BCH Exam 3 - Light reactions and the calvin cycle
1/30
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
31 Terms
Light reactions
Form ATP and NADH from photons
Dark reaction/calvin cycle
Use ATP and NADH from light reactions to turn CO2 into carbs
Where are sugars synthesized?
In the stroma
Where do the light reactions take place?
Thylakoid membranes
Chlorophyll
A pigment that acts as a photoreceptor and is made up of a tetrapyrole with a phytol, a long 20 carbon chain alcohol
How do light harvesting complexes work?
They funnel light/photons using antenna complexes to the reaction center, increasing photosynthetic efficiency
Why should you not eat green potatoes?
They produce chlorophyll and solanine, which inhibits acetylcholinesterase which controls nerve firing
How does photosystem I work?
Electrons from P700 reaction center flow to ferredoxin, which then gives its electrons to NADP+ with the help of ferredoxin-NADP+ reductase, resulting in production of NADPH
How does photosystem II work?
P680 transfers electrons from water to PSI using an ETC
PSI and PSII reaction center names
PSI - P700
PSII -P680
Cytochrome b6f
Generates a proton gradient and provides electrons to PI by pumping protons into the lumen from stroma, connecting PII to PI
Where does cytochrome b6f pump protons?
Into lumen from stroma
What is responsible for the extraction of electrons from water and the generation of oxygen in the light reactions?
P680 of photosystem II
How is ATP synthesized in photosynthesis?
Flow of electrons from water to NADP+ makes a proton gradient that drives the synthesis of ATP
Where are carbohydrates synthesized in photosynthesis?
In the stroma
Which herbicides inhibit photosystem II? Which herbicide inhibits photosystem I?
PSII - Diuron and atrazine, PSI -Paraquat
Stage 1 of Calvin Cycle
Fixation of CO2 by ribulose 1,5-bisphosphate to form 2 molecules of 3-phosphoglycerate+
Stage 2 of the calvin cycle
Reduction of 3-[phosphoglycerate to hexose sugar
Calvin cycle stage 3
Regeneration of ribulose 1,5-bisphosphate (molecule that fixes carbon dioxide)
Which molecule fixes carbon dioxide?
ribulose 1,5-bisphosphate
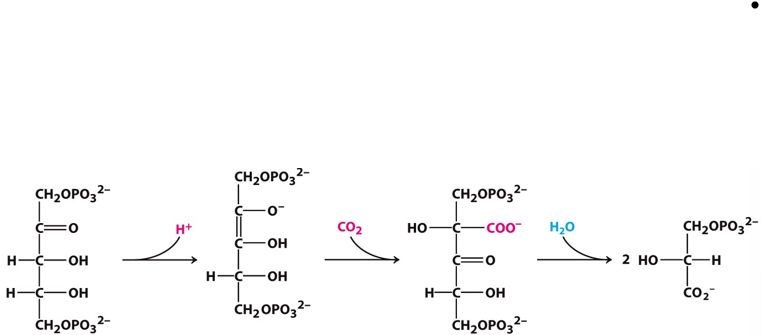
What step of the calvin cycle is this? Label each molecule (endiolate intermediate/3-phosphoglycerate/ribulose 1,5-bisphosphate/unstable intermediate)
Stage 1 (Ribulose 1,5- bisphosphate to 3-phosphoglycerate step)
1,5 Ribulose bisphosphate
Endiolate intermediate
Unstable intermediate
3-phosphoglycerate
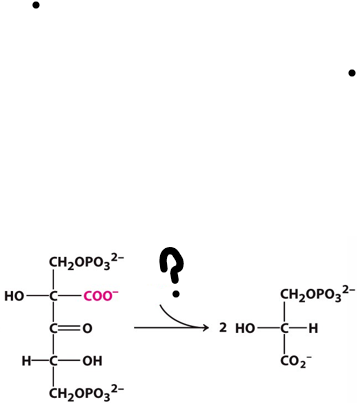
What molecules is needed to complete the reaction?
H2O
Which stage and specific steps of the Calvin cycle uses ATP and NADH from the light reactions?
Stage 2
3 phosphoglycerate to 1,3 bisphosphoglycerate uses 2 ATP
1,3-bisphosphoglycerate to G3P uses 2 NADPH
What is the conversion of 3-phosphoglycerate to hexose in the calvin cycle most similar to?
Gluconeogenesis
What 3 sugars make up the hexose monophosphate pool?
Glucose 1-phosphate, glucose 6-phosphate, and fructose 6-phosphate
How is ribulose 1,5-bisphosphate regenerated?
Fructose 6-phosphate, 2 G3P, 3ATP, and dihydroxyacetone phosphate are all used to make 3 ribulose 1,5-bisphosphate
How many ATP and NADPH’s are needed to incorporate a CO2 to a hexose?
3ATP and 2NADPH
What are the two major carbohydrate stores in plants and what are they used for?
Starch - branched long term storage of glucose
Sucrose - transport form of carbohydrates, such as sap which is 65% sucrose as well as some glucose and fructose
How is the calvin cycle regulated?
Thioredoxin and reduced ferredoxin and NADPH from photosystem II regulates many enzymes throughout the calvin cycle
How does ferredoxin-thioredoxin reductase affect calvin cycle enzymes?
Activates some enzymes by reducing disulfide bonds
What is the fate of G3P in the calvin cycle?
One leaves the cycle to be used to make glucose, 5 go into regenerating ribulose bisphosphate