolemic shock
What are the most common sources of Listeria monocytogenes?
processed/delicate meats, hot dogs, soft cheeses, pates, fruit
What is the concern if a pregnant woman becomes infected w/ Listeria?
transplacental transmission -results in premature birth, abortion, stilbirth, intrauterine infection
*risk of granulomatosis infantispetica
What is the abx tx for Listeria?
Ampicillin or PCN G; typically in combo w/ aminoglycoside (gentamicin)
What organism causes Botulism?
clostridium botulinum
What are common sources of Botulism in infants cases?
environmental dust/soil, homemade baby food that is improperly canned, not usually from honey
What are common sources of Botulism in foodborne cases?
aged fish, marine animals, “moonshine” in prisons, home fermented tofu or other bean products
What is the tx for Botulism?
anti-toxin
How does Botulism present?
acute bilateral neuropathies, symmetric descending weakness; ptosis, blurred vision; 4 Ds - diplopia, dysphonia, dysarthria, dysphagia
infants: flaccid paralysis, diaphragmatic weakness
What are the RF for C. diff?
hospitalization, longer stay = greater chance
exposure to abx (inc w/ FQ, clindamycin, 3rd gen ceph, Ampicillin, Amoxicillin)
What increases host susceptibility to C. diff?
age >65, underlying illness, GI surgery, PPI or H2RA, tube feedings, obesity, chemo, stem cell transplant
What is the gold standard diagnostic test for C. diff?
EIA for toxins A & B
What medications are used to tx C. diff?
STOP all unnecessary abx, antimotility w/ caution
Vanc, Metronidazole, or Fidaxomicin
fulminant: Vanc and Metro
recurrent: add bezlotoxumab
How does active TB present?
productive cough >2/3 weeks, fever, wt loss, hemoptysis, CP, dyspnea, anorexia, fatigue, night sweat, LAD; may have extrapulmonary sx
How does latent TB present?
+ test but no active disease, only 1/10 go on to active
Tx: INH/B6 + Rifapentine 1 q week x 12 weeks
Non-infectious, do NOT require isolation
How does disseminated TB (miliary) present?
immunocopromised, failure to thrive, anorexia, fever of unknown origin, dysfunction of 1+ organ system, respiratory problems, GI, HA
*untreated 100% mortality
What are the RF associated w/ progression from latent to active TB?
evidence of old untx TB on CXR, HIV/AIDS, corticosteroid use, ESRD, DM, malignant lymphoma, diminution of cell mediated immunity associated w/ age, cigarette smoking
What is the sputum collection process in testing TB?
3 sputum specimens obtained via cough or induction at least 8 hrs apart and including 1 early-morning specimen
What is the gold standard test for TB?
mycobacterial culture of sputum
What is the diagnostic test required at the end of the intensive treatment phase of TB that determines the duration of the continuation phase?
sputum AFB smear and culture
How do you read a PPD test?
Size of induration is measured NOT erythema -read 2-3 days after placing test
What constitutes a + PPD test?
5 mm: HIV, close contact to person newly infected w/ TB, immunosuppressed, fibrotic lesions on CXR, children < 1
10 mm: recent immigrants, children 1-4, live in high risk facilities, IVDU, DM, ESRD, silicosis, malnutrition, microbacteria lab personnel
15 mm: considered + in anyone
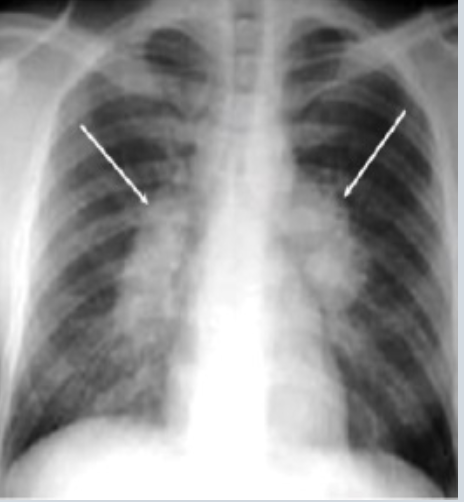
Which TB finding?
bilateral hilar adenopathy
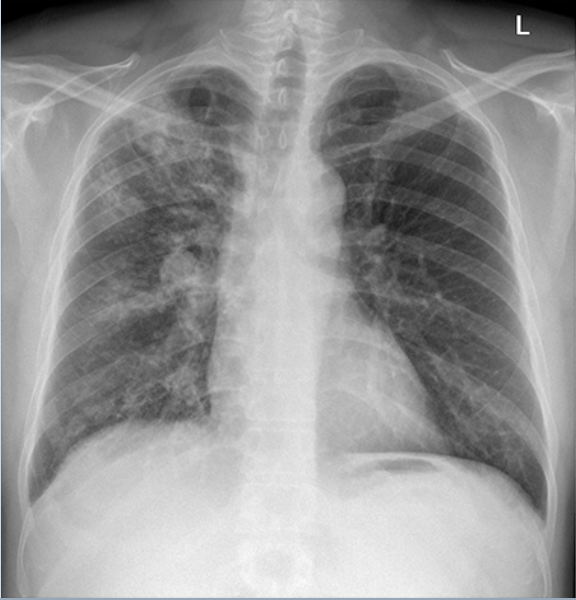
Which TB finding?
upper lobe consolidation
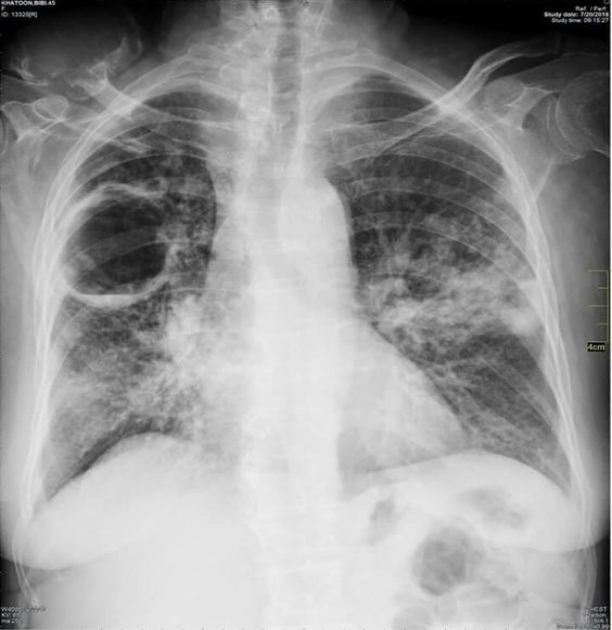
Which TB finding?
cavitating lesion of reactivated TB
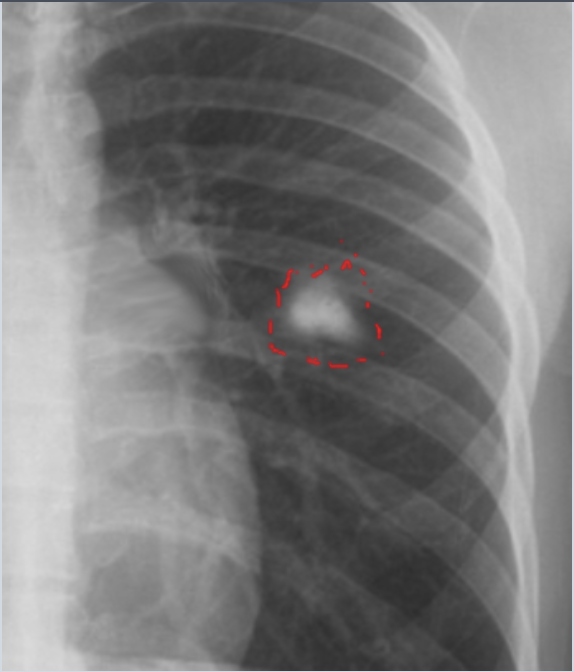
Which TB finding?
ghon lesion (calcified parenchymal granuloma from previous TB infxn)
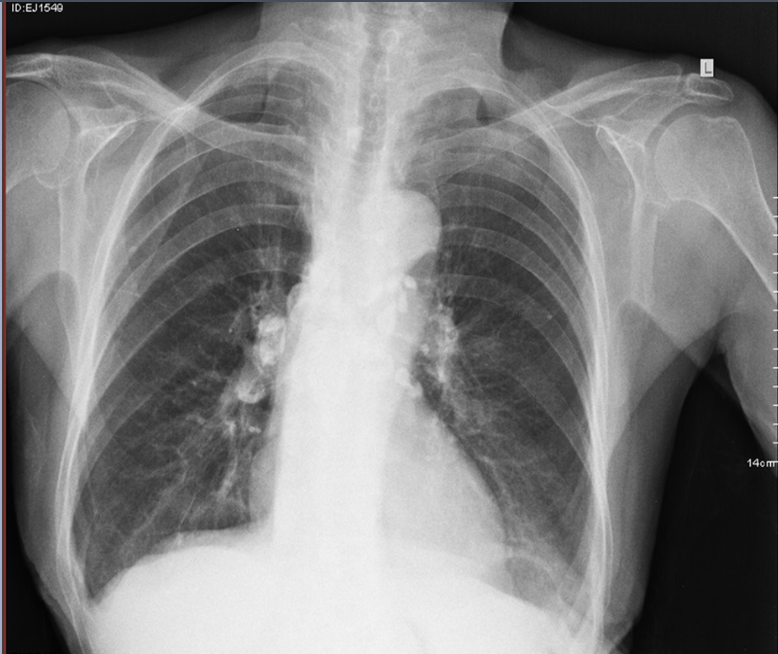
Which TB finding?
ranke complex (combo of late fibrocalcific lesion of lung and LN)
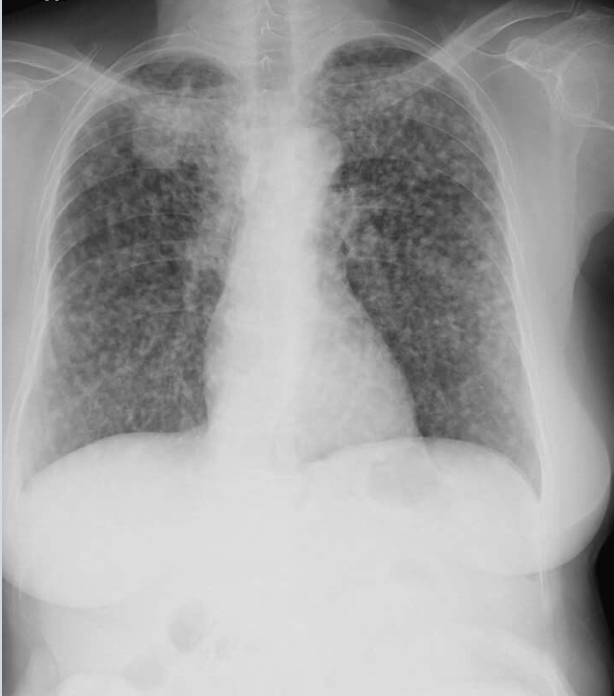
Which TB finding?
miliary TB -millet seed, disseminated
What is the tx of TB?
Step 1) Intensive: x 2months → Rifampin, Isoniazid/B6, Ethambutol, Pyrazinamide
Step 2) Continous: x 4months → Isoniazid/B6, Rifampin
-Isolation, direct observation, self-administration
What is the causative organism of Leprosy?
Mycobacterium leprae
What are the animal reservoirs of Leprosy?
nine-banded armadillos, chimpanzees, sooty mangabey monkeys, cynomolgus macaque
What country has the highest rate of Leprosy cases?
India
What are ssx of Leprosy?
Leprmatous: erythematous macules, papules, nodules
Loaded w/ acid fast bacillus, generalized nerve damage, body hair loss, nodular thickening of ear lobes, nasal stuffiness, saddle nose, can develop in organs
Skin lesions = primary external sign
What environment is Blastomycosis found in?
SE & SC states bordering Mississippi and Ohio river basin, Midwest bordering great lakes, small part of NY
-forests, decaying wood, animal manure, along streams/rivers
What are sx of Blastomycosis?
Pneumonia 91% of cases, verrucous lesions w/ irregular borders, micro abscess, subcutaneous nodules
What are the MC types of disseminated Blastomycosis?
osteoarticular (vertebrae, sacrum, pelvis), GU, CNS
Which abx is used to tx pulm disease d/t Blastomycosis?
Itraconazole
*CNS involvement→ add Amphotericin B
What environment is Coccidioidomycosis found in?
SW US -southern/central valleys of Cali, southern AZ, NM, TX, Utah, San Joaquin valley “Valley fever'“
*farming, archeological digs, landslides, dust storms
What extrapulmonary manifestations are associated w/ Coccidioidomycosis?
erythema multiforme, erythema nodosa
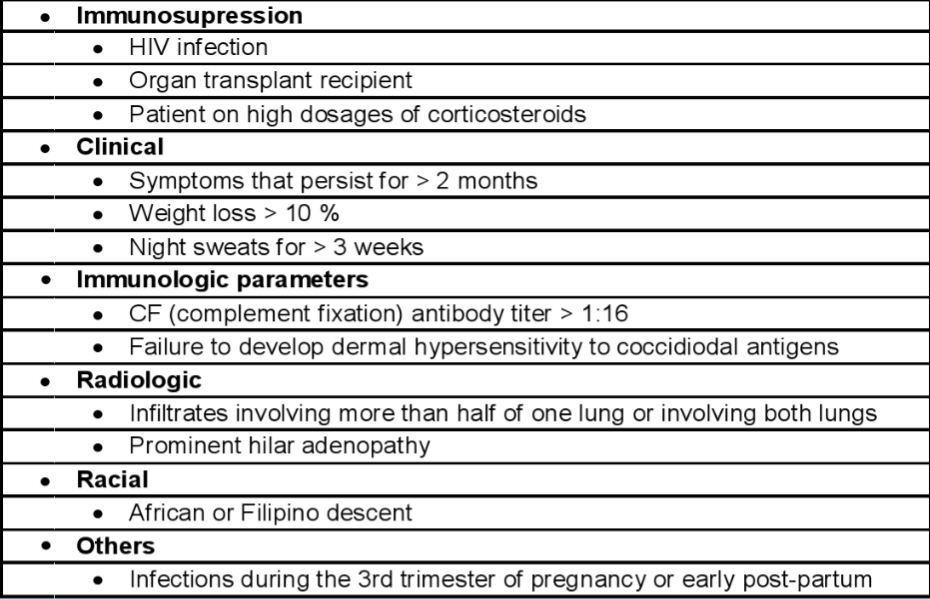
Who gets tx for Coccidioidomycosis?
based on several factors: immunosuppressed, clinical, racial, immunological, others (see table)
What environment is Histoplasmosis found in?
World-wide, Midwestern and central states along the Ohio and Mississippi River valleys “Ohio valley fever”, (Darling’s disease), soil w/ high nitrogen content
*excavation, construction, demolition, exploring caves, campsites, anything that disturbs pores
What sx are associated w/ acute pulmonary Histoplasmosis?
95% mild, flu-like; hilar or mediastinal LAD w/ focal infiltrates that are patchy or nodular on CXR
How does Histoplasmosis appear on sputum smears?
“fisheye” yeasts in macrophages
What is the MC source of Cryptococcosis?
pigeon droppings
What are ssx of Cryptococcosis?
Meningitis- fatal w/o therapy, MC: fever, malaise, HA
*AMS, confusion, stiff neck, photophobia, vomiting, personality changes
How the cutaneous lesions associated w/ disseminated Cryptococcosis appear?
papules, plaques, purpura, ulcers, cellulitis, superficial plaques, abscesses, sinus tracts; late gelatinous exudate
What is the diagnostic sign in CSF of Cryptococcosis?
cryptococcal antigen (CrAg)
What is the recommended tx for Cryptococcosis?
Mild/mod: Fluconazole
CNS/severe: Induction: Amphotericin B + Flucytosine; Consolidation: fluconazole
What are the superficial infections caused by Candidiasis?
thrush, vaginitis, onychomycosis
What individuals are most likely to develop thrush?
neonates/infants (inc if breastfeeding), DM on abx, immunosuppressed, not properly using inhaled steroids, HIV (especially if young), esophageal disease
What individuals are most likely to develop vaginal candidiasis?
sexually active, pregnant, diabetic, follows use of abx
What individuals are most likely to develop systemic Candidiasis?
Immunosuppression, disruption of skin/mucous membranes, indwelling devices, surgery, abx therapy, TPN, hematologic malignancy, DM
What part of the body is affected by Tinea corporis?
body surface
What part of the body is affected by Tinea pedis?
foot
What part of the body is affected by Tinea cruris?
groin
What part of the body is affected by Tinea capitis?
scalp hair
What part of the body is affected by Tinea unguium?
nail
What part of the body is affected by Tinea manuum?
hands
What part of the body is affected by Tinea facieie?
face