Exercise Physiology Exam 2 (KIN 4100)
1/51
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
52 Terms
Lactate threshold
Point at which blood lactate accumulation increases markedly
blood lactate accumulates significantly,% of V02 max
Anaerobic Energy Expenditure
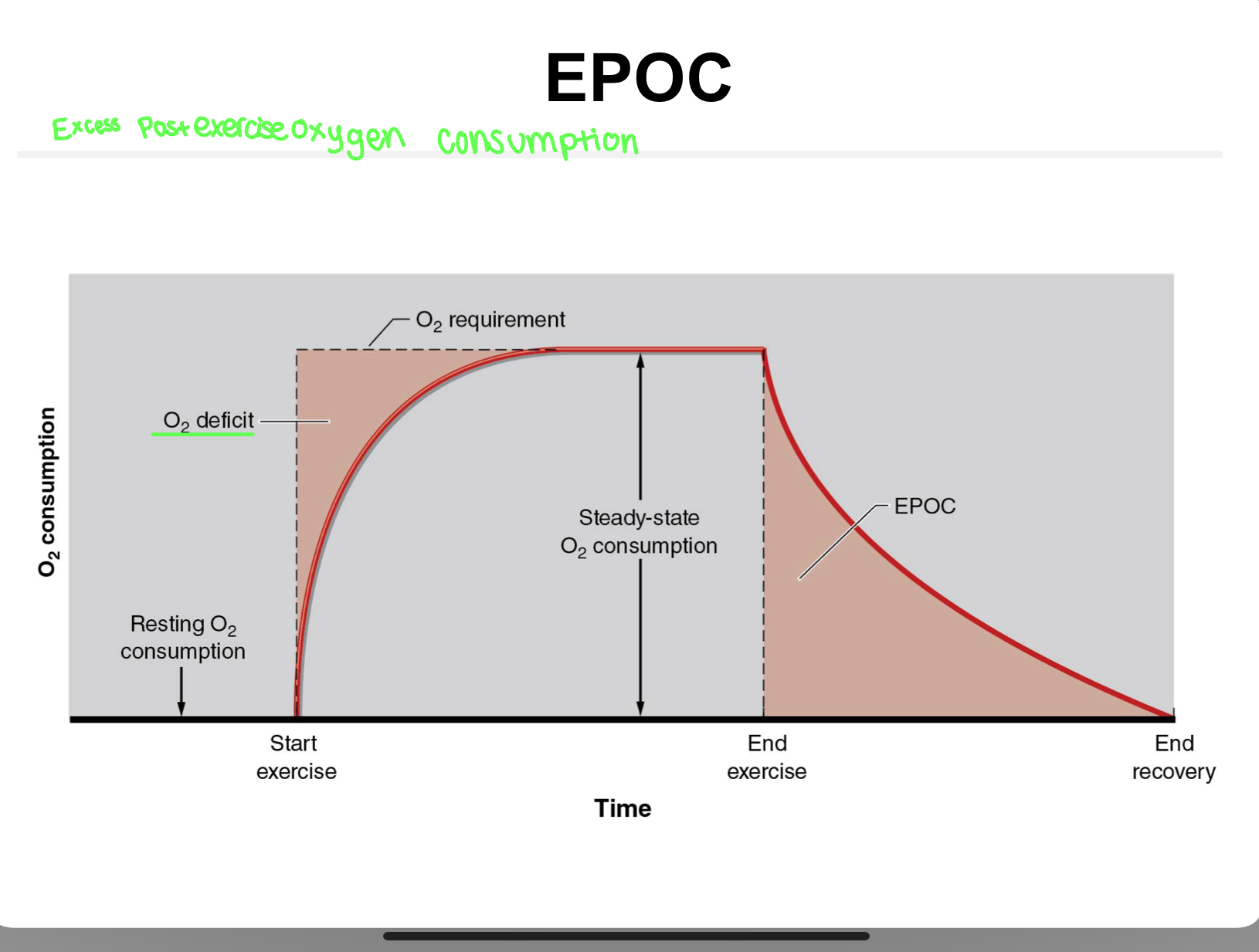
O2 demand > O2 consumed in early exercise
body enters O2 deficit
occurs when anaerobic pathways are used for ATP production
Post exercise O2 consumption
O2 consumed > O2 demand in early demand
excess post exercise O2 consumption (EPOC)
replenishes ATP/PCr stores, converts lactate to glycogen, clears CO2, replenishes hemo/myoglobin, clears CO2
VO2 max
point at which O2 consumption no longer increases (hit Vo2 max)
single best predictor of aerobic fitness
training allows athletes to compete at higher levels of VO2 max
Absolute: L/min
Relative: mL/kg/min
EPOC
Excess Postexercise Oxygen Consumption
replenishes ATP/PCr stores, converts lactate to glycogen, clears CO2, replenishes hemo/myoglobin, clears CO2
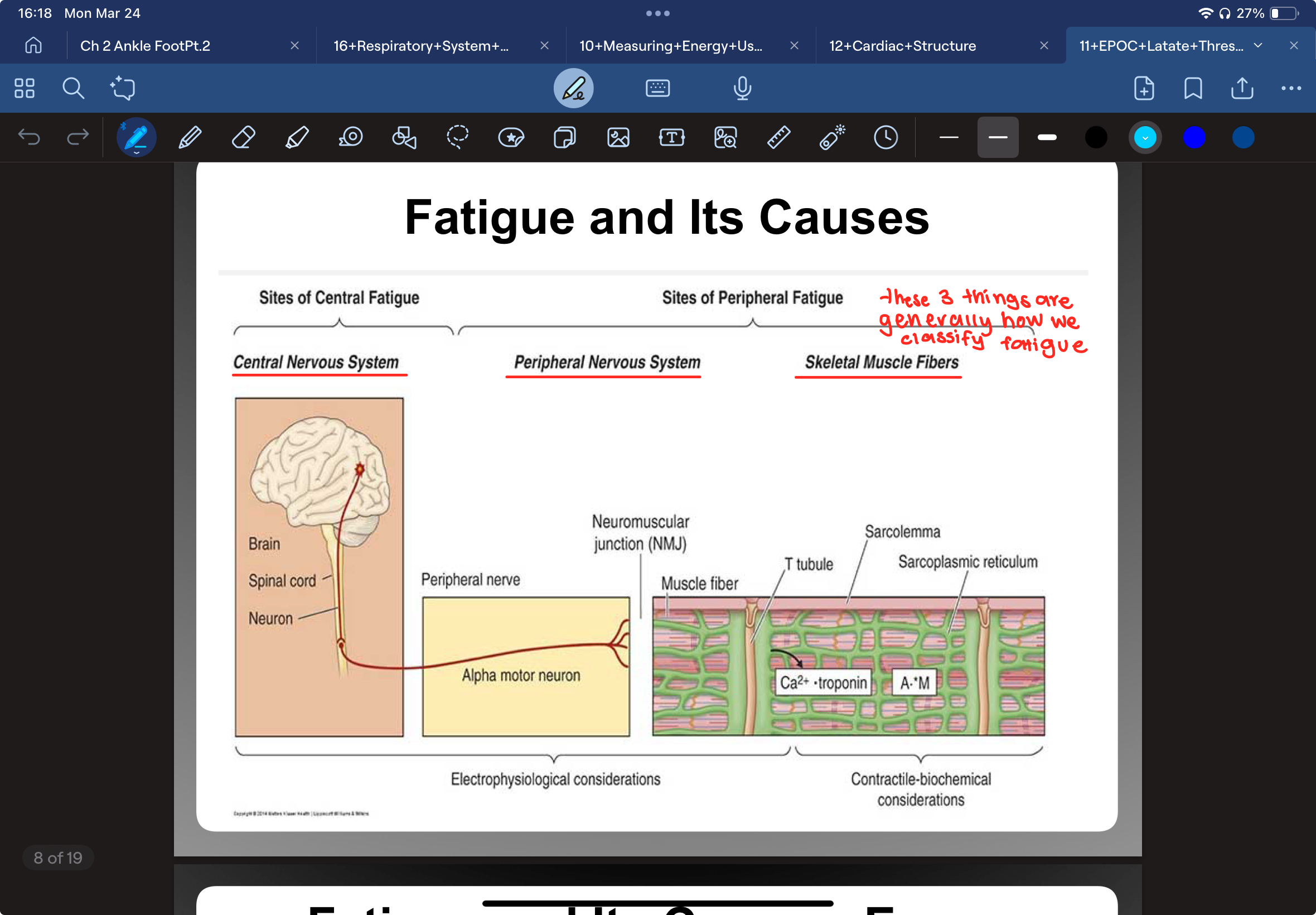
What are the 2 definitions of fatigue
decrements in muscular performance with continued effort, accompanied by sensations of tiredness
inability to maintain required power output to continue muscular work at given intensity
What is fatigue reversible by
Rest
What are the sites of central fatigue
Central Nervous System (CNS)
brain
spinal cord
neuron
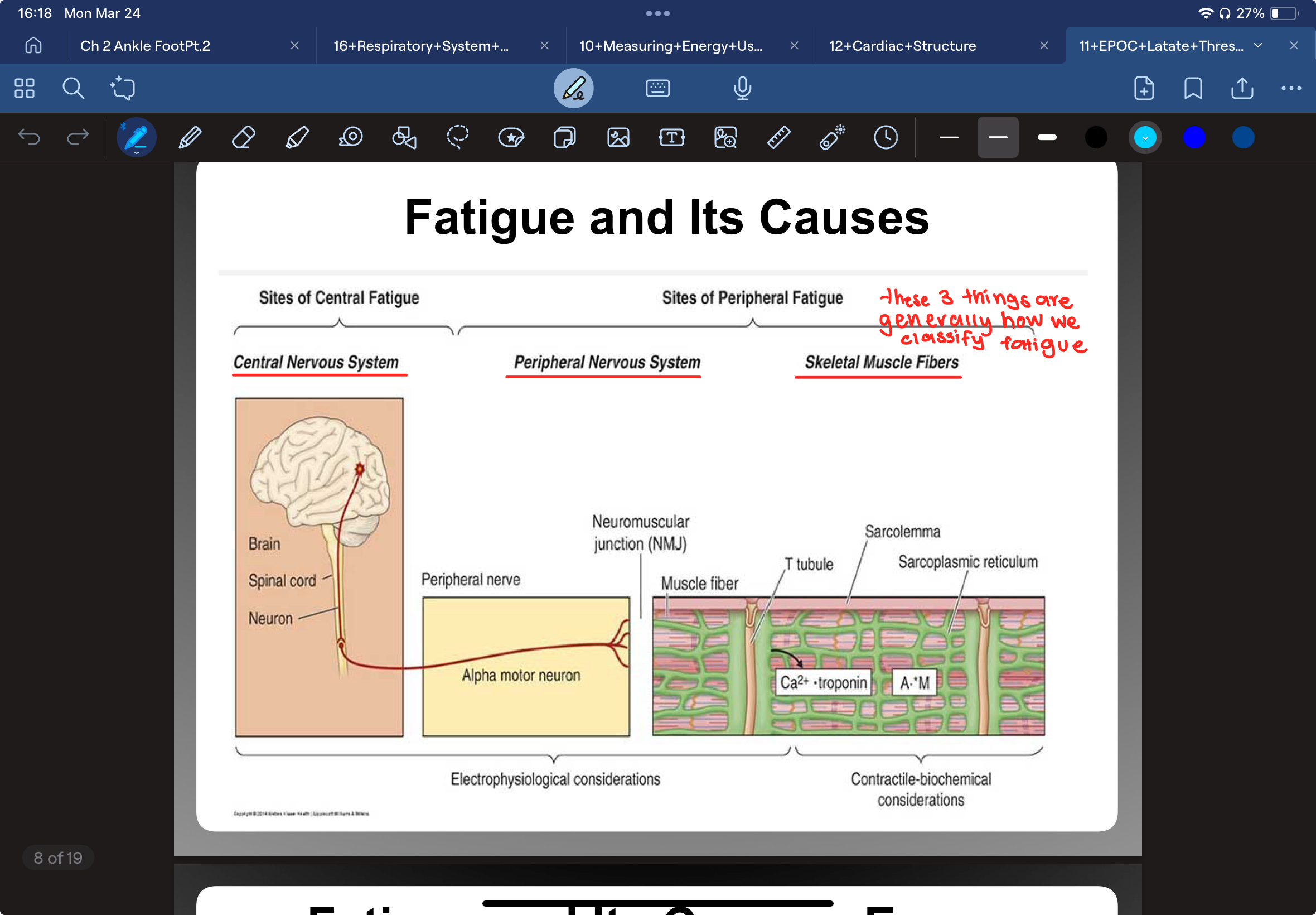
What are the sites of peripheral fatigue
Peripheral Nervous System
Skeletal Muscle Fibers
What are some of the causes of Fatigue (energy systems and glycogen depletion)
glycogen reserves: limited and get depleted quickly
deleted more quickly with high intensity exercise or first few minutes of exercise*
Depletion is correlated with fatigue
related to total glycogen depletion but unrelated to rate of glycogen depletion
Fiber type and recruitment patterns
fibers recruited first get depleted faster
type I fibers get depleted after mod endurance exercise
Recruitment dependent on exercise intensity (muscle fibers)
Type I: recruited first (light/mod intensity)
Type IIa: recruited next (mod/high intensity)
Type IIx: recruited last (max intensity)
Functions of the Cardiovascular System
deliver blood and nutrients, remover CO2 and waste
Transport hormones and aid in immune function
help maintain temperature, fluid, and acid-base homeostasis
Pulmonary Circulation (right heart)
Superior/Inferior vena cava → RA→ tricuspid valve → RV→pulmonary valve→pulmonary arteries → lungs
Systemic Circulation (left heart)
lungs → pulmonary veins → LA → mitral valve (bicuspid valve) → LV → aortic valve → aorta
What is the spontaneous rhythmicity of the heart?
100 bpm
SA node
pacemaker cells
cause contraction in RA and LA
AV node
found in the RA wall near heart center
delays signal so atria can contract before ventricles
relays to bundles after delay
AV bundle (bundle of his)
sends signal down to apex of heart
divides into left and right branches
Purkinje fibers
Stimulate ventricular contraction
Parasympathetic Nervous System
Reaches heart by vagus nerve and releases ACh
Decreases HR to RHR of 60-100
Sympathetic Nervous System
Releases norepinephrine
Increases HR up to 250 bpm
Diastole (relaxation phase)
2x as long as systole (contraction phase)
Ventricular Systole
QRS complex to T wave 1/3 of total cycle
Mitral and Tricuspid valves close (lub) semilunar valves open and blood is ejected
End systolic volume (ESV) - blood remaining in ventricles after systole
Ventricular Diastole
T wave to next QRS complex 2/3 of total cycle
Semilunar valves close (dub), Av valves open
End Diastolic Volume (EDV) blood in ventricles after atrial contraction
Stroke Volume (SV)
EDV-ESV
Ejection Fraction
SV / EDV
Cardiac Output (Q)
Q (L/min) = SV (mL/beat) x HR (bpm)
volume of blood pumped per minute
resting output 4.2-5.6 L/min and increases rapidly during rest to exercise transition (up to 25 L/min)
Cardiac Drift
A decrease in SV caused by decreased plasma volume, which causes Increased HR
Mean Arterial Pressure (MAP)
2/3 DBP + 1/3 SBP
Blood plasma
55-60 % of total volume
Can ± 10% due to dehydration, training
Formed elements (in blood and vessels)
40-45% total volume
Hematocrit =% of volume made up of formed elements
How many of each do you find in blood Hematocrit?
RBC: 99%
White blood cells -<1%
Platelets -<1%
Metabolic Mechanisms (VD intrinsic)
Buildup of metabolic products, CO2, and decreased O2
Endothelial mechanisms (VD, intrinsic)
Substances secreted by vascular endothelium (NO prostaglandins, ect)
Myogenic mechanisms (VD intrinsic)
Local pressure causes VD or VC
Neural control (extrinsic)
Sympathetic causes systemic VC and heart VD
At rest how much blood directs itself to the muscles and how much goes to the liver and kidneys?
Heart: 20%
Liver and Kidneys: 50%
During exercise how much blood goes to the muscles
>80% of bloodflow
What are the cardiovascular factors the increase stroke volume
increased preload
increased contractility
decreased afterload
Anticipatory response
HR increases above resting HR just before start of exercise
Steady state HR
point of plateau, optimal HR for meeting demands at given submax intensity
if intensity increases so does steady state HR
Stroke Volume (SV)
Increases with intensity to 40-60% VO2 max
plateaus beyond this except for elite endurance athletes
Hemoconcentration
Decrease plasma volume, increase hematocrit=increase in RBC concentration
Higher O2 carrying capacity (not always good)
What does the SAID principle stand for?
Specific Adaptations to Imposed Demands
Is inspiration active or passive
Active
Volume of blood pumped per beat per minute
cardiac output
What are the 3 major circulatory components of the cardiovascular system?
the heart (pump)
blood vessels
fluid medium (blood)
What is happening during QRS complex of an ECG
Ventricular depolarization
Inspiration
active process: expansion of chest cavity and lungs and a decrease in pressure in lungs
muscles used
Rest: diaphram and external intercostals
Exercise: scalenes, sternocleidomastoid, pectorals
Expiration
passive process at rest
muscles used
rest: non because it is a passive process
Exercise: internal intercostals, lats, quadratus lumborum, abs
Atmospheric pressure
760 mmHG