Molecular Polarity and Intermolecular Forces
5.0(1)
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/11
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
12 Terms
1
New cards
electronegativity
The ability of an atom to attract shared electrons within a bond.
2
New cards
nonpolar covalent bonding
Electrons are shared equally (ΔEN = ≤0.4).
3
New cards
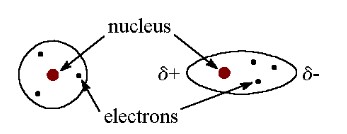
polar covalent bonding
Electrons are shared unequally (0.4 < ΔEN < 1.7).

4
New cards
ionic bonding
Electrons are being transferred (ΔEN ≥ 1.7).
5
New cards
bond polarity
The difference of electronegativity between electrons being bonded.
6
New cards
molecular polarity
Determined by the 3-D shape of the molecule; to be polar, a molecule must have a definite negative and positive end.
7
New cards
intramolecular forces
Forces __**within**__ a compound or molecule between the atoms in it.
\
* Ionic bonds, metallic bonds, nonpolar covalent bonds, polar covalent bonds
\
* Ionic bonds, metallic bonds, nonpolar covalent bonds, polar covalent bonds
8
New cards
intermolecular forces
Forces __**between molecules**__; can only exist between __**identical**__ molecules.
\
Responsible for the observed __**physical properties**__ of molecular compounds, such as boiling point, melting point, and electrical conductivity.
\
Determined by __**molecular shape**__ and __**molecular polarity**__.
\
Responsible for the observed __**physical properties**__ of molecular compounds, such as boiling point, melting point, and electrical conductivity.
\
Determined by __**molecular shape**__ and __**molecular polarity**__.
9
New cards
London Dispersion Forces
* Attraction between **temporary dipoles**
* Exists in __**all molecules**__ both polar and non-polar
* Caused by the electrons of one molecule being **attracted** to the nucleus of another molecule; forming __**temporary (instantaneous) induced dipoles**__.
* The **more** electrons a molecule has (from larger atoms / bigger atoms), the __**stronger**__ its London forces because there is a __more prominent temporary dipole__. This is called **polarizability** (**more distortable**).
* Exists in __**all molecules**__ both polar and non-polar
* Caused by the electrons of one molecule being **attracted** to the nucleus of another molecule; forming __**temporary (instantaneous) induced dipoles**__.
* The **more** electrons a molecule has (from larger atoms / bigger atoms), the __**stronger**__ its London forces because there is a __more prominent temporary dipole__. This is called **polarizability** (**more distortable**).
10
New cards
polarizability
The more electrons a molecule has (from larger atoms / bigger atoms), the __**stronger**__ its London forces because there is a __more prominent temporary dipole__ (more distortable)
11
New cards
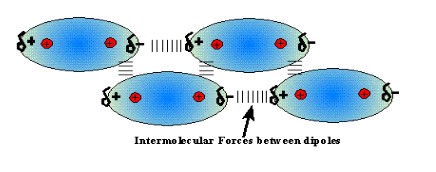
Dipole-Dipole Forces
* Attraction between **permanent dipoles**
* Occurs in __**all**__ **polar** molecules
* Caused by the attraction of the **partial positive** end (δ+) of __one__ molecule to the **partial negative** end (δ-) of __another__ molecule, and vice-versa
* Occurs in __**all**__ **polar** molecules
* Caused by the attraction of the **partial positive** end (δ+) of __one__ molecule to the **partial negative** end (δ-) of __another__ molecule, and vice-versa
12
New cards
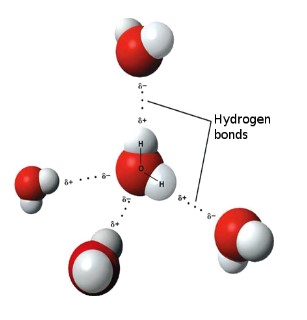
Hydrogen Bonding
* Attraction between **permanent dipoles: F-H, O-H, N-H** (FON)
* __**Special**__ type of __dipole-dipole__ force that is very strong
* Caused by the **attraction** of hydrogen atoms __**bonded**__ to __F, O, N__ (high EN) in __**one**__ molecule to the **lone pair** of electrons on the __F, O, N__ atom of __another__ molecule
* __**Special**__ type of __dipole-dipole__ force that is very strong
* Caused by the **attraction** of hydrogen atoms __**bonded**__ to __F, O, N__ (high EN) in __**one**__ molecule to the **lone pair** of electrons on the __F, O, N__ atom of __another__ molecule