IB Biology - U1L2 - Cell Types & Organelles
1/28
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
29 Terms
Cell building blocks.
Atoms are smallest units of elements
Molecules are made from atoms
Molecules combine to form organelles
A cell is made of organelles
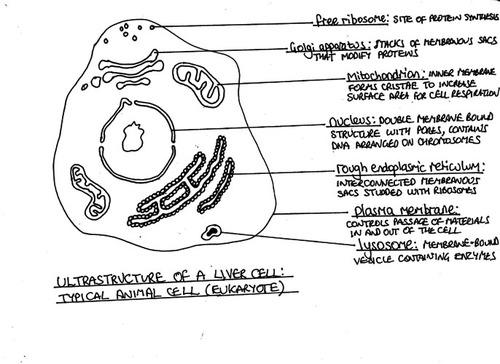
Cell Organelles.
Nucleus
Mitochondria
Endoplasmic Reticulum
Golgi Complex
Vesicles
Chloroplasts
Centrosome
Nucleus
Cellular control center that contains DNA.
Nucleolus
In the nucleus, the nucleolus is responsible for ribosome assembly.
Mitochondria
Cell power house: organelles for energy production (ATP synthesis).
Endoplasmic Reticulum.
Membrane network for protein production/synthesis.
Golgi Complex.
Modifies and packages proteins for transport.
Vesicles.
Small membrane sacs for transporting molecules.
Peroxisomes.
Cellular clean-up crew, break down fatty acids and detoxify harmful substances
Lysosomes.
Membrane-bound organelles containing digestive enzymes.
Vacuoles.
Membrane-bound sacs for storage, digestion, and maintaining cell turgor.
Chloroplasts (plants).
Organelles for photosynthesis. Green energy factories in plant cells.
Centrosome (animals).
Microtubule-organizing center in animal cells.
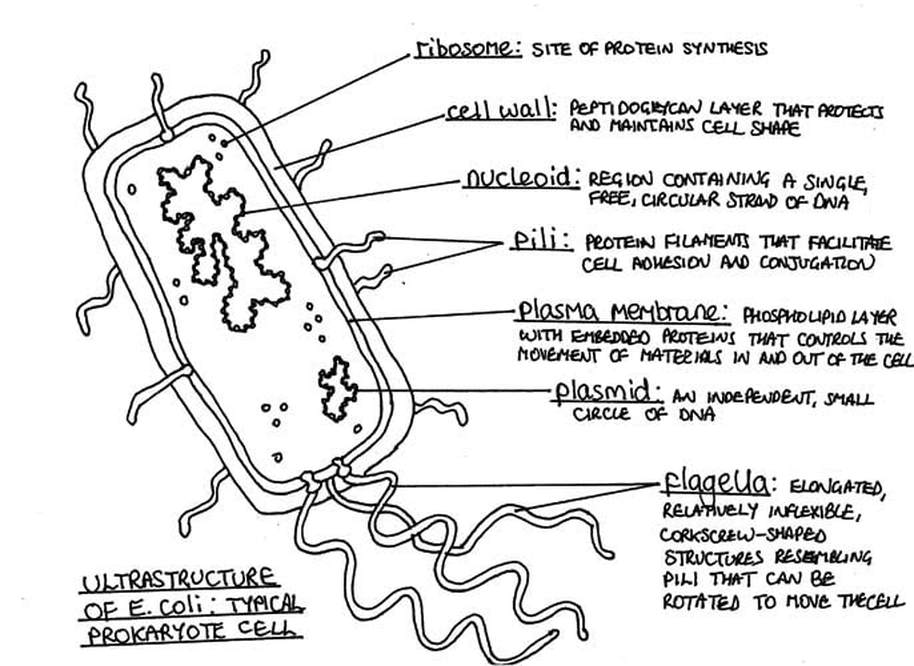
Prokaryote Cell.
Lack membrane-bound organelles, no compartmentalization
Single-celled, small ribosomes (70S)
Single DNA strand in nucleoid region, no nucleus
May have exchangeable plasmids via conjugation
Possess cell wall, potential slime capsule (glycocalyx)
Feature hair-like pilli for adhesion or plasmid exchange
Utilize whip-like flagella for movement
Examples: Bacteria, Archaea
Types of Prokaryotic Cells.
*****ASK AVNEET*****
Eukaryote Cells.
Eukaryotic cells are complex, with membrane-bound organelles, larger size, and evolved from prokaryotes through endosymbiosis. They store DNA in a double-membrane nucleus and are found in protists, fungi, animals, and plants.
Types of Eukaryotic Cells.
*****ASK AVNEET*****
Prokaryotes differ from Eukaryotes in that Dna is . . .
naked, circular with no introns
Prokaryotes differ from Eukaryotes in that Organelles are. . .
No nucleus, no compartements, 70S Ribosomes
Prokaryotes differ from Eukaryotes in that reproduction is. . .
Asexual only (binary fission-splits in two) and cells are haploid.
Prokaryotes differ from Eukaryotes in that average size is. . .
Smaller (>10μm) as they are Unicellular organisms
Eukaryotes differ from Prokaryotes in that DNA is. . .
is linear, has histones and Has introns
Eukaryotes differ from Prokaryotes in that Organelles are. . .
Has nucleus, Has compartments and 80S Ribosomes
Eukaryotes differ from Prokaryotes in that Reproduction is. . .
Asexual or sexual making the cells Haploid or diploid
Eukaryotes differ from Prokaryotes in that average size is. . .
Larger (~100μm) and they are Often multicellular
Advantages of Separation of Nucleus
allows eukaryotes to separate processes of transcription (nucleus) and translation (cytoplasm)
Allows for post-transcriptional modification of mRNA before it is translated by ribosomes.
improves efficiency of protein synthesis and allows for tight control of gene expression.
Advantage of Separation of Cytoplasm
membrane bound organelles allows for an internal chemistry that is different to cytoplasm (and suitable to its specific functions)
Allows for concentration of key enzymes and metabolites needed to optimise function of organelle and not digest contents of cell
improves efficiency of protein synthesis and allows for tighter control of gene expression
Memorise Drawings of ultrastructure of E.Coli
Memorise Drawings of ultrastructure of liver cell