Shapes of molecules
1/33
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
34 Terms
when drawing dot cross diagrams, which elements must have 8 in their outer shell
C, N, O, F
the other can have more or less
when drawing a dot cross diagram of a charged molecule, how do you go about it
alter the central atom in the diagram in relation to charge, then carry on as normal
e.g. CO32-
draw carbon atom to have 6 electrons in outer shell (2- charge) rather than regular 4 in outer shell
then draw as normal
define a metallic bond
strong electrostatic force of attraction between positive metal ions and negative delocalised electrons
what are van den waal forces and how do they occur
present between all molecules
electrons are constantly moving, therefore uneven electron distribution
causes a temporary dipole within a molecule which induces a dipole in neighbouring molecule
δ+ side of one molecule attracts δ- side of other molecule
how is a dative bond formed between X and Y
lone pair / both electrons on X is donated to Y
when drawing a diagram to show hydrogen bonding between 2 molecules, what are the key marking points
e.g. ammonia
lone pair on each N
partial charges on each molecule / atom
H bond from lone pair on N to Hδ+ on other NH3 molecule
what increases the strength of van den waals and why
the bigger the molecule, the stronger the VDW forces
more electrons
list the three types of forces between molecules in order from weakest to strongest
van der waals
permanent dipole dipole attraction
hydrogen bonding
when does permanent dipole dipole attraction occur
between polar molecules
why might a molecule have polar bonds but not permanent dipole dipole attraction
e.g. CCL4
tetrahedral symmetrical structure
polar bonds cancel out
therefore molecule is not polar
so no permanent dipole dipole attraction between molecules
when can hydrogen bonding occur
when H atom is bonded to F, O, or N
what is hydrogen bonding
strong attraction from lone pair of electrons on N/O/F of one molecule to the exposed H nucleus of another molecule
why is a Cl2 molecule non polar
both Cl atoms have the same electronegativity so the bonding electron are shared equally between the two atoms
do lone pairs of electrons repel more or less than bonding pairs
more
what is the shape and bond angle in a molecule with:
2 electron pairs
2 bonding pairs
0 lone pairs
linear
180 degrees
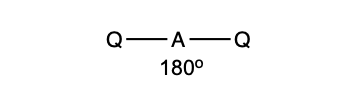
what is the shape and bond angle in a molecule with:
3 electron pairs in total
3 bonding pairs
0 lone pairs
trigonal planar
120 degrees
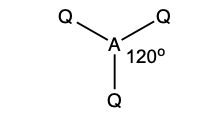
what is the shape and bond angle in a molecule with:
3 electron pairs in total
2 bonding pairs
1 lone pair
bent V shape
118 degrees
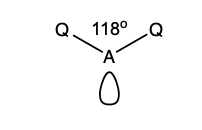
what is the shape and bond angle in a molecule with:
4 electron pairs in total
4 bonding pairs
0 lone pairs
tetrahedral
109.5 degrees
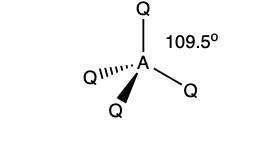
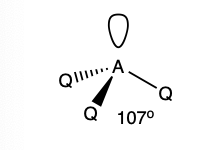
what is the shape and bond angle in a molecule with:
4 electron pairs in total
3 bonding pairs
1 lone pair
trigonal pyramidal
107 degrees
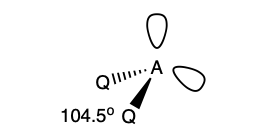
what is the shape and bond angle in a molecule with:
4 electron pairs in total
2 bonding pairs
2 lone pairs
bent v shape
104.5 degrees
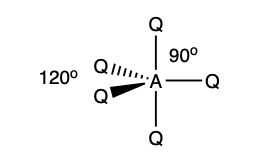
what is the shape and bond angles in a molecule with:
5 electron pairs in total
5 bonding pairs
0 lone pairs
trigonal bipyramidal
90 degrees
120 degrees
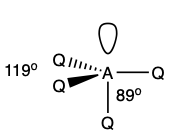
what is the shape and bond angles in a molecule with:
5 electron pairs in total
4 bonding pairs
1 lone pair
trigonal pyramidal
119 degrees
89 degrees
what is the shape and bond angle in a molecule with:
5 electron pairs in total
3 bonding pairs
2 lone pairs
trigonal planar or T shape
120 degrees or 89 degrees
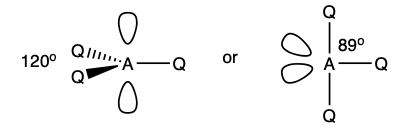
what is the shape and bond angle in a molecule with:
6 electron pairs in total
6 bonding pairs
0 lone pairs
octahedral
90 degrees
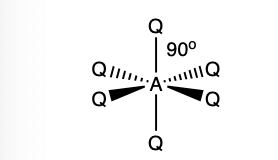
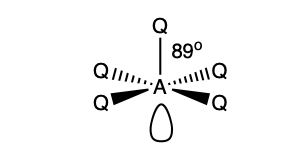
what is the shape and bond angle in a molecule with:
6 electron pairs in total
5 bonding pairs
1 lone pair
square pyramid
89 degrees
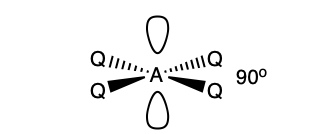
what is the shape and bond angle in a molecule with:
6 electron pairs in total
4 bonding pairs
2 lone pairs
square planar
90 degrees
define electronegativity
power of an atom to attract the pair of electrons in a covalent bond towards itself
what is the most electronegative element in the periodic table
what does this mean?
fluorine
best at attracting electron density towards itself when covalently bonded to another atom
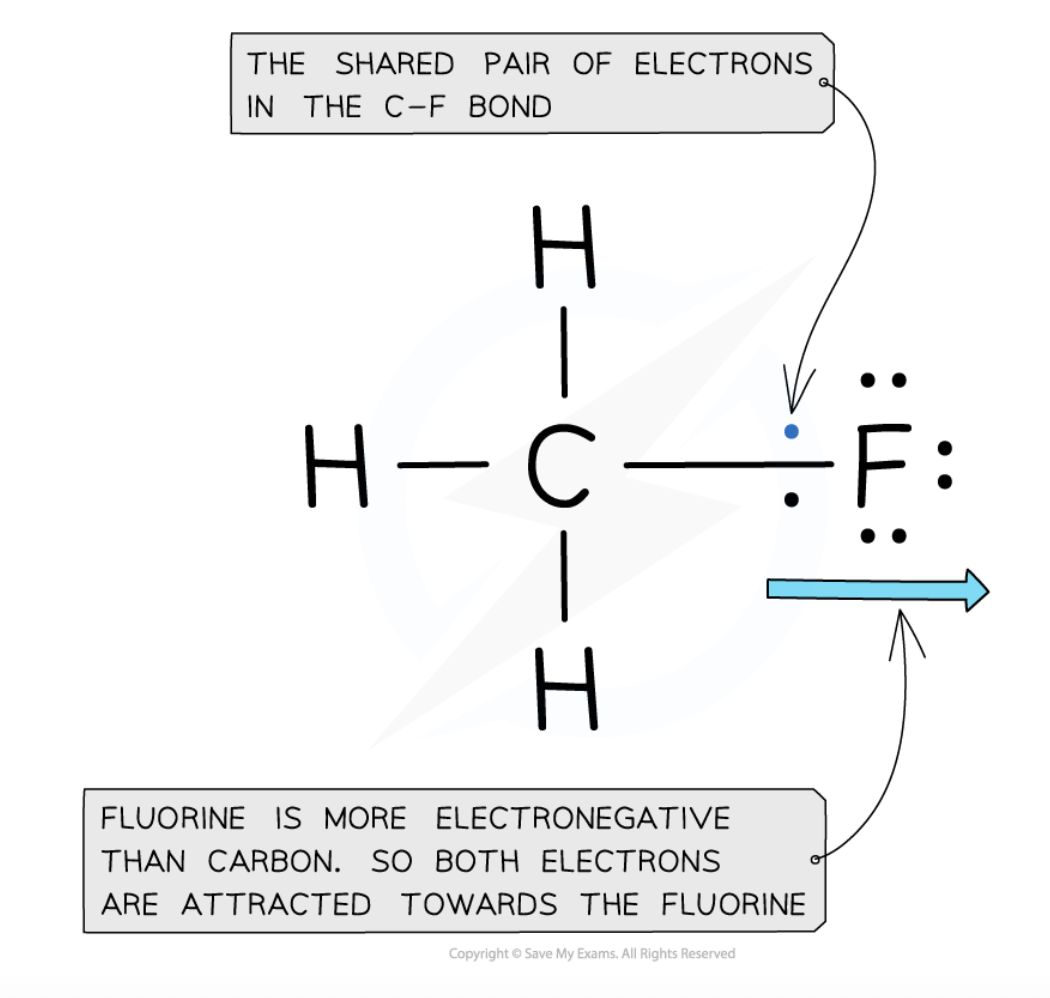
how do changes in nuclear charge affect electronegativity
increased nuclear charge = increased electronegativity
Attraction between positively charged protons in nucleus and negatively charged electrons in energy levels of atom
increase in number of protons→ increase in nuclear attraction for electrons in the outer shells